说明
本文是《操作系统概念(第九版)》3.4节“进程间通信”的练习。
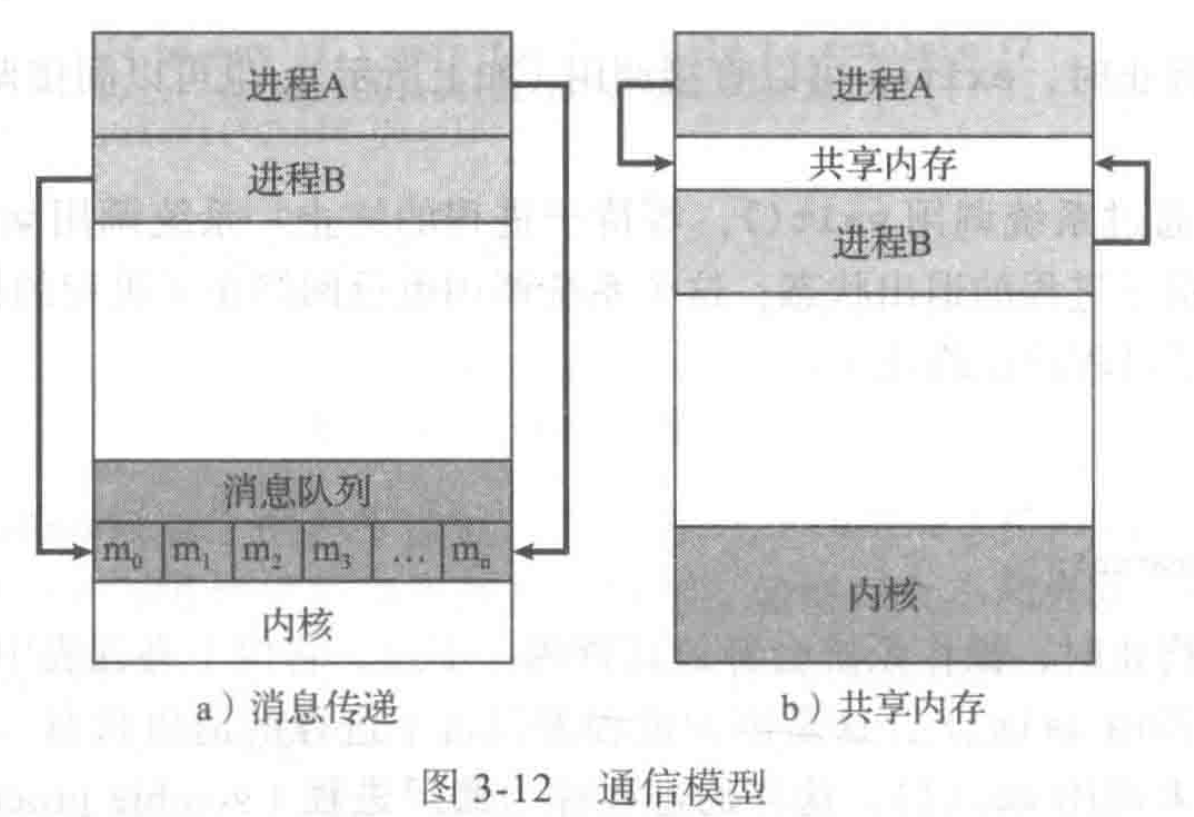
进程间通信主要由两种模型:
- 共享内存
- 消息传递
本文使用共享内存的方式实现进程间的通信
创建消息生产者
创建生产者的主要操作包括:
- 定义共享内存的大小、名称,以及通信消息的具体message内容
- 定义共享内存的对象和内存映射文件指针
- 用shm_open()方法,实例化共享内存对象(其参数包括共享内存名称和对象权限等)
- 用ftruncate()方法,配置共享内存对象的大小
- 用mmap()方法,创建内存映射文件,以便包含共享内存对象,它返回一个指向内存映射文件的指针,可用其访问共享内存对象
- 最后,对共享内存的写入,是通过调用sprintf()方法和向内存映射文件指针写入格式化字符串实现(每次写入之后,都要用所写字节的数量递增指针)
创建生产者的详细代码如下,可以新建一个producer.c文件,然后将代码拷贝进去:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
/* the size of shared memory object */
const int SIZE = 4096;
/* name of the shared memory object */
const char *name = "OS";
/* strings written to the shared memory */
const char *message_0 = "Hello";
const char *message_1 = "World!";
/* shared memory file descriptor */
int shm_fd;
/* pointer to shared memory object */
void *ptr;
/* create the shared memory object */
shm_fd = shm_open(name, O_CREAT | O_RDWR, 0666);
/* configure the size of the shared memory object */
ftruncate(shm_fd, SIZE);
/* memory map the shared memory object */
ptr = mmap(0, SIZE, PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, shm_fd, 0);
/* write to the shared memory object */
sprintf(ptr, "%s", message_0);
ptr += strlen(message_0);
sprintf(ptr, "%s", message_1);
ptr += strlen(message_1);
printf("Written done!");
return 0;
}
创建消息消费者
创建消费者的代码和创建消费者的代码有一些类似的地方,但是也有一些区别:
- 不需要创建一个共享内存对象,而是通过名称去打开一个共享内存对象
- 访问内存对象之后,调用了shm_unlink()方法移除了共享内存段
创建消费者的详细代码如下,可以新建一个consumer.c文件,然后将下列代码拷贝进去:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
int main(){
/* the size of shared memory object */
const int SIZE = 4096;
/* name of the shared memory object */
const char *name = "OS";
/* shared memory file descriptor */
int shm_fd;
/* pointer to shared memory object */
void *ptr;
/* open the shared memory object */
shm_fd = shm_open(name, O_RDONLY, 0666);
/* memory map the shared memory object */
ptr = mmap(0, SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, shm_fd, 0);
/* read from the shared memory object */
printf("%s", (char *)ptr);
/* remove the shared memroy object */
shm_unlink(name);
printf("\n");
printf("Read done!\n");
return 0;
}
编译和运行
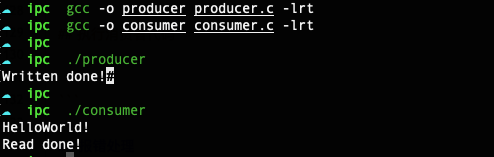
接下来是编译两个c文件,然后执行生产者代码,最后执行消费者代码
# 编译生产者代码
gcc -o producer producer.c -lrt
## 编译消费者代码
gcc -o consumer consumer.c -lrt
## 执行生产者代码
./producer
## 执行消费者代码
./consumer
最终的执行效果如下:
报错处理
致命错误:stlib.h:没有那个文件或目录
如果有下面的报错,那么是因为引用的文件名称错误,正确的应该是 #include <stdlib.h> (我看到的书上少了一个‘d’)
producer.c:6:10: 致命错误:sys/stath:没有那个文件或目录
#include <sys/stath>
^~~~~~~~~~~
编译中断。
错误:‘O_RDRW’ undeclared (first use in this function); did you mean ‘O_RDWR’?
如果是下面的报错,则应该将O_RDRW改成O_RDWR
producer.c:27:36: 错误:‘O_RDRW’ undeclared (first use in this function); did you mean ‘O_RDWR’?
shm_fd = shm_open(name, O_CREAT | O_RDRW, 0666);
^~~~~~
O_RDWR
producer.c:27:36: 附注:每个未声明的标识符在其出现的函数内只报告一次

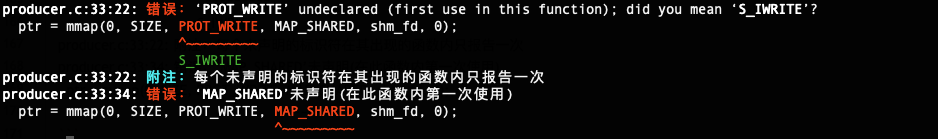
‘PROT_WRITE’ undeclared, ‘MAP_SHARED’未声明
以下报错,需要新增两个文件引用:
#include <sys/mman.h>#include <unistd.h>
producer.c:33:22: 错误:‘PROT_WRITE’ undeclared (first use in this function); did you mean ‘S_IWRITE’?
ptr = mmap(0, SIZE, PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, shm_fd, 0);
^~~~~~~~~~
S_IWRITE
producer.c:33:34: 错误:‘MAP_SHARED’未声明(在此函数内第一次使用)
ptr = mmap(0, SIZE, PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, shm_fd, 0);
^~~~~~~~~~
对‘shm_open’未定义的引用
解决办法: 在编译命令最后加 -lrt
/tmp/ccnkitBK.o:在函数‘main’中:
producer.c:(.text+0x39):对‘shm_open’未定义的引用
collect2: 错误:ld 返回 1

![[java安全]CommonsCollections2](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/d02adff34555ed8016e244d44a5888b7.png)