这篇文章讲解:
- 把 Agent 和 Fine-Tuning 的知识串起来,在更高的技术视角看大模型应用;
- 加深对 Agent 工作原理的理解;
- 加深对 Fine-Tuning 训练数据处理的理解。
1. 认识大模型 Agent
1.1 大模型 Agent 的应用场景
揭秘Agent核心原理与企业级应用场景
再设想以下几个和 AI 交互的场景,并思考有什么特点:
- 帮我查一下今天的销售额?
- (开车时)前方为啥堵车了?
- 上海天气如何?
再比如:
- 帮我订一张周五去上海的机票;
- 请帮我约一个和搜索产品部的需求沟通会,本周三至周五我日历上空闲的时间都可以。
【重点】大模型应用需要 Agent 技术的原因:
- 大模型的“幻觉”问题,很难在从模型本身上彻底解决,在严肃的应用场景需要通过引入外部知识确保答案的准确;
- 大模型参数无法做到实时更新,本身也无法与真实世界产生实时连接,在多数场景下难以满足实际需求;
- 复杂的业务场景,不是一问一答就能解决的,需要任务拆解、多步执行与交互。
大模型应用,不仅要“会说话”,更要“会做事”!
1.2 大模型 Agent 的技术框架
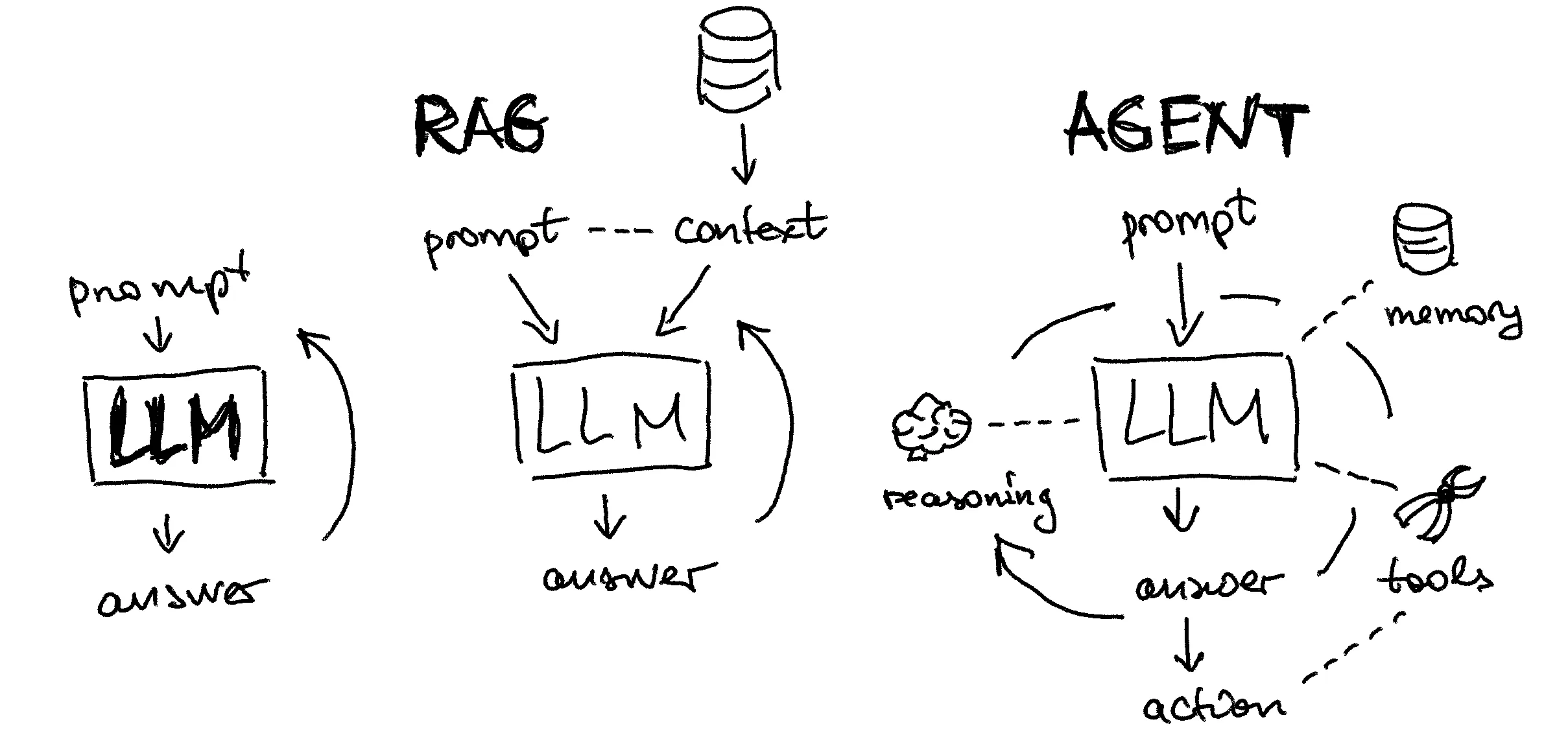

1.3 为什么需要做 Agent Tuning ?
如何实现 Agent?利用 Prompt Engineering 可以实现吗?
答案显然是可以!前面学的 AutoGPT 就是例子。
既然通过 Prompt Engineering 可以实现 Agent,那为什么还要训练 Agent 模型呢?
【重点】因为可以这么做的前提是:模型足够“聪明”,靠看“说明书”就能执行, Prompt Engineering 实际上是把“说明书”写得更加清晰易懂。
- 实践证明,除了 GPT-4 level 的大模型,其他大模型(包括 GPT-3.5 )无法很好遵从 prompt 要求完成复杂的 Agent 任务;
- 很多场景下无法使用最强的大模型 API ,需要私有化部署小模型,需要控制推理成本;
- 通过训练,一个小参数量的大模型(13B、7B等)也能达到较好的能力,更加实用。
1.4 Agent Tuning 的研发流程

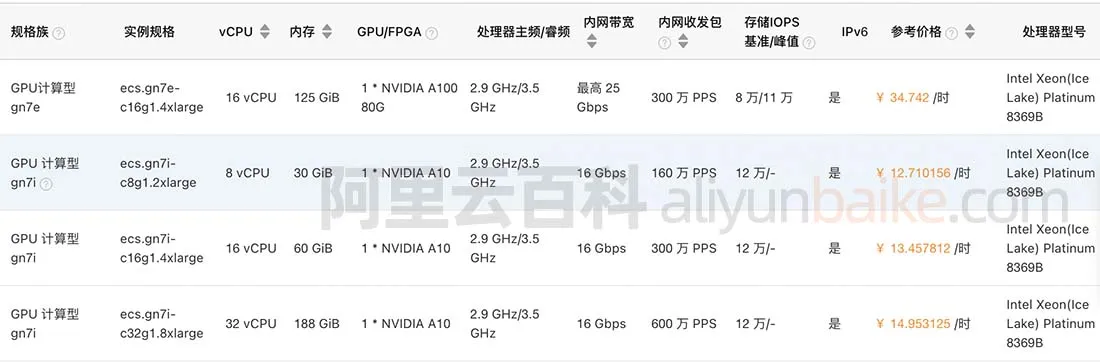
训练成本参考:
-
训练框架: HuggingFace Trainer + DeepSpeed Zero3
-
配置说明:max_len:4096 + Flash Attention + bf16 (batchsize=1、AdamW优化器)
| 模型 | 训练最低配置 | 训练数据规模(token数) | 建议训练 epoch 数 | 平均训练时长 | 训练成本(估算) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7B (全参数) | 4卡A100(4 * 80G) | 470M | 5 | 25h * 5 = 125h | 34.742 * 4 * 125 = 17371.0 元 |
| 14B (全参数) | 8卡A100(8 * 80G) | 470M | 4 | 24h * 4 = 96h | 34.742 * 8 * 96 = 26681.9 元 |
| 72B (全参数) | 32卡A100(32 * 80G) | 470M | 2 | 40h * 2 = 80h | 34.742 * 32 * 80 = 88939.5 元 |
- 以当前阿里云 A100 租用价格计算:
2. Agent Prompt 模板设计
常见的 Agent Prompt 模板,除了大家学习过的 AutoGPT 外,还有 ReACT、ModelScope、ToolLLaMA 等不同的形式。
2.1 主流 Agent Prompt 模板
| 模版 | 描述 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ReACT | ReACT prompt较为简单,先设定Question,再以Thought、Action、Action Input、Observation执行多轮,最后输出Final Answer | prompt 简单 | 1. API 参数只能有一个 2. 没有设定反思等行为,对于错误的思考不能及时纠正 |
| ModelScope | 更为直接的生成回复,调用只需要加入<|startofthink|>和<|endofthink|>字段,并在其中填入command_name和args | 简单直接 | 没有设定反思等行为,对于错误的思考不能及时纠正 |
| AutoGPT | - prompt 较为复杂,分为生成工具调用 和 生成最终答案 两套prompt - 生成工具调用 prompt 详细设立了Constraints(例如不需要用户协助)、Resources(例如网络搜索)、Best Practices(例如每个API都需要花费,尽量少的调用),最终严格以json格式输出 | prompt 限制多,会较好地进行自我反思、任务规划等 | prompt 较长,花费较大 |
| ToolLLaMA | 模仿AutoGPT和ReACT,输出以Thought、Action、Action Input 格式而非 json 格式,增加了 give_up_and_restart,支持全部推导重来,重来的prompt会把历史失败的记录加进去训模型用了1.6w Rapid API | prompt 限制多,会较好地进行自我反思、任务规划等,并支持全部推倒重来 | 1. prompt 较长,花费较大 2. 全部推倒重来花费会更大 |
eg:
# 导入依赖库
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
# 加载 .env 文件中定义的环境变量
_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
# 初始化 OpenAI 客户端
client = OpenAI() # 默认使用环境变量中的 OPENAI_API_KEY 和 OPENAI_BASE_URL
# 基于 prompt 生成文本
# 默认使用 gpt-3.5-turbo 模型
def get_completion(prompt, response_format="text", model="gpt-4o-mini"):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}] # 将 prompt 作为用户输入
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
temperature=0, # 模型输出的随机性,0 表示随机性最小
# 返回消息的格式,text 或 json_object
response_format={"type": response_format},
)
print(response)
return response.choices[0].message.content # 返回模型生成的文本
# 任务描述
instruction = """
Answer the following questions as best you can. You have access to the following tools:
[
Name: web_search. Description: Perform a web search using the specified query.
Name: get_weather. Description: Retrieve the current weather information for a specified location.
]
Use the following format:
Question: the input question you must answer
Thought: you should always think about what to do
Action: the action to take, should be one of [web_search, get_weather]
Action Input: the input to the action
Observation: the result of the action
... (this Thought/Action/Action Input/Observation can repeat N times)
Thought: I now know the final answer
Final Answer: the final answer to the original input question
Begin!
"""
# 用户输入
input_text = """
北京天气怎么样?
"""
# 工具结果
tool_output = """
"""
# prompt 模版。instruction 和 input_text 会被替换为上面的内容
prompt = f"""
{instruction}
Question:
{input_text}
{tool_output}
"""
# 调用大模型
response = get_completion(prompt)
print("------------------------------------------")
print(response)# 导入依赖库
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
# 加载 .env 文件中定义的环境变量
_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
# 初始化 OpenAI 客户端
client = OpenAI() # 默认使用环境变量中的 OPENAI_API_KEY 和 OPENAI_BASE_URL
# 基于 prompt 生成文本
# 默认使用 gpt-3.5-turbo 模型
def get_completion(prompt, response_format="text", model="gpt-4o-mini"):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}] # 将 prompt 作为用户输入
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
temperature=0, # 模型输出的随机性,0 表示随机性最小
# 返回消息的格式,text 或 json_object
response_format={"type": response_format},
)
print(response)
return response.choices[0].message.content # 返回模型生成的文本
# 任务描述
instruction = """
<|system|>
You are AutoGPT, you can use many tools (functions) to do the following task. First I will give you the task description, and your task start. At each step, you need to give your thought to analyze the status now and what to do next, with a function call to actually execute your step. Your output should follow this format:
Thought:
Action:
Action Input:
After the call, you will get the call result, and you are now in a new state. Then you will analyze your status now, then decide what to do next.
After many (Thought-call) pairs, you finally perform the task, then you can give your final answer.
Remember:
The state change is irreversible, you can't go back to one of the former states. If you want to restart the task, say "I give up and restart".
All the thoughts are short, at most 5 sentences.
You can do more than one try, so if your plan is to continuously try some conditions, you can do one of the conditions per try.
Let's Begin!
Task description: You should use functions to help handle the real-time user queries. Remember:
ALWAYS call the "Finish" function at the end of the task. The final answer should contain enough information to show to the user. If you can't handle the task, or you find that function calls always fail (the function is not valid now), use function Finish->give_up_and_restart.
Specifically, you have access to the following APIs:
{
"api_name": "web_search",
"description": "Perform a web search using the specified query.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The search query to be executed.",
"example_value": "华为发布会"
}
},
"required": ["query"],
"optional": []
}
}
{
"api_name": "get_weather",
"description": "Retrieve the current weather information for a specified location.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The name of the location (city, country, etc.) to get the weather for.",
"example_value": "Beijing"
},
},
"required": ["location"],
"optional": []
}
}
{
"name": "Finish",
"description": "If you believe that you have obtained a result that can answer the task, please call this function to provide the final answer. Alternatively, if you recognize that you are unable to proceed with the task in the current state, call this function to restart. Remember: you must ALWAYS call this function at the end of your attempt, and the only part that will be shown to the user is the final answer, so it should contain sufficient information.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"return_type": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["give_answer", "give_up_and_restart"]
},
"final_answer": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The final answer you want to give the user. You should have this field if "return_type"=="give_answer""
}
},
"required": ["return_type"]
}
}
"""
# 用户输入
input_text = """
北京天气怎么样?
"""
# 工具结果
tool_output = """
"""
# prompt 模版。instruction 和 input_text 会被替换为上面的内容
prompt = f"""
{instruction}
<|user|>
{input_text}
{tool_output}
<|assistant|>
"""
# 调用大模型
response = get_completion(prompt)
print("------------------------------------------")
print(response)2.2 Agent Prompt 模板设计
我们可以设计两套Prompt模板,一套用于任务规划和工具调用指令生成(模板-1),一套用于总结生成最终答案(模板-2)。
I. Agent Prompt 1(模板-1):
你是一个很专业的AI任务规划师,给定目标或问题,你的决策将独立执行而不依赖于人类的帮助,请发挥LLM的优势并且追求高效的策略进行任务规划。
Constraints: 1.你有~4000字的短期记忆 2.不需要用户的帮助 3.只使用双引号中列出的commands,例如:“command_name” 4.互联网搜索、信息聚合和鉴别真伪的能力 5.保持谦逊,对自己没把握的问题,尽可能调用command,但尽量少调用,不能重复调用 6.当你从自身知识或者历史记忆中能得出结论,请聪明且高效,完成任务并得出结论 7.经常建设性地自我批评整个行为大局,反思过去的决策和策略,以改进你的方法 8.你最多只能进行5步思考,规划5个任务,所以尽可能高效规划任务 9.你有反思能力,如果已完成的任务和结果暂不能得到回答问题所需信息或尚不能完成目标,应继续规划
Commands: 1:{"name": "web_search", "description": "Perform an internet search.", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"text": {"type": "str", "description": "Search query."}}}, "returns": {"description": "Multiple webpage links along with brief descriptions.", "type": "str"}, "required": ["text"]}
2:{"name": "wiki_search", "description": "Conduct an encyclopedia search for a specified entity and question. Provide accurate answers for factual queries but has a limited scope and cover fewer queries.", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"entity": {"type": "str", "description": "The target entity for the search."}, "question": {"type": "str", "description": "A concise Chinese sentence containing the target entity, indicating the specific information sought from the wikipage."}}}, "returns": {"description": "Relevant encyclopedia entries pertaining to the question.", "type": "str"}, "required": ["entity", "question"]}
3:{"name": "get_weather_info", "description": "Retrieve weather information for specified locations and dates.", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"location": {"type": "str", "description": "Locations in English separated by commas, e.g., "Beijing,Vancouver,...,Chicago"."}, "start_date": {"type": "str", "description": "Start date in format "yyyy-MM-dd"."}, "end_date": {"type": "str", "description": "End date in format "yyyy-MM-dd"."}, "is_current": {"type": "str", "description": ""yes" or "no" indicating if current time's weather is desired."}}}, "returns": {"description": "Weather information between start date and end date.", "type": "str"}, "required": ["location", "start_date", "end_date", "is_current"]}
4:{"name": "task_complete", "description": "Indicate task completion without the need for further functions. ", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {}}, "returns": {"description": "", "type": ""}, "required": []}
GOAL: 用户的输入
Completed tasks: 已完成任务(短时记忆)
Conversation history: 对话历史(短时记忆)
Knowledge: 知识(短时记忆)
Current Time: 当前时间
根据目标和已有任务,规划一个新Task(不能重复),你只能以以下json列表的格式生成Task { "task_name": "任务描述", "command":{ "name":"command name", "args":{ "arg name":"value" } } }
确保Task可以被Python的json.loads解析
当已完成的Tasks能够帮助回答这个目标问题,则尽可能生成任务完成Task,否则生成一个其他Task。一个新Task:
Agent Prompt 1 的组成部分:
-
Profile(角色):
定义 Agent 的身份、背景甚至性格特点等。这帮助模型在回答时保持一致性和个性化。例如,一个 Agent 可能被设定为一个友好且专业的助理。
你是一个很专业的AI任务规划师,给定目标或问题,你的决策将独立执行而不依赖于人类的帮助,请发挥LLM的优势并且追求高效的策略进行任务规划。
-
Instruction(指令):
提供具体的操作指令,指导Agent如何完成任务。这些指令明确地告诉Agent在特定情境下应该做什么或避免做什么。
Constraints:
1.你有~4000字的短期记忆
2.不需要用户的帮助
3.只使用双引号中列出的commands,例如:“command_name”
4.互联网搜索、信息聚合和鉴别真伪的能力
5.保持谦逊,对自己没把握的问题,尽可能调用command,但尽量少调用,不能重复调用
6.当你从自身知识或者历史记忆中能得出结论,请聪明且高效,完成任务并得出结论
7.经常建设性地自我批评整个行为大局,反思过去的决策和策略,以改进你的方法
8.你最多只能进行5步思考,规划5个任务,所以尽可能高效规划任务
9.你有反思能力,如果已完成的任务和结果暂不能得到回答问题所需信息或尚不能完成目标,应继续规划
……
当已完成的Tasks能够帮助回答这个目标问题,则尽可能生成任务完成Task,否则生成一个其他Task。一个新Task:-
Tools(工具集):
列出Agent可以使用的工具或功能,需要根据实际业务需求来构建。
Commands:
1:{"name": "web_search", "description": "Perform an internet search.", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"text": {"type": "str", "description": "Search query."}}}, "returns": {"description": "Multiple webpage links along with brief descriptions.", "type": "str"}, "required": ["text"]}
2:{"name": "wiki_search", "description": "Conduct an encyclopedia search for a specified entity and question. Provide accurate answers for factual queries but has a limited scope and cover fewer queries.", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"entity": {"type": "str", "description": "The target entity for the search."}, "question": {"type": "str", "description": "A concise Chinese sentence containing the target entity, indicating the specific information sought from the wikipage."}}}, "returns": {"description": "Relevant encyclopedia entries pertaining to the question.", "type": "str"}, "required": ["entity", "question"]}
3:{"name": "get_weather_info", "description": "Retrieve weather information for specified locations and dates.", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"location": {"type": "str", "description": "Locations in English separated by commas, e.g., "Beijing,Vancouver,...,Chicago"."}, "start_date": {"type": "str", "description": "Start date in format "yyyy-MM-dd"."}, "end_date": {"type": "str", "description": "End date in format "yyyy-MM-dd"."}, "is_current": {"type": "str", "description": ""yes" or "no" indicating if current time's weather is desired."}}}, "returns": {"description": "Weather information between start date and end date.", "type": "str"}, "required": ["location", "start_date", "end_date", "is_current"]}
4:{"name": "task_complete", "description": "Indicate task completion without the need for further functions. ", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {}}, "returns": {"description": "", "type": ""}, "required": []}
-
Goal(目标,用户的Query):
定义Agent的主要任务或目的。这帮助Agent聚焦于最终目标,例如帮助用户解答问题、撰写文章等。
GOAL: 我想登顶北京最高峰,请帮我做个规划
-
Memory(记忆):
保持上下文或会话记忆,以提供连续性。这使得Agent能够参考之前的对话或用户提供的信息,提供更相关和个性化的回应。
【重点】Memory部分可以包括:
- Completed Tasks(已完成任务):之前已调用工具完成的任务,通常包含任务名、工具名、工具参数、工具返回结果等信息;
- Conversation History(对话历史):记录用户和 Agent 系统的对话历史;
- Knowledge(知识):存储业务中所需的知识用于参考,例如用户上传的文档、个性化知识等。
将知识,对话历史,任务历史进行存储,然后在对话的过程中进行检索和筛选,筛选后的信息加入prompt中作为参考。底层使用的向量数据库进行信息的存储,检索采用es和embedding进行双路召回。
Completed tasks: [
{
"task_name": "查询北京最高山",
"command": {
"name": "wiki_search",
"args": {
"entity": "北京"
"question": "北京最高山是什么山"
}
},
"task_id": 1,
"result": "北京市,通称北京(汉语拼音:Běijīng;邮政式拼音:Peking),简称“京”,曾称“北平”[注 2]。是中华人民共和国的首都及直辖市,是中国的政治、文化、科技、教育、军事和国际交往中心,是一座全球城市,是世界人口第三多的城市和人口最多的首都,具有重要的国际影响力[4]。北京位于华北平原的北部边缘,背靠燕山,永定河流经老城西南,毗邻天津市、河北省,为京津冀城市群的重要组成部分..."
},
{
"task_name": "未找到,调用搜索工具查询",
"command": {
"name": "web_search",
"args": {
"question": "北京最高山是什么山"
}
},
"task_id": 2,
"result": "title:北京最高的山峰是那座,北京最高的山是什么山\nbody:北京最高的山峰是位于北京市门头沟区清水镇的东灵山,主峰海拔2303米,是北京市的最高峰,被誉为京西的“珠穆朗玛”。 景色介绍东灵山自然风景区位于京西门头沟的西北部, ... url: https://m.mafengwo.cn/travel-news/219777.html ..."
}
]
Conversation history: [
{
"user": "刘德华多少岁了?",
"assistant": "刘德华(Andy Lau)生于1961年9月27日。截至2024年7月,他已经62岁了。"
},
{
"user": "北京今天天气怎么样?",
"assistant": "北京当日天气多云,28摄氏度,微风"
}
]
Knowledge: [
{
"北京最高的山峰是东灵山,海拔2303米。",
"北京市地处中国北部、华北平原北部,东与天津市毗连,其余均与河北省相邻,中心位于东经116°20′、北纬39°56′,北京市地势西北高、东南低。",
"2023年,北京市全年实现地区生产总值43760.7亿元,按不变价格计算,比上年增长5.2%。"
}
]
思考:如果 Memory 太多,Prompt 无法容纳怎么办?-
Format(输出格式):
定义Agent生成输出的格式和风格。这确保了Agent的回应符合预期的结构和表达方式,例如简洁、正式或非正式等。
根据目标和已有任务,规划一个新Task(不能重复),你只能以以下json列表的格式生成Task
{
"task_name": "任务描述",
"command":{
"name":"command name",
"args":{
"arg name":"value"
}
}
}
确保Task可以被Python的json.loads解析-
其他必要信息:
可以根据业务场景的需求,在Prompt中添加必要的常用信息,如:当前时间、地点、IP等。
3. Agent Tuning
3.1 Agent Tuning 的目的(再次理解)
回顾: 既然通过 Prompt Engineering 可以实现 Agent,那为什么还要训练 Agent 模型呢?
因为可以这么做的前提是:模型足够“聪明”,靠看“说明书”就能执行, Prompt Engineering 实际上是把“说明书”写得更加清晰易懂。
- 实践证明,除了 GPT-4 level 的大模型,其他大模型(包括 GPT-3.5 )无法很好遵从 prompt 要求完成复杂的 Agent 任务;
- 很多场景下无法使用最强的大模型 API ,需要私有化部署小模型,需要控制推理成本;
- 通过训练,一个小参数量的大模型(13B、7B等)也能达到较好的能力,更加实用。
3.2 训练数据准备

-
大模型 fine-tuning 的数据形式:

-
Agent Tuning 是一种特殊的 fine-tuning,有时也被称作 Tool SFT,特殊之处在于:
1)Agent Tuning 的 Prompt 更复杂,约束条件更多;
2)通常 Agent 工作过程是多步的,因此训练数据也需要是多步骤的,多步之间前后有关联。

重点Agent Tuning 训练数据构建的步骤:
- 根据实际业务收集大量 query,要尽可能覆盖各种场景;
- 将每一个 query 与 prompt 模板结合,构成 agent prompt,也就是训练数据中的输入部分;
- 为每一个 agent prompt 构建对应的标准答案,也就是训练数据中的输出部分,这项工作可以借助 GPT-4 level 的大模型来降本提效;
- 如果第三步是用大模型来生成答案,则最好通过人工修正或筛选高质量的 Output,数据质量越高,最终 Agent Tuning 得到的模型效果越好。
eg:
你是一个很专业的AI任务规划师, 给定目标或问题,你的决策将独立执行而不依赖于人类的帮助,请发挥LLM的优势并且追求高效的策略进行任务规划。
Constraints:
1.你有~4000字的短期记忆
2.不需要用户的帮助
3.只使用双引号中列出的commands,例如:“command_name”
4.互联网搜索、信息聚合和鉴别真伪的能力
5.保持谦逊,对自己没把握的问题,尽可能调用command,但尽量少调用,不能重复调用
6.当你从自身知识或者历史记忆中能得出结论,请聪明且高效,完成任务并得出结论
7.经常建设性地自我批评整个行为大局,反思过去的决策和策略,以改进你的方法
8.你最多只能进行5步思考,规划5个任务,所以尽可能高效规划任务
9.你有反思能力,如果已完成的任务和结果暂不能得到回答问题所需信息或尚不能完成目标,应继续规划
Commands:
1:Web Search:"web_search",args:"text":"<search>"
2:Browse Website:"browse_website",args:"url":"<url>, "question":"<what_you_want_to_find_on_website>"
3:Wikipedia search:"wiki_search",args:"entity":<entity>,"question":"<what_you_want_to_find_on_wikipage>"
4:Wikipage browser:"browse_wikipage",args:"url":<url_return_by_wiki_search>,"question":"<what_you_want_to_find_on_wikipage>"
5:Video Search:"video_search",args:"query":"<search-query-in-chinese>"
6:Do Nothing: "do_nothing",args:
7:Task Complete (Shutdown):"task_complete",args: "reason":"<reason>"
Commands Tips:
1.使用browse_website时,尽可能只访问先前搜索得到的网址,不要瞎编生成无效网站链接
2.wiki_search返回的信息尽管更准确,但搜索范围小,问题覆盖率低,question只能是包含中心实体的简单中文短句
3.每次调用command都会收取费用,尽可能少调用
Current Time: 2023-07-07 18:35:32.214612
GOAL: 请找出蔡徐坤2023年的演唱会名称,以及与演唱会相关的最新几则新闻。
根据目标和已有任务,规划一个新Task(不能重复),你只能以以下json列表的格式生成Task
{
"task_name": "任务描述",
"command":{
"name":"command name",
"args":{
"arg name":"value"
}
}
}
确保Task可以被Python的json.loads解析
当已完成的Tasks已经能够帮助回答这个目标,则尽可能生成任务完成Task,否则生成一个其他Task。一个新Task:3.3 模型训练
注意:Agent 模型通常需要全参数训练,LoRA 效果不好。
高阶经验(大家了解即可):
- 应用加速训练、节省显存的方法,例如:混合精度、分布式训练(Deepspeed Zero3)、梯度检查点(Gradient Checkpointing)、梯度累积(Gradient Accumulation)、Flash Attention 等;
- 推理用 vllm 等框架加速。
3.4 效果评估
3.4.1 自动评估

自动评估的主要目的是在模型训练过程中监控模型的效果,评估指标的对比意义大于绝对值意义。
- 采用 GPT-4 + 人工修正的方式构建自动评测的 benchmark(一般从训练数据中随机分出一部分即可);
- 将 Agent 输出结果与 benchmark 中的参考答案进行对比,计算得到分值。
示例:
Ground Truth:
{
"task_name": "查询北京实时天气",
"command": {
"name": "get_weather_info",
"args": {
"location": "北京",
"start_date": "2024-07-01",
"end_date": "2024-07-01",
"is_current": "yes"
}
}
}Agent Response:
{
"task_name": "查询北京当前天气",
"command": {
"name": "get_weather_info",
"args": {
"location": "北京",
"start_date": "2024-07-01",
"end_date": "2024-07-01",
"is_current": "no"
}
}
}

其中,Tn,i 为 Groud Truth 中的工具名称,Tn,j′ 为 待测试的 Agent Response 中的工具名称,EM为精确匹配(Exact Match,直接进行字符串精确匹配),结果为 0 或 1;
Th,i 为 Groud Truth 中的任务描述(示例中的“task_name”),Th,j′ 为 待测试的 Agent Response 中的任务描述,
可以是任何文本生成质量评估的方法(例如 ROUGE、 BLEU),做模糊匹配评分,分值为0-1;
类似地:
自动测试结果示例:
| Scale | Planning | Tool-use | Reflection | Concluding | Profile | Overall Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-3.5-turbo | - | 18.55 | 26.26 | 8.06 | 37.26 | 35.42 | 25.63 |
| Qwen | 7B | 13.34 | 18.00 | 7.91 | 36.24 | 34.99 | 21.17 |
| Qwen2 | 7B | 20.11 | 29.03 | 21.01 | 40.36 | 42.06 | 29.57 |
| Baichuan2 | 13B | 6.70 | 16.10 | 6.76 | 24.97 | 19.08 | 14.89 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| Qwen-MAT | 7B | 31.64 | 43.30 | 33.34 | 44.85 | 44.78 | 39.85 |
| Baichuan2-MAT | 13B | 37.27 | 52.97 | 37.00 | 48.01 | 41.83 | 45.34 |
人工评估
最靠谱的评估当然还是需要人工来做,人工评估的难点在于标准的制定,以及对评估人员的培训。
评估标准示例:
评分分为五个等级,具体定义如下:
1分:核心信息存在重大不准确性,大部分或全部内容不正确; 2分:核心信息不正确,或超过60%的内容有错误; 3分:核心信息准确,但10%到60%的补充信息不正确; 4分:小有出入,核心信息准确,补充信息中的错误不超过10%; 5分:完全正确。
得分为4分或5分的回答被认为是可用的。
遇到违规内容一票否决,直接判0分。
人工评估效率低、成本高,所以不能频繁使用,一般在大的模型版本上使用。
4. Agent 泛化性提升
如果想进一步提升 Agent 的泛化性,比如希望用一个 Agent 服务于多个业务,能适应不同的 Prompt 模板,可以灵活地接入新的业务,那么训练数据应该如何构建呢?
4.1 训练数据的多样性
基座大模型本身的理解能力和 Agent Tuning 训练数据的多样性共同决定了 Agent 的泛化能力。在指定了基座模型的情况下,我们可以做的是提升训练数据的多样性。
我们可以将训练数据 Input 部分拆解为3个变量:Query、Tools、Agent Prompt模板,最终的数据就是这3个变量的组合。

-
Query:
-
覆盖全部场景:对于内部业务工具构造特定query,尽可能覆盖所有可能的业务场景,避免有遗漏;
-
困难负样本:构造正样本(需要用到工具的query) + 困难负样本(看似和工具有关,但实际上不调用),其中大部分是正样本,但不能全是正样本
示例:上海明天天气怎么样?(正样本)| 北京今天下雨吗?(正样本) | 今天天气真好(困难负样本)
经验值:正样本和困难负样本比例 4:1,仅供参考。 -
样本复杂度多样:简单样本和复杂样本都需要构造,简单样本为一步即可完成的任务,复杂样本为涉及多步推理、多种工具的任务;(实践中评测时发现,仅减少550复杂query,测试集中的事实准确率下降6个百分点)
示例:这周末适合去北京郊区露营吗?如果适合,请推荐几个地方? | 刘德华的女儿几岁了?(涉及到多步工具调用)
经验值:简单样本与复杂样本比例 6:1,仅供参考。
-
-
Tools
有两种维度:Tools描述格式多样性和Tools类型多样性。
-
Tools 描述格式多样性:
- OpenAI function:{"name": "web_search", "description": "Perform an internet search.", "parameters": {"type": "object", "properties": {"text": {"type": "str", "description": "Search query."}}}, "returns": {"description": "Multiple webpage links along with brief descriptions.", "type": "str"}, "required": ["text"]} - AutoGPT:Web Search:"web_search",args:"text":"" - ReACT:duckduckgo_search: A wrapper around DuckDuckGo Search. Useful for when you need to answer questions about current events. Input should be a search query.
-
Tools 类型多样性:
除了引入业务本身的工具之后,还可以添加更加丰富的工具,比如可以从ToolLLaMA(1w+)、ModelScope(几百)、AutoGPT等项目中选取API,可以提升工具的泛化性。
-
-
Agent Prompt 模板
提升 Agent Prompt 模板的多样性,参见下一节 Meta-Agent 内容。
【重点】对 Query、Tools、Agent Prompt 模板 这三个变量分别构造了各种类型的数据,然后进行组合构成多样性的 Input( Prompt )数据,再调用GPT-4生成 Output( Response ),多样性的数据可以使模型不只拟合特定的 Prompt 模板,适应各种类型的 Query 以及 Tools 集合,提高模型的泛化性。
4.2 Meta-Agent
Agent Prompt 模板多样性提升
4.2.1 背景
ReACT、ToolLlama、ModelScope、AutoGPT 都有一套各自运行在其中内部的一套 prompt 模板,模型如果只是在一套 prompt 模板下训练,那么可能只是拟合了这一套 prompt ,如果换一套 prompt 性能会急剧下降;我们希望 Agent 不受到特定 Prompt 模板的限制,提升模型本质的 Agent 能力,提出了核心思想 Meta-Agent 方法。
这些 Agent Prompt 模板虽然表述方式各不相同,但都可以分为 <Profile>、<Instruction>、<Tools>、<Goal>、<Memory>、<Format>部分,那是不是可以调用GPT4来自动化生成包含这些部分且表达方式多样性的模板呢?
4.2.2 方法
我们可以通过 Prompt Engineering 来设计一个基于 GPT-4 的 Agent,用于生成多样性的 Agent Prompt 模板,我们称之为:Meta-Agent (元-Agent)。
Meta-Agent Prompt: 用于调用 GPT-4 生成 Agent Prompt 模板的 Prompt,我们称之为 Meta-Agent Prompt。
我们可以手动写一个固定的 Meta-Agent Prompt 作为 GPT-4 的输入,利用大模型内容生成的多样性来生成不同的模板,但实际上多样性效果有限,更好的方式是用不同的种子 query 做引导,提升多样性。
- 根据实际业务收集大量 query,要尽可能覆盖各种场景;
- 选取相似的数条 query 组成多个集合,如果数量不足,这一步也可以借助 GPT-4 来对 query 做扩展;
- 设计一个 Meta-Agent Prompt 模板,将不同的 query 集合插入设计好的模板中组合成不同的 Meta-Agent Prompt;
- 调用 GPT-4 生成不同的 Agent Prompt 模板候选。
利用这种方法便可以生成包含<Profile>、<Instruction>、<Tools>、<Goal>、<Memory>、<Format>要素的多样化的模板。

由于自动化生成的 Agent Prompt 模板质量可能参差不齐,我们还需要对这些模板以及生成的训练数据进行筛选。对于关键信息缺失,有明显缺陷的的模板,我们直接删除即可。剩下的模板效果如何则需要在实际数据上检验,我们同样也可以借助 GPT-4 (做裁判)来完成。具体步骤如下:
- 将一批相同的 query 分别插入到经过验证的标杆模板中(如AutoGPT、ToolLLaMA等)和 Meta-Agent 生成的 prompt 模版中,形成 prompt pair;
- 将 prompt pair 中的两个 prompt 分别输入给GPT-4,生成对应的回复;
- 利用 GPT-4 对两个回复的质量分别打分 score1(标杆模板的实例)、score2(候选模板的实例),如果 score2−score1>ϵ,则保留该 prompt 实例,否则删除;
- 对于同一个模板的所有实例求平均分,得到模板的得分,当分值大于一定阈值,保留该模板,否则删除该模板以及对应的prompt实例。
4.1.3 示例
-
Mate-Agent Prompt(GPT-4 的输入):
# 导入依赖库
from openai import OpenAI
from dotenv import load_dotenv, find_dotenv
# 加载 .env 文件中定义的环境变量
_ = load_dotenv(find_dotenv())
# 初始化 OpenAI 客户端
client = OpenAI() # 默认使用环境变量中的 OPENAI_API_KEY 和 OPENAI_BASE_URL
# 基于 prompt 生成文本
# 默认使用 gpt-3.5-turbo 模型
def get_completion(prompt, response_format="text", model="gpt-4o-mini"):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}] # 将 prompt 作为用户输入
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
temperature=0, # 模型输出的随机性,0 表示随机性最小
# 返回消息的格式,text 或 json_object
response_format={"type": response_format},
)
print(response)
return response.choices[0].message.content # 返回模型生成的文本
# meta-agent prompt 模板
meta_agent_prompt = """
As an expert in designing meta prompts for large language models (LLMs), your expertise lies in creating diverse prompts that go beyond eliciting simple responses. Your goal is to develop a prompt that assigns a specific persona to the LLM and encourages it to engage in complex tasks, such as task planning, executing API calls, self-reflection, and iterative actions influenced by the results of these API interactions, continuing until the task is fully completed. You should use "you" instead of "I" as the main voice in the meta prompt.
Your prompt must explicitly reserve slots for <<QUERY>> and <<APIs>>. Each slot should ideally occupy a separate line. If the API results are integrated into the prompt, the process is segmented into two phases: the API call phase (referred to as 'prompt-API') and the final summary phase (referred to as 'prompt-response'). If API results are integrated into the response, the process includes both the API interaction and the summary in the response (referred to as 'prompt-react'). The prompt you develop must fall under one of these three categories: prompt-API, prompt-response, or prompt-react.
Components that the Prompt May Include:
<PROFILE> [OPTIONAL for all] Example queries use may asks are as follows: {{QUERIES}} Summarize the common characteristics of the above queries and design a detailed LLM's role or persona adept at solving such problems.
<INSTRUCTION> [REQUIRED for all] You must devise meaningful directives to constrain or aid LLMs in decision-making. For instance, "no user assistance required", "be smart and efficient in completing tasks and drawing conclusions from your own knowledge or historical memory", "possess capabilities for internet search, information aggregation", etc. Use your imagination to expand on these guidelines.
<QUERY> [REQUIRED for all] Directly add slot <<QUERY>> into your prompt. The slot will be replaced with an actual user query. Do NOT provide the specific query.
<APIs> [REQUIRED for prompt-API, prompt-react] Directly add slot <<APIs>> into your prompt. The slot will be replaced with specific APIs. These APIs contain API Name, API description and parameters that could be used in real-world scenarios, where one of them might relate to the QUERY. Do NOT provide the specific APIs.
<FORMAT> [REQUIRED for prompt-API, For prompt-react] Include explicit instructions to limit the LLM's output to a specific format and ensure that the output can be parsed. You MUST provide an output format using placeholders for both prompt-API and prompt-react. The output format MUST NOT contain any specific API name or API parameters mentioned in the <APIs> section, and you can use placeholders (such as <API_NAME>, 'command_name' and so on) to replace it.
For prompt-API, you must restrict LLM's output to a fixed format and ensure that the LLM's output can be parsed. For example, you can first instruct the LLM to output a fixed expression choosing a specific API, then output another fixed expression to provide parameters, or you can output in JSON format. Please be creative and do not feel limited by the above examples. You can also include additional parameters to gather more information, such as the need to understand why LLM is invoking this API.
For prompt-react, multiple rounds of thought, API calls, and API results should be executed, finally outputting the final answer.
Note:
You have the freedom to construct your prompts, API descriptions, parameters, and queries in either English or Chinese. The examples provided above are only for reference. Use your imagination and creativity beyond the given examples. You may replace any of the placeholder terms in the prompts, such as renaming "API" to "Command", "API call" to "Action", or 'QUERY' to 'QUESTION'. Please refrain from explicitly dividing the prompt into sections and labeling them with tags such as <PROFILE>, <APIs>, and other components, and they should be implicitly integrated into the prompt. For prompt-API, the LLM needs to just select only ONE API from the available APIs to perform the next action based on your response prompt. You must mention this in your prompt. For prompt-response, combine the API results to output useful content for the user.
Please generate a prompt of the {{PROMPT_TYPE}} type directly in {{LANGUAGE}}. Do not include any explanations.
"""
# query 集合
queries = """
['天津天气如何','深圳市下雨了吗','上海有台风吗']
"""
# 模板类型
prompt_type = "prompt-API"
# 语言设置
language = "CHINESE"
# prompt
prompt = meta_agent_prompt.replace("{{QUERIES}}", queries).replace("{{PROMPT_TYPE}}", prompt_type).replace("{{LANGUAGE}}", language)
# 调用大模型
response = get_completion(prompt)
print("------------------------------------------")
print(response)4.3 训练数据构建关键经验
构建机器学习训练数据是保证模型性能的关键环节。以下是一些注意事项:
- 数据质量:
- 准确性:确保数据的标注正确且准确。错误标注会导致模型学到错误的模式。
- 一致性:数据应该保持一致,避免同样的输入在不同记录中对应相互冲突的答案。
2. **数据量**: - **数量**:足够大的数据量有助于模型捕捉复杂的模式。数据量不足可能导致模型过拟合。 - **多样性**:数据应包含尽可能多的不同情况,避免模型对某些特定模式的偏好。
3. **数据平衡**:确保各种类型的数据量相对平衡。例如对于分类问题,类别不平衡会导致模型偏向多数类。
4. **数据增强**: - **数据扩充**:对于图像、文本等数据,通过旋转、翻转、添加噪声等方法扩充数据量。 - **合成数据**:在数据量不足时,考虑生成合成数据。
5. **数据清洗**: - **去重**:删除重复的数据记录,避免模型学习到重复信息。 - **提质**:对于含有瑕疵的数据,合理补充修正或直接删除。
6. **隐私和合规性**: - **隐私保护**:确保数据的收集和使用符合隐私保护法规。 - **数据匿名化**:对敏感数据进行匿名化处理,保护个人隐私。
7. **数据分割**: - **训练集、验证集、测试集**:将数据合理分割为训练集、验证集和测试集,确保模型的泛化能力。 - **避免数据泄漏**:确保训练数据中不包含测试数据的信息,避免模型在测试时表现出非真实的高精度。
8. **持续更新**: - **数据更新**:随着时间推移,定期更新训练数据,保持模型的准确性和可靠性。 - **模型监控**:监控模型性能,及时发现和解决数据相关的问题。
通过关注这些注意事项,可以提高训练数据的质量,从而构建出更准确、更可靠的机器学习模型。
一般大厂都会专门开发一套机器学习数据管理的系统,并且有专业的数据标注团队(全职+外包)来完成机器学习数据的建设。
5. 几个 Agent Tuning 开源项目简介
1) ToolBench (ToolLLaMA)
- 发布机构:面壁智能
* 4.6k stars
* https://github.com/OpenBMB/ToolBench
提供数据集、相应的训练和评估脚本,以及在ToolBench上经过微调的强大模型ToolLLaMA。
数据:ToolBench,包含 469585 条数据(工具数量:3451;API数量:16464);
模型:ToolLLaMA-2-7b-v2、ToolLLaMA-7b-v1、ToolLLaMA-7b-LoRA-v1

2) AgentTuning
- 发布机构:智谱华章
* 1.3k stars
* https://github.com/THUDM/AgentTuning
利用多个 Agent 任务交互轨迹对 LLM 进行指令调整的方法。评估结果表明,AgentTuning 让 LLM 在未见过的 Agent 任务中也展现出强大的泛化能力,同时通用语言能力也基本保持不变。
数据:AgentInstruct,包含 1866 个高质量交互、6 个多样化的真实场景任务;
模型:AgentLM 由 Llama2-chat 开源模型系列在 AgentInstruct,ShareGPT 混合数据集上微调得到,有7B、13B、70B三个模型。
3) KwaiAgents
- 发布机构:快手
* 1k stars
* https://github.com/KwaiKEG/KwaiAgents
快手联合哈尔滨工业大学研发,使 7B/13B 的 “小” 大模型也能达到超越 GPT-3.5 的效果。
数据:KAgentInstruct,超过20w(部分人工编辑)的Agent相关的指令微调数据;KAgentBench:超过3k条经人工编辑的自动化评测Agent能力数据;
模型:采用 Meta-Agent 方法训练,包括 Qwen-7B-MAT、Qwen-14B-MAT、Qwen-7B-MAT-cpp、Qwen1.5-14B-MAT、Baichuan2-13B-MAT。
6. 总结
1. 理解大模型应用需要 Agent 技术的原因:消除“幻觉”、连接真实世界、处理复杂任务;
2. 理解 Agent Tuning 的主要动机:希望通过训练让大模型,尤其是小参数大模型(7B、14B)也能具备特定业务场景的 Agent 能力;
3. 了解 Agent Prompt 的构造方法,通常包括Profile、Instruction、Tools、Format、Memory、Goal等部分;
4. 了解 Agent Tuning 训练数据的构建方法和微调训练方式,并学习模型效果评估的方法;
5. 了解提升 Agent 泛化性的方法:从Query、Tools 和 Agent Prompt 模板三个方面提升训练数据的多样化,引申了解机器学习训练数据构建的关键经验;
6. 介绍了三个 Agent Tuning 的开源项目。
最后推荐大家一起学习B站上吴恩达老师的,讲的很不错。
链接:04can-a-large-language-model-master-wordle_哔哩哔哩_bilibili








![[Windows] 游戏常用运行库- Game Runtime Libraries Package(6.2.25.0409)](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/55ca519964b01db8e0d3b2a1e7961c42.webp?x-oss-process=image/format,png)









