目录
一、pcl中 点云配准算法
二、关于svd原理求解部分
三、pcl IterativeClosestPoint 完成demo
一、pcl中 点云配准算法
PCL 库中 ICP 的接口及其变种:
- 点到点:pcl::IterativeClosestPoint< PointSource, PointTarget, Scalar >
- 点到面:pcl::IterativeClosestPointWithNormals< PointSource, PointTarget, Scalar >
- 面到面:pcl::GeneralizedIterativeClosestPoint< PointSource, PointTarget >
其中,IterativeClosestPoint 模板类是 ICP 算法的一个基本实现,其优化求解方法基于 Singular Value Decomposition (SVD),算法迭代结束条件包括:
- 最大迭代次数:Number of iterations has reached the maximum user imposed number of iterations (via setMaximumIterations)
- 两次变换矩阵之间的差值:The epsilon (difference) between the previous transformation and the current estimated transformation is smaller than an user imposed value (via setTransformationEpsilon)
- 均方误差:The sum of Euclidean squared errors is smaller than a user defined threshold (via setEuclideanFitnessEpsilon)
基本用法:
IterativeClosestPoint<PointXYZ, PointXYZ> icp;
// Set the input source and target
icp.setInputCloud (cloud_source);
icp.setInputTarget (cloud_target);
// Set the max correspondence distance to 5cm (e.g., correspondences with higher distances will be ignored)
icp.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance (0.05);
// Set the maximum number of iterations (criterion 1)
icp.setMaximumIterations (50);
// Set the transformation epsilon (criterion 2)
icp.setTransformationEpsilon (1e-8);
// Set the euclidean distance difference epsilon (criterion 3)
icp.setEuclideanFitnessEpsilon (1);
// Perform the alignment
icp.align (cloud_source_registered);
// Obtain the transformation that aligned cloud_source to cloud_source_registered
Eigen::Matrix4f transformation = icp.getFinalTransformation ();两帧点云配置算法可以看这里
How to incrementally register pairs of clouds — Point Cloud Library 0.0 documentation (pcl.readthedocs.io)
GitHub - geekerboy/pairwise_incremental_registration: 修复参考书代码中Segmentation fault (core dumped) 问题
二、关于svd原理求解部分
高翔视觉SLAM十四讲求解 ICP 的代码
void pose_estimation_3d3d(const vector<Point3f>& pts1,
const vector<Point3f>& pts2,
Mat& R, Mat& t)
{
// 求质心
Point3f p1, p2;
int N = pts1.size();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
p1 += pts1[i];
p2 += pts2[i];
}
p1 /= N;
p2 /= N;
// 去质心
vector<Point3f> q1(N), q2(N);
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
q1[i] = pts1[i] - p1;
q2[i] = pts2[i] - p2;
}
// 计算 q1*q2^T
Eigen::Matrix3d W = Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
{
W += Eigen::Vector3d(q1[i].x, q1[i].y, q1[i].z) * Eigen::Vector3d(q2[i].x,
q2[i].y, q2[i].z).transpose();
}
cout << "W=" << W << endl;
// 对W进行SVD求解Rt
Eigen::JacobiSVD<Eigen::Matrix3d> svd(W, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);
Eigen::Matrix3d U = svd.matrixU();
Eigen::Matrix3d V = svd.matrixV();
cout << "U=" << U << endl;
cout << "V=" << V << endl;
Eigen::Matrix3d R_ = U * (V.transpose());
Eigen::Vector3d t_ = Eigen::Vector3d(p1.x, p1.y, p1.z) - R_ * Eigen::Vector3d(p2.x, p2.y, p2.z);
// Eigen 转换成 cv::Mat
R = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) <<
R_(0, 0), R_(0, 1), R_(0,2),
R_(1, 0), R_(1, 1), R_(1,2),
R_(2, 0), R_(2, 1), R_(2,2));
t = (Mat_<double>(3, 1) << t_(0, 0), t_(1, 0), t_(2, 0));
}另外的方法求RT,本质也是svd分解
/// <summary>
/// 通过svd分解求解旋转和平移
/// </summary>
/// <param name="A"></param>
/// <param name="B"></param>
/// <returns>返回值为4*4变换矩阵T</returns>
Eigen::Matrix4d best_fit_transform(const Eigen::MatrixXd& A, const Eigen::MatrixXd& B) {
/*
Notice:
1/ JacobiSVD return U,S,V, S as a vector, "use U*S*Vt" to get original Matrix;
2/ matrix type 'MatrixXd' or 'MatrixXf' matters.
*/
Eigen::Matrix4d T = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(4, 4);
Eigen::Vector3d centroid_A(0, 0, 0);
Eigen::Vector3d centroid_B(0, 0, 0);
Eigen::MatrixXd AA = A;
Eigen::MatrixXd BB = B;
int row = A.rows();
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
centroid_A += A.block<1, 3>(i, 0).transpose();
centroid_B += B.block<1, 3>(i, 0).transpose();
}
centroid_A /= row;
centroid_B /= row;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
AA.block<1, 3>(i, 0) = A.block<1, 3>(i, 0) - centroid_A.transpose();
BB.block<1, 3>(i, 0) = B.block<1, 3>(i, 0) - centroid_B.transpose();
}
Eigen::MatrixXd H = AA.transpose() * BB;
Eigen::MatrixXd U;
Eigen::VectorXd S;
Eigen::MatrixXd V;
Eigen::MatrixXd Vt;
Eigen::Matrix3d R;
Eigen::Vector3d t;
JacobiSVD<Eigen::MatrixXd> svd(H, ComputeFullU | ComputeFullV);
U = svd.matrixU();
S = svd.singularValues();
V = svd.matrixV();
Vt = V.transpose();
R = Vt.transpose() * U.transpose();
if (R.determinant() < 0) {
Vt.block<1, 3>(2, 0) *= -1;
R = Vt.transpose() * U.transpose();
}
t = centroid_B - R * centroid_A;
T.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = R;
T.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = t;
return T;
}
icp求解是利用pcl工具来做,省时省力。
Introduction — Point Cloud Library 1.12.1-dev documentation (pointclouds.org)
Interactive Iterative Closest Point — Point Cloud Library 1.12.1-dev documentation (pointclouds.org)
三、pcl IterativeClosestPoint 完成demo
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <numeric>
#include "icp.h"
#include "Eigen/Eigen"
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
/// <summary>
/// 通过svd分解求解旋转和平移
/// </summary>
/// <param name="A"></param>
/// <param name="B"></param>
/// <returns>返回值为4*4变换矩阵T</returns>
Eigen::Matrix4d best_fit_transform(const Eigen::MatrixXd& A, const Eigen::MatrixXd& B) {
/*
Notice:
1/ JacobiSVD return U,S,V, S as a vector, "use U*S*Vt" to get original Matrix;
2/ matrix type 'MatrixXd' or 'MatrixXf' matters.
*/
Eigen::Matrix4d T = Eigen::MatrixXd::Identity(4, 4);
Eigen::Vector3d centroid_A(0, 0, 0);
Eigen::Vector3d centroid_B(0, 0, 0);
Eigen::MatrixXd AA = A;
Eigen::MatrixXd BB = B;
int row = A.rows();
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
centroid_A += A.block<1, 3>(i, 0).transpose();
centroid_B += B.block<1, 3>(i, 0).transpose();
}
centroid_A /= row;
centroid_B /= row;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
AA.block<1, 3>(i, 0) = A.block<1, 3>(i, 0) - centroid_A.transpose();
BB.block<1, 3>(i, 0) = B.block<1, 3>(i, 0) - centroid_B.transpose();
}
Eigen::MatrixXd H = AA.transpose() * BB;
Eigen::MatrixXd U;
Eigen::VectorXd S;
Eigen::MatrixXd V;
Eigen::MatrixXd Vt;
Eigen::Matrix3d R;
Eigen::Vector3d t;
JacobiSVD<Eigen::MatrixXd> svd(H, ComputeFullU | ComputeFullV);
U = svd.matrixU();
S = svd.singularValues();
V = svd.matrixV();
Vt = V.transpose();
R = Vt.transpose() * U.transpose();
if (R.determinant() < 0) {
Vt.block<1, 3>(2, 0) *= -1;
R = Vt.transpose() * U.transpose();
}
t = centroid_B - R * centroid_A;
T.block<3, 3>(0, 0) = R;
T.block<3, 1>(0, 3) = t;
return T;
}
/*
typedef struct{
Eigen::Matrix4d trans;
std::vector<float> distances;
int iter;
} ICP_OUT;
*/
ICP_OUT icp(const Eigen::MatrixXd& A, const Eigen::MatrixXd& B, int max_iterations, int tolerance) {
int row = A.rows();
Eigen::MatrixXd src = Eigen::MatrixXd::Ones(3 + 1, row);
Eigen::MatrixXd src3d = Eigen::MatrixXd::Ones(3, row);
Eigen::MatrixXd dst = Eigen::MatrixXd::Ones(3 + 1, row);
NEIGHBOR neighbor;
Eigen::Matrix4d T;
Eigen::MatrixXd dst_chorder = Eigen::MatrixXd::Ones(3, row);
ICP_OUT result;
int iter = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
src.block<3, 1>(0, i) = A.block<1, 3>(i, 0).transpose();
src3d.block<3, 1>(0, i) = A.block<1, 3>(i, 0).transpose();
dst.block<3, 1>(0, i) = B.block<1, 3>(i, 0).transpose();
}
double prev_error = 0;
double mean_error = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < max_iterations; i++)
{
neighbor = nearest_neighbot(src3d.transpose(), B);
for (int j = 0; j < row; j++)
{
dst_chorder.block<3, 1>(0, j) = dst.block<3, 1>(0, neighbor.indices[j]);
}
T = best_fit_transform(src3d.transpose(), dst_chorder.transpose());
src = T * src;
for (int j = 0; j < row; j++)
{
src3d.block<3, 1>(0, j) = src.block<3, 1>(0, j);
}
mean_error = std::accumulate(neighbor.distances.begin(), neighbor.distances.end(), 0.0) / neighbor.distances.size();
if (abs(prev_error - mean_error) < tolerance)
{
break;
}
prev_error = mean_error;
iter = i + 2;
}
T = best_fit_transform(A, src3d.transpose());
result.trans = T;
result.distances = neighbor.distances;
result.iter = iter;
return result;
}
/*
typedef struct{
std::vector<float> distances;
std::vector<int> indices;
} NEIGHBOR;
*/
NEIGHBOR nearest_neighbot(const Eigen::MatrixXd& src, const Eigen::MatrixXd& dst) {
int row_src = src.rows();
int row_dst = dst.rows();
Eigen::Vector3d vec_src;
Eigen::Vector3d vec_dst;
NEIGHBOR neigh;
float min = 100;
int index = 0;
float dist_temp = 0;
for (int ii = 0; ii < row_src; ii++) {
vec_src = src.block<1, 3>(ii, 0).transpose();
min = 100;
index = 0;
dist_temp = 0;
for (int jj = 0; jj < row_dst; jj++) {
vec_dst = dst.block<1, 3>(jj, 0).transpose();
dist_temp = dist(vec_src, vec_dst);
if (dist_temp < min) {
min = dist_temp;
index = jj;
}
}
// cout << min << " " << index << endl;
// neigh.distances[ii] = min;
// neigh.indices[ii] = index;
neigh.distances.push_back(min);
neigh.indices.push_back(index);
}
return neigh;
}
float dist(const Eigen::Vector3d& pta, const Eigen::Vector3d& ptb) {
return sqrt((pta[0] - ptb[0]) * (pta[0] - ptb[0]) + (pta[1] - ptb[1]) * (pta[1] - ptb[1]) + (pta[2] - ptb[2]) * (pta[2] - ptb[2]));
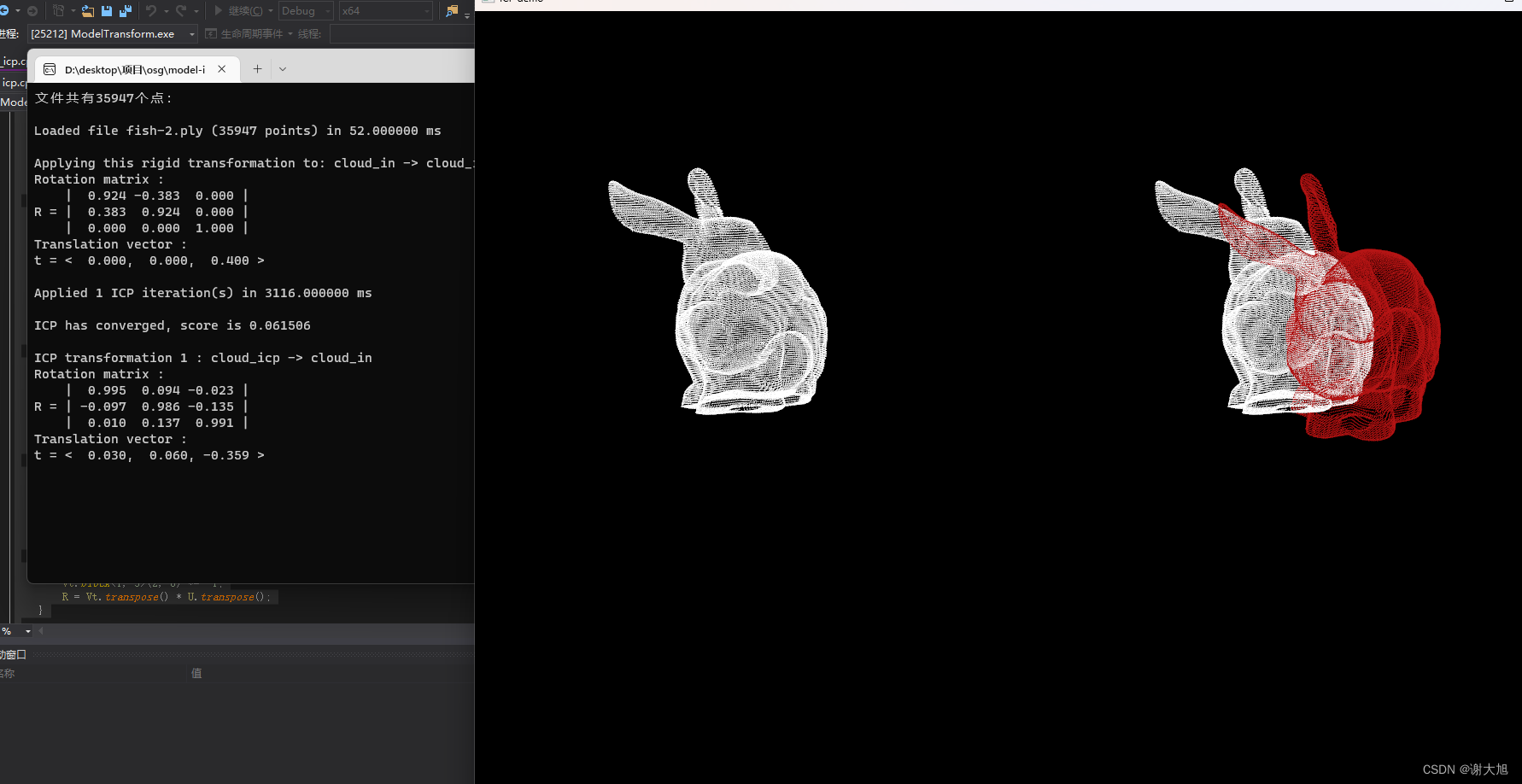
}截图:








![[附源码]java毕业设计社区健康服务平台管理系统lunwen](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/46631ce80b8a41a99f6f28cfd9e913e5.png)