前言
为什么要写这一篇文章?
- 加深对promise的理解,以及再实际工作中的灵活运用。
- 知其然,知其所以然。
- 面试需要。(重点!!!)
1:声明promise
首先我们先来聊聊promise的几个特性:
- 一个promise有三种状态:pengding,fulfilled,rejected.
- promise状态一旦被改变,就不允许被改变了。
- new Promise构造函数接受一个函数参数,这个函数有两个参数分别为resole和reject函数。
其实代码很好写,我们就来检验以下resolve的参数是否能正确传递吧
const PENDING = "pengding";
const FUFILLED = "fulfilled";
const REJECTED = "rejected";
class MP {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
executor(this.resolve, this.reject);
}
resolve(value) {
this.value = value;
console.log("resolve:" + this.value);
}
reject(season) {}
}
// test
new MP((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("你好");
});
打开控制台,我们发现无法设置属性value,
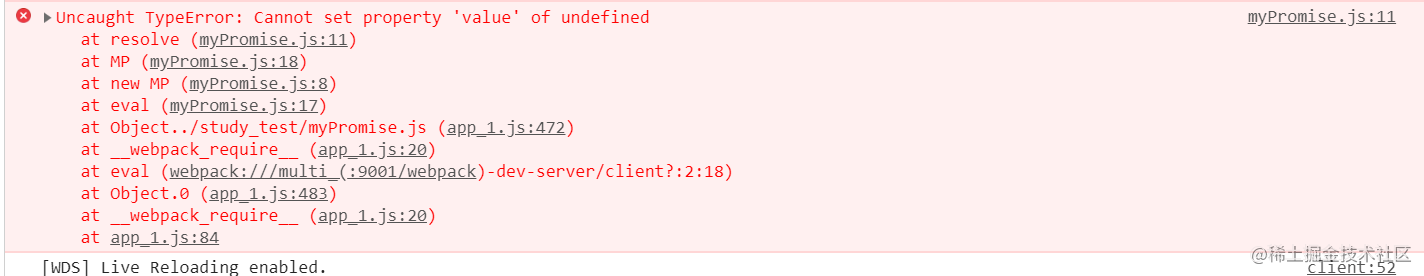 查看代码我们很容易发现其实代码this绑定的问题,我们用bind绑定以下就好了。
查看代码我们很容易发现其实代码this绑定的问题,我们用bind绑定以下就好了。
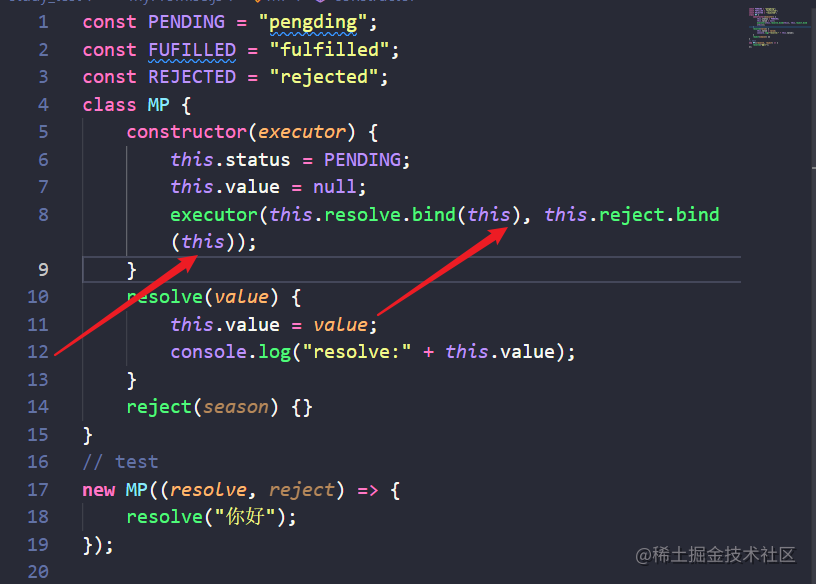
 this问题解决了,但是还有一个问题,状态只能改变一次。所以我们在resolve和reject函数执行的时候要判断一下状态。
this问题解决了,但是还有一个问题,状态只能改变一次。所以我们在resolve和reject函数执行的时候要判断一下状态。
const PENDING = "pengding";
const FUFILLED = "fulfilled";
const REJECTED = "rejected";
class MP {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
executor(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this));
}
resolve(value) {
if(this.status == PENDING){
this.status = FUFILLED;
this.value = value;
console.log("resolve:" + this.value);
}
}
reject(season) {
if (this.status == PENDING) {
this.status = REJECTED;
this.value = season;
console.log("reject:" + this.value);
}
}
}
// test
new MP((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("你好");
});
2:then的基础构建
2.1:then的用法
- 接受两个参数,当promise成功执行第一个函数参数,失败执行第二个函数参数。
- then里面也可以不传参数。
- then里面的函数为异步操作。(promise是微任务)
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 判断两个参数是不是函数类型,如果不是函数,需要手动封装,否则下面执行时会报错。
if (typeof onFulfilled !== "function") {
onFulfilled = () => {};
} else if (typeof onRejected !== "function") {
onRejected = () => {};
}
if (this.status === "fulfilled") {
onFulfilled(this.value);
} else if (this.status === "rejected") {
onRejected(this.value);
} else {
}
}
// test
new MP((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("你好");
}).then(
res => {
console.log("then res", res);
},
rej => {
console.log(rej);
}
);
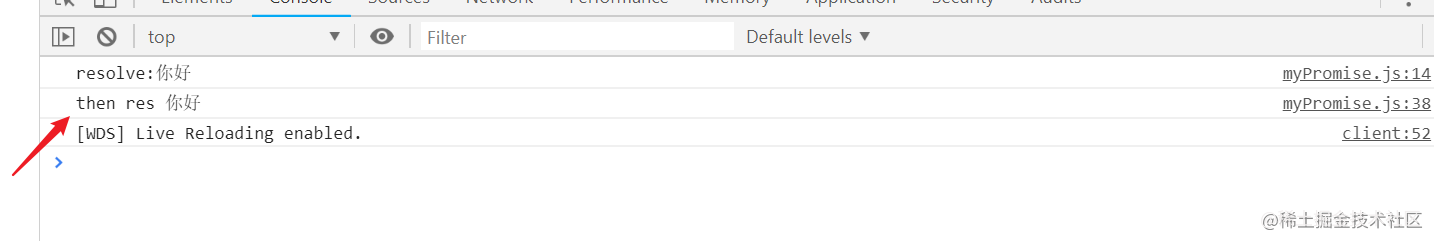 then可以接收到resolve传过来的数据。
then可以接收到resolve传过来的数据。
2.2:异步操作(任务队列不懂的先去学学)
这里我们使用queueMicrotask来创建微任务:
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 判断两个参数是不是函数类型,如果不是函数,需要手动封装,否则下面执行时会报错。
if (typeof onFulfilled !== "function") {
onFulfilled = () => {};
} else if (typeof onRejected !== "function") {
onRejected = () => {};
}
if (this.status === "fulfilled") {
queueMicrotask(()=>{
onFulfilled(this.value);
});
} else if (this.status === "rejected") {
queueMicrotask(()=>{
onRejected(this.value);
});
;
} else {
}
}
}
// test
new MP((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("中国");
console.log('你好');
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res)
});
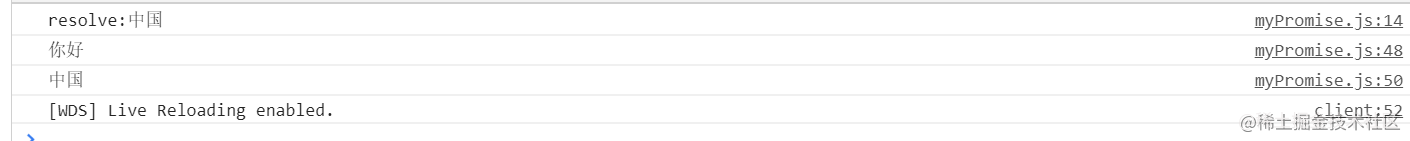
顺序是正确的,同步任务打印的你好优先于异步任务打印的中国。
2.3:then处理pengding状态
当我们在执行then方式的时候,状态还是没有改变的情况。(什么情况状态没有改变:异步执行resolve或者reject的时候 )之前的代码只判断了fulfilled和rejected的状态。
// test
new MP((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("异步操作");
},1000);
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res);
});
这个时候控制台是不答应任何东西的,因为还没有处理这个状态。所以说我们之前的思路就有一点问题,在then函数中我们不应该控制then里面的两个参数函数的执行,应该去保存它,在resolve和reject方式再去执行。
const PENDING = "pengding";
const FUFILLED = "fulfilled";
const REJECTED = "rejected";
class MP {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
// 将回调函数保存起来
this.callbacks = [];
executor(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this));
}
resolve(value) {
if (this.status == PENDING) {
let that = this;
this.status = FUFILLED;
this.value = value;
// // 触发回调函数
queueMicrotask(() => {
that.callbacks.map(callback => {
callback.onFulfilled(that.value);
});
});
}
}
reject(season) {
if (this.status == PENDING) {
let that = this;
this.status = REJECTED;
this.value = season;
// 触发回调函数
queueMicrotask(() => {
that.callbacks.map(callback => {
callback.onRejected(that.value);
});
});
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 判断两个参数是不是函数类型,如果不是函数,需要手动封装,否则下面执行时会报错。
if (typeof onFulfilled !== "function") {
onFulfilled = () => {};
} else if (typeof onRejected !== "function") {
onRejected = () => {};
}
if (this.status === "fulfilled") {
// 收集回调函数
this.callbacks.push({
onFulfilled
});
} else if (this.status === "rejected") {
// 收集回调函数
this.callbacks.push({
onRejected
});
} else {
// 收集回调函数
this.callbacks.push({
onFulfilled,
onRejected
});
}
}
}
2.4:then链式调用
- then返回的也是一个promise
- 之前promise的状态不会影响新的promise状态。
所以我们现在要继续处理我们的then方法,首先在then函数里肯定要返回一个promise的,其次在then函数里面我们要拿到onFulfilled, onRejected这两个回调函数的结果,作为这个新的promise的值。
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 判断两个参数是不是函数类型,如果不是函数,需要手动封装,否则下面执行时会报错。
if (typeof onFulfilled !== "function") {
onFulfilled = () => {};
} else if (typeof onRejected !== "function") {
onRejected = () => {};
}
// 直接返回一个新的promise 之前在then里面处理的代码迁移到新的promise里面处理
return new MP((resolve,reject)=>{
// 这时里面的this指向的不是新的promise
if (this.status === "fulfilled") {
this.callbacks.push({
// 这个改成箭头函数的形式,方便我们获取onFulfilled的值传递给新promise的resolve
onFulfilled:value=>{
let result = onFulfilled(value)
resolve(result)
}
});
} else if (this.status === "rejected") {
this.callbacks.push({
onRejected:value=>{
let result = onRejected(value);
resolve(result);
}
});
} else {
this.callbacks.push({
onFulfilled: value => {
onFulfilled(value);
},
onRejected: value => {
onRejected(value);
}
});
}
})
}
// test
new MP((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("异步操作");
}).then(
res => {
return '33333';
},
rej => {return '11111111'}
).then(res=>{
console.log(res)
});
在第二个then打印的结果应该是第一个then中返回的33333

2.5:then回调函数返回promise
new Promise((res,rej)=>{
res('1111')
}).then(res=>{
return new Promise((res,rej)=>{
res('22222')
})
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res)
});
打印结果应该为22222而不是promise对象。
 用我们手写的试试
用我们手写的试试
new MP((resolve, reject) => {
resolve("异步操作");
}).then(
res=>{
return new MP((res, rej) => {
res("22222");
});
}
).then(res=>{
console.log(res)
});
 返回的却是一个
返回的却是一个promise对象,这是因为我们在处理回调函数结果时,没有判断类型,直接将整个result都返回给下个then了,所以我们在返回之前,需要判断以下返回的结果。
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 判断两个参数是不是函数类型,如果不是函数,需要手动封装,否则下面执行时会报错。
if (typeof onFulfilled !== "function") {
onFulfilled = () => {};
} else if (typeof onRejected !== "function") {
onRejected = () => {};
}
return new MP((resolve,reject)=>{
if (this.status === "fulfilled") {
this.callbacks.push({
onFulfilled:value=>{
let result = onFulfilled(value);
// 结果时MP类型时
if(result instanceof MP){
// 我们可以直接通过这个promise的then方法来传递值
result.then(resolve, reject);
}else{
resolve(result);
}
}
});
} else if (this.status === "rejected") {
this.callbacks.push({
onRejected:value=>{
let result = onRejected(value);
// 结果时MP类型时
if (result instanceof MP) {
result.then(resolve, reject);
} else {
resolve(result);
}
}
});
} else {
this.callbacks.push({
onFulfilled: value => {
let result = onFulfilled(value);
// 结果时MP类型时
if (result instanceof MP) {
result.then(resolve, reject);
} else {
resolve(result);
}
},
onRejected: value => {
let result = onRejected(value);
// 结果时MP类型时
if (result instanceof MP) {
result.then(resolve, reject);
} else {
resolve(result);
}
}
});
}
})
}
打开控制台就是具体的值而不是promise.

2.6:prmise返回类型约束
看一段代码
let promise = new Promise((res,rej)=>{
res('111')
})
let p = promise.then(res=>{
return p
})
 我们发现控制台报错了,说明
我们发现控制台报错了,说明promise不能返回自己,对于返回类型是有约束的.
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
// 判断两个参数是不是函数类型,如果不是函数,需要手动封装,否则下面执行时会报错。
if (typeof onFulfilled !== "function") {
onFulfilled = () => {};
} else if (typeof onRejected !== "function") {
onRejected = () => {};
}
let promise = new MP((resolve,reject)=>{
if (this.status === "fulfilled") {
this.callbacks.push({
onFulfilled:value=>{
let result = onFulfilled(value);
if(result === promise){
throw new TypeError(
"Uncaught (in promise) TypeError: Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>"
);
}
// 结果时MP类型时
if(result instanceof MP){
result.then(resolve, reject);
}else{
resolve(result);
}
}
});
} else if (this.status === "rejected") {
this.callbacks.push({
onRejected:value=>{
let result = onRejected(value);
// 判断返回类型
if (result === promise) {
throw new TypeError(
"Uncaught (in promise) TypeError: Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>"
);
}
// 结果时MP类型时
if (result instanceof MP) {
result.then(resolve, reject);
} else {
resolve(result);
}
}
});
} else {
this.callbacks.push({
onFulfilled: value => {
let result = onFulfilled(value);
if (result === promise) {
throw new TypeError(
"Uncaught (in promise) TypeError: Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>"
);
}
// 结果时MP类型时
if (result instanceof MP) {
result.then(resolve, reject);
} else {
resolve(result);
}
},
onRejected: value => {
let result = onRejected(value);
if (result === promise) {
throw new TypeError(
"Uncaught (in promise) TypeError: Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>"
);
}
// 结果时MP类型时
if (result instanceof MP) {
result.then(resolve, reject);
} else {
resolve(result);
}
}
});
}
})
return promise
}
3:实现Promise.resolve和Promise.reject
例子:
Promise.resolve('111').then(res=>{
console.log(res)
})
Promise.reject('111').then(res=>{
console.log(res)
},rej=>{
console.log(rej)
})
其实这个方法就是帮助我们做了两件事情
- 创建一个promise
- 将promise的状态设置成功或者失败
static resolve(value){
return new MP(resolve => {
if (value instanceof MP) {
value.then(resolve);
} else {
resolve(value);
}
});
}
reject同理就不用写了哈。
4:实现Promise.all
Promise.all方法会返回一个promise,当参数数组中所有promise都成功后,就会返回成功的promise.看到所有时,我们就需要一个计数器,每次成功一个记录一次,当记录结果和传入数组长度一样时,就返回成功的,当一个失败时,就直接返回失败的。
static all(promises){
let length = promises.length;
// 记录每个promise成功时结果,同时用于返回
let arr = [];
return new MP((resolve, reject) => {
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
promises[i].then(
res => {
arr[i] = res;
if (arr.length === length) {
resolve(arr);
}
},
rej => {
reject(rej);
}
);
}
});
}
结尾
喜欢的小伙伴可以点赞收藏哈,有没有一起备战面试的,大家一起加油哈~