一、基本介绍:
1、引入:
(1)前面我们保存多个数据使用的是数组,但数组不足的地方有:
1)长度开始时必须指定,而且一旦指定,不能更改
2)保存的必须为同一类型的元素
3)使用数组进行增加元素的示意代码—比较麻烦
(2)集合
1)可以动态保存任意多个对象,使用比较方便!
2)提供了一系列方便的操作对象的方法:add、remove、set、get等
3)使用集合添加,删除新元素的示意代码—简洁了
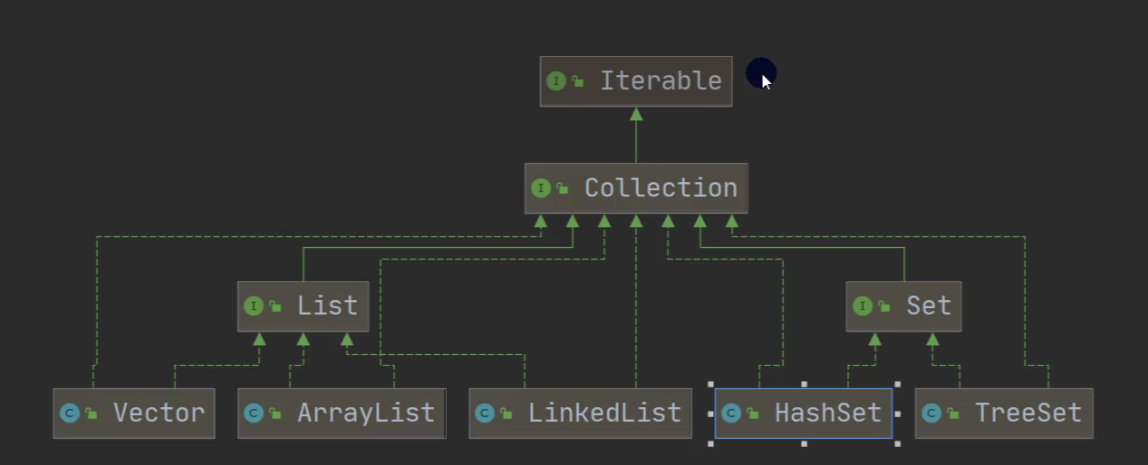
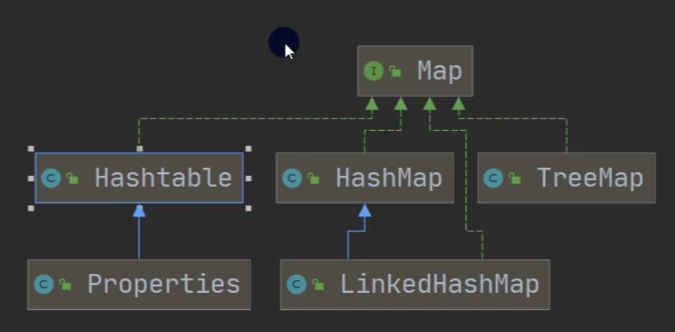
2、java的集合类很多,主要分为两大类:
3、快速入门
package Collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Collection01 {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
//单列集合,存放的是一个对象
ArrayList arrayList=new ArrayList();
arrayList.add("jack");
arrayList.add("tom");
//双列集合,存放的是键值对 K-V
HashMap hasMap=new HashMap();
hasMap.put("N01","Beijing");
hasMap.put("N02","Shanghai");
}
}
二、Collection接口和常用方法:
1、Collection接口实现类的特点:
(1)Collection实现子类可以存放多个元素,每个元素可以是Object
(2)有些Collection的实现类,可以存放重复的元素,有些不可以
(3)有些Collection的实现类,有些是有序的(List),有些不是有序的(Set)
(4)Collection接口没有直接地实现子类,是通过它的子接口Set和List来实现的
2、Collection接口常用方法:

package Collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class List_ {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();
list.add("jack");
list.add(10);
list.add(true);
System.out.println("lsit="+list);
//lsit=[jack, 10, true]
list.remove(true);
System.out.println("lsit删掉true了吗:"+list);
//lsit删掉true了吗:[jack, 10]
System.out.println("list是否包含jack:"+list.contains("jack"));
//list是否包含jack:true
System.out.println("list包含的元素个数:"+list.size());
//list包含的元素个数:2
System.out.println("list是否为空:"+list.isEmpty());
//list是否为空:false
list.clear();
System.out.println("list是否已经清空:"+list);
//list是否已经清空:[]
ArrayList list2=new ArrayList();
list2.add("tom");
list2.add("smith");
list.addAll(list2);
System.out.println("list把list2的元素全部添加:"+list);
//list把list2的元素全部添加:[tom, smith]
System.out.println("在list中查找list2的全部元素:"+list.containsAll(list2));
//在list中查找list2的全部元素:true
list.removeAll(list2);
System.out.println("把list中list2的元素全部删掉:"+list);
//把list中list2的元素全部删掉:[]
}
}
3、Collection接口遍历元素方式:
(1)方式一:使用Iterator(迭代器)
1)Iterator对象称为迭代器,主要用于遍历Collection集合中的元素
2)所有实现了Collection接口的集合类都有一个Iterator()方法,用以返回一个实现了Iterator接口的对象,即可以返回一个迭代器
3)Iterator仅用于遍历集合,Iterator本身并不存放对象

4)
5)
package Collection_;
import java.awt.print.Book;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Objects;
public class CollectionIterator {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col=new ArrayList();
col.add(new Book1("三国演义","罗贯中",10.1));
col.add(new Book1("小李飞刀","古龙",5.1));
col.add(new Book1("红楼梦","曹雪芹",34.6));
//遍历col集合输出
//1、先得到col对应的迭代器
//2、使用while循环,快捷键:itit,
//Ctrl+J可以查看更多的快捷键
//3、当退出while循环后,这时iterator迭代器,指向最后的元素,iterator.next();报错
//4、如果希望再次遍历,需要重置迭代器
Iterator iterator=col.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){//判断是否还有数据
//返回下一个元素,类型是Object,编译类型是Object,
// 但运行类型取决于col集合里添加的内容,可能是Book1,也可能是String
Object obj=iterator.next();
System.out.println("obj="+obj);
}
iterator=col.iterator();//重置迭代器
System.out.println("=========第二次遍历========");
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Object obj=iterator.next();
System.out.println("obj="+obj);
}
}
}
class Book1{
private String name;
private String author;
private double price;
public Book1(String name,String author,double price){
this.name=name;
this.author=author;
this.price=price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
//obj=Book{name='三国演义', author='罗贯中', price=10.1}
//obj=Book{name='小李飞刀', author='古龙', price=5.1}
//obj=Book{name='红楼梦', author='曹雪芹', price=34.6}
//=========第二次遍历========
//obj=Book{name='三国演义', author='罗贯中', price=10.1}
//obj=Book{name='小李飞刀', author='古龙', price=5.1}
//obj=Book{name='红楼梦', author='曹雪芹', price=34.6}
(2)方式二:for循环增强
1)特点:增加for就是简化版的iterator,本质一样,只能用于遍历集合或数组
2)基本语法:
for(元素类型 元素名:集合名式数组名){
访问元素;
}package Collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionFor {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection col=new ArrayList();
col.add(new Book1("三国演义","罗贯中",10.1));
col.add(new Book1("小李飞刀","古龙",5.1));
col.add(new Book1("红楼梦","曹雪芹",34.6));
//1、在Collection集合中使用增强for
//2、增强for,底层仍然是迭代器,所以增加for就是简化版的iterator
//3、增强for的快捷键是I
for(Object book:col){
System.out.println("bool="+book);
}
}
}
//bool=Book{name='三国演义', author='罗贯中', price=10.1}
//bool=Book{name='小李飞刀', author='古龙', price=5.1}
//bool=Book{name='红楼梦', author='曹雪芹', price=34.6}(3)练习题:

//我的代码:
package Collection_;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class CollectionExercise {
@SuppressWarnings({"all"})
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog1=new Dog("jack",1);
Dog dog2=new Dog("tom",2);
Dog dog3=new Dog("smith",3);
ArrayList list=new ArrayList();
list.add(dog1);
list.add(dog2);
list.add(dog3);
System.out.println("用迭代器来遍历:");
Iterator iterator=list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(list);
}
System.out.println("用增强for循环来遍历:");
for (Object dog :list) {
System.out.println(list);
}
}
}
class Dog{
private String name;
private int age;
public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
//用迭代器来遍历:
//[Dog{name='jack', age=1}, Dog{name='tom', age=2}, Dog{name='smith', age=3}]
//[Dog{name='jack', age=1}, Dog{name='tom', age=2}, Dog{name='smith', age=3}]
//[Dog{name='jack', age=1}, Dog{name='tom', age=2}, Dog{name='smith', age=3}]
//用增强for循环来遍历:
//[Dog{name='jack', age=1}, Dog{name='tom', age=2}, Dog{name='smith', age=3}]
//[Dog{name='jack', age=1}, Dog{name='tom', age=2}, Dog{name='smith', age=3}]
//[Dog{name='jack', age=1}, Dog{name='tom', age=2}, Dog{name='smith', age=3}]
//改进:
list.add(new Dog("jack",1));
list.add(new Dog("tom",2));
list.add(new Dog("smith",3));