写在前面
以下内容是基于Redis 6.2.6 版本整理总结
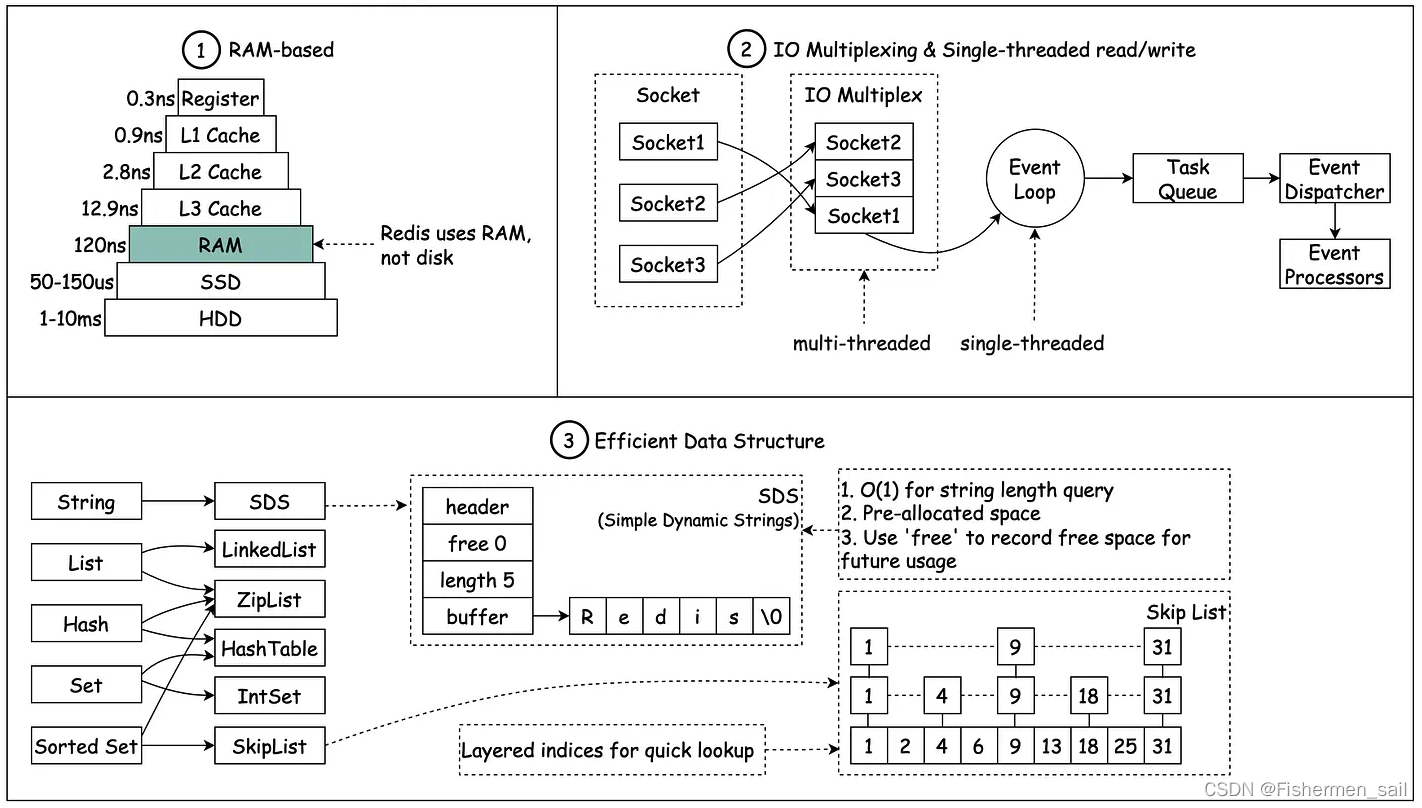
一、Redis数据库的组织方式
Redis服务器将所有的数据库 都保存在src/server.h/redisServer结构中的db数组中。db数组的每个entry都是src/server.h/redisDb结构,每个redisDb结构代表一个数据库。Redis默认有16个数据库。
1.1 redisServer结构定义
struct redisServer {
/* General */
pid_t pid; /* Main process pid. */
pthread_t main_thread_id; /* Main thread id */
...
redisDb *db; // db数组
...
int dbnum; // redis db的数量
...
};
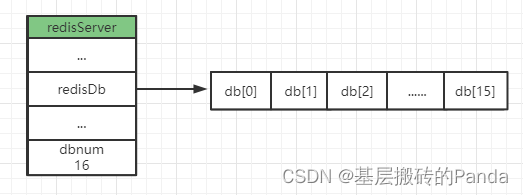
1.2 redisDb 结构定义
typedef struct redisDb {
dict *dict; /* The keyspace for this DB */ //键空间,保存数据库中所有的键值对
dict *expires; /* Timeout of keys with a timeout set */
dict *blocking_keys; /* Keys with clients waiting for data (BLPOP)*/
dict *ready_keys; /* Blocked keys that received a PUSH */
dict *watched_keys; /* WATCHED keys for MULTI/EXEC CAS */
int id; /* Database ID */
long long avg_ttl; /* Average TTL, just for stats */
unsigned long expires_cursor; /* Cursor of the active expire cycle. */
list *defrag_later; /* List of key names to attempt to defrag one by one, gradually. */
} redisDb;
各字段含义解释:
- dict保存了数据库中的所有键值对,这个字典也被称为:键空间(key space)。键空间的键就是数据库的键,每个键都是字符串对象;键空间的值就是数据库的值,每个值可以是五种对象中的任意一种对象。
- expires字典保存了数据库中所有键的过期时间,也叫过期字典。过期字典的键是指向键空间中的某个键的指针;值是一个long long类型的unix毫秒级时间戳。
- blocking_keys使用比较少,redis只有blpop、brpop等命令造成主动阻塞。
- ready_keys和blocking_keys配合使用,比如:一个客户端blpop阻塞等待数据,另一个客户端在push时,会检查blocking_keys中是否存在相应的key,如果有就将该key移动到ready_keys中,阻塞的客户端收到数据。
- watched_keys用来实现WATCH功能,实际线上环境不会使用,影响redis性能。
1.3 redisdb初始化
// src/server.c
void initServer(void) {
int j;
// ...
server.db = zmalloc(sizeof(redisDb)*server.dbnum);
// ...
/* Create the Redis databases, and initialize other internal state. */
for (j = 0; j < server.dbnum; j++) {
server.db[j].dict = dictCreate(&dbDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].expires = dictCreate(&dbExpiresDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].expires_cursor = 0;
server.db[j].blocking_keys = dictCreate(&keylistDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].ready_keys = dictCreate(&objectKeyPointerValueDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].watched_keys = dictCreate(&keylistDictType,NULL);
server.db[j].id = j;
server.db[j].avg_ttl = 0;
server.db[j].defrag_later = listCreate();
listSetFreeMethod(server.db[j].defrag_later,(void (*)(void*))sdsfree);
}
//...
}
二、过期键
2.1 设置键的过期时间
redis客户端提供了expire或pexpire命令来设置键的过期时间(Time to live, TTL),在经过指定秒数或者毫秒数后,redis服务器会自动删除生存时间为0的键。ttl命令是以秒为单位返回键的剩余生存时间,pttl命令则是以毫秒为单位。

也可以通过 setex 在设置某个键的同时为其设置过期时间:
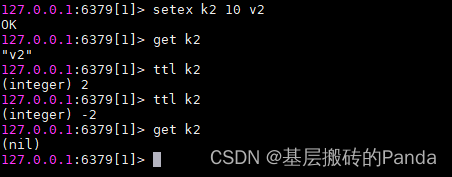
如果一个键没有设置过期时间或者设置了过期时间又通过persist命令取消了过期时间,则执行ttl查看键的过期时间返回-1

2.2 过期键的判定
开头我们在学习redisDb 结构的时候说过,过redisDb 中的expires过期字典保存了数据中的所有键的过期时间。要判断一个键是否过期:
- 检查给定键是不是在过期字典中,如果在,则拿到过期时间
- 跟当前unix时间戳比较,如果小于当前unix时间戳则过期,否则还没过期。
2.3 过期键的删除策略
惰性删除:放任过期键不管,但是每次从键空间获取键的时候,都会先检查键是否过期,如果过期了就删除,否则就正常返回。
优点:对CPU友好,对内存不友好,如果有访问的不到键,且已经过期了,则永远不会被删除。
定期删除:每隔一段时间,检查一次数据库,删除里面的过期键。要扫描多少个数据库,以及要删除多少过期键,由算法控制。
Redis服务器采用了上面两种策略的组合使用,很好的平衡了CPU的使用和内存的使用。
2.3.1 惰性删除的实现
惰性删除由expireIfNeeded函数实现,Redis在执行读写命令时都会先调用expireIfNeeded函数对键进行检查。如果已经过期,expireIfNeeded函数就会删除该键值对;如果没有过期,则什么都不做。
// db.c
int expireIfNeeded(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
// 如果没过期,什么都不做,直接返回
if (!keyIsExpired(db,key)) return 0;
/* If we are running in the context of a slave, instead of
* evicting the expired key from the database, we return ASAP:
* the slave key expiration is controlled by the master that will
* send us synthesized DEL operations for expired keys.
*
* Still we try to return the right information to the caller,
* that is, 0 if we think the key should be still valid, 1 if
* we think the key is expired at this time. */
if (server.masterhost != NULL) return 1;
/* If clients are paused, we keep the current dataset constant,
* but return to the client what we believe is the right state. Typically,
* at the end of the pause we will properly expire the key OR we will
* have failed over and the new primary will send us the expire. */
if (checkClientPauseTimeoutAndReturnIfPaused()) return 1;
/* Delete the key */
// 删除过期键
deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagate(db,key);
return 1;
}
/* Check if the key is expired. */
int keyIsExpired(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
mstime_t when = getExpire(db,key);
mstime_t now;
// 如果该键没有设置过期时间
if (when < 0) return 0; /* No expire for this key */
/* Don't expire anything while loading. It will be done later. */
// server加载过程中,不执行任何过期键删除操作
if (server.loading) return 0;
// 获取当前时间now
/* If we are in the context of a Lua script, we pretend that time is
* blocked to when the Lua script started. This way a key can expire
* only the first time it is accessed and not in the middle of the
* script execution, making propagation to slaves / AOF consistent.
* See issue #1525 on Github for more information. */
if (server.lua_caller) {
now = server.lua_time_snapshot;
}
/* If we are in the middle of a command execution, we still want to use
* a reference time that does not change: in that case we just use the
* cached time, that we update before each call in the call() function.
* This way we avoid that commands such as RPOPLPUSH or similar, that
* may re-open the same key multiple times, can invalidate an already
* open object in a next call, if the next call will see the key expired,
* while the first did not. */
else if (server.fixed_time_expire > 0) {
now = server.mstime;
}
/* For the other cases, we want to use the most fresh time we have. */
else {
now = mstime();
}
/* The key expired if the current (virtual or real) time is greater
* than the expire time of the key. */
// 如果当前时间大于过期时间,则该键过期,返回true
return now > when;
}
/* Return the expire time of the specified key, or -1 if no expire
* is associated with this key (i.e. the key is non volatile) */
// 从过期字典中获取key的过期时间
long long getExpire(redisDb *db, robj *key) {
dictEntry *de;
/* No expire? return ASAP */
// dictSize = db对应的ht[0].used+ht[1].used
// 在过期字典中找不到该key,则直接返回-1
if (dictSize(db->expires) == 0 ||
(de = dictFind(db->expires,key->ptr)) == NULL) return -1;
/* The entry was found in the expire dict, this means it should also
* be present in the main dict (safety check). */
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,key,dictFind(db->dict,key->ptr) != NULL);
// 如果找到了,返回键的unix时间戳
return dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de);
}
2.3.2 定时删除的实现
惰性删除由src/db.c/activeExpireCycle函数实现.
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP 20 /* Keys for each DB loop. */ // 每个数据库默认检查20个key
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION 1000 /* Microseconds. */ // 每个数据库默认检查20个key
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC 25 /* Max % of CPU to use. */ // CPU最大使用率25%
#define ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_ACCEPTABLE_STALE 10 /* % of stale keys after which
we do extra efforts. */
void activeExpireCycle(int type) {
/* Adjust the running parameters according to the configured expire
* effort. The default effort is 1, and the maximum configurable effort
* is 10. */
unsigned long
effort = server.active_expire_effort-1, /* Rescale from 0 to 9. */
config_keys_per_loop = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP +
ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_KEYS_PER_LOOP/4*effort,
config_cycle_fast_duration = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION +
ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST_DURATION/4*effort,
config_cycle_slow_time_perc = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW_TIME_PERC +
2*effort,
config_cycle_acceptable_stale = ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_ACCEPTABLE_STALE-
effort;
/* This function has some global state in order to continue the work
* incrementally across calls. */
static unsigned int current_db = 0; /* Next DB to test. */
static int timelimit_exit = 0; /* Time limit hit in previous call? */
static long long last_fast_cycle = 0; /* When last fast cycle ran. */
int j, iteration = 0;
int dbs_per_call = CRON_DBS_PER_CALL; // 每次默认检查16个数据库
long long start = ustime(), timelimit, elapsed;
/* When clients are paused the dataset should be static not just from the
* POV of clients not being able to write, but also from the POV of
* expires and evictions of keys not being performed. */
if (checkClientPauseTimeoutAndReturnIfPaused()) return;
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST) {
/* Don't start a fast cycle if the previous cycle did not exit
* for time limit, unless the percentage of estimated stale keys is
* too high. Also never repeat a fast cycle for the same period
* as the fast cycle total duration itself. */
if (!timelimit_exit &&
server.stat_expired_stale_perc < config_cycle_acceptable_stale)
return;
if (start < last_fast_cycle + (long long)config_cycle_fast_duration*2)
return;
last_fast_cycle = start;
}
/* We usually should test CRON_DBS_PER_CALL per iteration, with
* two exceptions:
*
* 1) Don't test more DBs than we have.
* 2) If last time we hit the time limit, we want to scan all DBs
* in this iteration, as there is work to do in some DB and we don't want
* expired keys to use memory for too much time. */
if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum || timelimit_exit)
dbs_per_call = server.dbnum;
/* We can use at max 'config_cycle_slow_time_perc' percentage of CPU
* time per iteration. Since this function gets called with a frequency of
* server.hz times per second, the following is the max amount of
* microseconds we can spend in this function. */
timelimit = config_cycle_slow_time_perc*1000000/server.hz/100;
timelimit_exit = 0;
if (timelimit <= 0) timelimit = 1;
if (type == ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_FAST)
timelimit = config_cycle_fast_duration; /* in microseconds. */
/* Accumulate some global stats as we expire keys, to have some idea
* about the number of keys that are already logically expired, but still
* existing inside the database. */
long total_sampled = 0;
long total_expired = 0;
// 遍历各个数据库
for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call && timelimit_exit == 0; j++) {
/* Expired and checked in a single loop. */
unsigned long expired, sampled;
// 获取当前要处理的数据库
redisDb *db = server.db+(current_db % server.dbnum);
/* Increment the DB now so we are sure if we run out of time
* in the current DB we'll restart from the next. This allows to
* distribute the time evenly across DBs. */
current_db++;
/* Continue to expire if at the end of the cycle there are still
* a big percentage of keys to expire, compared to the number of keys
* we scanned. The percentage, stored in config_cycle_acceptable_stale
* is not fixed, but depends on the Redis configured "expire effort". */
do {
unsigned long num, slots;
long long now, ttl_sum;
int ttl_samples;
iteration++;
/* If there is nothing to expire try next DB ASAP. */
// 如果当前数据库过期字典为空,跳过这个数据库
if ((num = dictSize(db->expires)) == 0) {
db->avg_ttl = 0;
break;
}
slots = dictSlots(db->expires);
now = mstime();
/* When there are less than 1% filled slots, sampling the key
* space is expensive, so stop here waiting for better times...
* The dictionary will be resized asap. */
if (slots > DICT_HT_INITIAL_SIZE &&
(num*100/slots < 1)) break;
/* The main collection cycle. Sample random keys among keys
* with an expire set, checking for expired ones. */
expired = 0;
sampled = 0;
ttl_sum = 0;
ttl_samples = 0;
if (num > config_keys_per_loop)
num = config_keys_per_loop;
/* Here we access the low level representation of the hash table
* for speed concerns: this makes this code coupled with dict.c,
* but it hardly changed in ten years.
*
* Note that certain places of the hash table may be empty,
* so we want also a stop condition about the number of
* buckets that we scanned. However scanning for free buckets
* is very fast: we are in the cache line scanning a sequential
* array of NULL pointers, so we can scan a lot more buckets
* than keys in the same time. */
long max_buckets = num*20;
long checked_buckets = 0;
while (sampled < num && checked_buckets < max_buckets) {
for (int table = 0; table < 2; table++) {
if (table == 1 && !dictIsRehashing(db->expires)) break;
unsigned long idx = db->expires_cursor;
idx &= db->expires->ht[table].sizemask;
dictEntry *de = db->expires->ht[table].table[idx];
long long ttl;
/* Scan the current bucket of the current table. */
checked_buckets++;
while(de) {
/* Get the next entry now since this entry may get
* deleted. */
dictEntry *e = de;
de = de->next;
ttl = dictGetSignedIntegerVal(e)-now;
if (activeExpireCycleTryExpire(db,e,now)) expired++;
if (ttl > 0) {
/* We want the average TTL of keys yet
* not expired. */
ttl_sum += ttl;
ttl_samples++;
}
sampled++;
}
}
db->expires_cursor++;
}
total_expired += expired;
total_sampled += sampled;
/* Update the average TTL stats for this database. */
if (ttl_samples) {
long long avg_ttl = ttl_sum/ttl_samples;
/* Do a simple running average with a few samples.
* We just use the current estimate with a weight of 2%
* and the previous estimate with a weight of 98%. */
if (db->avg_ttl == 0) db->avg_ttl = avg_ttl;
db->avg_ttl = (db->avg_ttl/50)*49 + (avg_ttl/50);
}
/* We can't block forever here even if there are many keys to
* expire. So after a given amount of milliseconds return to the
* caller waiting for the other active expire cycle. */
if ((iteration & 0xf) == 0) { /* check once every 16 iterations. */
elapsed = ustime()-start;
if (elapsed > timelimit) {
timelimit_exit = 1;
server.stat_expired_time_cap_reached_count++;
break;
}
}
/* We don't repeat the cycle for the current database if there are
* an acceptable amount of stale keys (logically expired but yet
* not reclaimed). */
} while (sampled == 0 ||
(expired*100/sampled) > config_cycle_acceptable_stale);
}
elapsed = ustime()-start;
server.stat_expire_cycle_time_used += elapsed;
latencyAddSampleIfNeeded("expire-cycle",elapsed/1000);
/* Update our estimate of keys existing but yet to be expired.
* Running average with this sample accounting for 5%. */
double current_perc;
if (total_sampled) {
current_perc = (double)total_expired/total_sampled;
} else
current_perc = 0;
server.stat_expired_stale_perc = (current_perc*0.05)+
(server.stat_expired_stale_perc*0.95);
}
三、Redis内存淘汰策略
Redis为什么要有内存淘汰策略?因为Redis是内存数据库,不能无限大,达到阈值时需要淘汰部分内存的数据,来存储新的数据。
redis内存配置参数:maxmemory,一般设置为系统内存的一半(经验值),比如你的系统运行内存有哦96G,就设置为48G。
1.1 淘汰策略
看你的业务是否使用了 expire 过期时间,如果使用了,
3.1 Redis针对过期key的淘汰策略如下:
看你的业务是否使用了 expire 过期时间,如果使用了,则:
- volatile-lru (Least Recently Used的缩写,即最近最少使用)
- volatile-lfu(east frequently used的缩写,即最少次数使用)
- volatile-ttl(time to live的缩写,最近要过期的)
- volatile-random (随机淘汰)
3.2 Redis最对所有key的淘汰策略:
- alllkeys-lru
- allkeys-lfu
- allkeys-random
3.3 禁止淘汰策略
redis还有一种淘汰策略,就是禁止淘汰,这种策略,当redis使用的内存达到设定的最大值时,后续的写进redis的操作会失败。
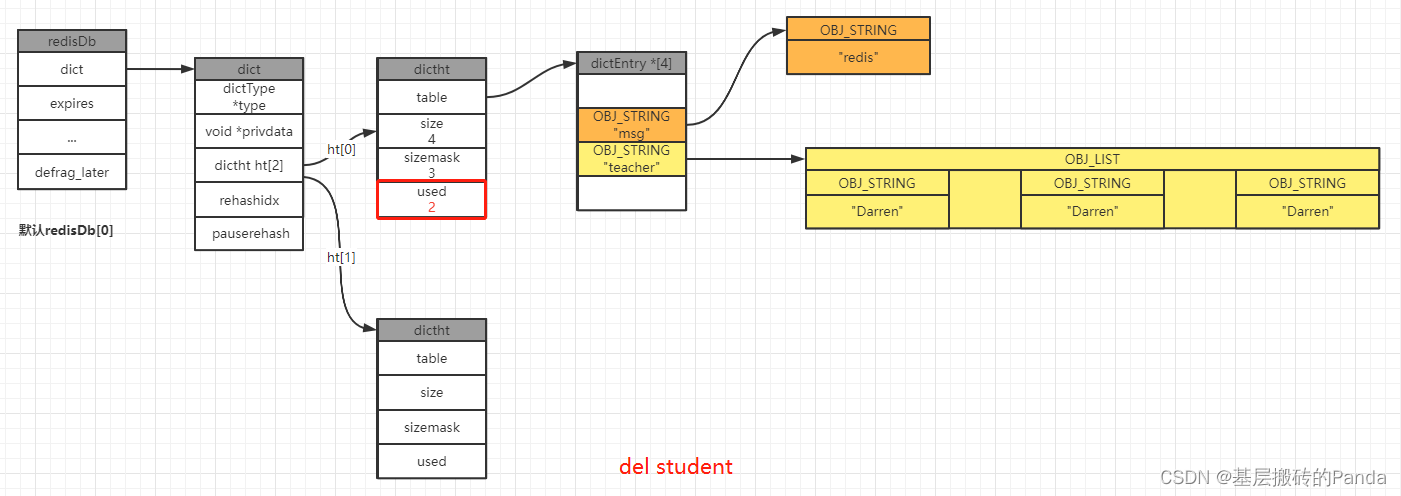
四、增删改查图解
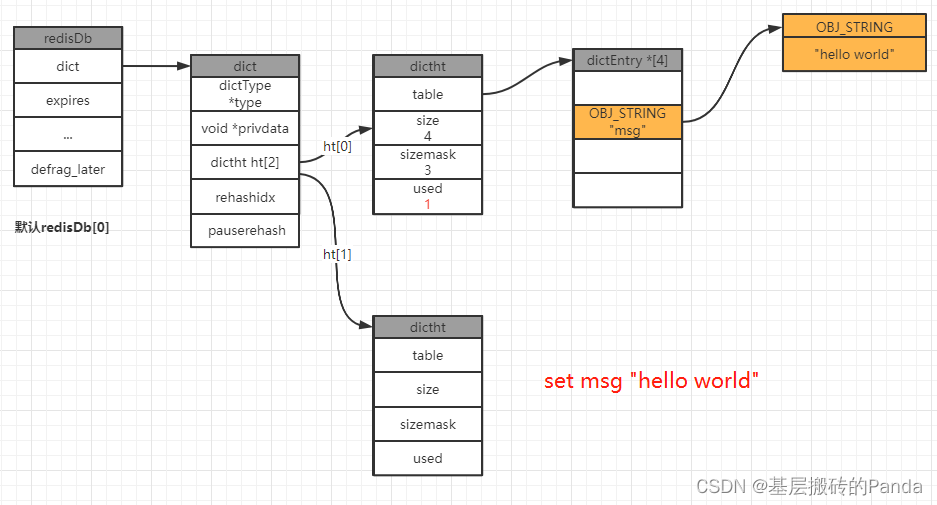
4.1 新增键值对
举例:我们在一个空的redis数据库中执行分别执行以下命令:
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
(empty array) // 表示此时数据库中没有任何数据
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> set msg "hello world"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> hmset student name panda age 20 addr beijing
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>
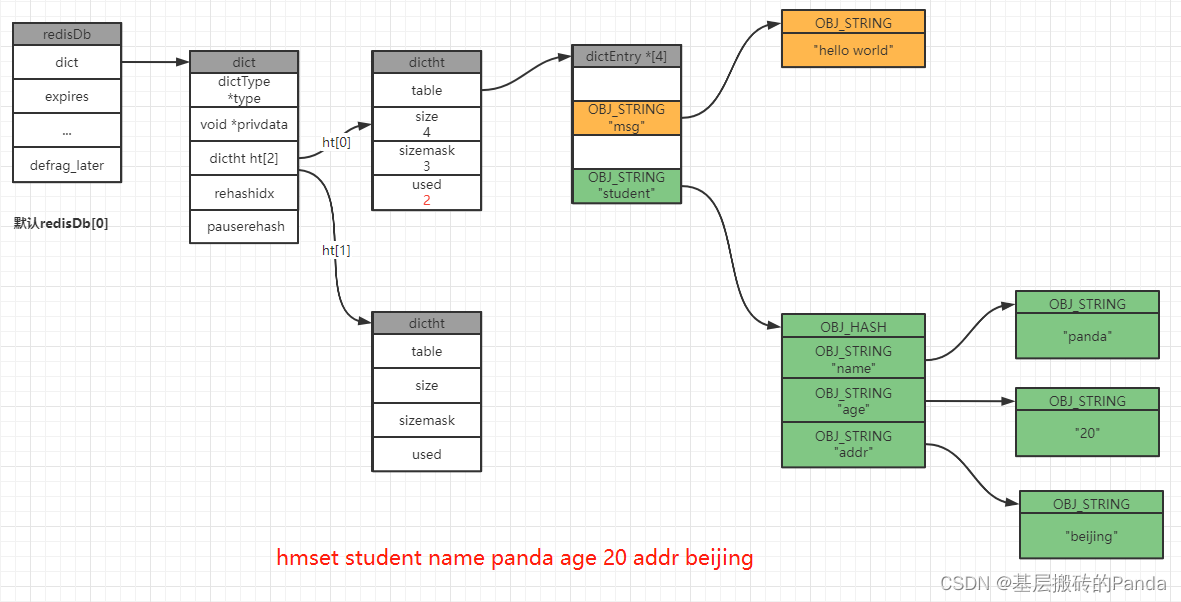
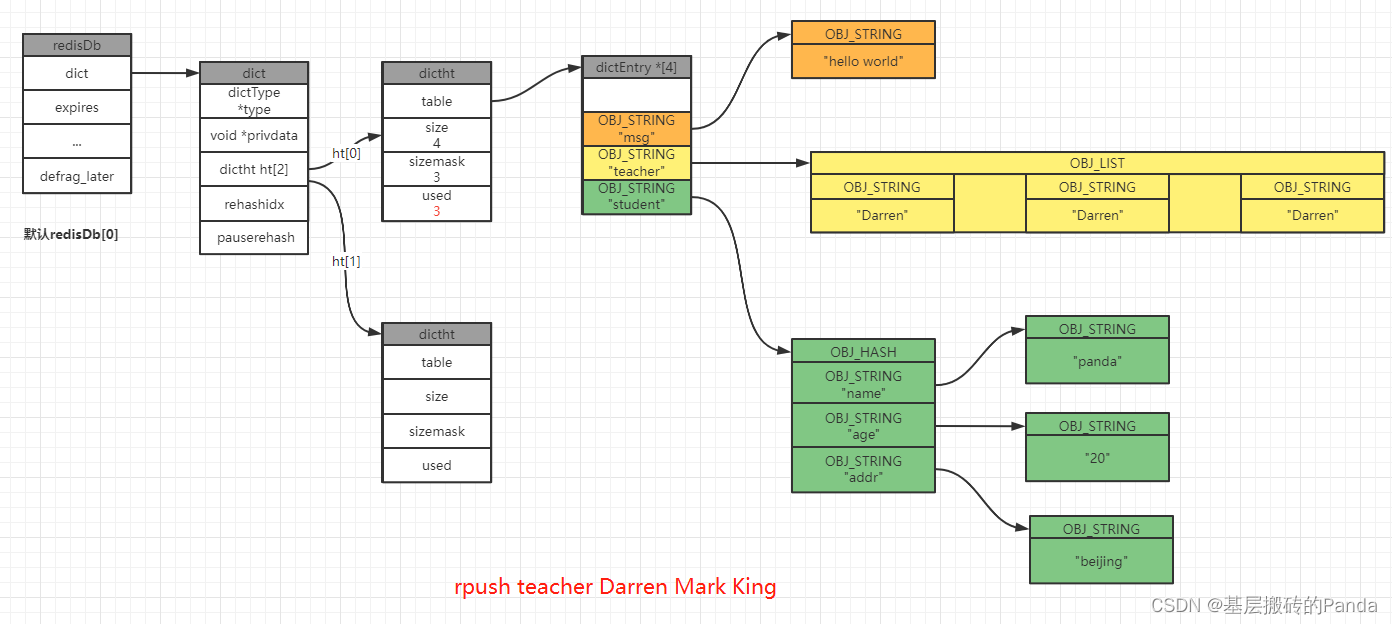
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> rpush teacher Darren Mark King
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>
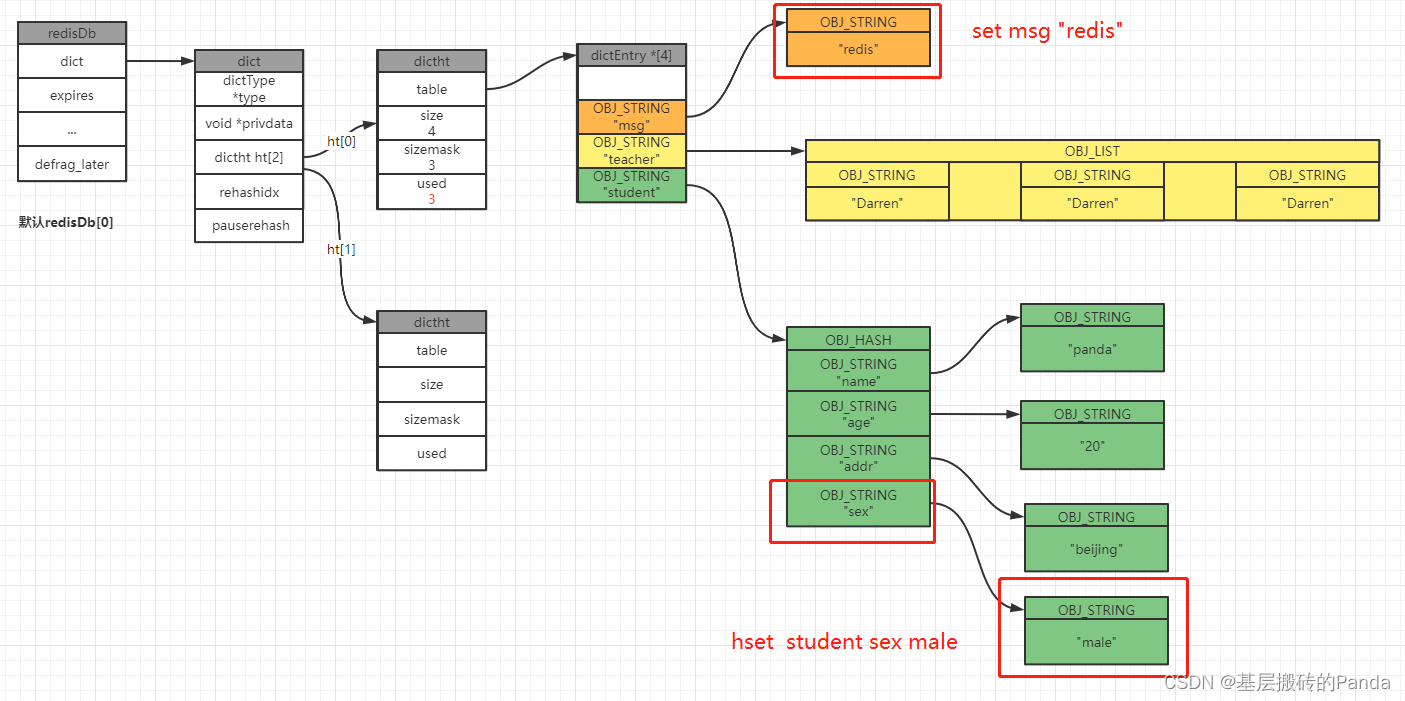
4.2 更新键值对
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> set msg "redis"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> get msg
"redis"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> hset student sex male
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>
4.3 获取键的值
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> get msg
"redis"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> hmget student name age addr sex
1) "panda"
2) "20"
3) "beijing"
4) "male"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>
4.4 删除键值对
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
1) "msg"
2) "student"
3) "teacher"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> del student
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
1) "msg"
2) "teacher"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]>