1 前言
对象拷贝,是我们在开发过程中,绕不开的过程,既存在于 Po、Dto、Do、Vo 各个表现层数据的转换,也存在于系统交互如序列化、反序列化。
Java 对象拷贝分为深拷贝和浅拷贝,目前常用的属性拷贝工具,包括 Apache 的 BeanUtils、Spring 的 BeanUtils、Cglib 的 BeanCopier、mapstruct 都是浅拷贝。
1.1 深拷贝
深拷贝:对基本数据类型进行值传递,对引用数据类型,创建一个新的对象,并复制其内容称为深拷贝。
深拷贝常见有以下四种实现方式:
-
构造函数
-
Serializable 序列化
-
实现 Cloneable 接口
-
JSON 序列化

1.2 浅拷贝
浅拷贝:对基本数据类型进行值传递,对引用数据类型进行引用传递般的拷贝称为浅拷贝。通过实现 Cloneabe 接口并重写 Object 类中的 clone()方法可以实现浅克隆。
2 常用对象拷贝工具原理剖析及性能对比
目前常用的属性拷贝工具,包括 Apache 的 BeanUtils、Spring 的 BeanUtils、Cglib 的 BeanCopier、mapstruct。
-
Apache BeanUtils:BeanUtils 是 Apache commons 组件里面的成员,由 Apache 提供的一套开源 api,用于简化对 javaBean 的操作,能够对基本类型自动转换。
-
Spring BeanUtils:BeanUtils 是 spring 框架下自带的工具,在 org.springframework.beans 包下, spring 项目可以直接使用。
-
Cglib BeanCopier:cglib(Code Generation Library)是一个强大的、高性能、高质量的代码生成类库,BeanCopier 依托于 cglib 的字节码增强能力,动态生成实现类,完成对象的拷贝。
-
mapstruct:mapstruct 是一个 Java 注释处理器,用于生成类型安全的 bean 映射类,在构建时,根据注解生成实现类,完成对象拷贝。
2.1 原理分析
2.1.1 Apache BeanUtils
使用方式:BeanUtils.copyProperties(target, source);BeanUtils.copyProperties 对象拷贝的核心代码如下:
// 1.获取源对象的属性描述PropertyDescriptor[] origDescriptors = this.getPropertyUtils().getPropertyDescriptors(orig);PropertyDescriptor[] temp = origDescriptors;int length = origDescriptors.length;String name;Object value;// 2.循环获取源对象每个属性,设置目标对象属性值for(int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {PropertyDescriptor origDescriptor = temp[i];name = origDescriptor.getName();// 3.校验源对象字段可读切目标对象该字段可写if (!"class".equals(name) && this.getPropertyUtils().isReadable(orig, name) && this.getPropertyUtils().isWriteable(dest, name)) {try {// 4.获取源对象字段值value = this.getPropertyUtils().getSimpleProperty(orig, name);// 5.拷贝属性this.copyProperty(dest, name, value);} catch (NoSuchMethodException var10) {}}}// 1.获取源对象的属性描述PropertyDescriptor[] origDescriptors = this.getPropertyUtils().getPropertyDescriptors(orig);PropertyDescriptor[] temp = origDescriptors;int length = origDescriptors.length;String name;Object value;// 2.循环获取源对象每个属性,设置目标对象属性值for(int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {PropertyDescriptor origDescriptor = temp[i];name = origDescriptor.getName();// 3.校验源对象字段可读切目标对象该字段可写if (!"class".equals(name) && this.getPropertyUtils().isReadable(orig, name) && this.getPropertyUtils().isWriteable(dest, name)) { try {// 4.获取源对象字段值 value = this.getPropertyUtils().getSimpleProperty(orig, name);// 5.拷贝属性 this.copyProperty(dest, name, value); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var10) { } }}
复制代码
循环遍历源对象的每个属性,对于每个属性,拷贝流程为:
-
校验来源类的字段是否可读 isReadable
-
校验目标类的字段是否可写 isWriteable
-
获取来源类的字段属性值 getSimpleProperty
-
获取目标类字段的类型 type,并进行类型转换
-
设置目标类字段的值
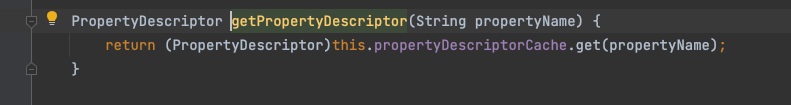
由于单字段拷贝时每个阶段都会调用 PropertyUtilsBean.getPropertyDescriptor 获取属性配置,而该方法通过 for 循环获取类的字段属性,严重影响拷贝效率。获取字段属性配置的核心代码如下:
PropertyDescriptor[] descriptors = this.getPropertyDescriptors(bean);if (descriptors != null) {for (int i = 0; i < descriptors.length; ++i) {if (name.equals(descriptors[i].getName())) {return descriptors[i];}}}PropertyDescriptor[] descriptors = this.getPropertyDescriptors(bean);if (descriptors != null) {for (int i = 0; i < descriptors.length; ++i) {if (name.equals(descriptors[i].getName())) {return descriptors[i];}}}
复制代码
2.1.2 Spring BeanUtils
使用方式: BeanUtils.copyProperties(source, target);BeanUtils.copyProperties 核心代码如下:
PropertyDescriptor[] targetPds = getPropertyDescriptors(actualEditable);List<String> ignoreList = ignoreProperties != null ? Arrays.asList(ignoreProperties) : null;PropertyDescriptor[] arr$ = targetPds;int len$ = targetPds.length;for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) {PropertyDescriptor targetPd = arr$[i$];Method writeMethod = targetPd.getWriteMethod();if (writeMethod != null && (ignoreList == null || !ignoreList.contains(targetPd.getName()))) {PropertyDescriptor sourcePd = getPropertyDescriptor(source.getClass(), targetPd.getName());if (sourcePd != null) {Method readMethod = sourcePd.getReadMethod();if (readMethod != null && ClassUtils.isAssignable(writeMethod.getParameterTypes()[0], readMethod.getReturnType())) {try {if (!Modifier.isPublic(readMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) {readMethod.setAccessible(true);}Object value = readMethod.invoke(source);if (!Modifier.isPublic(writeMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) {writeMethod.setAccessible(true);}writeMethod.invoke(target, value);} catch (Throwable var15) {throw new FatalBeanException("Could not copy property '" + targetPd.getName() + "' from source to target", var15);}}}}}PropertyDescriptor[] targetPds = getPropertyDescriptors(actualEditable);List<String> ignoreList = ignoreProperties != null ? Arrays.asList(ignoreProperties) : null;PropertyDescriptor[] arr$ = targetPds;int len$ = targetPds.length;for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) { PropertyDescriptor targetPd = arr$[i$]; Method writeMethod = targetPd.getWriteMethod(); if (writeMethod != null && (ignoreList == null || !ignoreList.contains(targetPd.getName()))) { PropertyDescriptor sourcePd = getPropertyDescriptor(source.getClass(), targetPd.getName()); if (sourcePd != null) { Method readMethod = sourcePd.getReadMethod(); if (readMethod != null && ClassUtils.isAssignable(writeMethod.getParameterTypes()[0], readMethod.getReturnType())) { try { if (!Modifier.isPublic(readMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) { readMethod.setAccessible(true); } Object value = readMethod.invoke(source); if (!Modifier.isPublic(writeMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers())) { writeMethod.setAccessible(true); } writeMethod.invoke(target, value); } catch (Throwable var15) { throw new FatalBeanException("Could not copy property '" + targetPd.getName() + "' from source to target", var15); } } } }}
复制代码
拷贝流程简要描述如下:
-
获取目标类的所有属性描述
-
循环目标类的属性值做以下操作
-
获取目标类的写方法
-
获取来源类的该属性的属性描述(缓存获取)
-
获取来源类的读方法
-
读来源属性值
-
写目标属性值
与 Apache BeanUtils 的属性拷贝相比,Spring 通过 Map 缓存,避免了类的属性描述重复获取加载,通过懒加载,初次拷贝时加载所有属性描述。
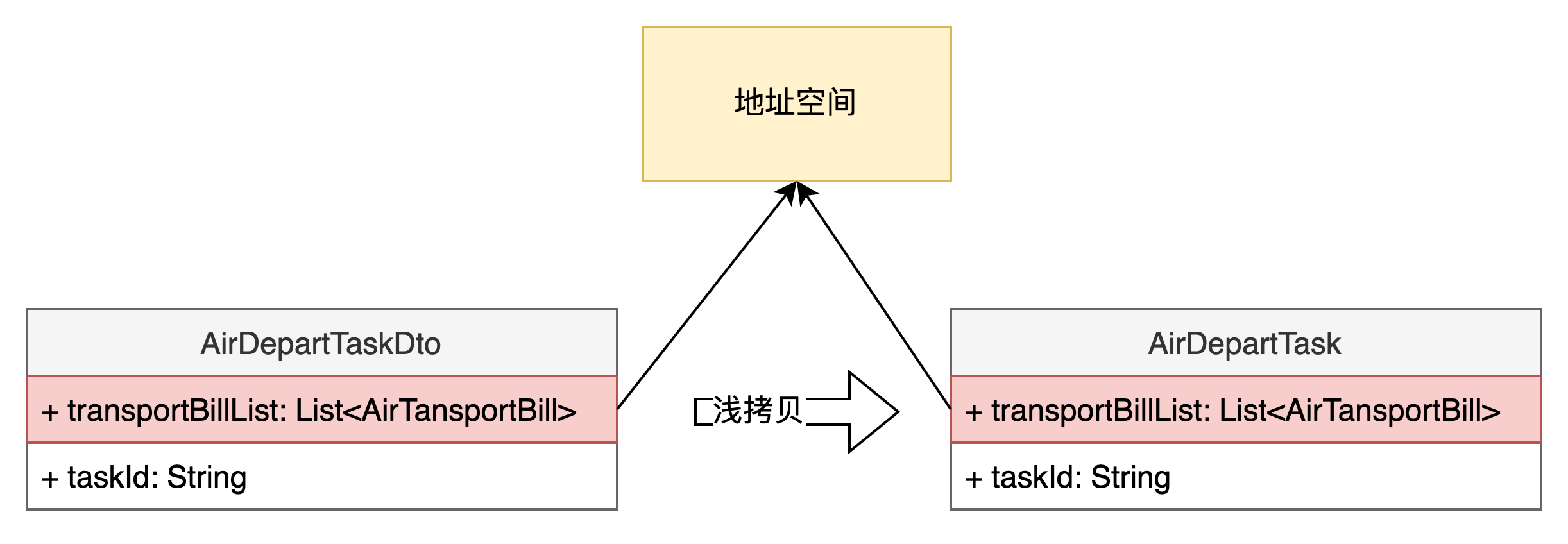
2.1.3 Cglib BeanCopier
使用方式:
BeanCopier beanCopier = BeanCopier.create(AirDepartTask.class, AirDepartTaskDto.class, false);beanCopier.copy(airDepartTask, airDepartTaskDto, null);
复制代码
create 调用链如下:
BeanCopier.create-> BeanCopier.Generator.create-> AbstractClassGenerator.create->DefaultGeneratorStrategy.generate-> BeanCopier.Generator.generateClass
BeanCopier 通过 cglib 动态代理操作字节码,生成一个复制类,触发点为 BeanCopier.create
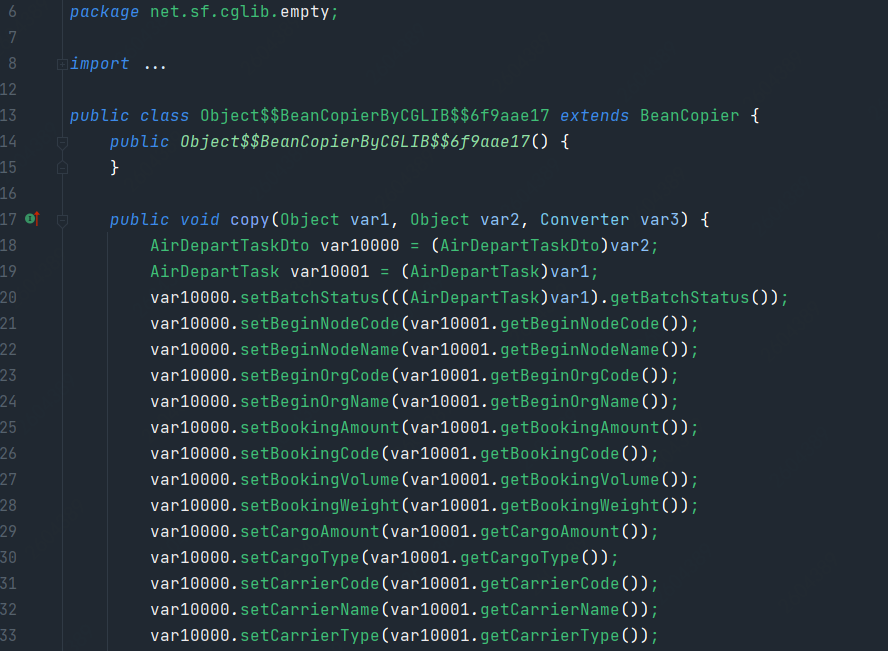
2.1.4 mapstruct
使用方式:
-
引入 pom 依赖
-
声明转换接口
mapstruct 基于注解,构建时自动生成实现类,调用链如下:MappingProcessor.process -> MappingProcessor.processMapperElementsMapperCreationProcessor.process:生成实现类 MapperMapperRenderingProcessor:将实现类 mapper,写入文件,生成 impl 文件使用时需要声明转换接口,例如:
@Mapper(nullValuePropertyMappingStrategy = NullValuePropertyMappingStrategy.IGNORE)public interface AirDepartTaskConvert {AirDepartTaskConvert INSTANCE = getMapper(AirDepartTaskConvert.class);AirDepartTaskDto convertToDto(AirDepartTask airDepartTask);}
复制代码
生成的实现类如下:
public class AirDepartTaskConvertImpl implements AirDepartTaskConvert {@Overridepublic AirDepartTaskDto convertToDto(AirDepartTask airDepartTask) {if ( airDepartTask == null ) {return null;}AirDepartTaskDto airDepartTaskDto = new AirDepartTaskDto();airDepartTaskDto.setId( airDepartTask.getId() );airDepartTaskDto.setTaskId( airDepartTask.getTaskId() );airDepartTaskDto.setPreTaskId( airDepartTask.getPreTaskId() );List<String> list = airDepartTask.getTaskBeginNodeCodes();if ( list != null ) {airDepartTaskDto.setTaskBeginNodeCodes( new ArrayList<String>( list ) );}// 其他属性拷贝airDepartTaskDto.setYn( airDepartTask.getYn() );return airDepartTaskDto;}}public class AirDepartTaskConvertImpl implements AirDepartTaskConvert { @Override public AirDepartTaskDto convertToDto(AirDepartTask airDepartTask) { if ( airDepartTask == null ) { return null; } AirDepartTaskDto airDepartTaskDto = new AirDepartTaskDto(); airDepartTaskDto.setId( airDepartTask.getId() ); airDepartTaskDto.setTaskId( airDepartTask.getTaskId() ); airDepartTaskDto.setPreTaskId( airDepartTask.getPreTaskId() ); List<String> list = airDepartTask.getTaskBeginNodeCodes(); if ( list != null ) { airDepartTaskDto.setTaskBeginNodeCodes( new ArrayList<String>( list ) ); } // 其他属性拷贝 airDepartTaskDto.setYn( airDepartTask.getYn() ); return airDepartTaskDto; }}
复制代码
2.2 性能对比
以航空业务系统中发货任务 po 到 dto 转换为例,随着拷贝数据量的增大,研究拷贝数据耗时情况
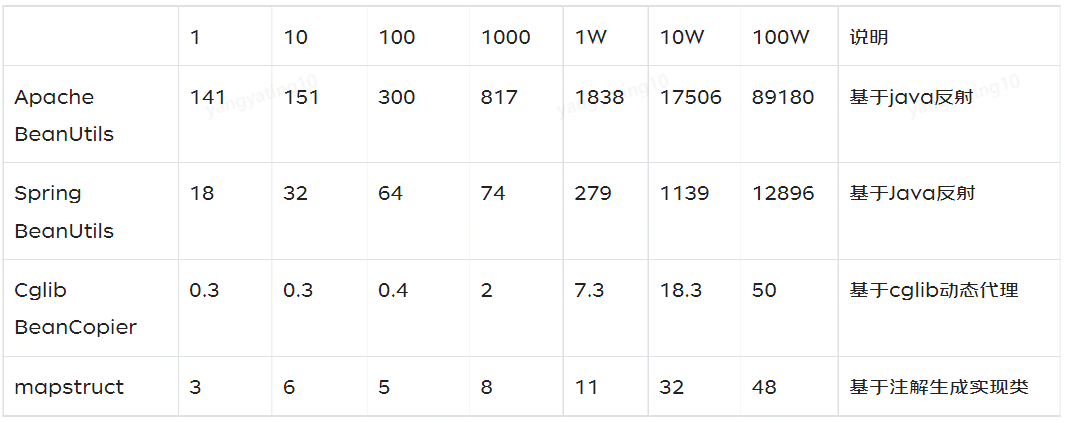
2.3 拷贝选型
经过以上分析,随着数据量的增大,耗时整体呈上升趋势
-
整体情况下,Apache BeanUtils 的性能最差,日常使用过程中不建议使用
-
在数据规模不大的情况下,spring、cglib、mapstruct 差异不大,spring 框架下建议使用 spring 的 beanUtils,不需要额外引入依赖包
-
数据量大的情况下,建议使用 cglib 和 mapstruct
-
涉及大量数据转换,属性映射,格式转换的,建议使用 mapstruct
3 最佳实践
3.1 BeanCopier
使用时可以使用 map 缓存,减少同一类对象转换时,create 次数
/*** BeanCopier的缓存,避免频繁创建,高效复用*/private static final ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanCopier> BEAN_COPIER_MAP_CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanCopier>();/*** BeanCopier的copyBean,高性能推荐使用,增加缓存** @param source 源文件的* @param target 目标文件*/public static void copyBean(Object source, Object target) {String key = genKey(source.getClass(), target.getClass());BeanCopier beanCopier;if (BEAN_COPIER_MAP_CACHE.containsKey(key)) {beanCopier = BEAN_COPIER_MAP_CACHE.get(key);} else {beanCopier = BeanCopier.create(source.getClass(), target.getClass(), false);BEAN_COPIER_MAP_CACHE.put(key, beanCopier);}beanCopier.copy(source, target, null);}/*** 不同类型对象数据copylist** @param sourceList* @param targetClass* @param <T>* @return*/public static <T> List<T> copyListProperties(List<?> sourceList, Class<T> targetClass) throws Exception {if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(sourceList)) {List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>(sourceList.size());for (Object source : sourceList) {T target = copyProperties(source, targetClass);list.add(target);}return list;}return Lists.newArrayList();}/*** 返回不同类型对象数据copy,使用此方法需注意不能覆盖默认的无参构造方法** @param source* @param targetClass* @param <T>* @return*/public static <T> T copyProperties(Object source, Class<T> targetClass) throws Exception {T target = targetClass.newInstance();copyBean(source, target);return target;}/*** @param srcClazz 源class* @param tgtClazz 目标class* @return string*/private static String genKey(Class<?> srcClazz, Class<?> tgtClazz) {return srcClazz.getName() + tgtClazz.getName();} /** * BeanCopier的缓存,避免频繁创建,高效复用 */ private static final ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanCopier> BEAN_COPIER_MAP_CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanCopier>(); /** * BeanCopier的copyBean,高性能推荐使用,增加缓存 * * @param source 源文件的 * @param target 目标文件 */ public static void copyBean(Object source, Object target) { String key = genKey(source.getClass(), target.getClass()); BeanCopier beanCopier; if (BEAN_COPIER_MAP_CACHE.containsKey(key)) { beanCopier = BEAN_COPIER_MAP_CACHE.get(key); } else { beanCopier = BeanCopier.create(source.getClass(), target.getClass(), false); BEAN_COPIER_MAP_CACHE.put(key, beanCopier); } beanCopier.copy(source, target, null); } /** * 不同类型对象数据copylist * * @param sourceList * @param targetClass * @param <T> * @return */ public static <T> List<T> copyListProperties(List<?> sourceList, Class<T> targetClass) throws Exception { if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(sourceList)) { List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>(sourceList.size()); for (Object source : sourceList) { T target = copyProperties(source, targetClass); list.add(target); } return list; } return Lists.newArrayList(); } /** * 返回不同类型对象数据copy,使用此方法需注意不能覆盖默认的无参构造方法 * * @param source * @param targetClass * @param <T> * @return */ public static <T> T copyProperties(Object source, Class<T> targetClass) throws Exception { T target = targetClass.newInstance(); copyBean(source, target); return target; } /** * @param srcClazz 源class * @param tgtClazz 目标class * @return string */ private static String genKey(Class<?> srcClazz, Class<?> tgtClazz) { return srcClazz.getName() + tgtClazz.getName(); }
复制代码
3.2 mapstruct
mapstruct 支持多种形式对象的映射,主要有下面几种
-
基本映射
-
映射表达式
-
多个对象映射到一个对象
-
映射集合
-
映射 map
-
映射枚举
-
嵌套映射
@Mapper(nullValuePropertyMappingStrategy = NullValuePropertyMappingStrategy.IGNORE)public interface AirDepartTaskConvert {AirDepartTaskConvert INSTANCE = getMapper(AirDepartTaskConvert.class);// a.基本映射@Mapping(target = "createTime", source = "updateTime")// b.映射表达式@Mapping(target = "updateTimeStr", expression = "java(new SimpleDateFormat( \"yyyy-MM-dd\" ).format(airDepartTask.getCreateTime()))")AirDepartTaskDto convertToDto(AirDepartTask airDepartTask);}@Mapperpublic interface AddressMapper {AddressMapper INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(AddressMapper.class);// c.多个对象映射到一个对象@Mapping(source = "person.description", target = "description")@Mapping(source = "address.houseNo", target = "houseNumber")DeliveryAddressDto personAndAddressToDeliveryAddressDto(Person person, Address address);}@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper {// d.映射集合Set<String> integerSetToStringSet(Set<Integer> integers);List<CarDto> carsToCarDtos(List<Car> cars);CarDto carToCarDto(Car car);// e.映射map@MapMapping(valueDateFormat = "dd.MM.yyyy")Map<String,String> longDateMapToStringStringMap(Map<Long, Date> source);// f.映射枚举@ValueMappings({@ValueMapping(source = "EXTRA", target = "SPECIAL"),@ValueMapping(source = "STANDARD", target = "DEFAULT"),@ValueMapping(source = "NORMAL", target = "DEFAULT")})ExternalOrderType orderTypeToExternalOrderType(OrderType orderType);// g.嵌套映射@Mapping(target = "fish.kind", source = "fish.type")@Mapping(target = "fish.name", ignore = true)@Mapping(target = "ornament", source = "interior.ornament")@Mapping(target = "material.materialType", source = "material")@Mapping(target = "quality.report.organisation.name", source = "quality.report.organisationName")FishTankDto map( FishTank source );}@Mapper(nullValuePropertyMappingStrategy = NullValuePropertyMappingStrategy.IGNORE)public interface AirDepartTaskConvert { AirDepartTaskConvert INSTANCE = getMapper(AirDepartTaskConvert.class); // a.基本映射 @Mapping(target = "createTime", source = "updateTime") // b.映射表达式 @Mapping(target = "updateTimeStr", expression = "java(new SimpleDateFormat( \"yyyy-MM-dd\" ).format(airDepartTask.getCreateTime()))") AirDepartTaskDto convertToDto(AirDepartTask airDepartTask);}@Mapperpublic interface AddressMapper { AddressMapper INSTANCE = Mappers.getMapper(AddressMapper.class); // c.多个对象映射到一个对象 @Mapping(source = "person.description", target = "description") @Mapping(source = "address.houseNo", target = "houseNumber") DeliveryAddressDto personAndAddressToDeliveryAddressDto(Person person, Address address);}@Mapperpublic interface CarMapper { // d.映射集合 Set<String> integerSetToStringSet(Set<Integer> integers); List<CarDto> carsToCarDtos(List<Car> cars); CarDto carToCarDto(Car car); // e.映射map @MapMapping(valueDateFormat = "dd.MM.yyyy") Map<String,String> longDateMapToStringStringMap(Map<Long, Date> source); // f.映射枚举 @ValueMappings({ @ValueMapping(source = "EXTRA", target = "SPECIAL"), @ValueMapping(source = "STANDARD", target = "DEFAULT"), @ValueMapping(source = "NORMAL", target = "DEFAULT") }) ExternalOrderType orderTypeToExternalOrderType(OrderType orderType); // g.嵌套映射 @Mapping(target = "fish.kind", source = "fish.type") @Mapping(target = "fish.name", ignore = true) @Mapping(target = "ornament", source = "interior.ornament") @Mapping(target = "material.materialType", source = "material") @Mapping(target = "quality.report.organisation.name", source = "quality.report.organisationName") FishTankDto map( FishTank source );}
复制代码
4 总结
以上就是我在使用对象拷贝过程中的一点浅谈。在日常系统开发过程中,要深究底层逻辑,哪怕发现一小点的改变能够使我们的系统更加稳定、顺畅,都是值得我们去改进的。
最后,希望随着我们的加入,系统会更加稳定、顺畅,我们会变得越来越优秀。