Qt Quick - Container使用总结
- 一、概述
- 二、使用容器
- 三、管理当前索引
- 四、容器实现
一、概述
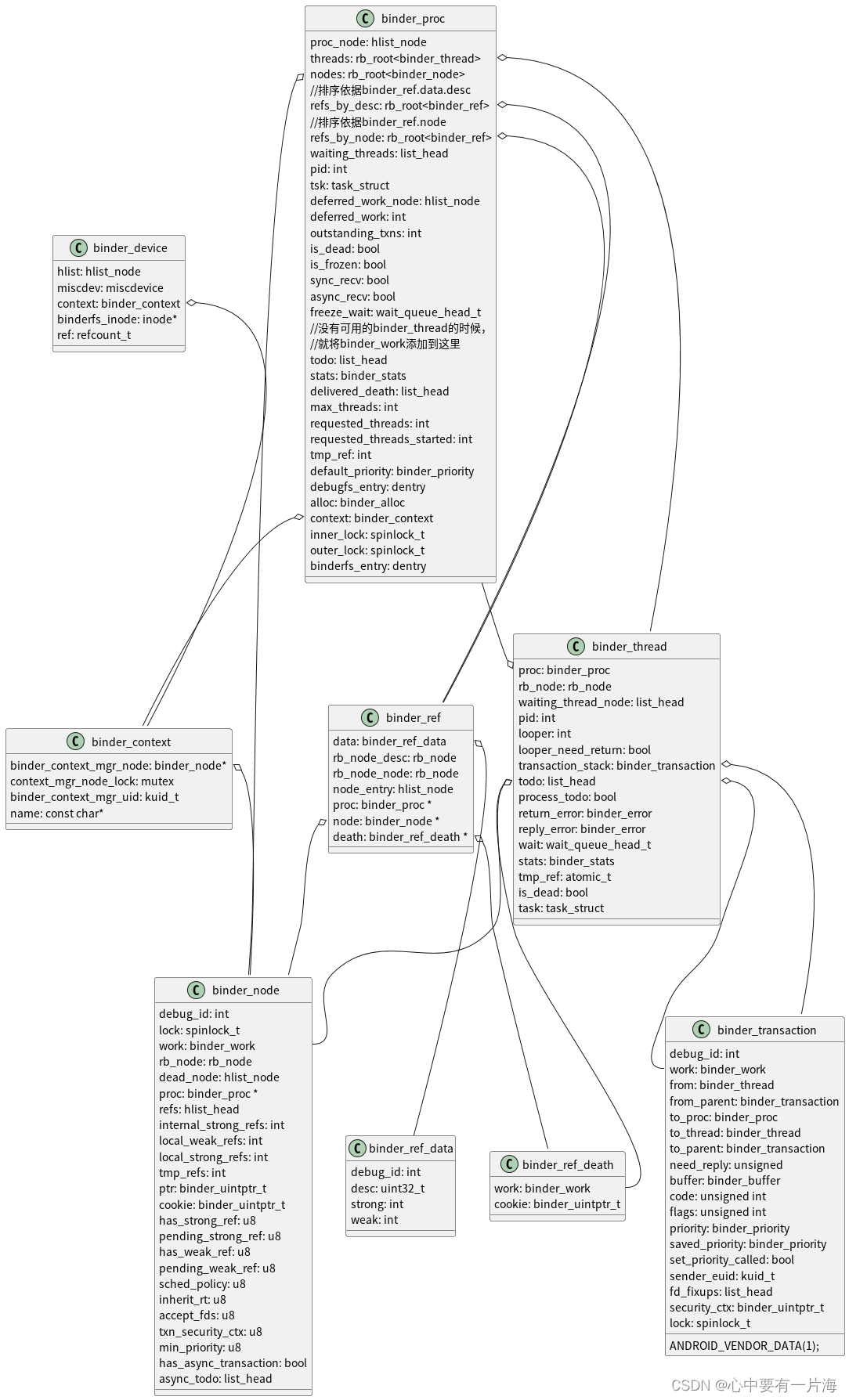
Container 提供容器通用功能的抽象基类。Container是类容器用户界面控件的基本类型,允许动态插入和删除Item。DialogButtonBox, MenuBar, SwipeView, 和 TabBar 都是继承至这个控件。
二、使用容器
通常情况下,Item被静态声明为Container的子Item,但也可以动态地添加、插入、移动和删除Item。可以使用itemAt()或contentChildren访问容器中的Item。
大多数容器都有“当前”项的概念。当前项是通过currentIndex属性指定的,可以通过只读的currentItem属性访问。
下面的例子演示了如何将Item动态插入TabBar,这是Container的具体实现之一。
Row {
TabBar {
id: tabBar
currentIndex: 0
width: parent.width - addButton.width
TabButton { text: "TabButton" }
}
Component {
id: tabButton
TabButton { text: "TabButton" }
}
Button {
id: addButton
text: "+"
flat: true
onClicked: {
tabBar.addItem(tabButton.createObject(tabBar))
console.log("added:", tabBar.itemAt(tabBar.count - 1))
}
}
}
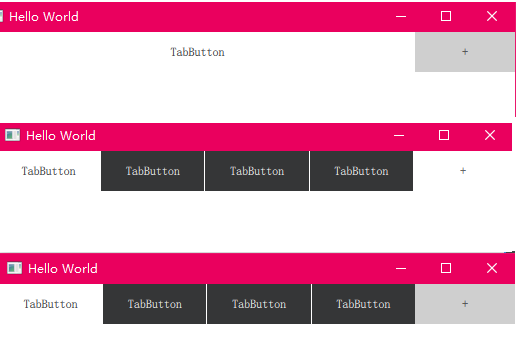
三、管理当前索引
当使用多个容器时,例如TabBar和SwipeView,它们的currentIndex属性可以相互绑定以保持它们同步。当用户与任何容器交互时,其当前索引的更改自动传播到另一个容器。
但是请注意,在JavaScript中为currentIndex赋值会删除相应的绑定。为了保留绑定,使用以下方法更改当前索引:
- incrementCurrentIndex ()
- decrementCurrentIndex ()
- setCurrentIndex ()
TabBar {
id: tabBar
currentIndex: swipeView.currentIndex
}
SwipeView {
id: swipeView
currentIndex: tabBar.currentIndex
}
Button {
text: qsTr("Home")
onClicked: swipeView.setCurrentIndex(0)
enabled: swipeView.currentIndex != 0
}
Button {
text: qsTr("Previous")
onClicked: swipeView.decrementCurrentIndex()
enabled: swipeView.currentIndex > 0
}
Button {
text: qsTr("Next")
onClicked: swipeView.incrementCurrentIndex()
enabled: swipeView.currentIndex < swipeView.count - 1
}
四、容器实现
Container不提供任何默认的可视化。它用于实现SwipeView和TabBar等容器。在实现自定义容器时,API中最重要的部分是contentModel,它提供了包含的项目,可以用作项目视图和重复器的委托模型。
Container {
id: container
contentItem: ListView {
model: container.contentModel
snapMode: ListView.SnapOneItem
orientation: ListView.Horizontal
}
Text {
text: "Page 1"
width: container.width
height: container.height
}
Text {
text: "Page 2"
width: container.width
height: container.height
}
}
请注意,page 项的大小是如何手动设置的。这是因为这个例子使用了一个普通的容器,它没有对视觉布局做任何假设。在具体的容器实现中,通常没有必要指定Item的大小,例如SwipeView和TabBar。



![[强化学习]学习路线和关键词拾零](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d38930816c1045968b03d2844d6bad8c.png)