目录
数据结构之链表OJ::
1.移除链表元素
2.反转链表
3.链表的中间结点
4.链表中倒数第k个结点
5.合并两个有序链表
6.链表分割
7.链表的回文结构
8.相交链表
9.环形链表
10.环形链表II
11.复制带随机指针的链表
数据结构之链表OJ::
1.移除链表元素
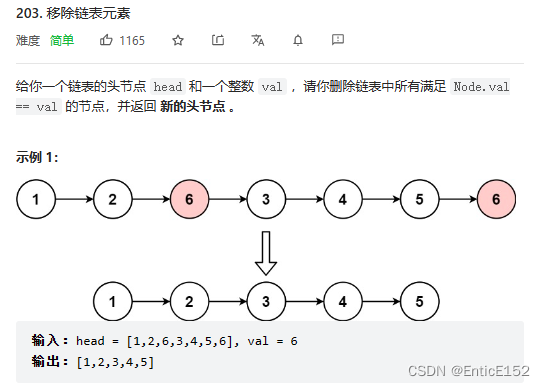
删除链表中等于给定值val的所有结点
struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
};
方法一
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* cur = head, * prev = NULL;
while (cur != NULL)
{
//1.头删
//2.非头删
if (cur->val == val)
{
if (cur == head)
{
head = head->next;
free(cur);
cur = head;
}
else
{
prev->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = prev->next;
}
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
不用二级指针的方法:返回头指针
main函数调用方式:plist = removeElements(plist,6);
方法二
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL, * tail = NULL;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->val != val)
{
if (tail == NULL)
{
newhead = tail = cur;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur;
tail = tail->next;
}
}
else
{
struct ListNode* del = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(del);
}
}
if (tail != NULL)
{
tail->next = NULL;
}
return newhead;
}
方法三:
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* guard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* tail = guard;
while (cur != NULL)
{
if (cur->val != val)
{
tail->next = cur;
tail = tail->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
struct ListNode* del = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(del);
}
}
最后结点是val 就会出现此问题
if (tail != NULL)
{
tail->next = NULL;
}
head = guard->next;
free(guard);
return head;
}
替代我们之前实现的二级指针
1.返回新的链表头 2.设计为带哨兵位2.反转链表
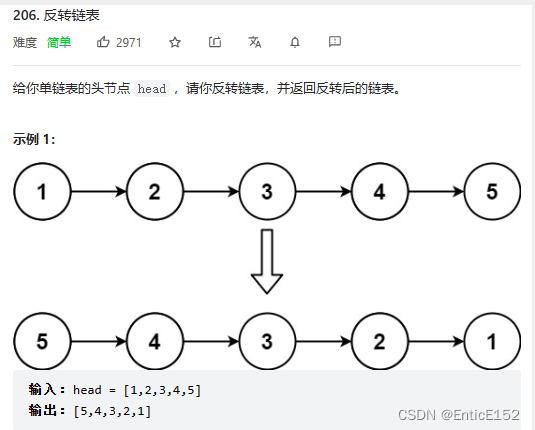
反转链表
方法一:取结点头插到新链表
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
while (cur)
{
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = newhead;
newhead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newhead;
}
方法二:翻转链表方向
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* n1, *n2, *n3;
n1 = NULL;
n2 = head;
n3 = NULL;
while (n2)
{
n3 = n2->next;
n2->next = n1;
迭代
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
}
return n1;
}3.链表的中间结点

链表的中间结点——快慢指针
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* slow, * fast;
slow = fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}4.链表中倒数第k个结点

链表中倒数第k个结点——快慢指针
方法一:
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, unsigned int k)
{
struct ListNode* fast, * slow;
fast = slow = pListHead;
while (k--) 走k步
{
k大于链表长度
if (fast == NULL)
return NULL;
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
方法二:
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, unsigned int k)
{
struct ListNode* fast, * slow;
fast = slow = pListHead;
while (fast && --k)走k-1步
{
k大于链表长度
fast = fast->next;
}
if (fast == NULL)
return NULL;
while (fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}5.合并两个有序链表
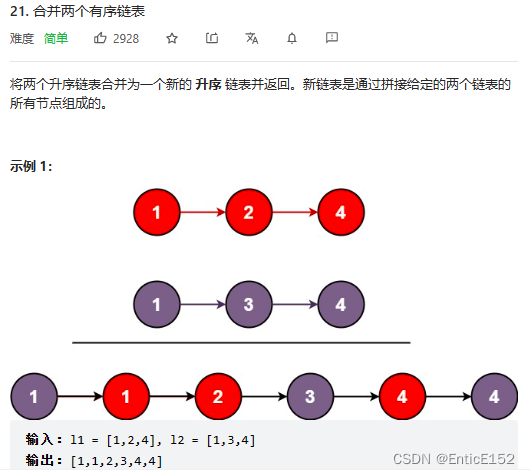
合并两个有序链表
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
struct ListNode* guard = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
guard->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail = guard;
struct ListNode* cur1 = list1, * cur2 = list2;
while (cur1 && cur2)
{
if (cur1->val < cur2->val)
{
tail->next = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
if (cur1)
tail->next = cur1;
if (cur2)
tail->next = cur2;
struct ListNode* head = guard->next;
free(guard);
return head;
}6.链表分割

链表分割
struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
struct ListNode* lessGuard, * lessTail, * greaterGuard, * greaterTail;
lessGuard = lessTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
greaterGuard = greaterTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
lessGuard->next = NULL;
greaterGuard->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = pHead;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val < x)
{
lessTail->next = cur;
lessTail = lessTail->next;
}
else
{
greaterTail->next = cur;
greaterTail = greaterTail->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
lessTail->next = greaterGuard->next;
greaterTail->next = NULL;
pHead = lessGuard->next;
free(greaterGuard);
free(lessGuard);
return pHead;
}7.链表的回文结构

链表的回文结构
方法一:找中间结点翻转链表
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* slow, * fast;
slow = fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* n1, * n2, * n3;
n1 = NULL;
n2 = head;
n3 = NULL;
while (n2)
{
n3 = n2->next;
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
}
return n1;
}
bool chkPalindrome(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* mid = middleNode(head);
struct ListNode* rmid = reverseList(mid);
while (head && rmid)
{
if (head->val != rmid->val)
return false;
head = head->next;
rmid = rmid->next;
}
return true;
}
方法二:整个链表逆置看和链表是否相同 但要注意需要重新拷贝原链表8.相交链表
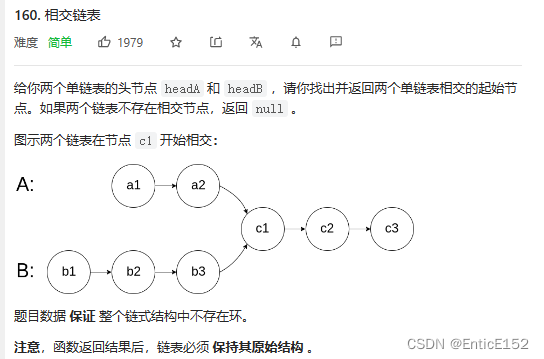
相交链表
判断是否相交判断尾结点的地址是否相同
找交点:求出长度lenA lenB 长的链表先走差距步 第一个相等的就是交点
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode* headA, struct ListNode* headB)
{
if (headA == NULL || headB == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* curA = headA, * curB = headB;
int lenA = 1;
找尾结点
while (curA->next)
{
curA = curA->next;
++lenA;
}
int lenB = 1;
while (curB->next)
{
curB = curB->next;
++lenB;
}
if (curA != curB)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* longList = headA, * shortList = headB;
if (lenA < lenB)
{
longList = headB;
shortList = headA;
}
长的链表先走差距步
int gap = abs(lenA - lenB);
while (gap--)
{
longList = longList->next;
}
同时走找交点
while (longList != shortList)
{
longList = longList->next;
shortList = shortList->next;
}
return longList;
}9.环形链表
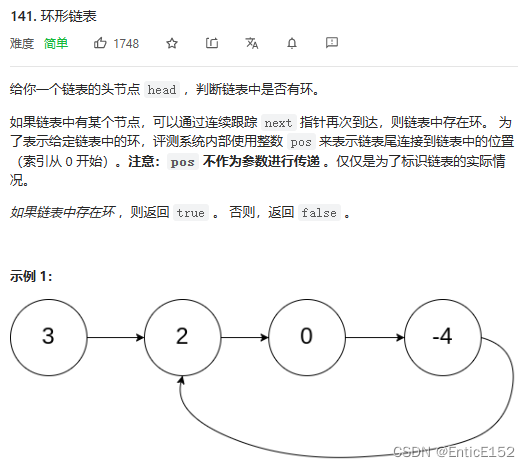
环形链表
快慢指针法:slow进环以后 fast开始追赶slow
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* fast, * slow;
fast = slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
return true;
}
return false;
}
请证明一下,slow走一步 fast一次走两步?
请证明一下,slow走一步 fast一次走三步?是否可以? 答:不一定
请证明一下,slow走一步 fast一次走X步?是否可以?每次缩小X-1
请证明一下,slow走X步 fast一次走Y步?是否可以?X<Y 每次缩小X-Y
fast走两步时:假设slow进环以后 fast slow之间的差距为N 即追赶距离为N
slow和fast每移动一步 距离缩小1 距离缩小为N N-1 N-2...1 0 距离为0即相遇
fast走三步时:假设slow进环以后 fast slow之间的差距为N 即追赶距离为N
slow每追赶一次 它们之间距离缩小两步 距离变化为N N-2 N-4 N-6...
如果N为偶数则能追上 如果为奇数距离由1变为-1 意味着它们之间的距离变为了C-1(C是环的长度)
如果环减一是偶数再追一圈就能追上 如果环减一为奇数 则永远追不上10.环形链表II
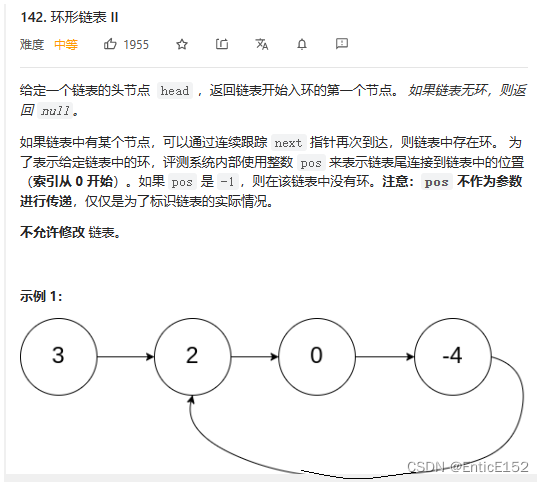
环形链表II
1.公式证明推导
2.转换成相交问题
fast走的距离 = 2*slow走的距离
假设进环前的长度是L
假设环的长度是C
假设入口点到相遇点距离是X
slow走的距离是L+X
fast走的距离是L+C=X
假设slow进环前 fast在环里面转了N圈 N>=1
2(L+X) = L+X+N*C
(L+X) = N*C
L = N*C-X
L = (N-1)*C+C-X
结论:一个指针A从头开始走 一个指针B从相遇点开始走 它们会在入口点相遇
1.公式证明推导
struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* slow = head, * fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
{
struct ListNode* meet = slow;
while (meet != head)
{
meet = meet->next;
head = head->next;
}
return meet;
}
}
return NULL;
}
2.转换成相交问题
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode* headA, struct ListNode* headB)
{
if (headA == NULL || headB == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* curA = headA, * curB = headB;
int lenA = 1;
找尾结点
while (curA->next)
{
curA = curA->next;
++lenA;
}
int lenB = 1;
while (curB->next)
{
curB = curB->next;
++lenB;
}
if (curA != curB)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* longList = headA, * shortList = headB;
if (lenA < lenB)
{
longList = headB;
shortList = headA;
}
长的链表先走差距步
int gap = abs(lenA - lenB);
while (gap--)
{
longList = longList->next;
}
同时走找交点
while (longList != shortList)
{
longList = longList->next;
shortList = shortList->next;
}
return longList;
}
struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* slow = head, * fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
{
转换成相交
struct ListNode* meet = slow;
struct ListNode* next = meet->next;
meet->next = NULL;
struct ListNode* entryNode = getIntersectionNode(head, next);
恢复环
meet->next = next;
return entryNode;
}
}
return NULL;
}11.复制带随机指针的链表
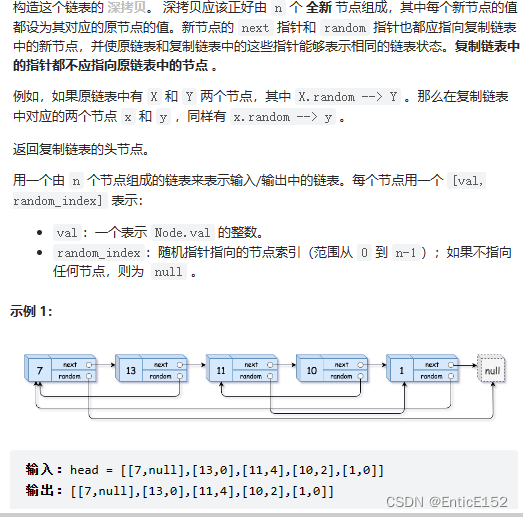
复制带随机指针的链表
方法一:1.遍历原链表 复制结点 尾插
2.更新random 找random原链表中第i个 新链表中对应第i个
方法二:1.拷贝原结点 链接到所有原结点的后面
ps:原结点和拷贝结点建立一个链接关系 找到原结点就可以找到拷贝结点
2.更新每个拷贝结点的random
3.将拷贝结点解下来 链接成新链表
struct Node
{
int val;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* random;
};
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
1.插入copy结点
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* copy = NULL;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (cur)
{
next = cur->next;
copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = next;
cur = next;
}
2.更新copy->random
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
3.copy结点要解下来链接在一起 恢复原链表
struct Node* copyHead = NULL, * copyTail = NULL;
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = copy->next;
取结点尾插
if (copyTail == NULL)
{
copyHead = copyTail = copy;
}
else
{
copyTail->next = copy;
copyTail = copyTail->next;
}
恢复原链表链接
cur->next = next;
cur = next;
}
return copyHead;
}