一、引入

- Object Oriented Adapters
二、XX 模式
aka:Wrapper (包装器)
2.1 Intent 意图
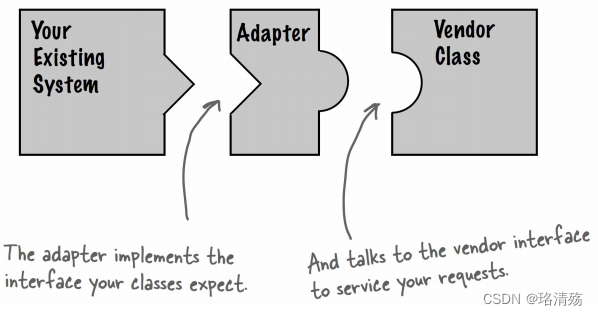
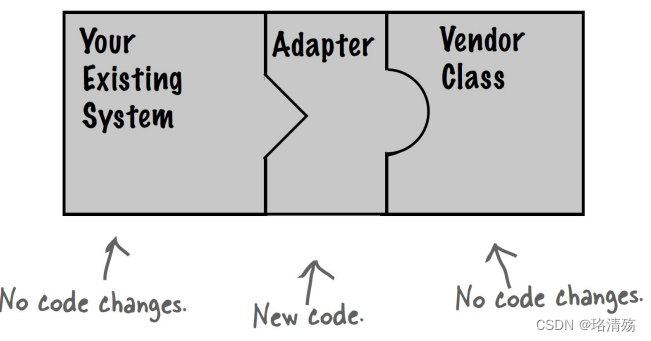
- Convert the interface of a class into another interface clients expect. 将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口.
- 作为两个不兼容的接口之间的桥梁
- 适配器模式使得原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的那些类可以一起工作
2.2 Applicability 适用性
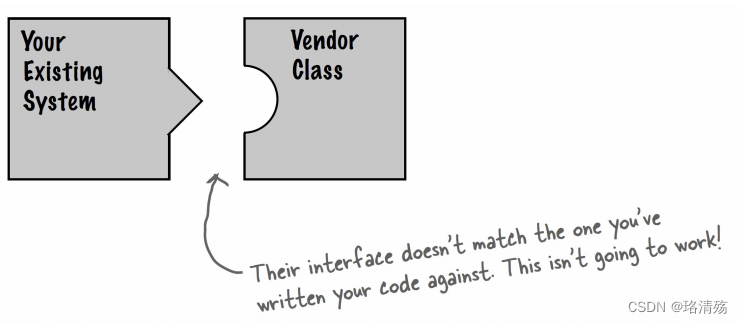
- You want to use an existing class, and its interface does not match the one you need.
- you want to create a reusable class that cooperates with unrelated or unforeseen classes, that is, classes that don’t necessarily have compatible interfaces.
- (object adapter only,仅对象适配器) you need to use several existing subclasses, but it’s impractical to adapt their interface by subclassing every one. 需要使用几个现有的子类,但是通过对每个子类进行子类化来适配它们的接口是不切实际的。
- An object adapter can adapt the interface of its parent class. 对象适配器可以适配其(所有子类)父类的接口.
2.3 类图
- 类适配器:多继承(not for java)、多实现
- 对象适配器:关联,依赖组合
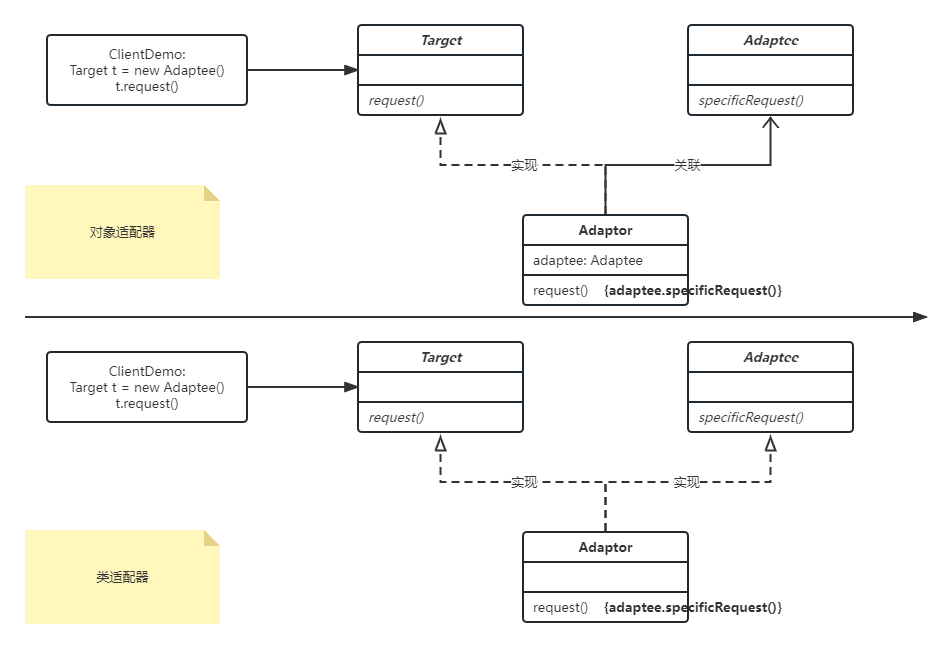
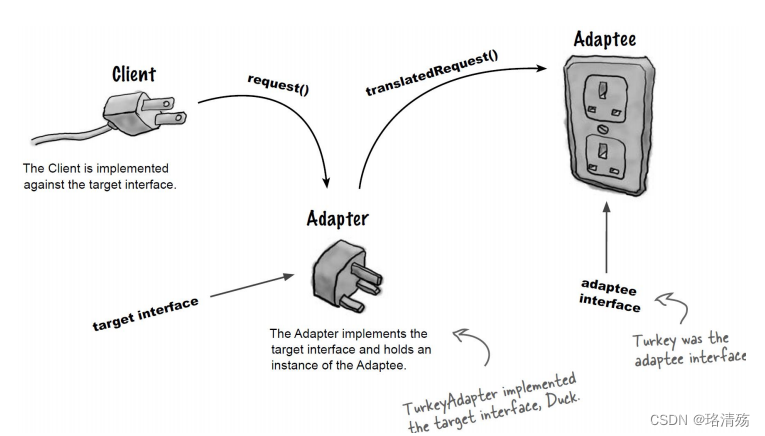
- Client: Collaborates with objects conforming to the Target interface. 与符合目标接口的对象进行协作
- Target: Defines the domain-specific interface that Client uses, It should be an interface. 定义 Client 使用的特定领域的接口,它应该是一个接口
- Adaptee: Defines an existing interface that needs adapting, could be an interface, or abstract class, or class. 定义需要适配的现有接口,Adaptee 可以是接口、抽象类或类
- Adapter: Adapts the interface of Adaptee to the Target interface. 适配 Adaptee 的接口到目标接口
2.4 实例:鸭子与火鸡
鸭子与火鸡:
If it walks like a duck and quacks like a duck, then it might be a turkey wrapped with a duck adapter
如果它像鸭子一样走路,那么它可能是一只带着鸭子适配器的火鸡
- 鸭子
public interface Duck {
public void quack();
public void fly();
}
public class MallardDuck implements Duck {
public void quack() {
System.out.println("Quack");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println("I'm flying");
}
}
- 火鸡
public interface Turkey {
public void gobble();
public void fly();
}
public class WildTurkey implements Turkey {
public void gobble() {
System.out.println("Gobble gobble");
}
public void fly() {
System.out.println("I'm flying a short distance");
}
}
- 火鸡适配器:适配火鸡接口
public class TurkeyAdapter implements Duck {
Turkey turkey;
public TurkeyAdapter(Turkey turkey) {
this.turkey = turkey;
}
public void quack() {
turkey.gobble();
}
public void fly() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
turkey.fly();
}
}
}
public class DuckTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MallardDuck duck = new MallardDuck();
WildTurkey turkey = new WildTurkey();
Duck turkeyAdapter = new TurkeyAdapter(turkey);
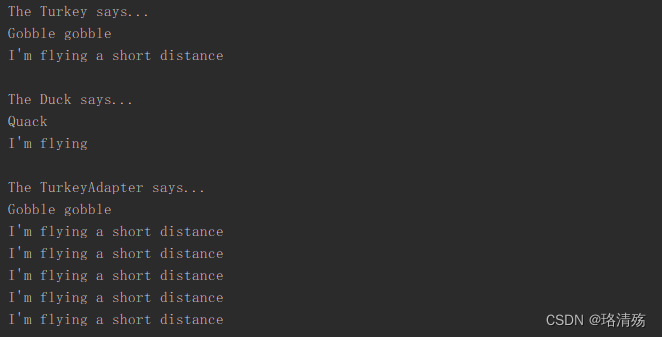
System.out.println("The Turkey says...");
turkey.gobble();
turkey.fly();
System.out.println("\nThe Duck says...");
testDuck(duck);
System.out.println("\nThe TurkeyAdapter says...");
testDuck(turkeyAdapter);
}
static void testDuck(Duck duck) {
duck.quack();
duck.fly();
}
}
- 鸭子适配器:适配鸭子
public class DuckAdapter implements Turkey {
Duck duck;
Random rand;
public DuckAdapter(Duck duck) {
this.duck = duck;
rand = new Random();
}
public void gobble() {
duck.quack();
}
public void fly() {
if (rand.nextInt(5) == 0) {
duck.fly();
}
}
}
public class TurkeyTestDrive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MallardDuck duck = new MallardDuck();
Turkey duckAdapter = new DuckAdapter(duck);
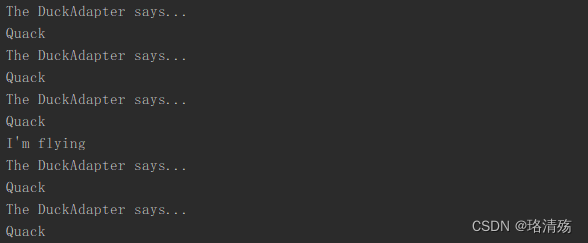
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("The DuckAdapter says...");
duckAdapter.gobble();
duckAdapter.fly();
}
}
}
2.5 实例:适配枚举到迭代器
The early collections types (Vector, Stack, Hashtable, and a few others) implement a method elements(), which returns an Enumeration.
Adapting an Enumeration to an Iterator.
- Target:Iterator
- Adaptee:Enumeration
- Adapter:EnumerationIterator
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public class EnumerationIterator implements Iterator {
Enumeration enumeration;
public EnumerationIterator(Enumeration enumeration) {
this.enumeration = enumeration;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return enumeration.hasMoreElements();
}
public Object next() {
return enumeration.nextElement();
}
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
public class EnumerationIteratorTestDrive {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main (String args[]) {
// Vector v = new Vector(Arrays.asList(args));
Vector v = new Vector(Arrays.asList("A", "B", "C", "E", "F", "G"));
Iterator iterator = new EnumerationIterator(v.elements());
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
以迭代器形式遍历枚举。