转自我的博客:https://shar-pen.github.io/2025/05/05/torch-distributed-series/nccl_communication/
from IPython.display import Image
import logging
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
pytorch 分布式相关api
torch.distributed.init_process_group(),初始化进程组,必须先用这条命令才能使用torch.distrubuted相关操作。torch.distributed.get_rank(),可以获得当前进程的 rank;torch.distributed.get_world_size(),可以获得进程组的进程数量。torch.distributed.barrier(),同步进程组内的所有进程,阻塞所有进程直到所有进程都执行到操作。
节点获取信息
def main():
dist.init_process_group("nccl")
rank = dist.get_rank()
world_size = dist.get_world_size()
logging.info(f'world size: {world_size}, rank: {rank}')
dist.destroy_process_group()
命令: torchrun --nproc_per_node 2 torch_nccl_test.py
输出结果为
INFO:root:world size: 2, rank: 0
INFO:root:world size: 2, rank: 1
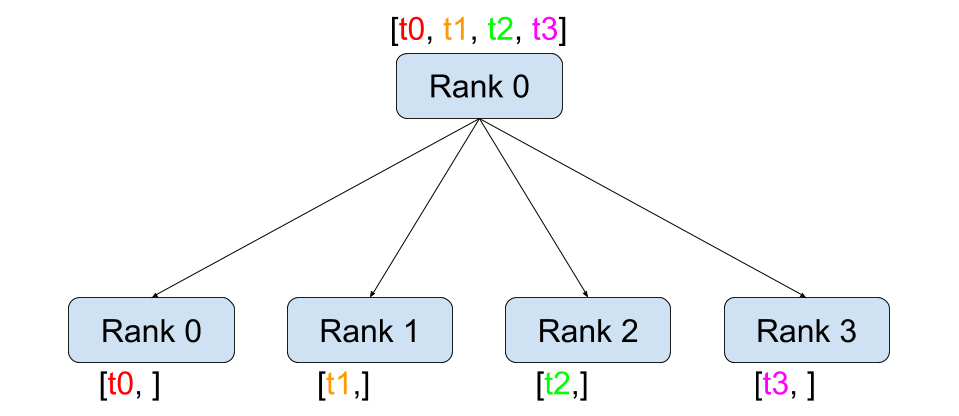
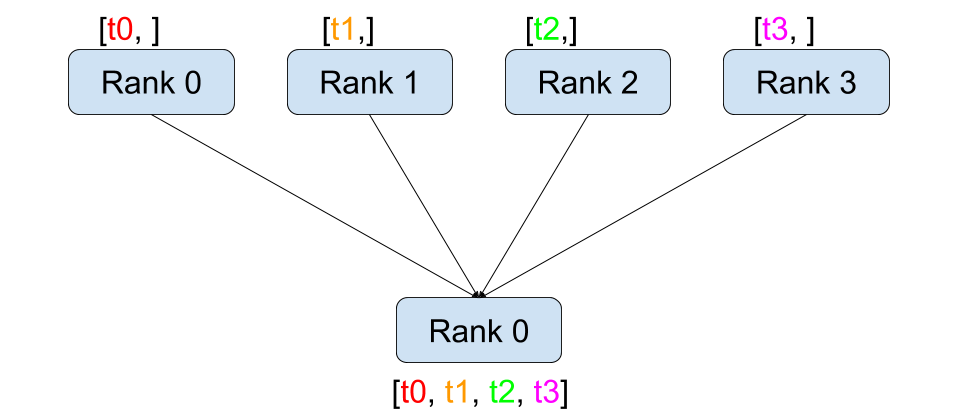
scatter
Image(url='https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/3aa3584628cb0526c8b0e9d02b15d876.png', width=400)
def dist_scatter():
dist.barrier()
rank = dist.get_rank()
world_size = dist.get_world_size()
if rank == 0:
logging.info(f"rank: {rank} is scattering data")
tensor = torch.zeros(world_size)
before_tensor = tensor.clone()
if dist.get_rank() == 0:
# Assumes world_size of 2.
# Only tensors, all of which must be the same size.
t_ones = torch.ones(world_size)
t_fives = torch.ones(world_size) * 5
# [[1, 1], [5, 5]]
scatter_list = [t_ones, t_fives]
else:
scatter_list = None
dist.scatter(tensor, scatter_list, src=0)
logging.info(f"scatter, rank: {rank}, before scatter: {repr(before_tensor)} after scatter: {repr(tensor)}")
dist.barrier()
scatter 的用法就是从某个节点把数据分散到所有节点,包括自己。scatter_list 本身两个数组,在指定 src=0 (source)(由 rank 0 来分散数据)时,scatter_list数据被分别发送给 rank 0 和 rank 1,最终赋值到 tensor 上。
INFO:root:rank: 0 is scattering data
INFO:root:scatter, rank: 1, before scatter: tensor([0., 0.], device='cuda:1') after scatter: tensor([5., 5.], device='cuda:1')
INFO:root:scatter, rank: 0, before scatter: tensor([0., 0.], device='cuda:0') after scatter: tensor([1., 1.], device='cuda:0')
gather
Image(url='https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/7e8670a3b7cdc7848394514ef1da090a.png', width=400)
def dist_gather():
dist.barrier()
rank = dist.get_rank()
world_size = dist.get_world_size()
tensor = torch.tensor([rank], dtype=torch.float32)
before_tensor = tensor.clone()
gather_list = [torch.zeros(1) for _ in range(world_size)] if rank == 0 else None
dist.gather(tensor, gather_list, dst=0)
logging.info(f"gather, rank: {rank}, before gather: {repr(before_tensor)} after gather: {repr(gather_list)}")
dist.barrier()
gather 的作用是 scatter 相反作用的,让所有 rank 上的 tensor 收集到 rank 为 dst (destination) 的卡上
INFO:root:gather, rank: 0, before gather: tensor([0.], device='cuda:0') after gather: [tensor([0.], device='cuda:0'), tensor([1.], device='cuda:0')]
INFO:root:gather, rank: 1, before gather: tensor([1.], device='cuda:1') after gather: None
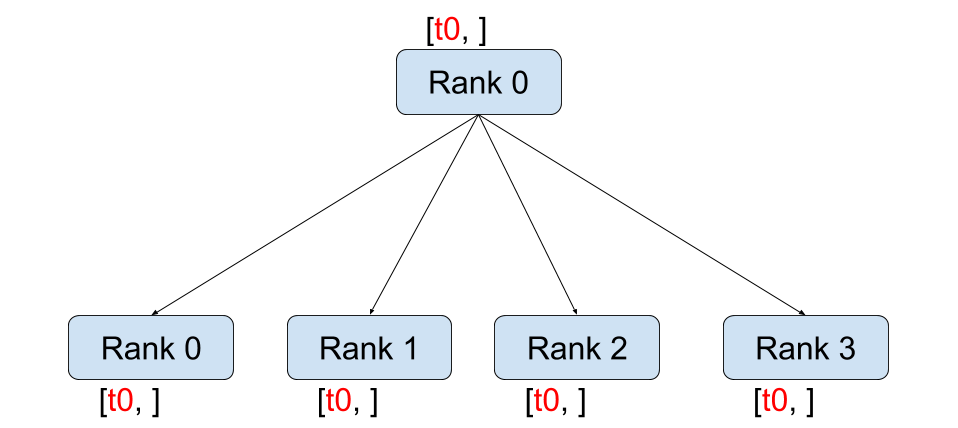
broadcast
Image(url='https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/525847c9d4b48933cb231204a2d13e0e.png', width=400)
def dist_broadcast():
dist.barrier()
rank = dist.get_rank()
world_size = dist.get_world_size()
src_rank = 0
tensor = torch.tensor(rank)
before_tensor = tensor.clone()
dist.broadcast(tensor, src=src_rank)
logging.info(f"broadcast, rank: {rank}, before broadcast tensor: {repr(before_tensor)} after broadcast tensor: {repr(tensor)}")
dist.barrier()
broadcast 的作用就是把 rank 为 src_rank 的 tensor 广播到其他 rank 上。
INFO:root:broadcast, rank: 1, before broadcast tensor: tensor(1, device='cuda:1') after broadcast tensor: tensor(0, device='cuda:1')
INFO:root:broadcast, rank: 2, before broadcast tensor: tensor(2, device='cuda:2') after broadcast tensor: tensor(0, device='cuda:2')
INFO:root:broadcast, rank: 3, before broadcast tensor: tensor(3, device='cuda:3') after broadcast tensor: tensor(0, device='cuda:3')
INFO:root:broadcast, rank: 0, before broadcast tensor: tensor(0, device='cuda:0') after broadcast tensor: tensor(0, device='cuda:0')
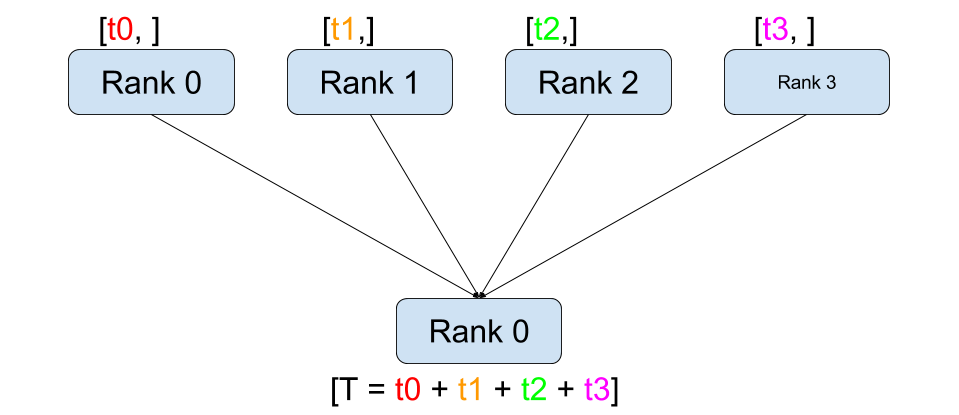
reduce
Image(url='https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/a9ef6dbfcf0761f7fb20154c4db4d3f2.png', width=400)
from torch.distributed import ReduceOp
def dist_reduce():
dist.barrier()
rank = dist.get_rank()
world_size = dist.get_world_size()
tensor = torch.tensor([rank], dtype=torch.float32)
before_tensor = tensor.clone()
dist.reduce(tensor, op=ReduceOp.SUM, dst=0)
logging.info(f"reduce, rank: {rank}, before reduce: {repr(before_tensor)} after reduce: {repr(tensor)}")
dist.barrier()
reduce 的作用和 gather 类似,都是把所有卡上数据集合到某个卡上,但不会组合为 list,会直接对这些数据进行结合式的计算。
INFO:root:reduce, rank: 1, before reduce: tensor([1.], device='cuda:1') after reduce: tensor([1.], device='cuda:1')
INFO:root:reduce, rank: 0, before reduce: tensor([0.], device='cuda:0') after reduce: tensor([6.], device='cuda:0')
INFO:root:reduce, rank: 2, before reduce: tensor([2.], device='cuda:2') after reduce: tensor([2.], device='cuda:2')
INFO:root:reduce, rank: 3, before reduce: tensor([3.], device='cuda:3') after reduce: tensor([3.], device='cuda:3')
rank 0 上的 tensor 值为 0+1+2+3 = 6
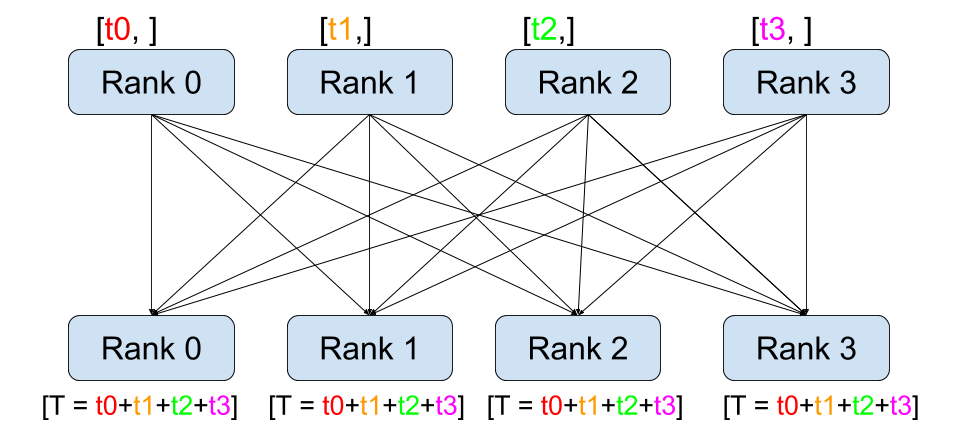
all-reduce
Image(url='https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/8172236b90e6b20b75b2428bb4376adc.png', width=400)
def dist_allreduce():
print_rank_0("all_reduce:")
dist.barrier()
rank = dist.get_rank()
# world_size = torch.distributed.get_world_size()
tensor = torch.tensor([rank], dtype=torch.float32)
input_tensor = tensor.clone()
dist.all_reduce(tensor)
logging.info(f"all_reduce, rank: {rank}, before allreduce tensor: {repr(input_tensor)}, after allreduce tensor: {repr(tensor)}")
dist.barrier()
all_reduce 相当于 reduce + broadcast,all 体现在所有 rank 都要执行所有操作,可以视为 reduce + broadcast,实际应该是所有 rank 都执行 reduce。
INFO:root:all_reduce, rank: 0, before allreduce tensor: tensor([0.], device='cuda:0'), after allreduce tensor: tensor([6.], device='cuda:0')
INFO:root:all_reduce, rank: 2, before allreduce tensor: tensor([2.], device='cuda:2'), after allreduce tensor: tensor([6.], device='cuda:2')
INFO:root:all_reduce, rank: 1, before allreduce tensor: tensor([1.], device='cuda:1'), after allreduce tensor: tensor([6.], device='cuda:1')
INFO:root:all_reduce, rank: 3, before allreduce tensor: tensor([3.], device='cuda:3'), after allreduce tensor: tensor([6.], device='cuda:3')
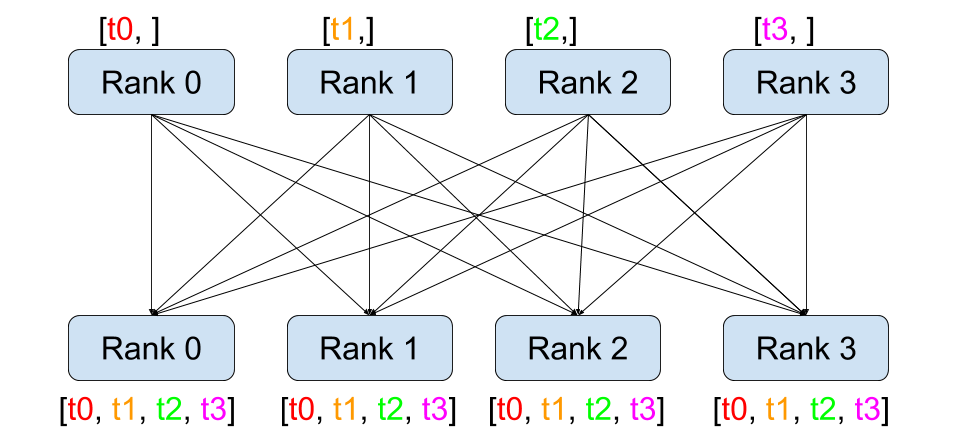
all gather
Image(url='https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/4a48977cd9545f897942a4a4ef1175ac.png', width=400)
def dist_allgather():
dist.barrier()
rank = dist.get_rank()
world_size = dist.get_world_size()
input_tensor = torch.tensor(rank)
tensor_list = [torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.int64) for _ in range(world_size)]
dist.all_gather(tensor_list, input_tensor)
logging.info(f"allgather, rank: {rank}, input_tensor: {repr(input_tensor)}, output tensor_list: {tensor_list}")
dist.barrier()
all_gather 也是类似所有 rank 执行 gather
INFO:root:allgather, rank: 0, input_tensor: tensor(0, device='cuda:0'), output tensor_list: [tensor([0], device='cuda:0'), tensor([1], device='cuda:0')]
INFO:root:allgather, rank: 1, input_tensor: tensor(1, device='cuda:1'), output tensor_list: [tensor([0], device='cuda:1'), tensor([1], device='cuda:1')]
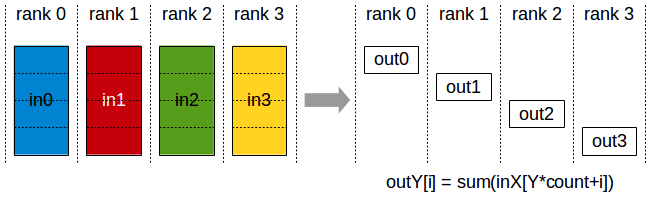
reduce-scatter
Image(url='https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/66ea136cfe7f3e7394fd0b056fd9d949.png', width=400)
def dist_reducescatter():
dist.barrier()
rank = dist.get_rank()
world_size = dist.get_world_size()
output = torch.empty(1, dtype=torch.int64)
input_list = [torch.tensor(rank*2+1), torch.tensor(rank*2+2)]
dist.reduce_scatter(output, input_list, op=ReduceOp.SUM)
dist.barrier()
logging.info(f"reduce_scatter, rank: {rank}, input_list: {input_list}, tensor: {repr(output)}")
dist.barrier()
reduce_scatter 是每个 rank 上都有完整的数据,但 reduce 后再 scatter 到所有 rank 上。
INFO:root:reduce_scatter, rank: 0, input_list: [tensor(1, device='cuda:0'), tensor(2, device='cuda:0')], tensor: tensor([4], device='cuda:0')
INFO:root:reduce_scatter, rank: 1, input_list: [tensor(3, device='cuda:1'), tensor(4, device='cuda:1')], tensor: tensor([6], device='cuda:1')
rank 0 上是 [1,2], rank 1 上是 [3,4], 执行 reduce 效果是 [4,6], 再加上 scatter 效果变成了 rank 0 上是 4, rank 1 上是 6。