学习到现在,作为我们的java萌新来说,是时候来学习一点偷懒的武林秘籍了,今天我给大家介绍的就是在无上秘宝--mybatis持久型框架.
学习一个东西之前,我们得首先了解他的前世今生...
前世:原是Apache的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年6月这个项目由ApacheSoftware Foundation 迁移到了 Google Code,随着开发团队转投GoogleCode 旗下, iBatis3.x正式更名为MyBatis。
适用范围:
- MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码手动设置参数以及手动获取结果集的操作。
- MyBatis 可以使用 XML 或注解来配置和映射,将数据库中的记录映射成Java 的 POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的 Java 对象),是一种 ORM(ORMObject Relational Mapping 对象关系映射)实现.
(映射(只能多对一,不能一对多)相信大家应该都不陌生,在数学中指的是一一对应的关系,单射 满射 同时满足这两点的是双射,比如下图所示)
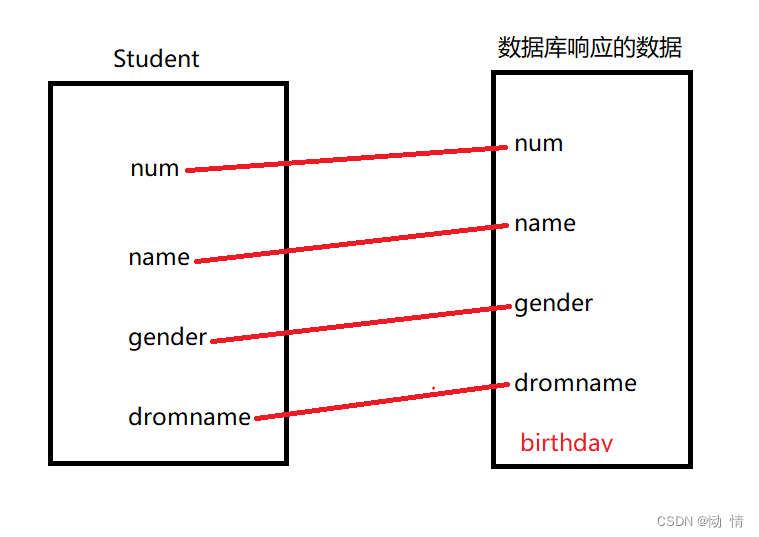
前面集合的元素与后面集合的元素有且只有一个与之相对应,一个只能对一个,这是单射,后面集合的元素都可以在前面集合中找到与之相对应的元素叫做满射,mybatis就是用了这个映射机制,对数据进行自动封装,可以减轻我们部分无聊且乏味的代码量.
那我们开始进入正题,怎么才能灵活运用这款神器呢?
MyBatis环境搭建:
1.导入MyBatis Jar包数据库驱动包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>2.创建MyBatis全局配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config
3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="" />
<property name="url" value="" />
<property name="username" value="" />
<property name="password" value=""/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
</configuration>3.创建 sql 映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE
mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="接口地址">
定义 sql 语句
</mapper>以下是我总结的一点干货:
1.将一个wab前端先封装成一个Maven项目
2.创建后端三层架构:Dao-数据库进行连接 model-创建实体对象 service-进行逻辑语言的封装
3.在pom.xml中配置所需要的Jar包(最基本的就是Sql,mybatis,junit)
4.在resources中创建一个mappers的包,然后在resources下创建一个mybatis-config.xml(配置mybatis全局配置文件),然后另外一个就是config-properties(定义连接数据库的路径)
5.在Util中创建一个关于mybitisUtil(官方提供)
6.在dao中写接口(里面写方法),在mappers中写接口的映射文件(SQL语句)
Mybatis-Dao 层 Mapper 接口化开发
Mapper 接口开发方式只需要程序员编写 Mapper 接口,由 Mybatis 框架创建接
口的动态代理对象,使用 sqlsession.getMapper(接口.class);获得代理对象.
Mapper 接口开发需要遵循以下规范:
1、 Mapper.xml 文件中的 namespace 与 mapper 接口的类路径相同.
2、 Mapper 接口方法名和 Mapper.xml 中定义的每个 statement 的 id 相同.
3、 Mapper 接口方法的输入参数类型和 mapper.xml 中定义的每个 sql 的
parameterType 的类型相同.
4、 Mapper 接口方法的输出参数类型和 mapper.xml 中定义的每个 sql 的
resultType 的类型相同.
在mybatis中,我们可以清楚地直到运行的过程,这里有一个叫做日志的功能
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>参数传递
单个参数直接传递
User selectUsers(int id);
多个参数使用@Param(“id”)绑定
User selectUsers(@Param(“id”)int id,@Param(“name”)String name);
<select id="selectUsers" resultType="User">
select id, username, password
from users where id = #{id} and username=#{name}
</select>
如果传入一个复杂的对象,就需要使用 parameterType 参数进行类型定义,例如:
void insertUser(User user);
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="User">
insert into users (id, username, password)
values (#{id}, #{username}, #{password})
</insert>这的有个特别要强调的一个容易弄混的一个知识点
#{}和${}的区别
#{参数名}:传值时预编译,更安全,只用于向sql中传值
${参数名}:传值时直接将参数拼接上去的(不建议),只要用来动态的向sql中传列名,排序
字符串传递时,需要绑定处理
对象映射
现在有一种情况,前面的集合中的一个元素又是另外一个新的集合,但是数据库返回的值并没有自动区分的能力,所以这种情况是会报错的,看下图
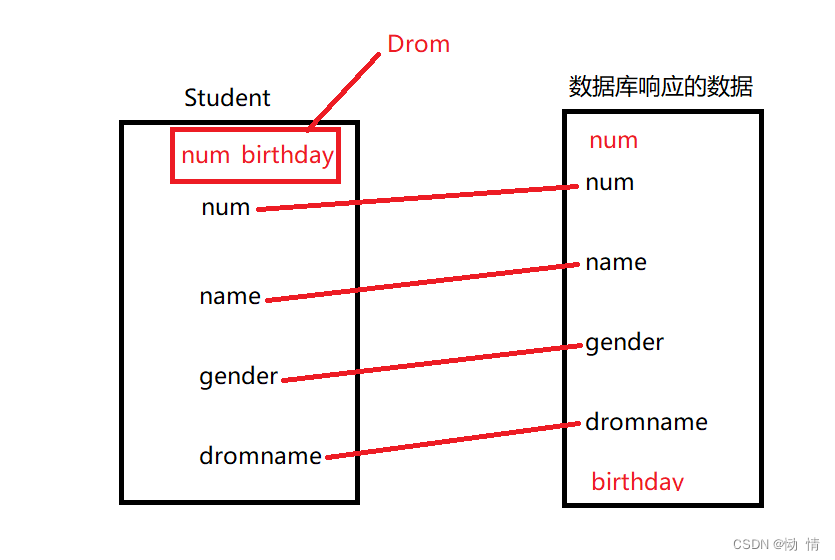
从数据库同时传过来一个学生num和一个宿舍num,如果我们什么都不做,mybatis是无法区分这两个哪个是哪个的,所以,作为优雅的mybatis,自然也会有相应的处理方法
特殊处理定义 resultMap
<!--
mybatis默认配置是,一旦出现了嵌套关联查询,就不自动映射
-->
<resultMap id="studentmap" type="Student">//返回的是一个Student对象
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="num" property="num"></result>
<result column="name" property="name"></result>
<result column="gender" property="gender"></result>
<result column="birthday" property="brithday"></result>
<result column="oper_time" property="operTime"></result>
<result column="dromNum" property="num"></result>
<!--
用来封装关联的对象信息 property="dorm", 就会创建一个关联的对象
-->
<association property="admin" javaType="Admin">//Student的定义的成员变量--Admin
<result column="account" property="account"></result>
</association>
<association property="drom" javaType="Drom">//Student的定义的成员变量--Drom
<result column="dromNum" property="dromNum"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="findStudentById" parameterType="int" resultMap="studentmap" >
SELECT
s.id,
s.num,
s.name,
s.gender,
s.birthday,
d.num dromNum,
a.account,
s.oper_time
FROM student s LEFT JOIN admin a ON s.adminid=a.id
LEFT JOIN drom d ON s.dromid=d.id
where s.id=#{id} </select>- resutlMap 的 id 属性是 resutlMap 的唯一标识,本例中定义为“useresultMap”
- resutlMap 的 id 属性是映射的 POJO 类
- id 标签映射主键,result 标签映射非主键
- property 设置 POJO 的属性名称,column 映射查询结果的列名称
注解查询
@Insert: 插入 sql , 和 xml insert sql 语法完全一样
@Select: 查询 sql, 和 xml select sql 语法完全一样
@Update: 更新 sql, 和 xml update sql 语法完全一样
@Delete: 删除 sql, 和 xml delete sql 语法完全一样
@Param: 入参
@Results : 设置结果集合
@Result: 结果
//@Delete("SQL语句")//注解标签,用于比较简单的SQL查询语句,也用于单标查询,也可以进行映射
Student findStudentById1(int id);Mybatis 动态 SQL
<!-- 动态的sql语句,where标签,当where标签内有if成立时,会自动生成where关键字,如果where后面有and or关键字也会自动删除 /-->
<!-- 在以前这个问题也是一个比较麻烦的问题,程序员经常用1=1或者设置一个状态进行处理这个问题,这是不优雅的-->
<select id="findStudent" resultType="Student">
select * from student
<!-- <where> 如果where元素与你的期望的不太一样,你也可以通过自定义trim元素定制where元素的功能-->
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and|or">//自定义where以及where自动过滤的符号
<if test="name!=null">
and name=#{name}
</if>
<if test="num!=null">
and num=#{num}
</if>
<if test="gender!=null">
and gender=#{gender}
</if>
</trim>
<!-- </where>-->
</select>
<select id="findStudent2" resultType="Student">
select * from student
where
<choose>//如果...如果...否则...(只能执行一个)
<when test="name!=null">
name=#{name}
</when>
<when test="num!=null">
and num=#{num}
</when>
<otherwise>
and gender=#{gender}
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
<update id="upDateStudent" parameterType="Student">
update student
<set>//自动屏蔽最后一个逗号
<if test="name!=null">
name=#{name},
</if>
<if test="num!=null">
num=#{num},
</if>
<if test="gender!=null">
gender=#{gender}
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteStudents" parameterType="list">
delete from student
<where>
<foreach collection="list" item="id" open="id in(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>//主要用在构建 in 条件中,它可以在 SQL 语句中进行迭代一个集合
</where>
</delete>特殊符号处理
xml和html都是标记语言,都是由标签组成,故在写SQL语句中有些符号不能直接写,比如:< > &
<!--在mybatis中的xml中,xml是一个标记语言,故存在一些特殊的符号, < < > > & & 还有一种方式进行选择,<![CDATA[ ]]> xml 会自动编译成对应的图书符号 -->
mybatis 缓存
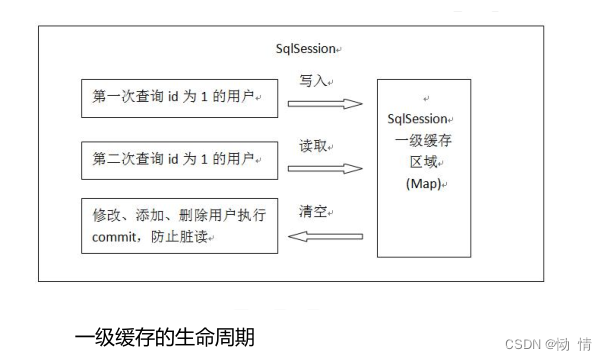
/* mybatis 存在一级缓存和二级缓存 * 缓存是什么? 缓存的作用是减少数据库的压力,提高查询性能,缓存实现的原理是从数据库查询到的数据 * 使用完之后没有即使销毁,而是存放在内存中(缓存中),当再次需要获取高对象中,直接在内存中惊醒获取 * 不在数据库中执行SQl语句进行获取,因此提高了数据库的性能 * 一级缓存:会随着SqlSession关闭而清楚缓存 * 二级缓存:会创立一个有时间限制一个缓存,不会因为SqlSession关闭而清楚 */
一级缓存的生命周期:
二级缓存的生命周期:
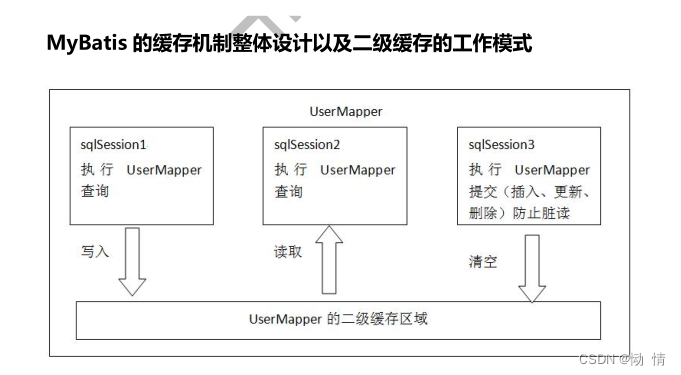
但是二级缓存不像一级缓存一样,二级缓存需要我们手动的进行配置
第一步:启用二级缓存
在 SqlMapperConfig.xml 中启用二级缓存,如下代码所示,当
cacheEnabled 设置为 true 时启用二级缓存,设置为 false 时禁用二级缓存。
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
第二步:对象序列化
将所有的 POJO 类实现序列化接口 Java.io. Serializable。
第三步:配置映射文件
在 Mapper 映射文件中添加<cache />,表示此 mapper 开启二级缓存。
当 SqlSeesion 关闭时,会将数据存入到二级缓存.
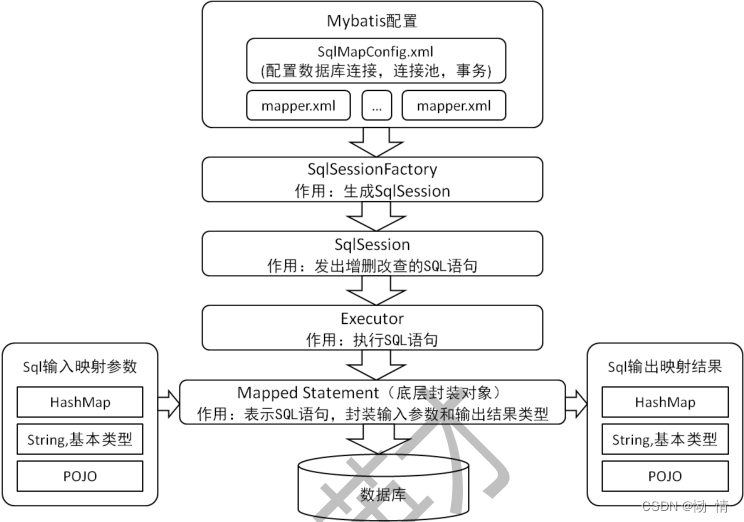
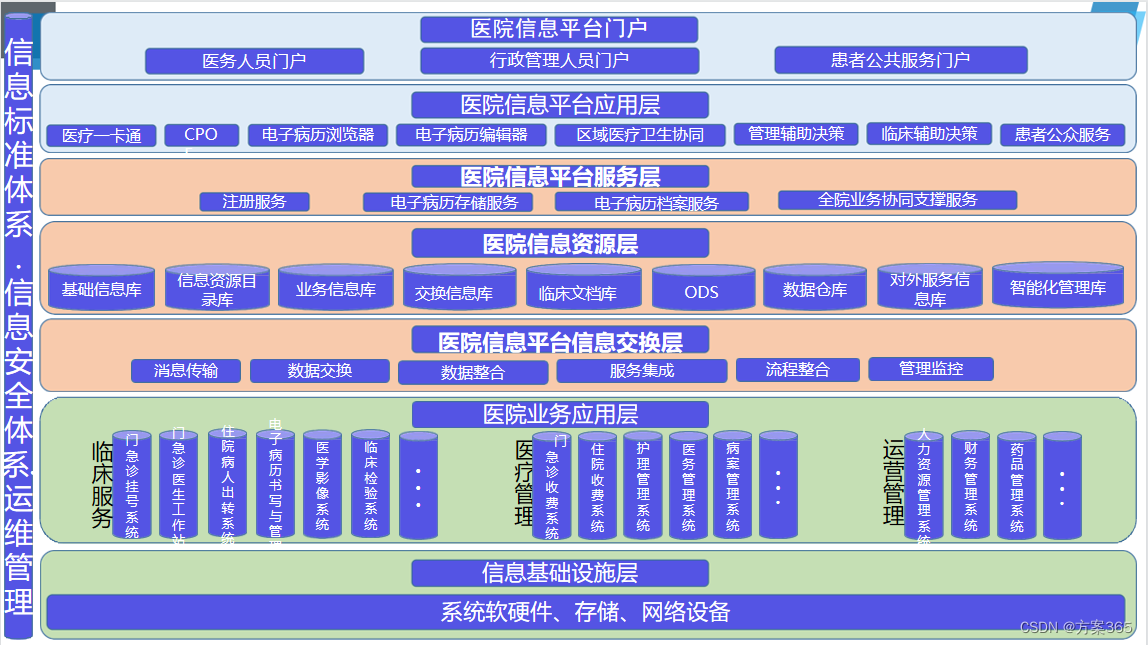
给大家分享一个mybatis的基本流程图: