机器人C++库(12)Robotics Library 之路径规划算法:PRM、RRT、EET算法
RL库的运动规划(rl::plan)模块集成了以下经典的路径规划算法:
- PRM算法:概率路线图算法
- RRT算法:快速探索随机树算法
- EET算法:搜索树算法-基于采样:https://blog.csdn.net/yohnyang/article/details/127783244
另外,补充一个开源运动规划库OMPL:https://ompl.kavrakilab.org/index.html
下边参考官方给出来的例程讲述路径规划算法原理及使用,规划效果如下图所示:
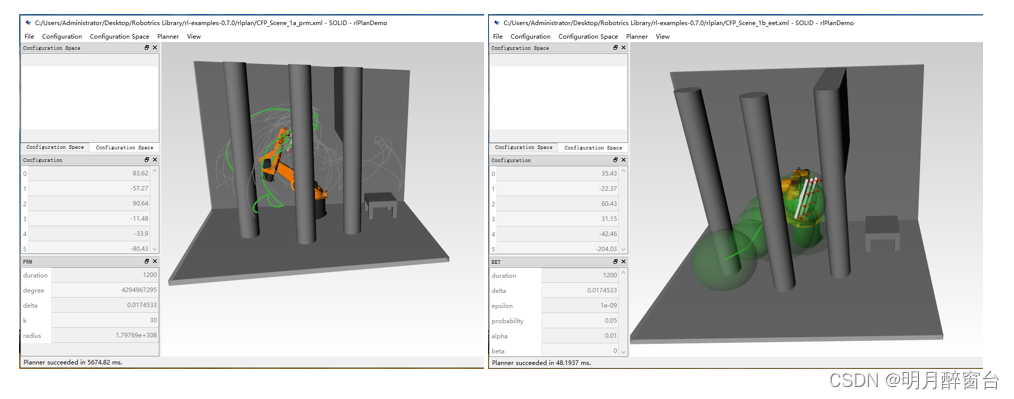
左图是PRM算法进行路径规划的结果,灰色路径是拟生成所有路径,绿色路径是最优路径;右图是采用EET搜索树算法进行规划的结果,绿色球球心连接起点与终点的最短路径即为最优路径。
1.PRM算法
概率路线图(Probabilistic Roadmap,PRM)属于综合查询方法,其步骤如下:
- Step1:预处理

- Step2:搜索
采用图搜索算法对无向图G进行搜索(A*搜索),如果能找到起始点A到终点B的路线,说明存在可行的运动规划方案。

- RL库实现:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <boost/lexical_cast.hpp>
#include <rl/mdl/Kinematic.h>
#include <rl/math/Unit.h>
#include <rl/plan/KdtreeNearestNeighbors.h>
#include <rl/plan/Prm.h> //1
#include<rl/plan/Rrt.h>
#include <rl/plan/RecursiveVerifier.h>
#include <rl/plan/SimpleModel.h>
#include <rl/plan/SimpleOptimizer.h>
#include <rl/plan/UniformSampler.h>
#include <rl/sg/Model.h>
#define RL_SG_BULLET 1
#ifdef RL_SG_BULLET
#include <rl/sg/bullet/Scene.h>
#endif // RL_SG_BULLET
#ifdef RL_SG_FCL
#include <rl/sg/fcl/Scene.h>
#endif // RL_SG_FCL
#ifdef RL_SG_ODE
#include <rl/sg/ode/Scene.h>
#endif // RL_SG_ODE
#ifdef RL_SG_PQP
#include <rl/sg/pqp/Scene.h>
#endif // RL_SG_PQP
#ifdef RL_SG_SOLID
#include <rl/sg/solid/Scene.h>
#endif // RL_SG_SOLID
int main()
{
std::string scene_path = "./puma560/unimation-puma560_boxes.xml";
std::string model_path = "./puma560/unimation-puma560.xml";
//末端位姿
float X0 = 0;
float Y0 = 0;
float Z0 = 0;
float R = 90;
float P = 0;
float Y = 0;
std::vector<rl::math::Real>angles0{ 90,-180,90,0,0,0 };
std::vector<rl::math::Real>angles1{ 0,0,90,0,0,0 };
//定义场景碰撞检测模型
std::shared_ptr<rl::sg::Scene> scene;
scene = std::make_shared<rl::sg::bullet::Scene>();
//读入场景图像
scene->load(scene_path);
//读入机械臂模型
std::shared_ptr<rl::kin::Kinematics> kinematics(rl::kin::Kinematics::create(model_path));
//word为末端位姿?
rl::math::Transform world = rl::math::Transform::Identity();
world = rl::math::AngleAxis(R * ::rl::math::DEG2RAD, ::rl::math::Vector3::UnitZ())
* ::rl::math::AngleAxis(P * ::rl::math::DEG2RAD, ::rl::math::Vector3::UnitY())
* ::rl::math::AngleAxis(Y * ::rl::math::DEG2RAD, ::rl::math::Vector3::UnitX());
world.translation().x() = X0;
world.translation().y() = Y0;
world.translation().z() = Z0;
kinematics->world() = world;
rl::plan::SimpleModel model;
model.kin = kinematics.get();
model.model = scene->getModel(0);
model.scene = scene.get();
rl::plan::KdtreeNearestNeighbors nearestNeighbors(&model);
rl::plan::Prm planner;
rl::plan::UniformSampler sampler;
rl::plan::RecursiveVerifier verifier;
sampler.seed(0);
planner.model = &model;
planner.setNearestNeighbors(&nearestNeighbors);
planner.sampler = &sampler;
planner.verifier = &verifier;
sampler.model = &model;
verifier.delta = 1.0f * rl::math::DEG2RAD;
verifier.model = &model;
rl::math::Vector start(kinematics->getDof());
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < kinematics->getDof(); ++i)
{
start(i) = boost::lexical_cast<rl::math::Real>(angles0[i]) * rl::math::DEG2RAD;
}
planner.start = &start;
rl::math::Vector goal(kinematics->getDof());
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < kinematics->getDof(); ++i)
{
goal(i) = boost::lexical_cast<rl::math::Real>(angles1[i]) * rl::math::DEG2RAD;
}
planner.goal = &goal;
planner.duration = std::chrono::seconds(20);
std::cout << "construct() ... " << std::endl;;
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point startTime = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
planner.construct(15);
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point stopTime = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
std::cout << "construct() " << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<double>>(stopTime - startTime).count() * 1000 << " ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << "solve() ... " << std::endl;;
startTime = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
bool solved = planner.solve();
stopTime = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
std::cout << "solve() " << (solved ? "true" : "false") << " " << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<double>>(stopTime - startTime).count() * 1000 << " ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << "NumVertices: " << planner.getNumVertices() << " NumEdges: " << planner.getNumEdges() << std::endl;
//读取路径
rl::plan::VectorList paths = planner.getPath();
/*rl::plan::VectorList::const_iterator i = paths.begin();
for (; i != paths.end(); ++i)
{
std::cout << *i*rl::math::RAD2DEG << std::endl;
}*/
//插值
rl::plan::VectorList path_;
rl::plan::VectorList::iterator i = paths.begin();
rl::plan::VectorList::iterator j = ++paths.begin();
rl::math::Real length = 0;
rl::math::Real delta = 0.05;
for (; i != paths.end() && j != paths.end(); ++i, ++j)
{
length += model.distance(*i, *j);
std::cout << "*i = " << (*i).transpose() * rl::math::RAD2DEG << std::endl << " , *j = " << (*j).transpose() * rl::math::RAD2DEG << std::endl;
rl::math::Real steps = std::ceil(model.distance(*i, *j) / delta);
rl::math::Vector inter(model.getDofPosition());
for (std::size_t k = 1; k < steps + 1; ++k)
{
model.interpolate(*i, *j, k / steps, inter);
std::cout << "k = " << k << ": " << inter.transpose() * rl::math::RAD2DEG << std::endl;
path_.push_back(inter);
}
}
std::cout << "length = " << length << std::endl;
if (solved)
{
/*if (boost::lexical_cast<std::size_t>(argv[4]) >= planner.getNumVertices() &&
boost::lexical_cast<std::size_t>(argv[5]) >= planner.getNumEdges())*/
if (17 >= planner.getNumVertices() &&
16 >= planner.getNumEdges())
{
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
else
{
std::cerr << "NumVertices and NumEdges are more than expected for this test case.";
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
2.RRT算法
RT 算法(快速扩展随机树,rapidly exploring random tree)是一种随机性算法,它可以直接应用于非完整约束系统的规划,不需进行路径转换,所以它的算法复杂度较小,尤为适用于高维多自由度的系统。
- 缺点是得到的路径质量不是很好。需要后处理进一步优化。
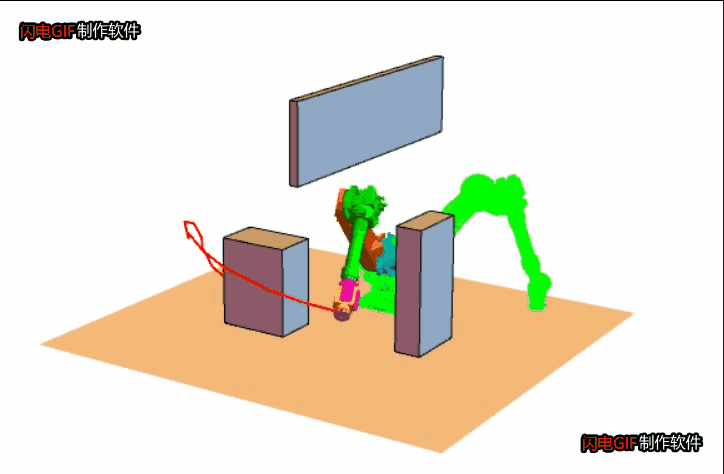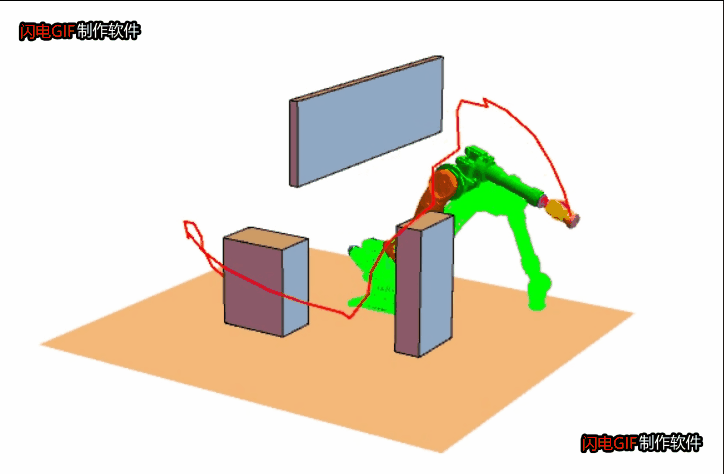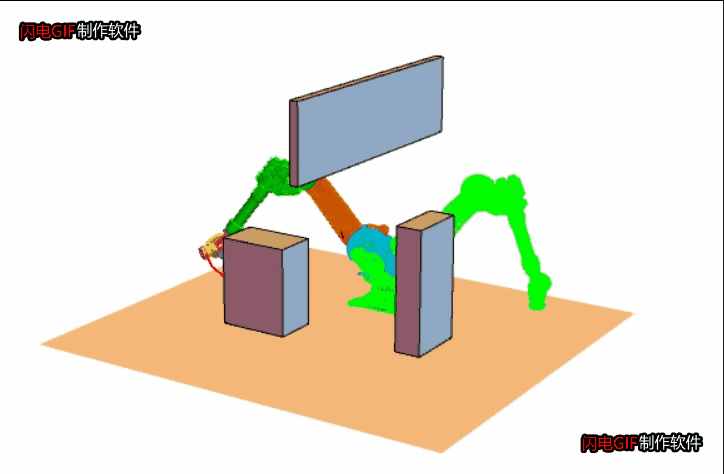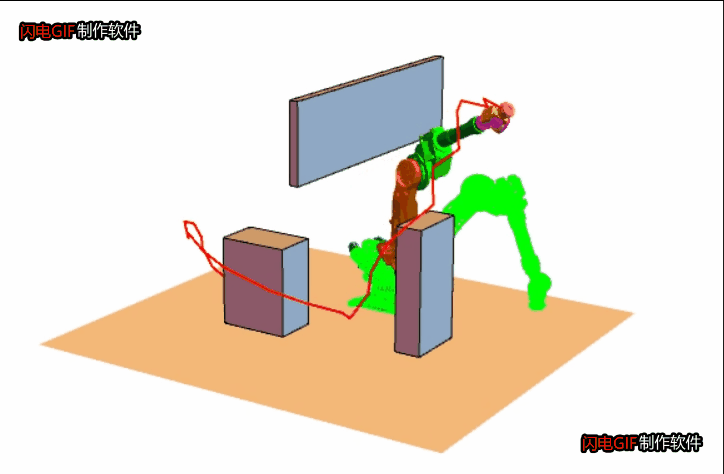
思想是快速扩张一群像树一样的路径以探索(填充)空间的大部分区域,伺机找到可行的路径。 - RRT 的基本步骤是:
1. 起点作为一颗种子,从它开始生长枝丫;
2. 在机器人的“构型”空间中,生成一个随机点X;
3. 在树上找到距离X最近的那个点,记为Y吧;
4. 朝着X的方向生长,如果没有碰到障碍物就把生长后的树枝和端点添加到树上,返回 2;
- 伪代码:
function BuildRRT(qinit, K, Δq)
T.init(qinit)
for k = 1 to K
qrand = Sample() -- chooses a random configuration
qnearest = Nearest(T, qrand) -- selects the node in the RRT tree that is closest to qrand
if Distance(qnearest, qgoal) < Threshold then
return true
qnew = Extend(qnearest, qrand, Δq) -- moving from qnearest an incremental distance in the direction of qrand
if qnew ≠ NULL then
T.AddNode(qnew)
return false
function Sample() -- Alternatively,one could replace Sample with SampleFree(by using a collision detection algorithm to reject samples in C_obstacle
p = Random(0, 1.0)
if 0 < p < Prob then
return qgoal
elseif Prob < p < 1.0 then
return RandomNode()
3.EET算法
提出一种基于工作空间信息的在探索和开发之间逐步转换的机制,详见:https://blog.csdn.net/yohnyang/article/details/127783244
- RL库算法实现:这个算法模型比较复杂,参数比较多,调参对算法结果影响很大
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <boost/lexical_cast.hpp>
//#include <rl/kin/Kinematics.h>
#include <rl/mdl/Kinematic.h>
#include <rl/math/Unit.h>
#include <rl/plan/DistanceModel.h>
#include <rl/plan/Eet.h>
#include <rl/plan/LinearNearestNeighbors.h>
#include <rl/plan/UniformSampler.h>
#include <rl/plan/WorkspaceSphereExplorer.h>
#include<rl/mdl/XmlFactory.h>
#include <rl/sg/Model.h>
#define RL_SG_BULLET 1
#ifdef RL_SG_BULLET
#include <rl/sg/bullet/Scene.h>
#endif // RL_SG_BULLET
#ifdef RL_SG_FCL
#include <rl/sg/fcl/Scene.h>
#endif // RL_SG_FCL
#ifdef RL_SG_PQP
#include <rl/sg/pqp/Scene.h>
#endif // RL_SG_PQP
#ifdef RL_SG_SOLID
#include <rl/sg/solid/Scene.h>
#endif // RL_SG_SOLID
int main()
{
/*if (argc < 6)
{
std::cout << "Usage: rlEetTest ENGINE SCENEFILE KINEMATICSFILE EXPECTED_NUM_VERTICES_MAX EXPECTED_NUM_EDGES_MAX START1 ... STARTn GOAL1 ... GOALn" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}*/
std::string scene_path = "./CFP/CFP_Scene_1.xml";
std::string kin_path = "./CFP/kuka-kr60-3.xml";
//定义场景模型
std::shared_ptr<rl::sg::Scene> scene;
scene = std::make_shared<rl::sg::bullet::Scene>();
//读入模型文件
scene->load(scene_path);
std::shared_ptr<rl::kin::Kinematics> kinematics(rl::kin::Kinematics::create(kin_path));
std::vector<rl::math::Real>angles0{ 83.62, -57.27, 90.64, -11.48, -33.9, -80.43 };
std::vector<rl::math::Real>angles1{ 35.43, -22.37, 60.43, 31.15, -42.46, -204.03 };
Eigen::Matrix<rl::math::Unit, Eigen::Dynamic, 1> qUnits(kinematics->getDof());
kinematics->getPositionUnits(qUnits);
//起点转角
rl::math::Vector start(kinematics->getDof());
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < kinematics->getDof(); ++i)
{
start(i) = boost::lexical_cast<rl::math::Real>(angles0[i]);
if (rl::math::UNIT_RADIAN == qUnits(i))
{
start(i) *= rl::math::DEG2RAD;
}
std::cout << start(i) << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
//终点转角
rl::math::Vector goal(kinematics->getDof());
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < kinematics->getDof(); ++i)
{
goal(i) = boost::lexical_cast<rl::math::Real>(angles1[i]);
if (rl::math::UNIT_RADIAN == qUnits(i))
{
goal(i) *= rl::math::DEG2RAD;
}
std::cout << goal(i) << " ";
}
std::cout<<std::endl;
rl::plan::DistanceModel model;
model.kin = kinematics.get();
model.model = scene->getModel(0);
model.scene = scene.get();
rl::plan::WorkspaceSphereExplorer explorer;
rl::plan::Eet::ExplorerSetup explorerSetup;
rl::plan::LinearNearestNeighbors nearestNeighbors(&model);
rl::plan::Eet planner;
rl::plan::UniformSampler sampler;
rl::math::Vector3 explorerGoal;
rl::math::Vector3 explorerStart;
explorer.seed(0);
planner.seed(0);
sampler.seed(0);
explorer.goal = &explorerGoal;
explorer.greedy = rl::plan::WorkspaceSphereExplorer::GREEDY_SPACE;
explorer.model = &model;
explorer.radius = 0.025;
explorer.range = 2.19;
explorer.samples = 100;
explorer.start = &explorerStart;
explorerSetup.goalConfiguration = &goal;
explorerSetup.goalFrame = -1;
explorerSetup.startConfiguration = &start;
explorerSetup.startFrame = -1;
planner.alpha = 0.01f;
planner.alternativeDistanceComputation = false;
planner.beta = 0;
planner.delta = 1.0f * rl::math::DEG2RAD;
planner.distanceWeight = 0.1f;
planner.epsilon = 1.0e-9f;
planner.explorers.push_back(&explorer);
planner.explorersSetup.push_back(explorerSetup);
planner.gamma = 1.0f / 3.0f;
planner.goal = &goal;
planner.goalEpsilon = 0.1f;
planner.goalEpsilonUseOrientation = false;
planner.max.x() = 2.77634;
planner.max.y() = 2.5;
planner.max.z() = 3.5;
planner.model = &model;
planner.min.x() = -0.72466;
planner.min.y() = -2.5;
planner.min.z() = 0;
planner.setNearestNeighbors(&nearestNeighbors, 0);
planner.sampler = &sampler;
planner.start = &start;
sampler.model = &model;
std::cout << "solve() ... " << std::endl;;
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point startTime = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
bool solved = planner.solve();
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point stopTime = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
std::cout << "solve() " << (solved ? "true" : "false") << " " << std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<double>>(stopTime - startTime).count() * 1000 << " ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << "NumVertices: " << planner.getNumVertices() << " NumEdges: " << planner.getNumEdges() << std::endl;
//读取路径
rl::plan::VectorList paths = planner.getPath();
rl::plan::VectorList::const_iterator i = paths.begin();
std::cout << "paths.size() =" << paths.size() << std::endl;
int t = 0;
for (; i != paths.end(); ++i)
{
rl::math::Vector pos = *i * rl::math::RAD2DEG;
std::cout << t <<": "<< pos.transpose() << std::endl;
t++;
}
if (solved)
{
/*if (boost::lexical_cast<std::size_t>(argv[4]) >= planner.getNumVertices() &&
boost::lexical_cast<std::size_t>(argv[5]) >= planner.getNumEdges())*/
if (120 >= planner.getNumVertices() &&
100 >= planner.getNumEdges())
{
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
else
{
std::cerr << "NumVertices and NumEdges are more than expected for this test case.";
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
参考:
1.概率路线图(PRM)算法
2.RRT算法



![[附源码]SSM计算机毕业设计志愿者管理系统论文2022JAVA](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8d927ba6340a45399f785bb846d8bc0d.png)