一. SystemServer进程启动概括
Android系统中,第一个启动的是init进程,通过解析init.rc文件启动对应的service。Zygote就是由init启动起来的。Zygote作为应用的孵化器,所有的应用程序都是由他创建而来的。
Zygote是C/S架构的,当他被fork出来之后会创建Java虚拟机,注册JNI环境 注册完成之后调用ZygoteInit.Main进入Java层。在ZygoteInit.Main中会创建ZygoteServerSocket,forkSystemServer以及循环等待客户端的请求,当请求到来之后会调用processOneCommandfork子进程和设置子进程的信息(创建ProcessState 初始化binder startThreadPoll),之后根据客户端请求的startClass 通过反射找到Main函数,并执行,这样Zygote整体的流程 和 处理请求就结束了。现在我们就来看看SystemServer。
Android系统中各个进程的先后顺序为:
init进程 –-> Zygote进程 –> SystemServer进程 –>应用进程
其中Zygote进程由init进程启动,SystemServer进程和应用进程都是由Zygote进程启动。
SystemServer进程主要是用于创建系统服务的,例如AMS、WMS、PMS。
二. zygote 进程启动SystemServer进程
在zygote 进程启动的时候, AndroidRuntime.start() 执行到最后通过反射调用到ZygoteInit.main()
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,
ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
long capabilities = posixCapabilitiesAsBits(
OsConstants.CAP_IPC_LOCK,
OsConstants.CAP_KILL,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_ADMIN,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BROADCAST,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_RAW,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_MODULE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_NICE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_PTRACE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TIME,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG,
OsConstants.CAP_WAKE_ALARM,
OsConstants.CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND
);
/* Containers run without some capabilities, so drop any caps that are not available. */
StructCapUserHeader header = new StructCapUserHeader(
OsConstants._LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, 0);
StructCapUserData[] data;
try {
data = Os.capget(header);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to capget()", ex);
}
capabilities &= ((long) data[0].effective) | (((long) data[1].effective) << 32);
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String[] args = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,"
+ "1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010,3011",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"--target-sdk-version=" + VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT,
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteArguments parsedArgs;
int pid;
try {
ZygoteCommandBuffer commandBuffer = new ZygoteCommandBuffer(args);
try {
parsedArgs = ZygoteArguments.getInstance(commandBuffer);
} catch (EOFException e) {
throw new AssertionError("Unexpected argument error for forking system server", e);
}
commandBuffer.close();
Zygote.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
Zygote.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
if (Zygote.nativeSupportsMemoryTagging()) {
/* The system server has ASYNC MTE by default, in order to allow
* system services to specify their own MTE level later, as you
* can't re-enable MTE once it's disabled. */
String mode = SystemProperties.get("arm64.memtag.process.system_server", "async");
if (mode.equals("async")) {
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.MEMORY_TAG_LEVEL_ASYNC;
} else if (mode.equals("sync")) {
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.MEMORY_TAG_LEVEL_SYNC;
} else if (!mode.equals("off")) {
/* When we have an invalid memory tag level, keep the current level. */
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.nativeCurrentTaggingLevel();
Slog.e(TAG, "Unknown memory tag level for the system server: \"" + mode + "\"");
}
} else if (Zygote.nativeSupportsTaggedPointers()) {
/* Enable pointer tagging in the system server. Hardware support for this is present
* in all ARMv8 CPUs. */
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.MEMORY_TAG_LEVEL_TBI;
}
/* Enable gwp-asan on the system server with a small probability. This is the same
* policy as applied to native processes and system apps. */
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.GWP_ASAN_LEVEL_LOTTERY;
if (shouldProfileSystemServer()) {
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER;
}
/* Request to fork the system server process */
// 1. 通过 zygote fork 一个systemserver 进程
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid,
parsedArgs.mGids,
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.mPermittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.mEffectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
// fork 出来的systemserver 是zygote 子进程,
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
// systemserver 进程要关闭这个 socket
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
// 2. 返回一个runnable,执行 handleSystemServerProcess
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return null;
}
1. 通过 zygote fork 出systemserver 进程
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/Zygote.java
*/
static int forkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
int[][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities) {
ZygoteHooks.preFork();
// 通过native 层去fork 一个进程
int pid = nativeForkSystemServer(
uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits,
permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities);
// Set the Java Language thread priority to the default value for new apps.
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon();
return pid;
}
/frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
static jint com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkSystemServer(
JNIEnv* env, jclass, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray gids,
jint runtime_flags, jobjectArray rlimits, jlong permitted_capabilities,
jlong effective_capabilities) {
std::vector<int> fds_to_close(MakeUsapPipeReadFDVector()),
fds_to_ignore(fds_to_close);
fds_to_close.push_back(gUsapPoolSocketFD);
if (gUsapPoolEventFD != -1) {
fds_to_close.push_back(gUsapPoolEventFD);
fds_to_ignore.push_back(gUsapPoolEventFD);
}
if (gSystemServerSocketFd != -1) {
fds_to_close.push_back(gSystemServerSocketFd);
fds_to_ignore.push_back(gSystemServerSocketFd);
}
// 1-1)fork systemserver 进程 zygote::ForkCommon
pid_t pid = zygote::ForkCommon(env, true,
fds_to_close,
fds_to_ignore,
true);
if (pid == 0) {
// System server prcoess does not need data isolation so no need to
// know pkg_data_info_list.
// 1-2)当前子进程pid 为0,执行 SpecializeCommon
SpecializeCommon(env, uid, gid, gids, runtime_flags, rlimits, permitted_capabilities,
effective_capabilities, MOUNT_EXTERNAL_DEFAULT, nullptr, nullptr, true,
false, nullptr, nullptr, /* is_top_app= */ false,
/* pkg_data_info_list */ nullptr,
/* allowlisted_data_info_list */ nullptr, false, false);
// zygote 设置全局的系统进程pid: gSystemServerPid。会打印log,属于是父进程zygote
} else if (pid > 0) {
// The zygote process checks whether the child process has died or not.
ALOGI("System server process %d has been created", pid);
gSystemServerPid = pid;
1-1)fork systemserver 进程 zygote::ForkCommon
pid_t zygote::ForkCommon(JNIEnv* env, bool is_system_server,
const std::vector<int>& fds_to_close,
const std::vector<int>& fds_to_ignore,
bool is_priority_fork,
bool purge) {
SetSignalHandlers();
// Curry a failure function.
auto fail_fn = std::bind(zygote::ZygoteFailure, env,
is_system_server ? "system_server" : "zygote",
nullptr, _1);
。。。。。
// fork 进程
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
if (is_priority_fork) {
// 设置优先级为最大
setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, 0, PROCESS_PRIORITY_MAX);
} else {
setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, 0, PROCESS_PRIORITY_MIN);
}
// The child process.
PreApplicationInit();
// Clean up any descriptors which must be closed immediately
DetachDescriptors(env, fds_to_close, fail_fn);
// Invalidate the entries in the USAP table.
ClearUsapTable();
// Re-open all remaining open file descriptors so that they aren't shared
// with the zygote across a fork.
gOpenFdTable->ReopenOrDetach(fail_fn);
// Turn fdsan back on.
android_fdsan_set_error_level(fdsan_error_level);
// Reset the fd to the unsolicited zygote socket
gSystemServerSocketFd = -1;
} else {
ALOGD("Forked child process %d", pid);
}
// We blocked SIGCHLD prior to a fork, we unblock it here.
UnblockSignal(SIGCHLD, fail_fn);
return pid;
}
fork()创建新进程,采用copy on write方式,这是linux创建进程的标准方法,会有两次return,对于pid==0为子进程的返回,对于pid>0为父进程的返回。 到此system_server进程已完成了创建的所有工作,接下来开始了system_server进程的真正工作。
1-2)systemserver 子进程pid 为0,执行 SpecializeCommon
// Utility routine to specialize a zygote child process.
static void SpecializeCommon(JNIEnv* env, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray gids, jint runtime_flags,
jobjectArray rlimits, jlong permitted_capabilities,
jlong effective_capabilities, jint mount_external,
jstring managed_se_info, jstring managed_nice_name,
bool is_system_server, bool is_child_zygote,
jstring managed_instruction_set, jstring managed_app_data_dir,
bool is_top_app, jobjectArray pkg_data_info_list,
jobjectArray allowlisted_data_info_list, bool mount_data_dirs,
bool mount_storage_dirs) {
const char* process_name = is_system_server ? "system_server" : "zygote";
auto fail_fn = std::bind(ZygoteFailure, env, process_name, managed_nice_name, _1);
auto extract_fn = std::bind(ExtractJString, env, process_name, managed_nice_name, _1);
auto se_info = extract_fn(managed_se_info);
auto nice_name = extract_fn(managed_nice_name);
auto instruction_set = extract_fn(managed_instruction_set);
auto app_data_dir = extract_fn(managed_app_data_dir);
// Keep capabilities across UID change, unless we're staying root.
if (uid != 0) {
EnableKeepCapabilities(fail_fn);
}
SetInheritable(permitted_capabilities, fail_fn);
DropCapabilitiesBoundingSet(fail_fn);
bool need_pre_initialize_native_bridge = !is_system_server && instruction_set.has_value() &&
android::NativeBridgeAvailable() &&
// Native bridge may be already initialized if this
// is an app forked from app-zygote.
!android::NativeBridgeInitialized() &&
android::NeedsNativeBridge(instruction_set.value().c_str());
MountEmulatedStorage(uid, mount_external, need_pre_initialize_native_bridge, fail_fn);
// Make sure app is running in its own mount namespace before isolating its data directories.
ensureInAppMountNamespace(fail_fn);
2. fork 出来的systemserver 是zygote 子进程,执行 handleSystemServerProcess。
往下执行就是在 system_server 进程了
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
private static Runnable handleSystemServerProcess(ZygoteArguments parsedArgs) {
// set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions.
Os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
if (parsedArgs.mNiceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.mNiceName);
}
final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
performSystemServerDexOpt(systemServerClasspath);
// Capturing profiles is only supported for debug or eng builds since selinux normally
if (parsedArgs.mInvokeWith != null) {
。。。。
}
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.mInvokeWith,
parsedArgs.mNiceName, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(), null, args);
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected return from WrapperInit.execApplication");
} else {
// 获取到 ClassLoader ,mInvokeWith 是为null的
ClassLoader cl = getOrCreateSystemServerClassLoader();
if (cl != null) {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/
// 执行 zygoteInit 方法,mRemainingArgs 有 "com.android.server.SystemServer"
return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.mDisabledCompatChanges,
parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs, cl);
}
/* should never reach here */
}
*/
public static Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, long[] disabledCompatChanges,
String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
// 去调用 SystemServer 的main 方法
return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, disabledCompatChanges, argv,
classLoader);
}
去调用 SystemServer 的main 方法
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, long[] disabledCompatChanges,
String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setDisabledCompatChanges(disabledCompatChanges);
final Arguments args = new Arguments(argv);
// The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
通过反射获取到main 方法
findStaticMain 方法,通过反射机制获取到main 方法
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
// 获取到main 方法
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
static class MethodAndArgsCaller implements Runnable {
/** method to call */
private final Method mMethod;
/** argument array */
private final String[] mArgs;
public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
mMethod = method;
mArgs = args;
}
public void run() {
try {
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
调用到 com.android.server.SystemServer 的main 函数
/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
实例化SystemServer 对象,然后执行run 方法
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
执行run 方法
private void run() {
TimingsTraceAndSlog t = new TimingsTraceAndSlog();
try {
t.traceBegin("InitBeforeStartServices");
// Record the process start information in sys props.
SystemProperties.set(SYSPROP_START_COUNT, String.valueOf(mStartCount));
SystemProperties.set(SYSPROP_START_ELAPSED, String.valueOf(mRuntimeStartElapsedTime));
SystemProperties.set(SYSPROP_START_UPTIME, String.valueOf(mRuntimeStartUptime));
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.SYSTEM_SERVER_START,
mStartCount, mRuntimeStartUptime, mRuntimeStartElapsedTime);
//
// Default the timezone property to GMT if not set.
//
String timezoneProperty = SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.timezone");
if (!isValidTimeZoneId(timezoneProperty)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "persist.sys.timezone is not valid (" + timezoneProperty
+ "); setting to GMT.");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.timezone", "GMT");
}
// If the system has "persist.sys.language" and friends set, replace them with
// "persist.sys.locale". Note that the default locale at this point is calculated
// using the "-Duser.locale" command line flag. That flag is usually populated by
// AndroidRuntime using the same set of system properties, but only the system_server
// and system apps are allowed to set them.
//
// NOTE: Most changes made here will need an equivalent change to
// core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {
final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
}
// The system server should never make non-oneway calls
Binder.setWarnOnBlocking(true);
// The system server should always load safe labels
PackageItemInfo.forceSafeLabels();
// Default to FULL within the system server.
SQLiteGlobal.sDefaultSyncMode = SQLiteGlobal.SYNC_MODE_FULL;
// Deactivate SQLiteCompatibilityWalFlags until settings provider is initialized
SQLiteCompatibilityWalFlags.init(null);
// Here we go!
// 会打印下列的log
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
final long uptimeMillis = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN, uptimeMillis);
if (!mRuntimeRestart) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
FrameworkStatsLog
.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__SYSTEM_SERVER_INIT_START,
uptimeMillis);
}
// In case the runtime switched since last boot (such as when
// the old runtime was removed in an OTA), set the system
// property so that it is in sync. We can't do this in
// libnativehelper's JniInvocation::Init code where we already
// had to fallback to a different runtime because it is
// running as root and we need to be the system user to set
// the property. http://b/11463182
//
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
// we've defined it before booting further.
Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();
// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
// explicitly specifying a user.
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
// Within the system server, any incoming Bundles should be defused
// to avoid throwing BadParcelableException.
BaseBundle.setShouldDefuse(true);
// Within the system server, when parceling exceptions, include the stack trace
Parcel.setStackTraceParceling(true);
// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
// Increase the number of binder threads in system_server
BinderInternal.setMaxThreads(sMaxBinderThreads);
// Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
// 设置系统进程的线程为前台优先级
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
// 主线程looper就在当前线程运行
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
Looper.getMainLooper().setSlowLogThresholdMs(
SLOW_DISPATCH_THRESHOLD_MS, SLOW_DELIVERY_THRESHOLD_MS);
SystemServiceRegistry.sEnableServiceNotFoundWtf = true;
// Initialize native services.
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
// Allow heap / perf profiling.
initZygoteChildHeapProfiling();
// Debug builds - spawn a thread to monitor for fd leaks.
if (Build.IS_DEBUGGABLE) {
spawnFdLeakCheckThread();
}
// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
// This call may not return.
performPendingShutdown();
// 2-1)初始化 system context.
createSystemContext();
// 初始化一些系统主要的类
ActivityThread.initializeMainlineModules();
// Sets the dumper service
ServiceManager.addService("system_server_dumper", mDumper);
mDumper.addDumpable(this);
// 创建 SystemServiceManager 对象
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setStartInfo(mRuntimeRestart,
mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime);
mDumper.addDumpable(mSystemServiceManager);
// 将 SystemServiceManager 保存到map 中
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
SystemServerInitThreadPool tp = SystemServerInitThreadPool.start();
mDumper.addDumpable(tp);
// Load preinstalled system fonts for system server, so that WindowManagerService, etc
// can start using Typeface. Note that fonts are required not only for text rendering,
// but also for some text operations (e.g. TextUtils.makeSafeForPresentation()).
if (Typeface.ENABLE_LAZY_TYPEFACE_INITIALIZATION) {
Typeface.loadPreinstalledSystemFontMap();
}
。。。。
// Setup the default WTF handler
RuntimeInit.setDefaultApplicationWtfHandler(SystemServer::handleEarlySystemWtf);
// 启动系统服务 services.
try {
t.traceBegin("StartServices");
startBootstrapServices(t);
startCoreServices(t);
startOtherServices(t);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
t.traceEnd(); // StartServices
}
StrictMode.initVmDefaults(null);
。。
// 执行 loop函数, 循环
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
// 2-1)初始化 system context.
createSystemContext();
// 创建 SystemServiceManager 对象
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setStartInfo(mRuntimeRestart,
mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime);
mDumper.addDumpable(mSystemServiceManager);
// 将 SystemServiceManager 保存到map 中
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
SystemServerInitThreadPool tp = SystemServerInitThreadPool.start();
mDumper.addDumpable(tp);
// Load preinstalled system fonts for system server, so that WindowManagerService, etc
// can start using Typeface. Note that fonts are required not only for text rendering,
// but also for some text operations (e.g. TextUtils.makeSafeForPresentation()).
if (Typeface.ENABLE_LAZY_TYPEFACE_INITIALIZATION) {
Typeface.loadPreinstalledSystemFontMap();
}
。。。。
// Setup the default WTF handler
RuntimeInit.setDefaultApplicationWtfHandler(SystemServer::handleEarlySystemWtf);
// 启动系统服务 services.
try {
t.traceBegin("StartServices");
2-2)启动系统服务:startBootstrapServices
startBootstrapServices(t);
2-3)启动系统服务:startCoreServices
startCoreServices(t);
2-4)启动系统服务:startOtherServices
startOtherServices(t);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
t.traceEnd(); // StartServices
}
StrictMode.initVmDefaults(null);
。。
// 执行 loop函数, 循环
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
2-1)初始化 systemcontext
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static ActivityThread systemMain() {
ThreadedRenderer.initForSystemProcess();
/// 创建了 ActivityThread 对象
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
// 执行 attach 方法
thread.attach(true, 0);
return thread;
}
ActivityThread 继承了 ClientTransactionHandler,执行handler 与应用进程交互
public final class ActivityThread extends ClientTransactionHandler
implements ActivityThreadInternal {
// 执行 attach 方法
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private void attach(boolean system, long startSeq) {
// 设置当前的 ActivityThread 为 this
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mConfigurationController = new ConfigurationController(this);
/// system 为 true
mSystemThread = system;
if (!system) {
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("<pre-initialized>",
UserHandle.myUserId());
。。。。。。不走如下逻辑
} else {
// Don't set application object here -- if the system crashes,
// we can't display an alert, we just want to die die die.
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("system_process",
UserHandle.myUserId());
try {
//创建Instrumentation 用来管理应用的生命周期
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
mInstrumentation.basicInit(this);
// 创建上下文
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(
this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo);
// `反射创建android.app.Application 并执行onCreate 这里创建的是framewok-res.apk`
mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null);
mInitialApplication.onCreate();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e);
}
}
ViewRootImpl.ConfigChangedCallback configChangedCallback = (Configuration globalConfig) -> {
2-2)启动系统服务:startBootstrapServices
/frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
private void startBootstrapServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
t.traceBegin("startBootstrapServices");
// Start the watchdog as early as possible so we can crash the system server
// if we deadlock during early boot
t.traceBegin("StartWatchdog");
// 获取 Watchdog 对象,执行 thread 的start 方法开启线程,执行run 方法
final Watchdog watchdog = Watchdog.getInstance();
watchdog.start();
t.traceEnd();
Slog.i(TAG, "Reading configuration...");
final String TAG_SYSTEM_CONFIG = "ReadingSystemConfig";
t.traceBegin(TAG_SYSTEM_CONFIG);
SystemServerInitThreadPool.submit(SystemConfig::getInstance, TAG_SYSTEM_CONFIG);
t.traceEnd();
// Platform compat service is used by ActivityManagerService, PackageManagerService, and
// possibly others in the future. b/135010838.
t.traceBegin("PlatformCompat");
PlatformCompat platformCompat = new PlatformCompat(mSystemContext);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.PLATFORM_COMPAT_SERVICE, platformCompat);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.PLATFORM_COMPAT_NATIVE_SERVICE,
new PlatformCompatNative(platformCompat));
AppCompatCallbacks.install(new long[0]);
t.traceEnd();
// FileIntegrityService responds to requests from apps and the system. It needs to run after
// the source (i.e. keystore) is ready, and before the apps (or the first customer in the
// system) run.
// StartFileIntegrityService服务
t.traceBegin("StartFileIntegrityService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(FileIntegrityService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Wait for installd to finish starting up so that it has a chance to
// create critical directories such as /data/user with the appropriate
// permissions. We need this to complete before we initialize other services.
t.traceBegin("StartInstaller");
// Installer服务
Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class);
t.traceEnd();
// In some cases after launching an app we need to access device identifiers,
// therefore register the device identifier policy before the activity manager.
t.traceBegin("DeviceIdentifiersPolicyService");
// DeviceIdentifiersPolicyService服务
mSystemServiceManager.startService(DeviceIdentifiersPolicyService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Uri Grants Manager.
t.traceBegin("UriGrantsManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UriGrantsManagerService.Lifecycle.class);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartPowerStatsService");
// Tracks rail data to be used for power statistics.
// PowerStatsService服务
mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerStatsService.class);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartIStatsService");
startIStatsService();
t.traceEnd();
// Start MemtrackProxyService before ActivityManager, so that early calls
// to Memtrack::getMemory() don't fail.
t.traceBegin("MemtrackProxyService");
startMemtrackProxyService();
t.traceEnd();
// Activity manager runs the show.
t.traceBegin("StartActivityManager");
// TODO: Might need to move after migration to WM.
// ActivityTaskManagerService 服务
ActivityTaskManagerService atm = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityTaskManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
// ActivityManagerService 服务
mActivityManagerService = ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.startService(
mSystemServiceManager, atm);
// 设置管理系统服务的管理者
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
mWindowManagerGlobalLock = atm.getGlobalLock();
t.traceEnd();
// Data loader manager service needs to be started before package manager
t.traceBegin("StartDataLoaderManagerService");
mDataLoaderManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
DataLoaderManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Incremental service needs to be started before package manager
t.traceBegin("StartIncrementalService");
mIncrementalServiceHandle = startIncrementalService();
t.traceEnd();
// Power manager needs to be started early because other services need it.
// Native daemons may be watching for it to be registered so it must be ready
// to handle incoming binder calls immediately (including being able to verify
// the permissions for those calls).
t.traceBegin("StartPowerManager");
// PowerManagerService 服务
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartThermalManager");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(ThermalManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartHintManager");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(HintManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Now that the power manager has been started, let the activity manager
// initialize power management features.
t.traceBegin("InitPowerManagement");
mActivityManagerService.initPowerManagement();
t.traceEnd();
// Bring up recovery system in case a rescue party needs a reboot
t.traceBegin("StartRecoverySystemService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(RecoverySystemService.Lifecycle.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Now that we have the bare essentials of the OS up and running, take
// note that we just booted, which might send out a rescue party if
// we're stuck in a runtime restart loop.
RescueParty.registerHealthObserver(mSystemContext);
PackageWatchdog.getInstance(mSystemContext).noteBoot();
// Manages LEDs and display backlight so we need it to bring up the display.
t.traceBegin("StartLightsService");
// LightsService 服务
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LightsService.class);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartSidekickService");
// Package manager isn't started yet; need to use SysProp not hardware feature
if (SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.enable_sidekick_graphics", false)) {
mSystemServiceManager.startService(WEAR_SIDEKICK_SERVICE_CLASS);
}
t.traceEnd();
// Display manager is needed to provide display metrics before package manager
// starts up.
t.traceBegin("StartDisplayManager");
// DisplayManagerService 服务
mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// We need the default display before we can initialize the package manager.
t.traceBegin("WaitForDisplay");
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
t.traceEnd();
// Only run "core" apps if we're encrypting the device.
String cryptState = VoldProperties.decrypt().orElse("");
if (ENCRYPTING_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Detected encryption in progress - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
} else if (ENCRYPTED_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Device encrypted - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
}
// Start the package manager.
if (!mRuntimeRestart) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
FrameworkStatsLog
.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__PACKAGE_MANAGER_INIT_START,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
t.traceBegin("StartDomainVerificationService");
DomainVerificationService domainVerificationService = new DomainVerificationService(
mSystemContext, SystemConfig.getInstance(), platformCompat);
mSystemServiceManager.startService(domainVerificationService);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartPackageManagerService");
// packagemanagermain 线程特Watchdog 殊处理
try {
Watchdog.getInstance().pauseWatchingCurrentThread("packagemanagermain");
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,
domainVerificationService, mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF,
mOnlyCore);
} finally {
Watchdog.getInstance().resumeWatchingCurrentThread("packagemanagermain");
}
// Now that the package manager has started, register the dex load reporter to capture any
// dex files loaded by system server.
// These dex files will be optimized by the BackgroundDexOptService.
SystemServerDexLoadReporter.configureSystemServerDexReporter(mPackageManagerService);
mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();
mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager();
t.traceEnd();
if (!mRuntimeRestart && !isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
FrameworkStatsLog
.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__PACKAGE_MANAGER_INIT_READY,
SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
// Manages A/B OTA dexopting. This is a bootstrap service as we need it to rename
// A/B artifacts after boot, before anything else might touch/need them.
// Note: this isn't needed during decryption (we don't have /data anyways).
if (!mOnlyCore) {
boolean disableOtaDexopt = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_otadexopt",
false);
if (!disableOtaDexopt) {
t.traceBegin("StartOtaDexOptService");
try {
Watchdog.getInstance().pauseWatchingCurrentThread("moveab");
OtaDexoptService.main(mSystemContext, mPackageManagerService);
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("starting OtaDexOptService", e);
} finally {
Watchdog.getInstance().resumeWatchingCurrentThread("moveab");
t.traceEnd();
}
}
}
t.traceBegin("StartUserManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UserManagerService.LifeCycle.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Initialize attribute cache used to cache resources from packages.
t.traceBegin("InitAttributerCache");
AttributeCache.init(mSystemContext);
t.traceEnd();
// Set up the Application instance for the system process and get started.
t.traceBegin("SetSystemProcess");
// ActivityManagerService 调用 setSystemProcess 方法
mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
t.traceEnd();
// The package receiver depends on the activity service in order to get registered.
platformCompat.registerPackageReceiver(mSystemContext);
// Complete the watchdog setup with an ActivityManager instance and listen for reboots
// Do this only after the ActivityManagerService is properly started as a system process
t.traceBegin("InitWatchdog");
// watchdog 初始化
watchdog.init(mSystemContext, mActivityManagerService);
t.traceEnd();
// DisplayManagerService needs to setup android.display scheduling related policies
// since setSystemProcess() would have overridden policies due to setProcessGroup
mDisplayManagerService.setupSchedulerPolicies();
// Manages Overlay packages
t.traceBegin("StartOverlayManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(new OverlayManagerService(mSystemContext));
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartSensorPrivacyService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(new SensorPrivacyService(mSystemContext));
t.traceEnd();
if (SystemProperties.getInt("persist.sys.displayinset.top", 0) > 0) {
// DisplayManager needs the overlay immediately.
mActivityManagerService.updateSystemUiContext();
LocalServices.getService(DisplayManagerInternal.class).onOverlayChanged();
}
// The sensor service needs access to package manager service, app ops
// service, and permissions service, therefore we start it after them.
t.traceBegin("StartSensorService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(SensorService.class);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceEnd(); // startBootstrapServices
}
主要创建了主要的服务:ActivityTaskManagerService, ActivityManagerService、PowerManagerService、DisplayManagerService、启动了 WatchDog。
服务均是通过 tartService 保存到 SystemserviceManager 中
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/SystemServiceManager.java
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
try {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " + name);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "StartService " + name);
// Create the service.
if (!SystemService.class.isAssignableFrom(serviceClass)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create " + name
+ ": service must extend " + SystemService.class.getName());
}
final T service;
try {
Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
// 通过反射创建 service 对象
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service could not be instantiated", ex);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service constructor threw an exception", ex);
}
startService(service);
return service;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Register it.
// 将service 保存到 mServices
mServices.add(service);
// Start it.
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
// 回调 service的 onStart 方法
service.onStart();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onStart");
}
2-3)启动系统服务:startCoreServices
private void startCoreServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
t.traceBegin("startCoreServices");
// Service for system config
t.traceBegin("StartSystemConfigService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(SystemConfigService.class);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartBatteryService");
// Tracks the battery level. Requires LightService.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BatteryService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Tracks application usage stats.
t.traceBegin("StartUsageService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UsageStatsService.class);
mActivityManagerService.setUsageStatsManager(
LocalServices.getService(UsageStatsManagerInternal.class));
t.traceEnd();
// Tracks whether the updatable WebView is in a ready state and watches for update installs.
if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_WEBVIEW)) {
t.traceBegin("StartWebViewUpdateService");
mWebViewUpdateService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(WebViewUpdateService.class);
t.traceEnd();
}
// Tracks and caches the device state.
t.traceBegin("StartCachedDeviceStateService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CachedDeviceStateService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Tracks cpu time spent in binder calls
t.traceBegin("StartBinderCallsStatsService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BinderCallsStatsService.LifeCycle.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Tracks time spent in handling messages in handlers.
t.traceBegin("StartLooperStatsService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LooperStatsService.Lifecycle.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Manages apk rollbacks.
t.traceBegin("StartRollbackManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(ROLLBACK_MANAGER_SERVICE_CLASS);
t.traceEnd();
// Tracks native tombstones.
t.traceBegin("StartNativeTombstoneManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(NativeTombstoneManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Service to capture bugreports.
t.traceBegin("StartBugreportManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BugreportManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Serivce for GPU and GPU driver.
t.traceBegin("GpuService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(GpuService.class);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceEnd(); // startCoreServices
}
2-4)启动系统服务:startOtherServices
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
t.traceBegin("startOtherServices");
final Context context = mSystemContext;
DynamicSystemService dynamicSystem = null;
。。。。。
try {
final String SECONDARY_ZYGOTE_PRELOAD = "SecondaryZygotePreload";
。。。。
// 启动telecom service
t.traceBegin("StartTelecomLoaderService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(TelecomLoaderService.class);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartTelephonyRegistry");
// 启动有关电话的 TelephonyRegistry
telephonyRegistry = new TelephonyRegistry(
context, new TelephonyRegistry.ConfigurationProvider());
ServiceManager.addService("telephony.registry", telephonyRegistry);
t.traceEnd();
。。。
t.traceBegin("StartInputManagerService");
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("DeviceStateManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(DeviceStateManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
if (!disableCameraService) {
t.traceBegin("StartCameraServiceProxy");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CameraServiceProxy.class);
t.traceEnd();
}
t.traceBegin("StartWindowManagerService");
// WMS needs sensor service ready
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_SENSOR_SERVICE);
// 创建 WindowManagerService 对象,也创建了 PhoneWindowManager 对象。在其构造方法中会创建 new RootWindowContainer对象
wm = WindowManagerService.main(context, inputManager, !mFirstBoot, mOnlyCore,
new PhoneWindowManager(), mActivityManagerService.mActivityTaskManager);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE, wm, /* allowIsolated= */ false,
DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL | DUMP_FLAG_PROTO);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_SERVICE, inputManager,
/* allowIsolated= */ false, DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("SetWindowManagerService");
// ActivityManagerService 和 ActivityTaskManager 与 WindowManagerService关联
mActivityManagerService.setWindowManager(wm);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("WindowManagerServiceOnInitReady");
wm.onInitReady();
t.traceEnd();
SystemServerInitThreadPool.submit(() -> {
TimingsTraceAndSlog traceLog = TimingsTraceAndSlog.newAsyncLog();
traceLog.traceBegin(START_HIDL_SERVICES);
// native 启动 hild 服务
startHidlServices();
traceLog.traceEnd();
}, START_HIDL_SERVICES);
if (!isWatch && enableVrService) {
t.traceBegin("StartVrManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(VrManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
}
t.traceBegin("StartInputManager");
// inputManager 设置callback 为 WindowManagerService的getInputManagerCallback
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputManagerCallback());
// 调用native start 方法,启动 inputManager
inputManager.start();
t.traceEnd();
// TODO: Use service dependencies instead.
t.traceBegin("DisplayManagerWindowManagerAndInputReady");
// ready 开始接受input 事件
mDisplayManagerService.windowManagerAndInputReady();
t.traceEnd();
。。。。。
// Needed by DevicePolicyManager for initialization
t.traceBegin("StartBootPhaseLockSettingsReady");
// 回调 service 的 onBootPhase 方法
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_LOCK_SETTINGS_READY);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartBootPhaseSystemServicesReady");
// 回调 PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY,会回调如:ActivityManagerService.java,NotificationManagerService的 onBootPhase方法
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("MakeWindowManagerServiceReady");
try {
// 调用 WindowManagerService的 systemReady方法
wm.systemReady();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("making Window Manager Service ready", e);
}
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("MakePowerManagerServiceReady");
try {
// TODO: use boot phase
// PowerManagerService的 systemReady 方法
mPowerManagerService.systemReady(mActivityManagerService.getAppOpsService());
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("making Power Manager Service ready", e);
}
。。。。
try {
// TODO: use boot phase
// AppOpsService 是关于权限管理的类
mPowerManagerService.systemReady(mActivityManagerService.getAppOpsService());
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("making Power Manager Service ready", e);
}
.。。
t.traceBegin("StartBootPhaseDeviceSpecificServicesReady");
// startBootPhase 为:PHASE_DEVICE_SPECIFIC_SERVICES_READY
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_DEVICE_SPECIFIC_SERVICES_READY);
。。。。
// 调用 ActivityManagerService的 systemReady方法,通知服务 PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY
// 调用下列方法 startPersistentApps(PackageManager.MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_AWARE); 会去启动全部Persistent 常驻进程
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> {
Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
t.traceBegin("StartActivityManagerReadyPhase");
// 有很多重要的逻辑
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartObservingNativeCrashes");
try {
mActivityManagerService.startObservingNativeCrashes();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("observing native crashes", e);
}
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("RegisterAppOpsPolicy");
try {
mActivityManagerService.setAppOpsPolicy(new AppOpsPolicy(mSystemContext));
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("registering app ops policy", e);
}
t.traceEnd();
// 第三方app 可以start
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START);
t.traceEnd();
// 最后启动system ui
try {
startSystemUi(context, windowManagerF);
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("starting System UI", e);
}
t.traceEnd();
ActivityManagerService 的构造函数调用:
// Note: This method is invoked on the main thread but may need to attach various
// handlers to other threads. So take care to be explicit about the looper.
public ActivityManagerService(Context systemContext) {
// 1.系统Context 和 ActivityThread (将systemserver进程作为应用进程管理)
mContext = systemContext;
mFactoryTest = FactoryTest.getMode();
mSystemThread = ActivityThread.currentActivityThread();
// 2.AMS工作的线程和Handler,处理显示相关的UiHandler ,调用那个looper就在对应的线程中运行
mHandlerThread = new ServiceThread(TAG,
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND, false /*allowIo*/);
mHandlerThread.start();
mHandler = new MainHandler(mHandlerThread.getLooper());
mUiHandler = new UiHandler();
// 3. 广播队列BroadcastQueue初始化:前台广播队列和后台广播队列
mFgBroadcastQueue = new BroadcastQueue(this, mHandler,"foreground", BROADCAST_FG_TIMEOUT, false);
mBgBroadcastQueue = new BroadcastQueue(this, mHandler,"background", BROADCAST_BG_TIMEOUT, true);
mBroadcastQueues[0] = mFgBroadcastQueue;
mBroadcastQueues[1] = mBgBroadcastQueue;
// 4. Service 和 Provider 管理
mServices = new ActiveServices(this);
mProviderMap = new ProviderMap(this);
// 5.系统数据存放目录:/data/system/
File dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory();
File systemDir = new File(dataDir, "system");
systemDir.mkdirs();
// 电池状态信息,进程状态 和 应用权限管理
mBatteryStatsService = new BatteryStatsService(systemDir, mHandler);
mProcessStats = new ProcessStatsService(this, new File(systemDir, "procstats"));
mAppOpsService = new AppOpsService(new File(systemDir, "appops.xml"), mHandler);
// 6.多用户管理
mStartedUsers.put(UserHandle.USER_OWNER, new UserState(UserHandle.OWNER, true));
mUserLru.add(UserHandle.USER_OWNER);
updateStartedUserArrayLocked();
// 7.最近任务,Activity,Task管理
mRecentTasks = new RecentTasks(this);
mStackSupervisor = new ActivityStackSupervisor(this, mRecentTasks);
mTaskPersister = new TaskPersister(systemDir, mStackSupervisor, mRecentTasks);
// 创建一个新线程,用于监控和定时更新系统CPU信息,30分钟更新一次CPU和电池信息
mProcessCpuTracker.init();
mProcessCpuThread = new Thread("CpuTracker") {}
// 加入Watchdog监控起来
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);
Watchdog.getInstance().addThread(mHandler);
}
2-4)关于 SystemServiceManager的startBootPhase 的方法 ,用于服务启动阶段
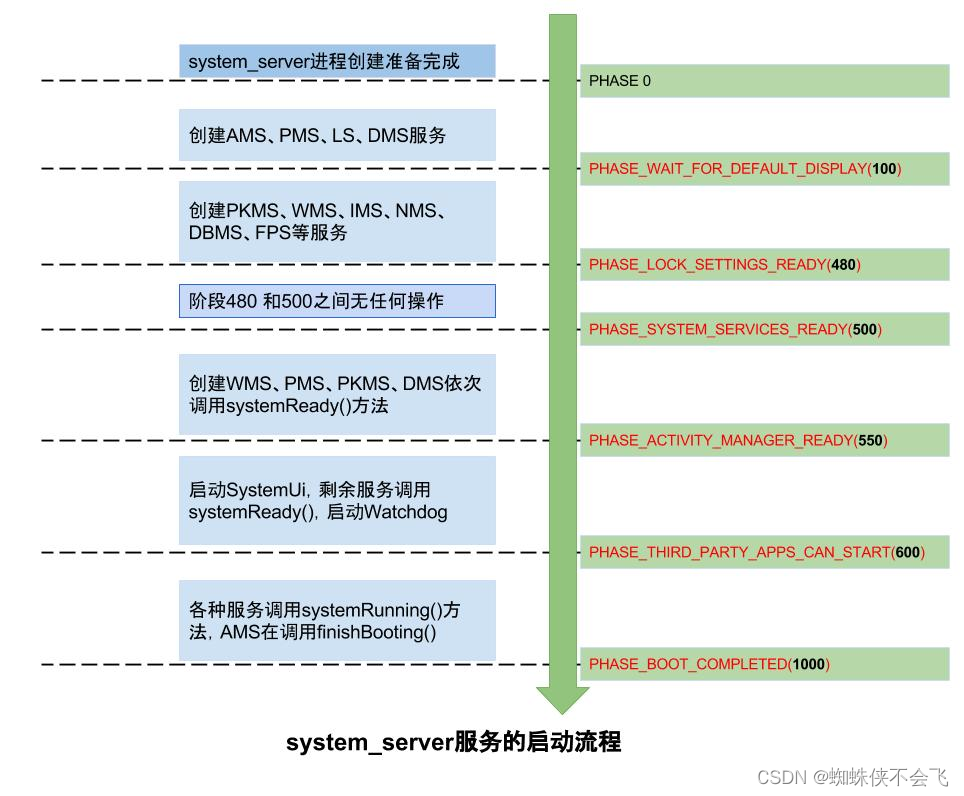
SystemServiceManager的startBootPhase()贯穿system_server进程的整个启动过程:
Phase0
创建四大引导服务:
- ActivityManagerService
- PowerManagerService
- LightsService
- DisplayManagerService
Phase100
进入阶段PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY=100回调服务
onBootPhase(100)
- DisplayManagerService
然后创建大量服务下面列举部分:
- PackageManagerService
- WindowManagerService
- InputManagerService
- NetworkManagerService
- DropBoxManagerService
- FingerprintService
- LauncherAppsService
- …
Phase480
进入阶段PHASE_LOCK_SETTINGS_READY=480回调服务
onBootPhase(480)
- DevicePolicyManagerService
阶段480后马上就进入阶段500.
Phase500
PHASE_SYSTEM_SERVICES_READY=500,进入该阶段服务能安全地调用核心系统服务.
onBootPhase(500)
- AlarmManagerService
- JobSchedulerService
- NotificationManagerService
- BackupManagerService
- UsageStatsService
- DeviceIdleController
- TrustManagerService
- UiModeManagerService
- BluetoothService
- BluetoothManagerService
- EthernetService
- WifiP2pService
- WifiScanningService
- WifiService
- RttService
各大服务执行systemReady():
- WindowManagerService.systemReady():
- PowerManagerService.systemReady():
- PackageManagerService.systemReady():
- DisplayManagerService.systemReady():
接下来就绪AMS.systemReady方法.
Phase550
PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY=550, AMS.mSystemReady=true, 已准备就绪,进入该阶段服务能广播Intent;但是system_server主线程并没有就绪.
onBootPhase(550)
- MountService
- TelecomLoaderService
- UsbService
- WebViewUpdateService
- DockObserver
- BatteryService
接下来执行: (AMS启动native crash监控, 加载WebView,启动SystemUi等),如下
- mActivityManagerService.startObservingNativeCrashes();
- WebViewFactory.prepareWebViewInSystemServer();
- startSystemUi(context);
- networkScoreF.systemReady();
- networkManagementF.systemReady();
- networkStatsF.systemReady();
- networkPolicyF.systemReady();
- connectivityF.systemReady();
- audioServiceF.systemReady();
- Watchdog.getInstance().start();
Phase600
PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START=600
onBootPhase(600)
- JobSchedulerService
- NotificationManagerService
- BackupManagerService
- AppWidgetService
- GestureLauncherService
- DreamManagerService
- TrustManagerService
- VoiceInteractionManagerService
接下来,各种服务的systemRunning过程:
WallpaperManagerService、InputMethodManagerService、LocationManagerService、CountryDetectorService、NetworkTimeUpdateService、CommonTimeManagementService、TextServicesManagerService、AssetAtlasService、InputManagerService、TelephonyRegistry、MediaRouterService、MmsServiceBroker这些服务依次执行其systemRunning()方法。
Phase1000
在经过一系列流程,再调用AMS.finishBooting()时,则进入阶段Phase1000。
到此,系统服务启动阶段完成就绪,system_server进程启动完成则进入Looper.loop()状态,随时待命,等待消息队列MessageQueue中的消息到来,则马上进入执行状态。
三. 总结
1.system_server是在Zygote启动的时候fork出来的子进程,调用的是ZygoteInit.forkSystemServer,最终返回MethodAndArgsCaller包装的是com.android.server.SystemServer.Main。
2.SystemServer.Main函数直接调用了run函数,在run函数中调用了createSystemContext通过ActivityThread.systemMain创建了ActivityThread,设置了mSystemContext并且调用ActivityThread.attach 通过反射创建Application 执行onCreate函数.这里创建的app是framewok-res.apk,是给系统使用的 比如系统的对话框。将mSystemServiceManager添加到LocalService的mService(ArrayMap)中去接着调用startBootstrapServices、startCoreServices、startOtherServices开启了非常多的服务Installer、ActivityTaskManagerService、ActivityManagerService、PowerManagerService、PackageManagerService等等。把他们添加到SystemServiceManager的mServices(ArrayList)中去。
3. 由前面分析 AMS、PMS不是独立的进程,由system_server启动,都运行在system_server进程中。

涉及3种IPC通信方式:Binder、Socket以及Handler,在图中分别用3种不同的颜色来代表这3种通信方式。一般来说,同一进程内的线程间通信采用的是 Handler消息队列机制,不同进程间的通信采用的是binder机制,另外与Zygote进程通信采用的Socket。
参考:
https://juejin.cn/post/7214493929566945340#heading-9
https://sharrychoo.github.io/blog/android-source/dc-handler