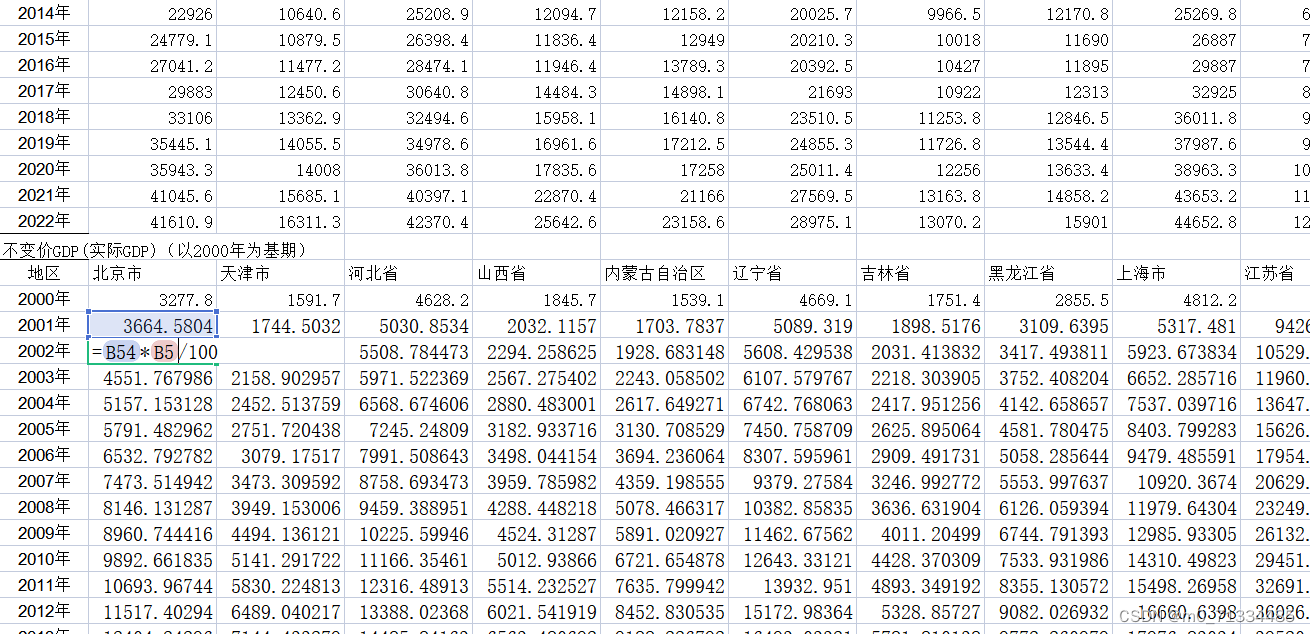
正弦信号的平均功率和峰值电压计算举例
一、问题
假设加载在纯电阻为R=1Ω,频率为50Hz和60Hz的正弦信号的平均功率分别为0.5W和2W,请求解这两个信号的峰值电压 U p 1 U_{p1} Up1和 U p 2 U_{p2} Up2。
二、解答:
根据欧姆定律可知:对于纯电阻R两端的瞬时电流为
I
=
U
R
=
U
p
s
i
n
(
2
π
f
t
)
R
(1)
I=\frac{U}{R}=\frac{U_{p}sin(2\pi ft)}{R}\tag{1}
I=RU=RUpsin(2πft)(1)
根据功率计算公式,则瞬时功率P为:
P
=
U
I
=
U
2
R
=
[
U
p
s
i
n
(
2
π
f
t
)
]
2
R
(2)
P=UI=\frac{U^2}{R}=\frac{ { [U_{p}sin(2\pi ft)} ]^2 } {R}\tag{2}
P=UI=RU2=R[Upsin(2πft)]2(2)
若求解平均功率 P ‾ \overline P P,根据式(2)可得:
P ‾ = 1 T ∫ 0 T [ U p sin ( 2 π f t ) ] 2 R d t (3) \overline P = \frac{1}{T}\int_0^T {\frac{{{{[{U_p}\sin (2\pi ft)]}^2}}}{R}dt} \tag{3} P=T1∫0TR[Upsin(2πft)]2dt(3)
进一步,得到
P
‾
=
1
T
∫
0
T
[
U
p
sin
(
2
π
f
t
)
]
2
R
d
t
=
U
p
2
T
R
∫
0
T
[
sin
(
2
π
f
t
)
]
2
d
t
(4)
\overline P = \frac{1}{T}\int_0^T {\frac{{{{[{U_p}\sin (2\pi ft)]}^2}}}{R}dt} \\= \frac{{U_p^2}}{{TR}}\int_0^T {{{[\sin (2\pi ft)]}^2}dt} \tag{4}
P=T1∫0TR[Upsin(2πft)]2dt=TRUp2∫0T[sin(2πft)]2dt(4)
又由于
∫
0
T
[
sin
(
2
π
f
t
)
]
2
d
t
\int_0^T {{{[\sin (2\pi ft)]}^2}dt}
∫0T[sin(2πft)]2dt可通过下面计算
T
2
−
sin
(
4
π
f
T
)
8
π
f
(5)
\dfrac{T}{2}-\dfrac{\sin\left(4\,\pi\,f\,T\right)}{8\,\pi\,f} \tag{5}
2T−8πfsin(4πfT)(5)
若取
T
T
T为正弦信号的一个周期,则
T
=
1
/
f
T=1/f
T=1/f,那么式(5)得到:
T
2
−
sin
(
4
π
)
8
π
f
=
T
2
(6)
\dfrac{T}{2}-\dfrac{\sin\left(4\,\pi\right)}{8\,\pi\,f}=\frac{T}{2} \tag{6}
2T−8πfsin(4π)=2T(6)
将式子(6)带入式子(4)得到:
P ‾ = 1 T ∫ 0 T [ U p sin ( 2 π f t ) ] 2 R d t = U p 2 T R ∫ 0 T [ sin ( 2 π f t ) ] 2 d t = U p 2 T R T 2 = U p 2 2 R (7) \overline P = \frac{1}{T}\int_0^T {\frac{{{{[{U_p}\sin (2\pi ft)]}^2}}}{R}dt} \\= \frac{{U_p^2}}{{TR}}\int_0^T {{{[\sin (2\pi ft)]}^2}dt} \\=\frac{{U_p^2}}{{TR}} \frac{T}{2} \\=\frac{{U_p^2}}{{2R}} \tag{7} P=T1∫0TR[Upsin(2πft)]2dt=TRUp2∫0T[sin(2πft)]2dt=TRUp22T=2RUp2(7)
根据题设若R=1欧姆,平均功率分别为0.5瓦特和2瓦特,则带入式子(7)得到:
0.5
W
=
U
p
1
2
2
⋅
1
Ω
(8a)
0.5W=\frac{U^2_{p1}}{2\cdot1Ω} \tag{8a}
0.5W=2⋅1ΩUp12(8a)
2
W
=
U
p
2
2
2
⋅
1
Ω
(8b)
2W=\frac{U^2_{p2}}{2 \cdot 1Ω} \tag{8b}
2W=2⋅1ΩUp22(8b)
根据式子(8a)和(8b)可得:
U
p
1
=
1
V
(9a)
U_{p1}=1V \tag{9a}
Up1=1V(9a)
U
p
2
=
2
V
(9b)
U_{p2}=2V \tag{9b}
Up2=2V(9b)
综上分析计算可得:加载在纯电阻为R=1Ω,频率为50Hz和60Hz的正弦信号的平均功率分别为0.5W和2W,请求解这两个信号的峰值电压 U p 1 U_{p1} Up1和$U_{p2}分别为1V和2V.
三、仿真
根据上面的分析,编写程序,进行仿真。
编写的程序如下:
clc
clear all
close all
Fs=1000;
dt=1/Fs;
t=0:dt:0.1;
U1=sin(2*pi*50*t);
U2=2*sin(2*pi*60*t);
figure(20230908)
subplot(2,2,1)
plot(t,U1,'b',"LineWidth",2)
xlabel('Time [s]')
ylabel('Voltage [V]')
title('Subplot 1: U1=sin(2*pi*50*t)')
subplot(2,2,2)
plot(t,U2,'g',"LineWidth",2)
xlabel('Time [s]')
ylabel('Voltage [V]')
title('Subplot 2: U2=2*sin(2*pi*60*t)')
subplot(2,2,[3,4])
plot(t,U1,'b',t,U2,'g',"LineWidth",2)
xlabel('Time [s]')
ylabel('Voltage [V]')
legend("U1","U2")
title('Subplot 3 and 4: Both')
运行结果:如图1所示。
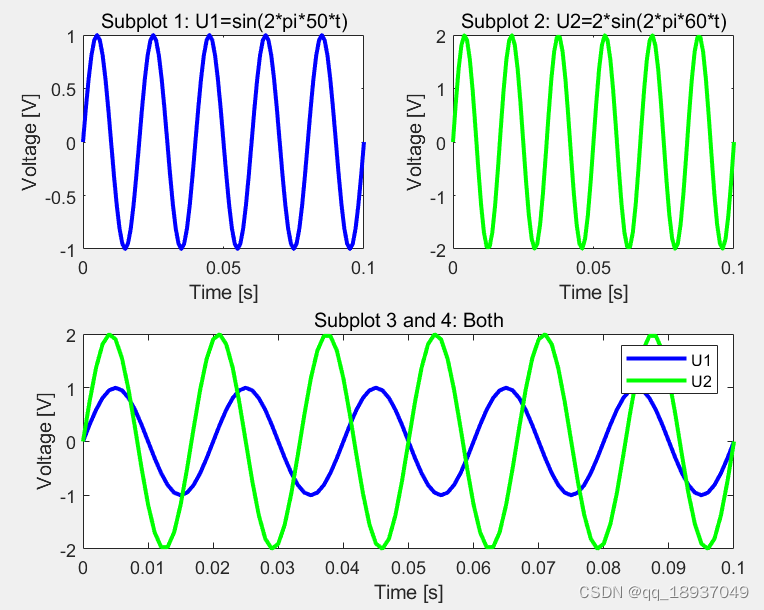
图1 仿真得到两个正弦信号




![[NLP]LLM---FineTune自己的Llama2模型](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a3137a07771c4a2598564de391049b6d.png)