主要思想:随机增加ROI区域的深度,模拟物体处在不同位置的形态。
首先打印一张深度图中的深度信息分布:
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import seaborn as sns
def plot_grayscale_histogram(image_path):
# 读取图像(保留16位深度)
img = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
print(img)
if img is None:
print("错误:无法读取图像,请检查文件路径")
return
# 验证图像格式
if len(img.shape) != 2 or img.dtype != np.uint16:
print("警告:非单通道16位图像,当前形状:", img.shape, "数据类型:", img.dtype)
# 创建带KDE的直方图
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# 使用展平后的图像数据
sns.histplot(
x=img.flatten(), # 将二维数组展平为一维
bins=50, # 增加bins数量以更好显示16位数据分布
color="lightblue",
edgecolor="black",
kde=True,
# stat="density" # 将计数转换为密度概率
)
# 设置标题和标签
plt.title("Depth Value Distribution", fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel("Depth Value (16-bit)", fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel("Density", fontsize=12)
# 添加网格和格式优化
plt.grid(axis="y", linestyle="--", alpha=0.5)
plt.xlim(0, 65535) # 设置16位数据范围
# 显示图形
plt.show()
# 显示原始深度图的归一化预览
normalized = cv2.normalize(img, None, 0, 255, cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
cv2.imshow('Normalized Preview', normalized)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == "__main__":
image_path = "C:/pyprojects/yolo11/Dataset_depth/images/train/1112_0-rgb.png"
plot_grayscale_histogram(image_path)结果如下:
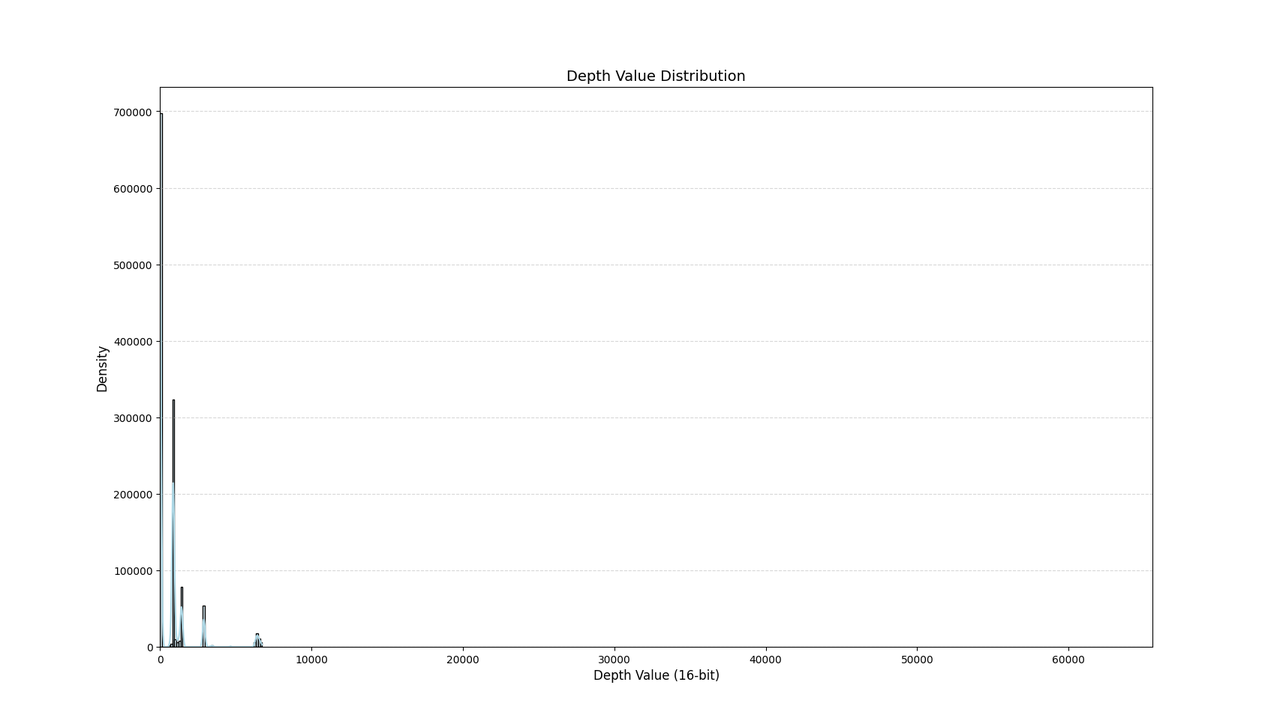

然后我们单独画一下中间的ROI区域:
img = img[342:515, 389:873]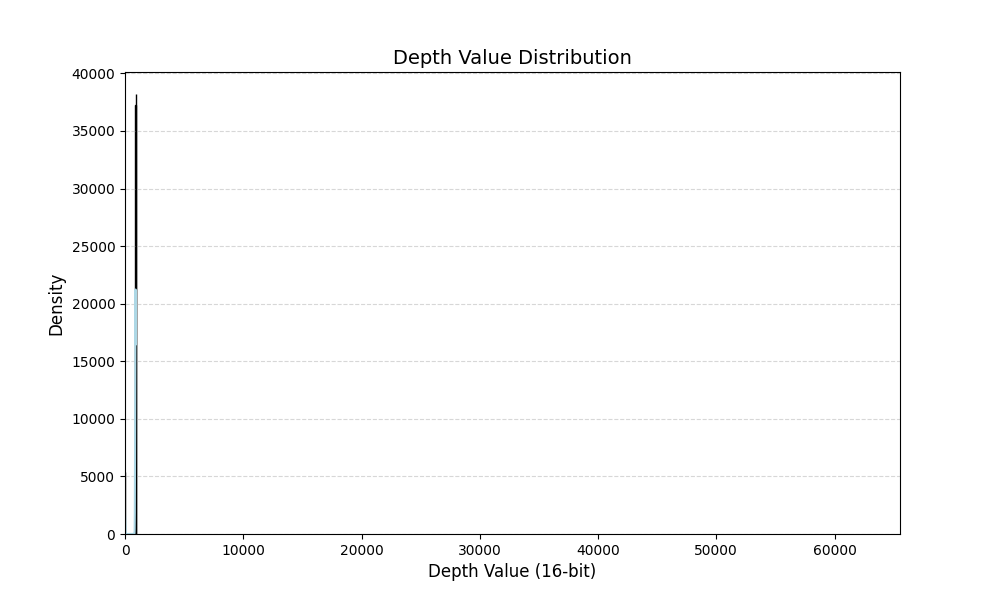
现在随机增加ROI区域的深度,模拟不同纵向的位置:
# 本数据集生成的代码
# 数据增强方法:随机增加ROI区域的深度,模拟箱子在不同纵向位置摆放
# 训练集:76665张,测试集:18975张
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
import shutil
image_file_dir = "C:/pyprojects/yolo11/fheiaunjk/images"
min_val = 0 # 最小偏移量
max_val = 500 # 最大偏移量
output_dir = "C:/pyprojects/yolo11/output"
# 正确拼接输出路径
img_output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, "images") # 正确写法
label_output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, "labels") # 正确写法
# 直接创建目标目录(无需使用 os.path.dirname)
os.makedirs(img_output_path, exist_ok=True) # 创建 output/images
os.makedirs(label_output_path, exist_ok=True) # 创建 output/labels
for filename in os.listdir(image_file_dir):
# 1. 构建图片完整路径
image_file_path = os.path.join(image_file_dir, filename)
# 2. 构建标签文件路径
labels_dir = image_file_dir.replace("images", "labels")
base_name = os.path.splitext(filename)[0] # 去掉文件扩展名
label_file_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, f"{base_name}.txt") # 正确路径
# 3. 检查标签文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(label_file_path):
print(f"警告:标签文件 {label_file_path} 不存在")
continue
# 4. 读取图片并检查有效性
image = cv2.imread(image_file_path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
if image is None:
print(f"错误:无法读取图片 {image_file_path}")
continue
# 5. 获取图像尺寸(兼容单通道/多通道)
if len(image.shape) == 2: # 单通道(H, W)
image_height, image_width = image.shape
print(f"图像尺寸:{image_width}x{image_height}")
else: # 多通道(H, W, C)
print(f"错误:图片 {image_file_path} 不是深度图")
continue
with open(label_file_path, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
i = 0
# 绘制每个检测框
for k, line in enumerate(lines):
parts = line.strip().split()
if len(parts) < 5:
continue
# 解析YOLO格式数据
class_id = int(parts[0])
x_center = float(parts[1]) * image_width
y_center = float(parts[2]) * image_height
width = float(parts[3]) * image_width
height = float(parts[4]) * image_height
# 计算坐标
x1 = int(x_center - width/2)
y1 = int(y_center - height/2)
x2 = int(x_center + width/2)
y2 = int(y_center + height/2)
# --- 生成单个随机数 ---
for m in range(5):
i = k * 5 + m
random_offset = np.random.randint(min_val, max_val + 1) # 生成一个随机整数
region = image[y1 : y2, x1 : x2]
modified_region = np.clip(region.astype(np.int32) + random_offset, 0, 65535).astype(np.uint16)
image[y1 : y2, x1 : x2] = modified_region
image_output_path = os.path.join(img_output_path, f"{base_name}_{i}.png")
cv2.imwrite(image_output_path, image) # 写入图片
# 拷贝标签
output_label_path = os.path.join(label_output_path, f"{base_name}_{i}.txt")
print(output_label_path)
shutil.copy2(label_file_path, output_label_path)0523更新:增加ROI区域边缘平滑功能,避免边缘出现明显的锯齿或突变:
# 本数据集生成的代码
# 数据增强方法:随机增加ROI区域的深度,模拟不同纵向位置摆放
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
import shutil
image_file_dir = "Dataset_depth/images/val"
min_val = 0 # 最小偏移量
max_val = 500 # 最大偏移量
output_dir = "/home/hary/ctc/ultralytics-main/output"
# 正确拼接输出路径
img_output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, "images") # 正确写法
label_output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, "labels") # 正确写法
# 直接创建目标目录(无需使用 os.path.dirname)
os.makedirs(img_output_path, exist_ok=True) # 创建 output/images
os.makedirs(label_output_path, exist_ok=True) # 创建 output/labels
for filename in os.listdir(image_file_dir):
# 1. 构建图片完整路径
image_file_path = os.path.join(image_file_dir, filename)
# 2. 构建标签文件路径
labels_dir = image_file_dir.replace("images", "labels")
base_name = os.path.splitext(filename)[0] # 去掉文件扩展名
label_file_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, f"{base_name}.txt") # 正确路径
# 3. 检查标签文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(label_file_path):
print(f"警告:标签文件 {label_file_path} 不存在")
continue
# 4. 读取图片并检查有效性
image = cv2.imread(image_file_path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
if image is None:
print(f"错误:无法读取图片 {image_file_path}")
continue
# 5. 获取图像尺寸(兼容单通道/多通道)
if len(image.shape) == 2: # 单通道(H, W)
image_height, image_width = image.shape
print(f"图像尺寸:{image_width}x{image_height}")
else: # 多通道(H, W, C)
print(f"错误:图片 {image_file_path} 不是深度图")
continue
with open(label_file_path, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
i = 0
# 绘制每个检测框
for k, line in enumerate(lines):
parts = line.strip().split()
if len(parts) < 5:
continue
# 解析YOLO格式数据
class_id = int(parts[0])
x_center = float(parts[1]) * image_width
y_center = float(parts[2]) * image_height
width = float(parts[3]) * image_width
height = float(parts[4]) * image_height
# 计算坐标
x1 = int(x_center - width/2)
y1 = int(y_center - height/2)
x2 = int(x_center + width/2)
y2 = int(y_center + height/2)
# --- 生成单个随机数 ---
for m in range(1):
i = k * 1 + m
random_offset = np.random.randint(min_val, max_val + 1) # 生成一个随机整数
# 保存原始ROI区域
original_roi = image[y1:y2, x1:x2].copy()
# 生成随机偏移后的ROI
modified_roi = np.clip(original_roi.astype(np.int32) + random_offset, 0, 65535).astype(np.uint16)
# 创建羽化遮罩(核心修改部分)
height, width = original_roi.shape[:2]
mask = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.float32)
# 创建椭圆渐变遮罩(比实际区域稍小)
cv2.ellipse(mask,
(int(width/2), int(height/2)),
(int(width/2*0.8), int(height/2*0.8)), # 控制羽化范围
0, 0, 360, 1.0, -1)
# 添加高斯模糊柔化边缘
mask = cv2.GaussianBlur(mask, (0, 0), sigmaX=width/8, sigmaY=height/8)
mask = mask / np.max(mask) # 归一化到[0,1]
# 混合原始和修改后的区域
blended_roi = original_roi.astype(np.float32) * (1 - mask) + \
modified_roi.astype(np.float32) * mask
# 写回图像并保持数据类型
image[y1:y2, x1:x2] = np.clip(blended_roi, 0, 65535).astype(np.uint16)
image_output_path = os.path.join(img_output_path, f"{base_name}_{i}.png")
cv2.imwrite(image_output_path, image) # 写入图片
# 拷贝标签
output_label_path = os.path.join(label_output_path, f"{base_name}_{i}.txt")
print(f"{output_label_path} has created!")
shutil.copy2(label_file_path, output_label_path)













![[项目总结] 基于Docker与Nginx对项目进行部署](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6b5052373d614e808bf978ad806d818c.png)
