# include <stdio.h> # include <unistd.h> # include <sys/types.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <string.h> # include <sys/wait.h> int main ( int argc, char const * argv[ ] )
{
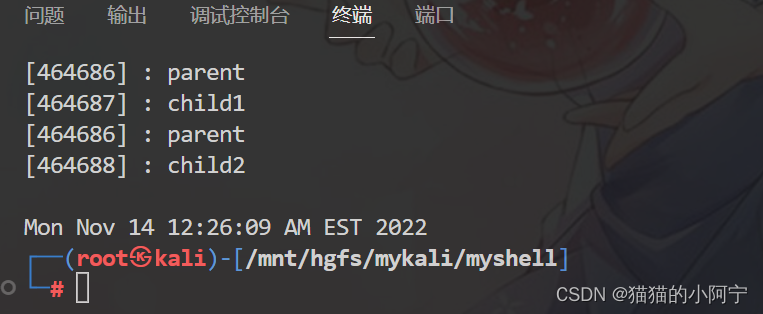
pid_t c1 = fork ( ) ;
if ( c1 == 0 )
{
printf ( "[%d] : child1\n" , getpid ( ) ) ;
execl ( "/bin/sh" , "sh" , "-c" , "date" , ( char * ) 0 ) ;
}
else if ( c1 > 0 )
{
printf ( "[%d] : parent\n" , getpid ( ) ) ;
pid_t c2 = fork ( ) ;
if ( c2 == 0 )
{
printf ( "[%d] : child2\n" , getpid ( ) ) ;
}
else if ( c2 > 0 )
{
printf ( "[%d] : parent\n" , getpid ( ) ) ;
int status;
wait ( & status) ;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
# include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <string.h> # include <unistd.h> # include <sys/types.h> # include <sys/wait.h> int main ( )
{
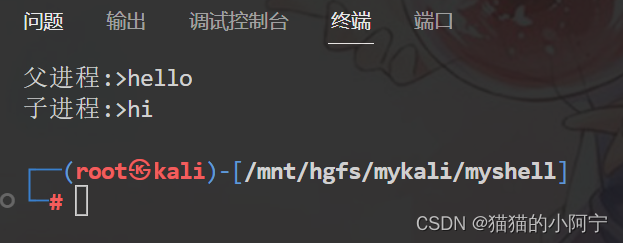
char * parent_talk[ ] = { "hello" , NULL } ;
char * child_talk[ ] = { "hi" , NULL } ;
int fd1[ 2 ] ;
int fd2[ 2 ] ;
int res = pipe ( fd1) ;
if ( res == - 1 )
{
printf ( "create pipe error.\n" ) ;
exit ( 1 ) ;
}
res = pipe ( fd2) ;
if ( res == - 1 )
{
printf ( "create pipe erroe.\n" ) ;
exit ( 1 ) ;
}
pid_t pid;
pid = fork ( ) ;
if ( pid == 0 )
{
close ( fd1[ 1 ] ) ;
close ( fd2[ 0 ] ) ;
char buf[ 256 ] ;
int i;
char * talk = child_talk[ i] ;
while ( talk != NULL )
{
sleep ( 5 ) ;
read ( fd1[ 0 ] , buf, 256 ) ;
printf ( "父进程:>%s\n" , buf) ;
write ( fd2[ 1 ] , talk, strlen ( talk) + 1 ) ;
i++ ;
talk = child_talk[ i] ;
}
close ( fd1[ 0 ] ) ;
close ( fd2[ 1 ] ) ;
}
else if ( pid > 0 )
{
close ( fd1[ 0 ] ) ;
close ( fd2[ 1 ] ) ;
char buf[ 256 ] ;
int i = 0 ;
char * talk = parent_talk[ i] ;
while ( talk != NULL )
{
write ( fd1[ 1 ] , talk, strlen ( talk) + 1 ) ;
read ( fd2[ 0 ] , buf, 256 ) ;
printf ( "子进程:>%s\n" , buf) ;
i++ ;
talk = parent_talk[ i] ;
}
close ( fd1[ 1 ] ) ;
close ( fd2[ 0 ] ) ;
int status;
wait ( & status) ;
}
return 0 ;
}
# include <stdio.h> # include <unistd.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <sys/types.h> # include <sys/wait.h> int main ( void )
{
int data = 0 ;
pid_t pid;
int choose = 0 ;
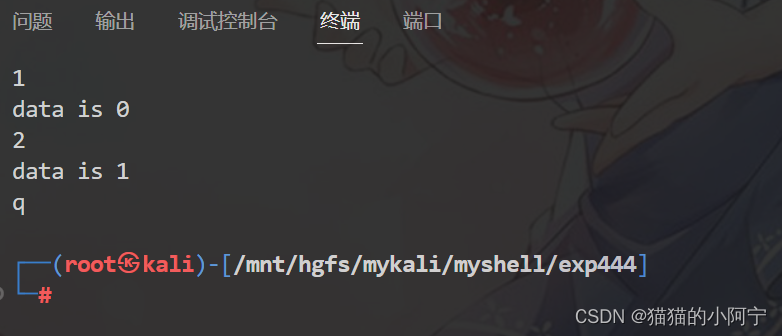
while ( ( choose = getchar ( ) ) != 'q' )
{
switch ( choose)
{
case '1' :
pid = fork ( ) ;
if ( pid < 0 )
printf ( "Error !\n" ) ;
if ( pid == 0 )
{
data++ ;
exit ( 0 ) ;
}
wait ( NULL ) ;
if ( pid > 0 )
printf ( "data is %d\n" , data) ;
break ;
case '2' :
pid = vfork ( ) ;
if ( pid < 0 )
perror ( "Error !\n" ) ;
if ( pid == 0 )
{
data++ ;
exit ( 0 ) ;
}
wait ( NULL ) ;
if ( pid > 0 )
printf ( "data is %d\n" , data) ;
break ;
default :
break ;
}
}
return 0 ;
}
# include <error.h> # include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <unistd.h> # include <sys/types.h> # include <sys/types.h> # include <sys/wait.h> int main ( )
{
char buf[ 88 ] ;
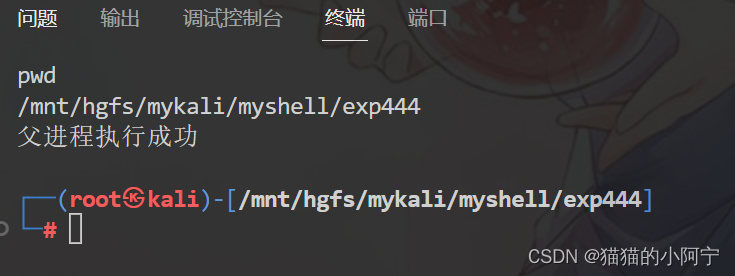
fgets ( buf, 88 , stdin ) ;
pid_t pid;
pid = fork ( ) ;
if ( pid < 0 )
perror ( "创建子进程失败" ) ;
else if ( 0 == pid)
{
execl ( "/bin/sh" , "sh" , "-c" , buf, ( char * ) 0 ) ;
}
else
{
wait ( NULL ) ;
printf ( "父进程执行成功" ) ;
}
}
管道文件的测试程序开始 管道文件测试正在进行 管道通信测试结束 # include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <string.h> # include <unistd.h> # include <sys/types.h> # include <sys/wait.h> int main ( )
{
char * parent_talk[ ] = { "管道文件的测试程序开始" , "管道文件测试正在进行" , "管道通信测试结束" , NULL } ;
char * child_talk[ ] = { "好的" , "一切正常" , "拜拜" , NULL } ;
int fd1[ 2 ] ;
int fd2[ 2 ] ;
int res = pipe ( fd1) ;
if ( res == - 1 )
{
printf ( "create pipe error.\n" ) ;
exit ( 1 ) ;
}
res = pipe ( fd2) ;
if ( res == - 1 )
{
printf ( "create pipe erroe.\n" ) ;
exit ( 1 ) ;
}
pid_t pid;
pid = fork ( ) ;
if ( pid == 0 )
{
close ( fd1[ 1 ] ) ;
close ( fd2[ 0 ] ) ;
char buf[ 256 ] ;
int i;
char * talk = child_talk[ i] ;
while ( talk != NULL )
{
sleep ( 5 ) ;
read ( fd1[ 0 ] , buf, 256 ) ;
printf ( "父进程:>%s\n" , buf) ;
write ( fd2[ 1 ] , talk, strlen ( talk) + 1 ) ;
i++ ;
talk = child_talk[ i] ;
}
close ( fd1[ 0 ] ) ;
close ( fd2[ 1 ] ) ;
}
else if ( pid > 0 )
{
close ( fd1[ 0 ] ) ;
close ( fd2[ 1 ] ) ;
char buf[ 256 ] ;
int i = 0 ;
char * talk = parent_talk[ i] ;
while ( talk != NULL )
{
write ( fd1[ 1 ] , talk, strlen ( talk) + 1 ) ;
read ( fd2[ 0 ] , buf, 256 ) ;
printf ( "子进程:>%s\n" , buf) ;
i++ ;
talk = parent_talk[ i] ;
}
close ( fd1[ 1 ] ) ;
close ( fd2[ 0 ] ) ;
int status;
wait ( & status) ;
}
return 0 ;
}
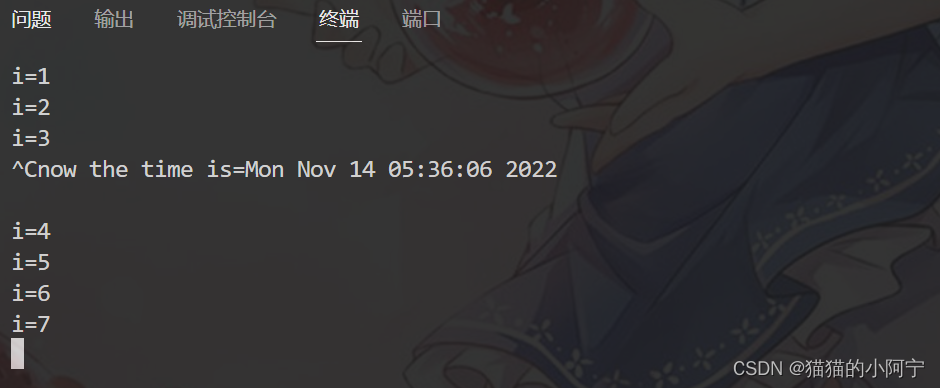
# include <signal.h> # include <sys/types.h> # include <unistd.h> # include <stdio.h> # include <time.h> void handler ( int signo)
{
signal ( SIGINT, SIG_IGN) ;
time_t timep;
time ( & timep) ;
printf ( "now the time is=%s\n" , asctime ( gmtime ( & timep) ) ) ;
signal ( SIGINT, handler) ;
}
int main ( )
{
int i;
signal ( SIGINT, handler) ;
for ( i = 1 ; i <= 100 ; i++ )
{
printf ( "i=%d\n" , i) ;
sleep ( 1 ) ;
}
printf ( "the program ends!\n" ) ;
return 0 ;
}
# include <unistd.h> # include <signal.h> # include <sys/types.h> # include <sys/wait.h> # include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> void killchild ( int pid_child) ;
void killchild ( int pid_child)
{
printf ( "killing child process \n" ) ;
int pidxx;
pidxx = wait ( NULL ) ;
printf ( "killed the child process, whose pid is %d \n" , pidxx) ;
exit ( 0 ) ;
}
void killyourself ( int ownid) ;
void killyourself ( int ownid)
{
printf ( "parent sent signal, child process killed itself \n" ) ;
exit ( 0 ) ;
}
int main ( )
{
( void ) signal ( SIGALRM, killchild) ;
int pid_child = 0 ;
int pid = fork ( ) ;
if ( pid == - 1 )
{
perror ( "fork failed\n" ) ;
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE) ;
}
if ( pid == 0 )
{
pid_child = getpid ( ) ;
( void ) signal ( SIGHUP, killyourself) ;
sleep ( 15 ) ;
kill ( getppid ( ) , SIGALRM) ;
}
else
{
sleep ( 6 ) ;
kill ( pid_child, SIGHUP) ;
exit ( 0 ) ;
}
}
# include <sys/types.h> # include <sys/ipc.h> # include <sys/shm.h> # include <fcntl.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <stdio.h> # include <string.h> struct shared_msg
{
int update;
char text[ BUFSIZ] ;
} ;
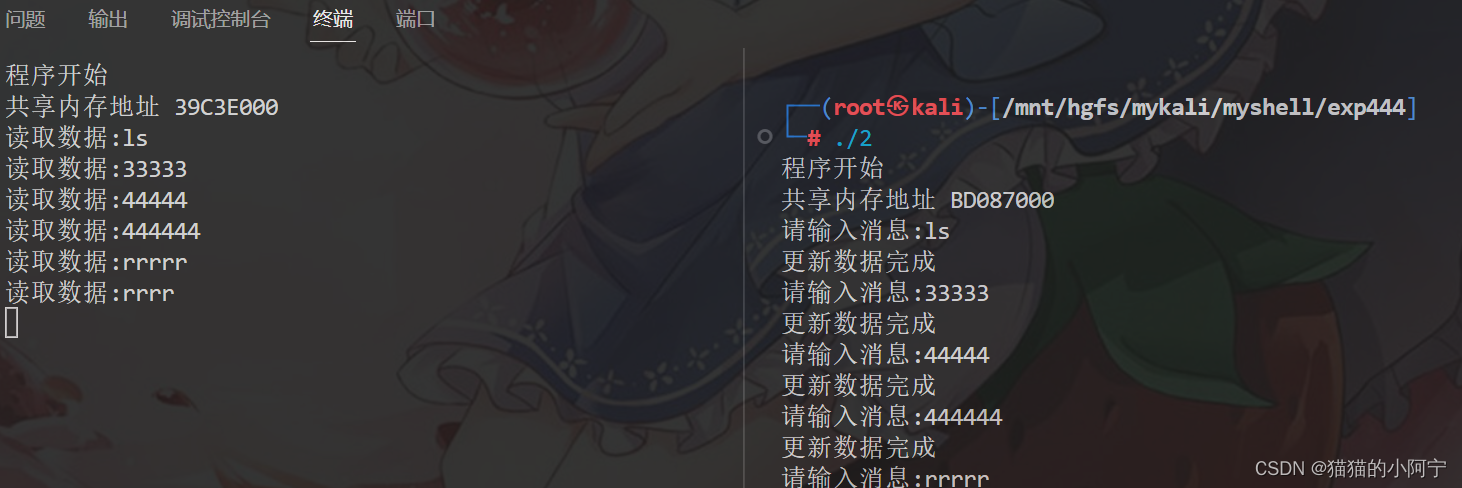
void main ( )
{
printf ( "程序开始\n" ) ;
key_t key;
int shmid;
char buf[ BUFSIZ] ;
struct shared_msg * msg;
key = ( key_t ) 1234 ;
shmid = shmget ( key, sizeof ( struct shared_msg ) , IPC_CREAT | 0666 ) ;
if ( shmid < 0 )
{
fprintf ( stderr , "创建共享内存失败\n" ) ;
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE) ;
}
msg = ( struct shared_msg * ) shmat ( shmid, NULL , 0 ) ;
if ( msg < ( struct shared_msg * ) 0 )
{
fprintf ( stderr , "共享内存段映射到进程失败n" ) ;
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE) ;
}
printf ( "共享内存地址 %X\n" , ( int * ) msg) ;
while ( 1 )
{
printf ( "请输入消息:" ) ;
fgets ( buf, BUFSIZ, stdin ) ;
strncpy ( msg-> text, buf, BUFSIZ) ;
msg-> update = 1 ;
printf ( "更新数据完成\n" ) ;
if ( strncmp ( buf, "EOF" , 3 ) == 0 )
{
break ;
}
}
if ( shmdt ( msg) < 0 )
{
fprintf ( stderr , "将共享内存和当前进程分离失败\n" ) ;
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE) ;
}
printf ( "程序结束\n" ) ;
exit ( EXIT_SUCCESS) ;
}
# include <sys/types.h> # include <sys/ipc.h> # include <sys/shm.h> # include <fcntl.h> # include <stdlib.h> # include <stdio.h> # include <string.h> struct shared_msg
{
int update;
char text[ BUFSIZ] ;
} ;
void main ( )
{
printf ( "程序开始\n" ) ;
key_t key;
int shmid;
struct shared_msg * msg;
char buf[ BUFSIZ] ;
key = ( key_t ) 1234 ;
shmid = shmget ( key, sizeof ( struct shared_msg ) , IPC_CREAT | 0666 ) ;
if ( shmid < 0 )
{
fprintf ( stderr , "创建共享内存失败\n" ) ;
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE) ;
}
msg = ( struct shared_msg * ) shmat ( shmid, NULL , 0 ) ;
if ( msg < ( struct shared_msg * ) 0 )
{
fprintf ( stderr , "共享内存段映射到进程失败n" ) ;
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE) ;
}
printf ( "共享内存地址 %X\n" , ( int * ) msg) ;
while ( 1 )
{
while ( msg-> update == 1 )
{
sprintf ( buf, "%s" , msg-> text) ;
printf ( "读取数据:%s" , buf) ;
msg-> update = 0 ;
}
if ( strncmp ( buf, "EOF" , 3 ) == 0 )
{
break ;
}
}
if ( shmdt ( msg) < 0 )
{
fprintf ( stderr , "将共享内存和当前进程分离失败\n" ) ;
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE) ;
}
if ( shmctl ( shmid, IPC_RMID, 0 ) == - 1 )
{
fprintf ( stderr , "删除共享内存失败\n" ) ;
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE) ;
}
printf ( "程序结束\n" ) ;
exit ( EXIT_SUCCESS) ;
}