文章目录
- 前言
- 特点
- 一、Hello Viz
- 1. 创建项目
- 2. 引入viz
- 3. 运行Hello Viz
- 4. 运行结果
- 注意
- 二、Hello Viz代码详解
- 导入组件
- 处理请求
- 主函数
- 三、常见用法
- 简单的处理程序
- 实现处理程序特质
- 路由传参
- 链式组合程序
- 中间件
- 参数接收器
- 路由
- 一个简单的路由
- CRUD操作
- 资源
- 总结
前言
Viz,是个基于RUst的,快速、健壮、灵活、轻量级的 Web 框架。
特点
- 安全,禁止不安全代码
- 轻量
- 简单 + 灵活的处理器和中间件
- 链式操作
- 强大的Routing路由
一、Hello Viz
1. 创建项目
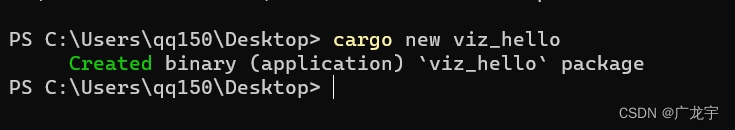
正如学习编程语言一样,我们先从官方入门案例学起,首先我们创建一个新项目
cargo new viz_hello
 然后使用vscode打开
然后使用vscode打开
2. 引入viz
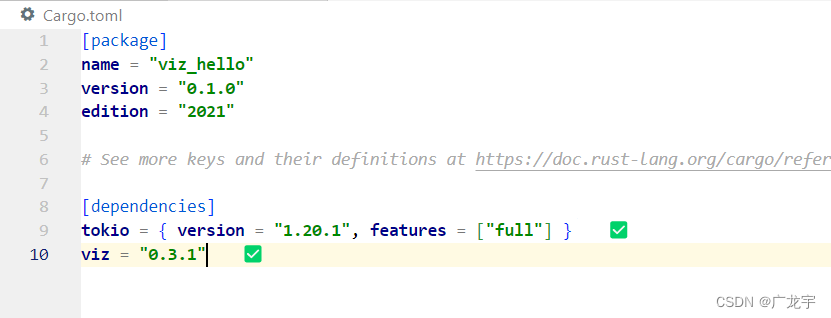
在Cargo.toml中写入,如下图
tokio = { version = "1.20.1", features = ["full"] }
viz = "0.3.1"
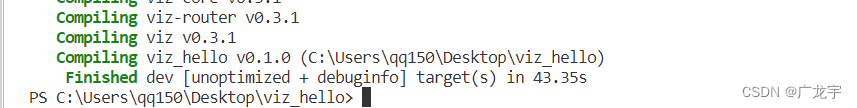
然后使用build来下载依赖
cargo build

安装完成
3. 运行Hello Viz
复制以下代码到main.rs,
use std::net::SocketAddr;
use viz::{Request, Result, Router, Server, ServiceMaker};
async fn index(_: Request) -> Result<&'static str> {
Ok("Hello Viz")
}
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<()> {
let addr = SocketAddr::from(([127, 0, 0, 1], 3000));
println!("listening on {}", addr);
let app = Router::new().get("/", index);
if let Err(err) = Server::bind(&addr)
.serve(ServiceMaker::from(app))
.await
{
println!("{}", err);
}
Ok(())
}
4. 运行结果
如果你以上步骤没有出错,那么在终端中运行
cargo run
效果如下图
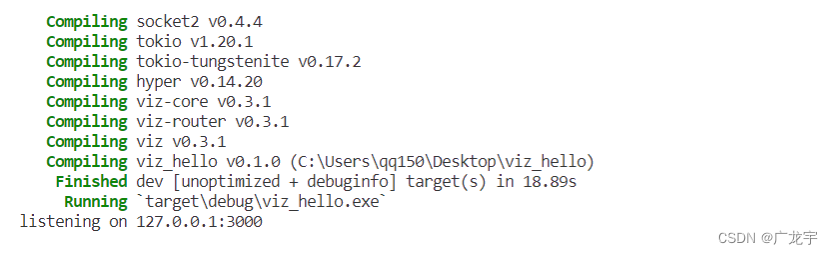 最后一行的意思是正在监听本地的127.0.0.1的3000端口,说明程序没有出错
最后一行的意思是正在监听本地的127.0.0.1的3000端口,说明程序没有出错
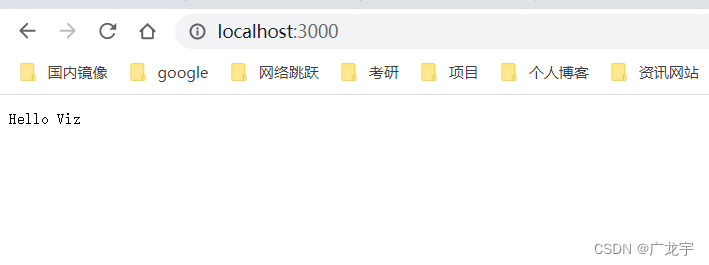
此时在浏览器打开网址
http://localhost:3000/
注意
localhost指向127.0.0.1
此时页面应该是这个样子的
二、Hello Viz代码详解
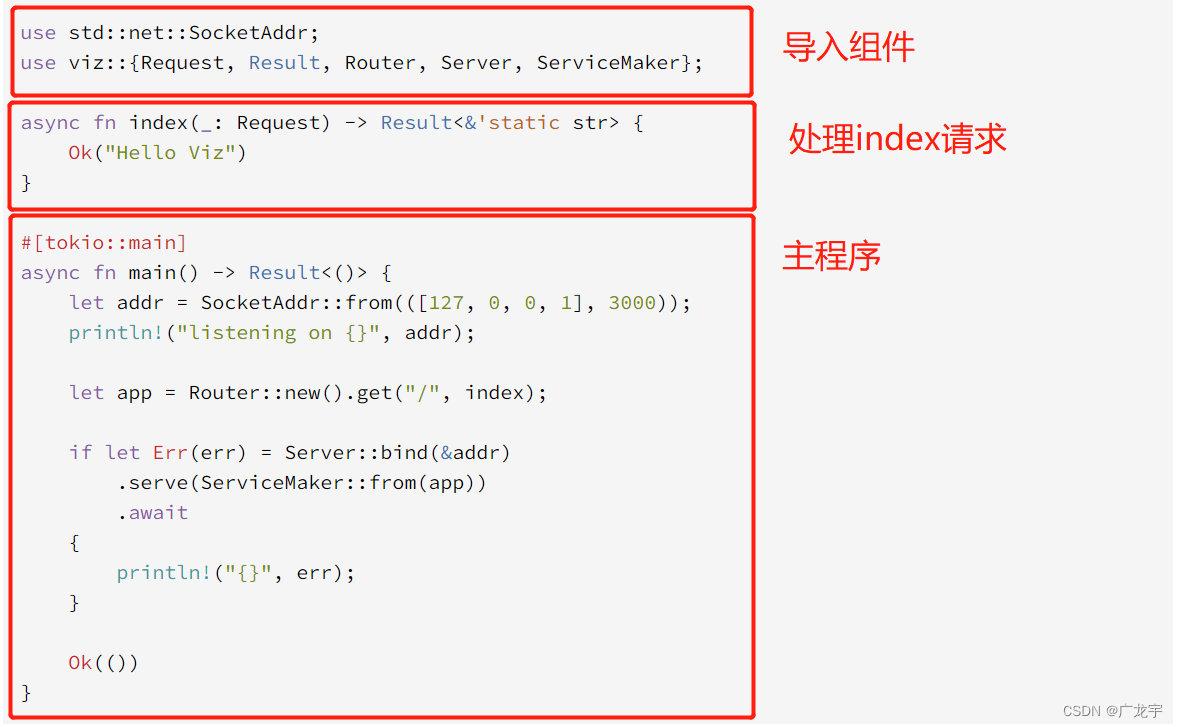
从整体上来看,这块代码主要分为3个部分,分别是导入组件,处理index请求和主程序
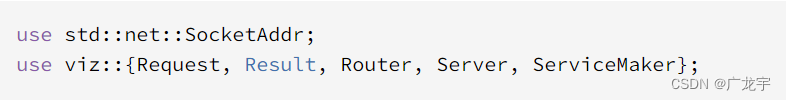
导入组件
首先导入了SocketAddr,用来表示socket地址,然后导入了Viz的一些组件
- Request 请求
- Result 响应
- Router 路由
- Server 服务器
- ServiceMaker 服务
处理请求
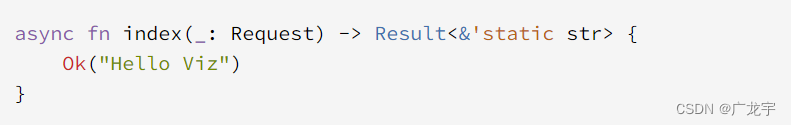 这里使用异步函数来实现index的处理,传入Request,这个过程系统会自动为我们处理。然后响应的是字符串类型,在函数体中返回了字符串“Hello Viz”
这里使用异步函数来实现index的处理,传入Request,这个过程系统会自动为我们处理。然后响应的是字符串类型,在函数体中返回了字符串“Hello Viz”
主函数
 在Viz中,主函数也是异步函数,使用addr表示本地地址和监听的端口,然后挂载Router,使与index处理器相联系,再开启服务器。
在Viz中,主函数也是异步函数,使用addr表示本地地址和监听的端口,然后挂载Router,使与index处理器相联系,再开启服务器。
三、常见用法
简单的处理程序
async fn index(_: Request) -> Result<Response> {
Ok(Response::text("Hello, World!"))
}
async fn about(_: Request) -> Result<&'static str> {
Ok("About Me!")
}
async fn not_found(_: Request) -> Result<impl IntoResponse> {
Ok("Not Found!")
}
实现处理程序特质
#[derive(Clone)]
struct MyHandler {
code: Arc<AtomicUsize>,
}
#[async_trait]
impl Handler<Request> for MyHandler {
type Output = Result<Response>;
async fn call(&self, req: Request) -> Self::Output {
let path = req.path().clone();
let method = req.method().clone();
let code = self.code.fetch_add(1, Ordering::SeqCst);
Ok(format!("code = {}, method = {}, path = {}", code, method, path).into_response())
}
}
路由传参
Viz 允许更灵活地组织代码。
async fn show_user(mut req: Request) -> Result<Response> {
let Params(id) = req.extract::<Params<u64>>().await?;
Ok(format!("post {}", id).into_response())
}
async fn show_user_ext(Params(id): Params<u64>) -> Result<impl IntoResponse> {
Ok(format!("Hi, NO.{}", id))
}
async fn show_user_wrap(req: Request) -> Result<impl IntoResponse> {
// https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/48919
// show_user_ext.call(req).await
FnExt::call(&show_user_ext, req).await
}
let app = Router::new()
.get("/users/:id", show_user)
.get("/users_wrap/:id", show_user_wrap)
.get("/users_ext/:id", show_user_ext.into_handler());
链式组合程序
HandlerExt是Handler的拓展特质,它提供了各种方便的组合函数。比如FutureExt和StreamExt特质。
async fn index(_: Request) -> Result<Response> {
Ok(Response::text("hyper"))
}
async fn before(req: Request) -> Result<Request> {
if req.method() == Method::POST {
Ok(req)
} else {
Err(StatusCode::METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED.into_error())
}
}
async fn around<H>((req, handler): Next<Request, H>) -> Result<Response>
where
H: Handler<Request, Output = Result<Response>> + Clone,
{
// before ...
let result = handler.call(req).await;
// after ...
result
}
async fn after(result: Result<Response>) -> Result<Response> {
result.map(|mut res| {
*res.status_mut() = StatusCode::NO_CONTENT;
res
})
}
let routing = Router::new()
.get("/", index.before(before).around(around).after(after));
中间件
Viz 的中间件和处理程序具有共同的Handler特质,因此它很容易实现和扩展中间件。
我们可以将中间件添加到单个处理程序或所有处理程序。
我们还可以在构造过程中使用Transform特质 trait 来包装内部处理程序。
async fn index(_: Request) -> Result<Response> {
Ok(StatusCode::OK.into_response())
}
async fn not_found(_: Request) -> Result<impl IntoResponse> {
Ok(StatusCode::OK)
}
async fn show_user(Params(id): Params<u64>) -> Result<impl IntoResponse> {
Ok(format!("post {}", id))
}
// middleware fn
async fn around<H>((req, handler): Next<Request, H>) -> Result<Response>
where
H: Handler<Request, Output = Result<Response>>,
{
// before ...
let result = handler.call(req).await;
// after ...
result
}
// middleware struct
#[derive(Clone)]
struct MyMiddleware {}
#[async_trait]
impl<H> Handler<Next<Request, H>> for MyMiddleware
where
H: Handler<Request>,
{
type Output = H::Output;
async fn call(&self, (i, h): Next<Request, H>) -> Self::Output {
h.call(i).await
}
}
// A configuration for Timeout Middleware
struct Timeout {
delay: Duration,
}
impl Timeout {
pub fn new(secs: u64) -> Self {
Self { delay: Duration::from_secs(secs) }
}
}
impl<H: Clone> Transform<H> for Timeout {
type Output = TimeoutMiddleware<H>;
fn transform(&self, h: H) -> Self::Output {
TimeoutMiddleware(h, self.delay)
}
}
// Timeout Middleware
#[derive(Clone)]
struct TimeoutMiddleware<H>(H, Duration);
#[async_trait]
impl<H> Handler<Request> for TimeoutMiddleware<H>
where
H: Handler<Request> + Clone,
{
type Output = H::Output;
async fn call(&self, req: Request) -> Self::Output {
self.0.call(req).await
}
}
let app = Router::new()
.get("/", index
// handler level
.around(around)
.around(MyMiddleware {})
.with(Timeout::new(1))
)
.route("/users/:id", get(
show_user
.into_handler()
.map_into_response()
// handler level
.around(around)
.with(Timeout::new(0))
)
.post(
(|_| async { Ok(Response::text("update")) })
// handler level
.around(around)
.with(Timeout::new(0))
)
// route level
.with_handler(MyMiddleware {})
.with(Timeout::new(2))
)
.get("/*", not_found
.map_into_response()
// handler level
.around(around)
.around(MyMiddleware {})
)
// router level
.with_handler(around)
.with_handler(MyMiddleware {})
.with(Timeout::new(4));
参数接收器
从Request中提取参数。
struct Counter(u16);
#[async_trait]
impl FromRequest for Counter {
type Error = Infallible;
async fn extract(req: &mut Request) -> Result<Self, Self::Error> {
let c = get_query_param(req.query_string());
Ok(Counter(c))
}
}
fn get_query_param(query: Option<&str>) -> u16 {
let query = query.unwrap_or("");
let q = if let Some(pos) = query.find('q') {
query.split_at(pos + 2).1.parse().unwrap_or(1)
} else {
1
};
cmp::min(500, cmp::max(1, q))
}
路由
识别URL和分配处理器。
一个简单的路由
async fn index(_: Request) -> Result<Response> {
Ok(().into_response())
}
let root = Router::new()
.get("/", index)
.route("/about", get(|_| async { Ok("about") }));
let search = Router::new()
.route("/", Route::new().get(|_| async { Ok("search") }));
CRUD操作
添加带请求方式的方法。
async fn index_todos(_: Request) -> Result<impl IntoResponse> {
Ok(())
}
async fn create_todo(_: Request) -> Result<&'static str> {
Ok("created")
}
async fn new_todo(_: Request) -> Result<Response> {
Ok(Response::html(r#"
<form method="post" action="/">
<input name="todo" />
<button type="submit">Create</button>
</form>
"#))
}
async fn show_todo(mut req: Request) -> Result<Response> {
let Params(id): Params<u64> = req.extract().await?;
Ok(Response::text(format!("todo's id is {}", id)))
}
async fn update_todo(_: Request) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
async fn destroy_todo(_: Request) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
async fn edit_todo(_: Request) -> Result<()> {
Ok(())
}
let todos = Router::new()
.route("/", get(index_todos).post(create_todo))
.post("/new", new_todo)
.route("/:id", get(show_todo).patch(update_todo).delete(destroy_todo))
.get("/:id/edit", edit_todo);
资源
// GET `/search`
async fn search_users(_: Request) -> Result<Response> {
Ok(Response::json::<Vec<u64>>(vec![])?)
}
// GET `/`
async fn index_users(_: Request) -> Result<Response> {
Ok(Response::json::<Vec<u64>>(vec![])?)
}
// GET `/new`
async fn new_user(_: Request) -> Result<&'static str> {
Ok("User Form")
}
// POST `/`
async fn create_user(_: Request) -> Result<&'static str> {
Ok("Created User")
}
// GET `/user_id`
async fn show_user(_: Request) -> Result<&'static str> {
Ok("User ID 007")
}
// GET `/user_id/edit`
async fn edit_user(_: Request) -> Result<&'static str> {
Ok("Edit User Form")
}
// PUT `/user_id`
async fn update_user(_: Request) -> Result<&'static str> {
Ok("Updated User")
}
// DELETE `/user_id`
async fn delete_user(_: Request) -> Result<&'static str> {
Ok("Deleted User")
}
let users = Resources::default()
.named("user")
.route("/search", get(search_users))
.index(index_users)
.new(new_user)
.create(create_user)
.show(show_user)
.edit(edit_user)
.update(update_user)
.destroy(delete_user);
总结
本期主要是对Rust的轻量级Web框架Viz进行了入门级的了解,并且给出了Viz官方的示例代码,包括中间件,响应处理,路由等组件的用法,可以看出Viz是个纯web框架,非常的简洁。在后续的文章中,将会陆续为大家介绍rust的数据库操作,json操作等相关技术,rust做web后端的相关技术补齐就开始项目实战。如果你对rust感兴趣,请关注本系列文章。