1.1
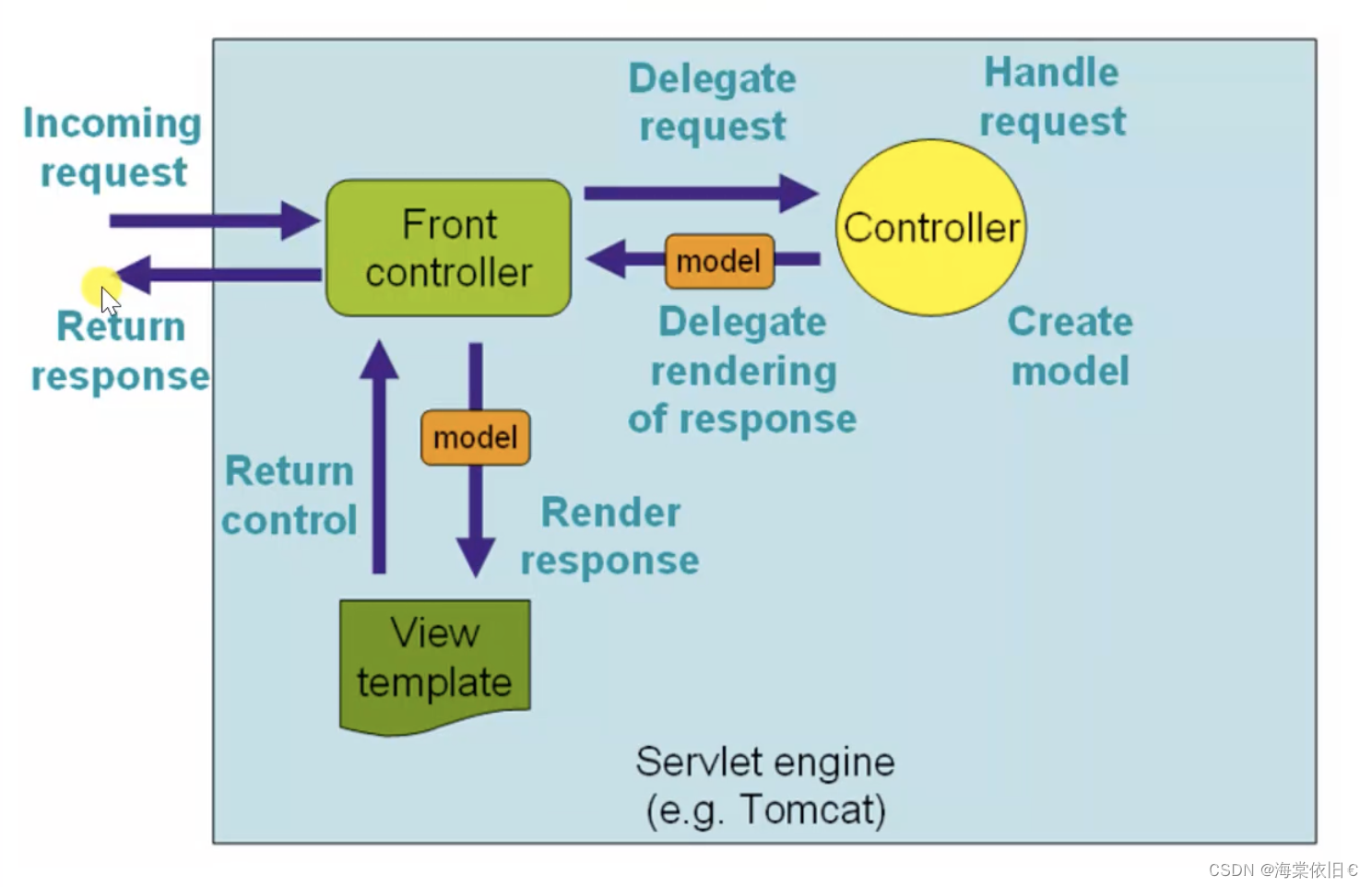

函数的返回值为空,因为可以使用response对象向浏览器返回数据。声明了request对象和response对象,dispatcherservlet自动将这两个对象传入
@RequestMapping("/http")
public void http(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
//获取请求数据
System.out.println(request.getMethod());
System.out.println(request.getServletPath());
Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();
while(headerNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = headerNames.nextElement();
String value = request.getHeader(name);
System.out.println(name + ": " + value);
}
System.out.println(request.getParameter("code"));
//返回响应数据
//新语法,直接在try后面括号内写创建write对象,就不需要再关闭流。
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8");
try(PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();) {
writer.write("<h1>牛客网</h1>");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
问号后面传参数,可以使用request.getParameter("code")获取。
//GET请求
//students?current=1&limit=20
@RequestMapping(path = "/students", method = RequestMethod.GET)//只能处理GET请求
@ResponseBody
public String getStudents(
@RequestParam(name = "current", required = false, defaultValue = "1") int current,
@RequestParam(name = "limit", required = false, defaultValue = "10") int limit) {
System.out.println(current);
System.out.println(limit);
return "some student";
}
//GET传参的第二种方法,一种是像上面使用问号传参数,另一种是直接拼在路径中
@RequestMapping(path = "/student/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getStudent(@PathVariable("id") int id) {
System.out.println(id);
return "a student";
}//POST浏览器向服务器提交数据
@RequestMapping(path = "/student", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String saveStudent(String name, int age) {//和表单的name一样
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
return "success";
}
//响应html数据
@RequestMapping(path = "/teacher", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView getTeacher() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("name", "张三");
modelAndView.addObject("age", "22");
modelAndView.setViewName("/demo/view");
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping(path = "/school", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getSchool(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", "北京大学");
model.addAttribute("age", "120");
return "/demo/view";
}
//响应JSON请求数据,一般用于异步请求
//Java对象-> JSON字符串 -> JS对象
@RequestMapping(path = "/emp", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody//dispatcherservlet看见加了这个注解,会自动将Map转成JSON数据
public List<Map<String, Object>> getEmp() {
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, Object> emp = new HashMap<>();
emp.put("name", "张三");
emp.put("age", 22);
list.add(emp);
return list;
}