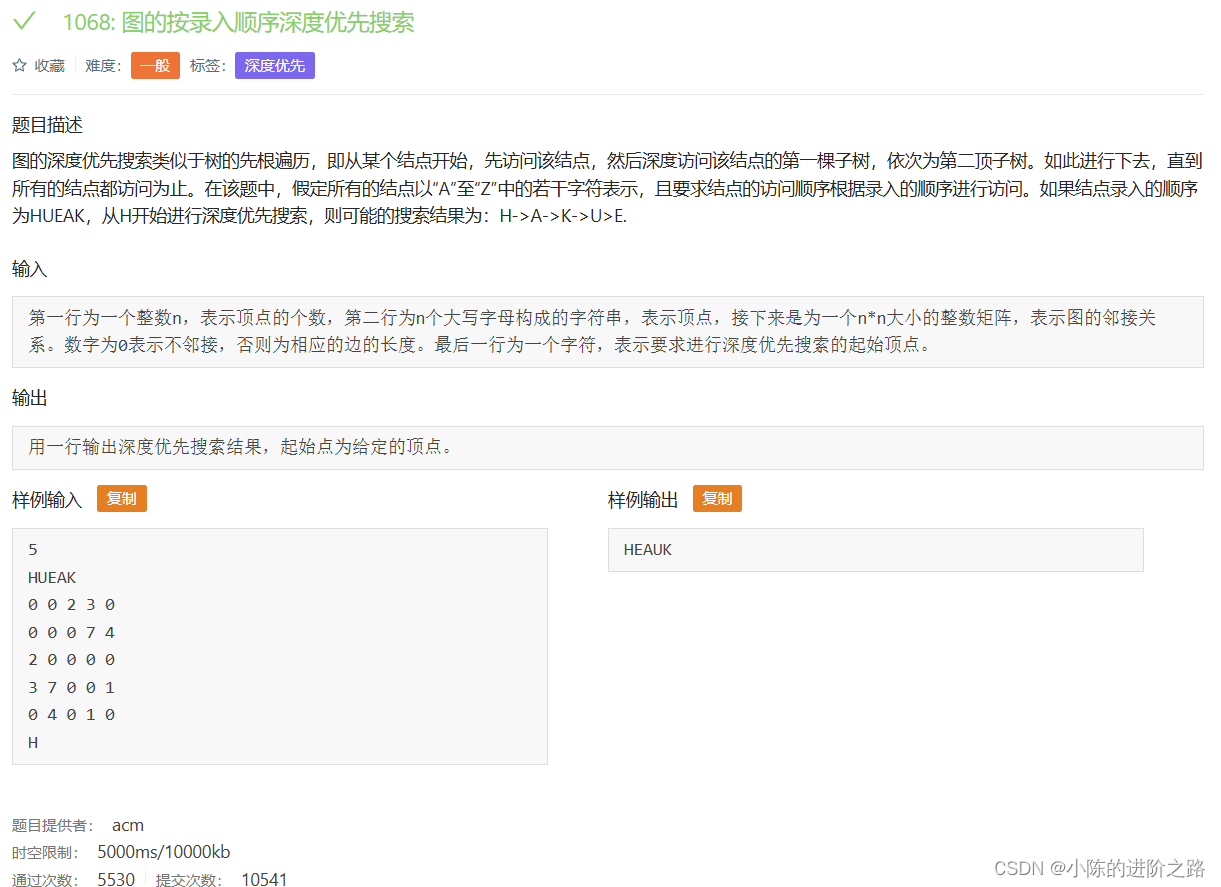
1068: 图的按录入顺序深度优先搜索
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
#include"cstring"
int visited[100];
char s[100];
int a[100][100];
int n;
void dfs(int k,int n)
{
if(visited[k]==0)
{
visited[k]=1;
cout<<s[k];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(visited[i]==0&&a[k][i]!=0)
{
dfs(i,n);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
cin>>s;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
char key=0;
cin>>key;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(s[i]==key)
{
dfs(i,n);
}
}
}
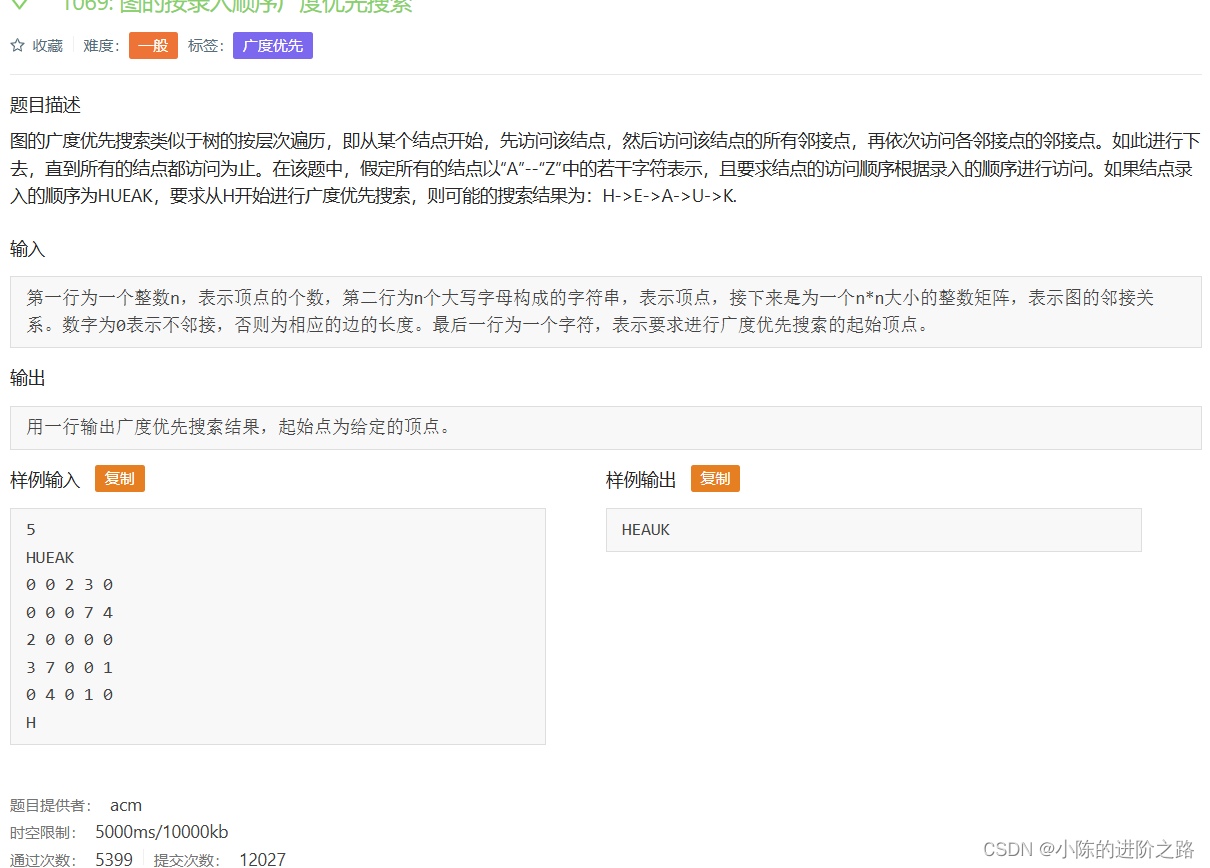
1069: 图的按录入顺序广度优先搜索
#include"iostream"
#include"cstring"
using namespace std;
int queue[100];
int visited[100];
char s[100];
int a[100][100];
void bfs(int k,int n)
{
int rear=-1,front=-1;
queue[++rear]=k;
visited[k]=1;
while(front!=rear)
{
k=queue[++front];
cout<<s[k];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[k][i]!=0&&visited[i]==0)
{
queue[++rear]=i;
visited[i]=1;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
cin >> s;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
char key;
cin >> key;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (s[i] == key) {
bfs(i, n);
}
}
return 0;
}
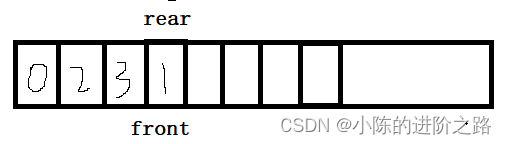
1070: 邻接矩阵存储简单路径
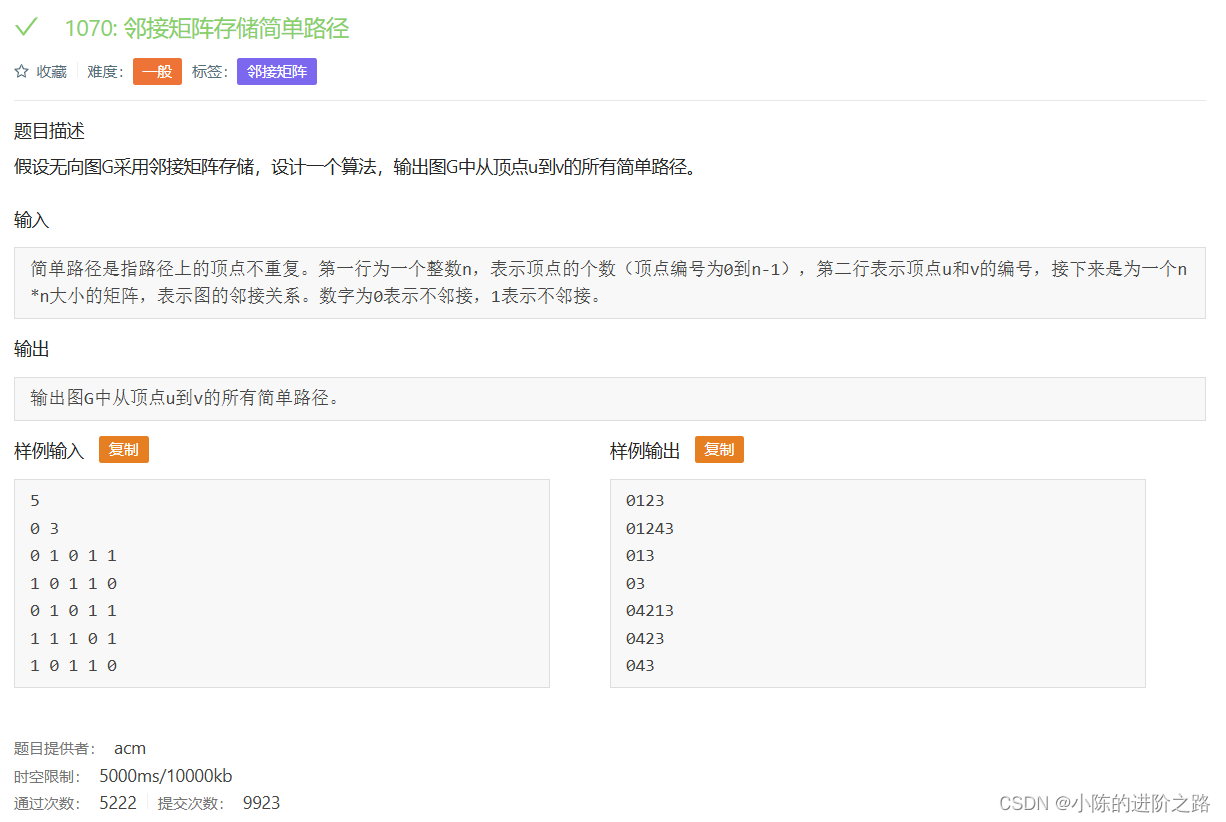
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
#include"cstring"
int n;
int start,last;
int a[100][100];
int stu[100];
int path[100];
void dfs(int u,int t)
{
path[t]=u;
if(u==last)
{
for(int i=0;i<t;i++)
{
cout<<path[i];
}
cout<<last<<endl;
return;
}
stu[u]=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(stu[i]==0&&a[u][i]==1)
{
dfs(i,t+1);
}
}
stu[u]=0;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
cin>>start>>last;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
dfs(start,0);
}
1055: 邻接矩阵到邻接表
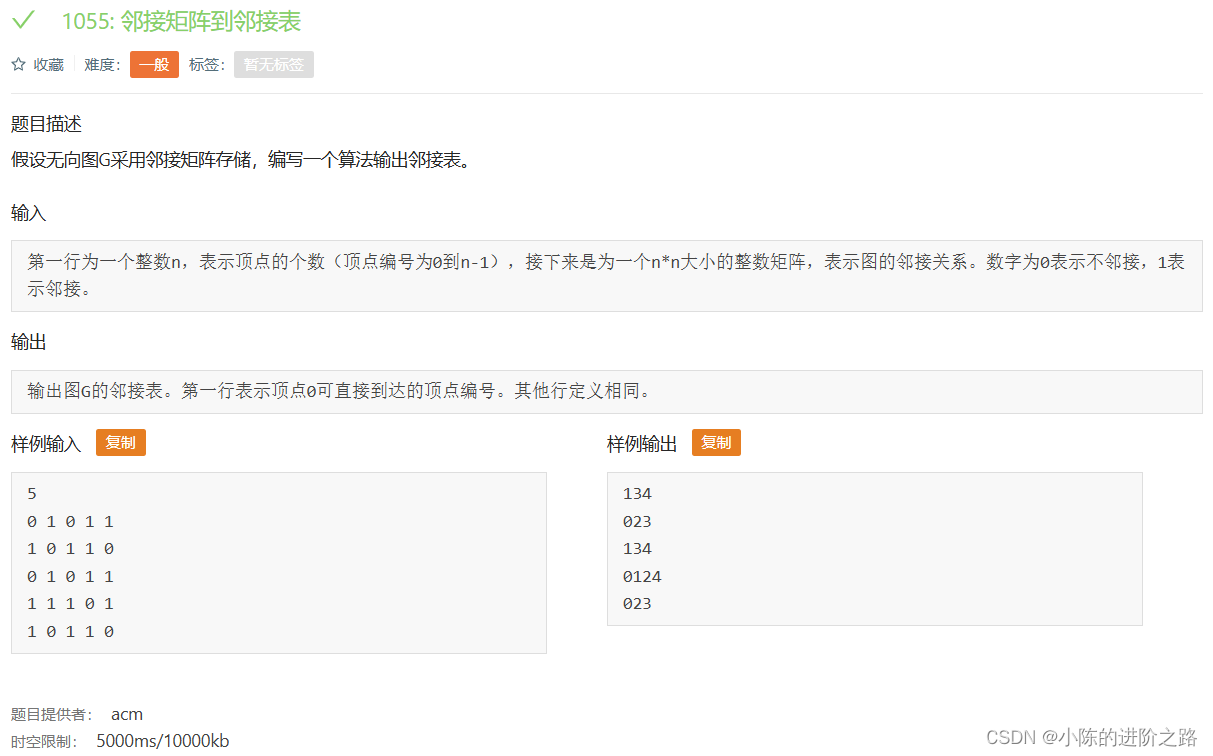
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
#include"cstring"
int n;
int a[100][100];
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]==1)
{
cout<<j;
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
1056: 邻接表到邻接矩阵
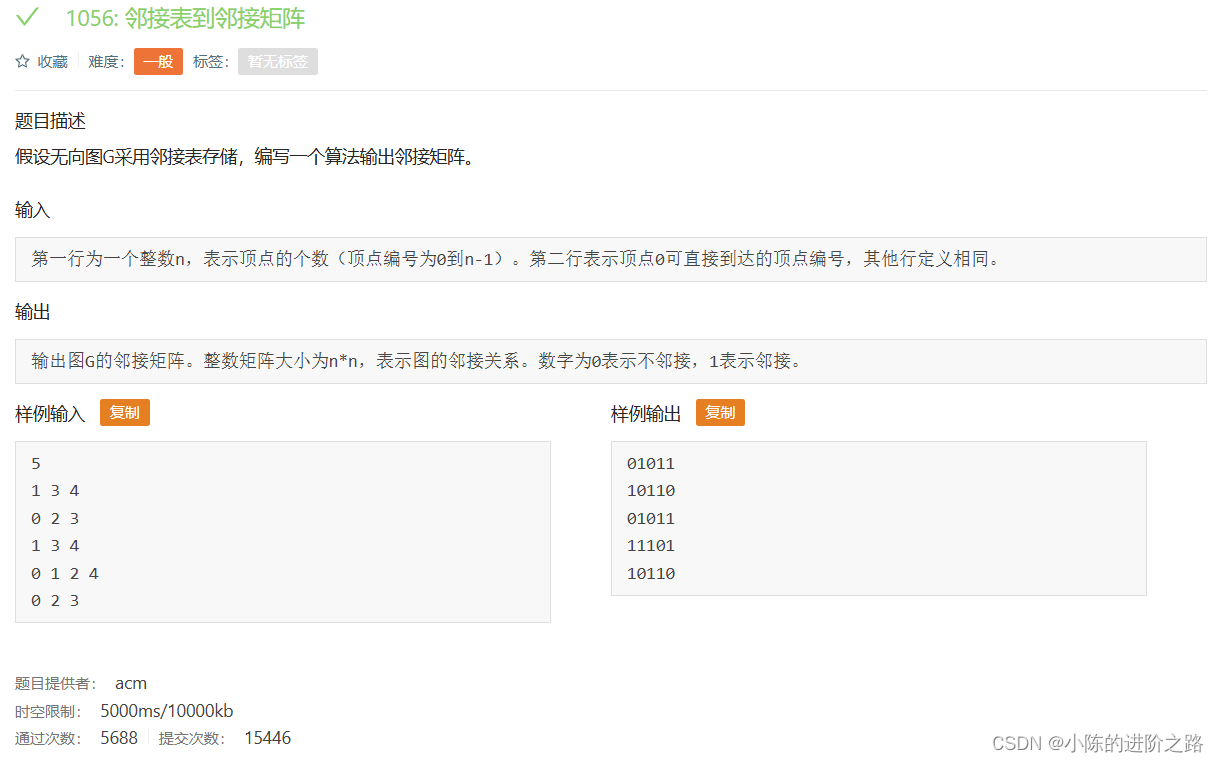
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
#include"cstring"
#include"stdio.h"
int n;
int a[100][100];
int x;
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
getchar();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;;j++)
{
scanf("%c",&x);
if(x=='\n') break;
a[i][x-'0']=1;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
printf("%d",a[i][j]);//写成cout超时
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
1057: 有向图的出度计算
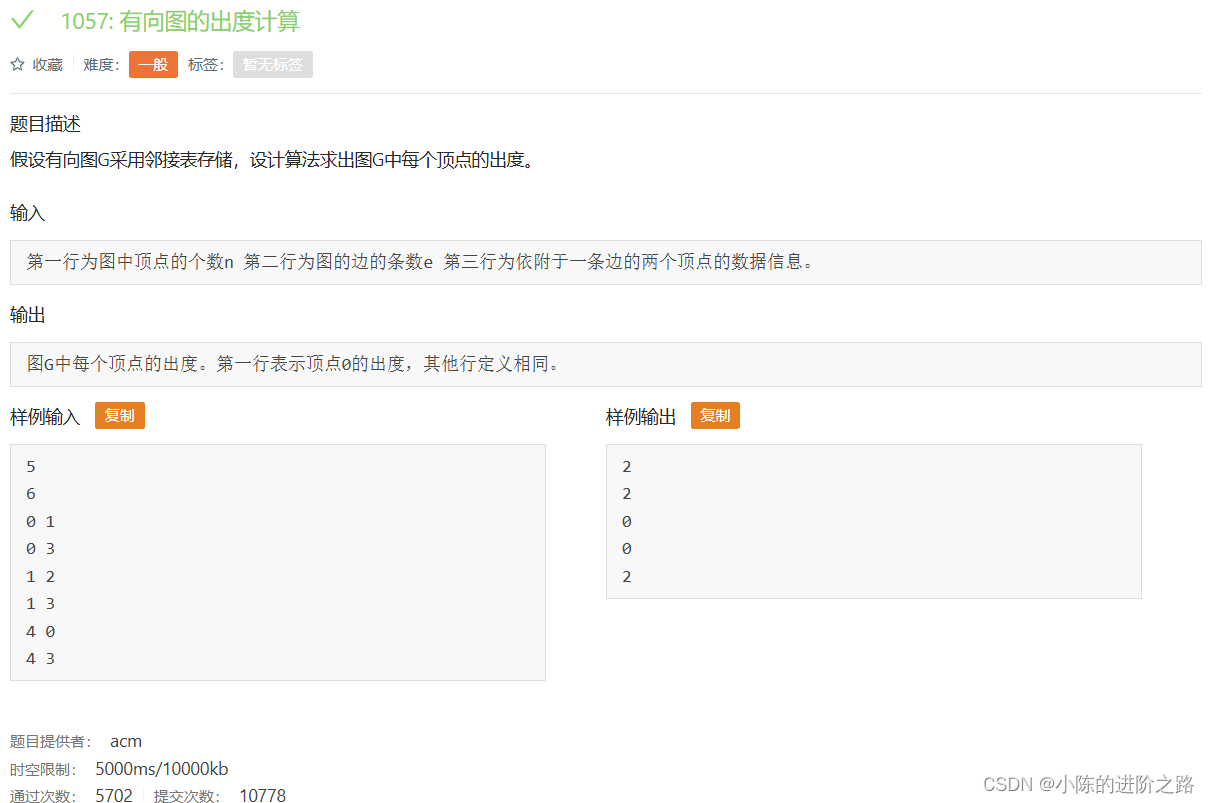
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
#include"cstring"
#include"stdio.h"
int n,e;
int a[100][100];
int b[100];
int start,last;
int main()
{
cin>>n>>e;
for(int i=0;i<e;i++)
{
cin>>start>>last;
a[start][last]=1;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]==1)
{
b[i]++;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cout<<b[i]<<endl;
}
}
1060: 无向图的最大度计算
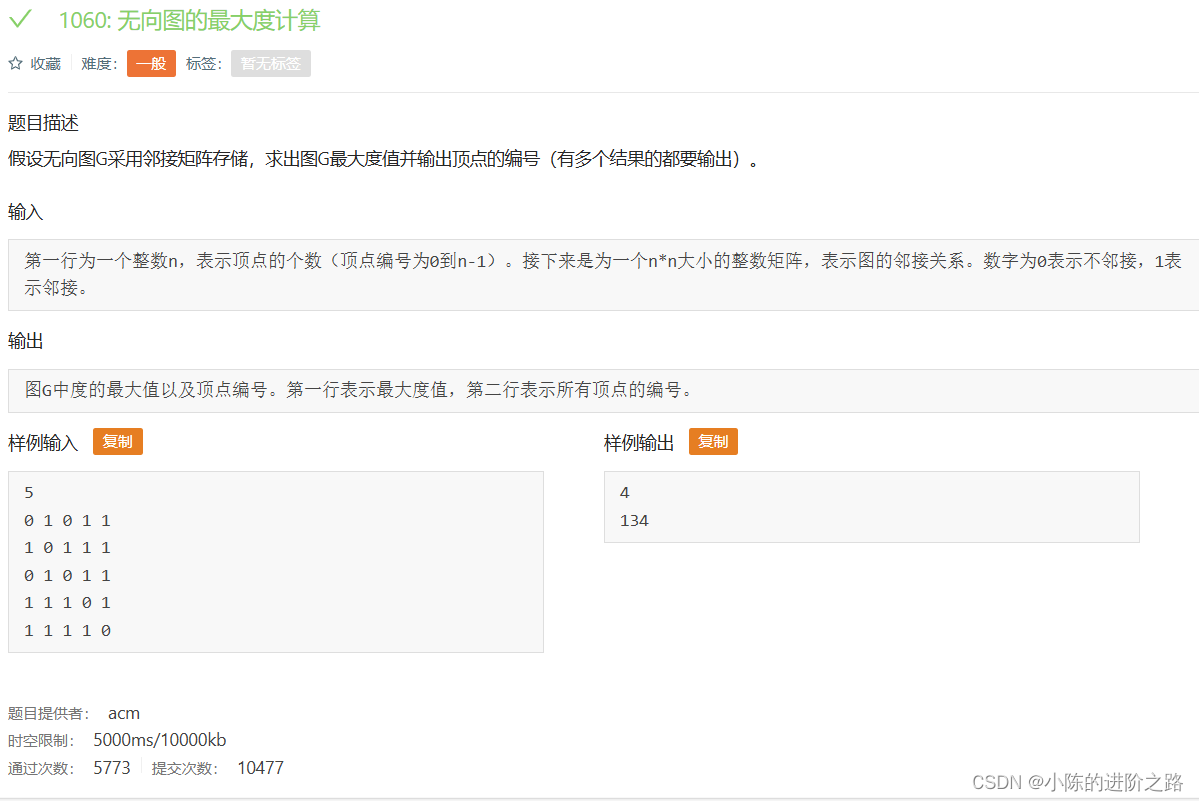
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
#include"cstring"
#include"stdio.h"
int n;
int a[100][100];
int mx;
int b[100];
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]==1)
{
b[i]++;
}
if(b[i]>mx)
{
mx=b[i];
}
}
}
cout<<mx<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(b[i]==mx)
{
cout<<i;
}
}
}
1062: 有向图的边存在判断
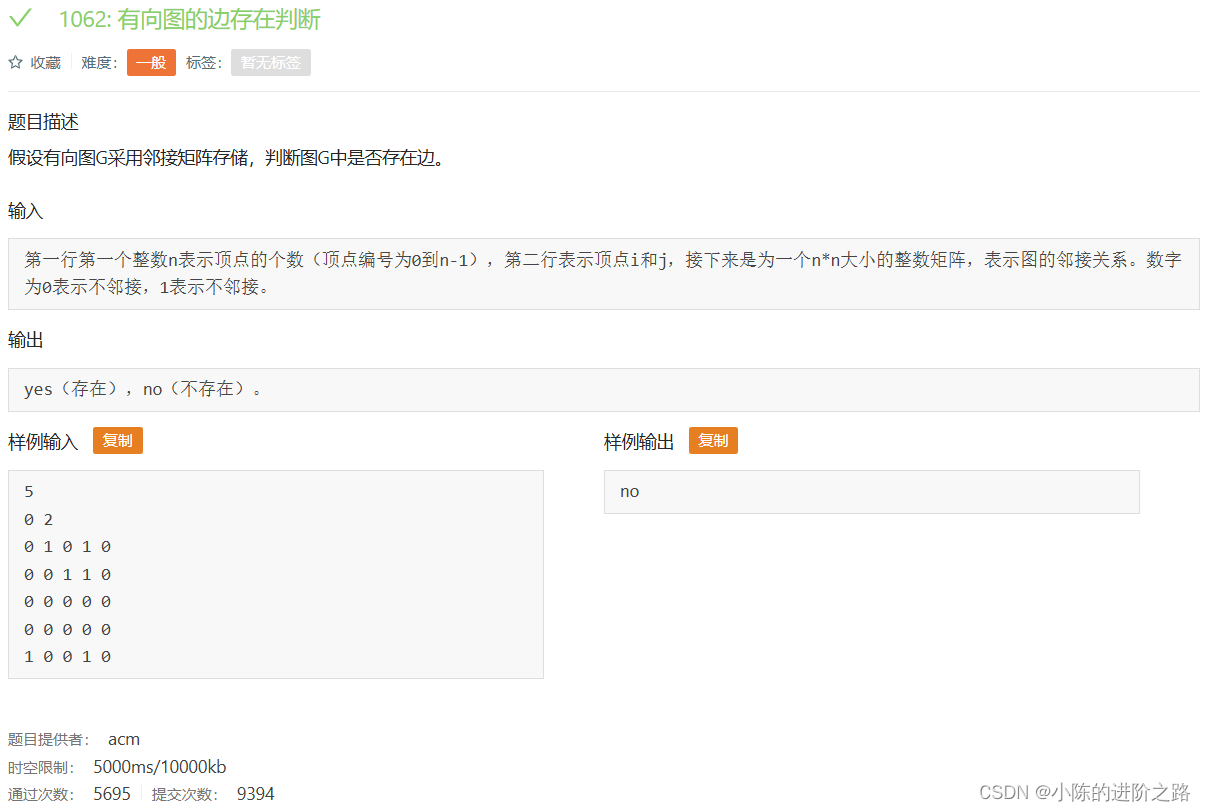
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
#include"cstring"
#include"stdio.h"
int n;
int start,last;
int a[100][100];
int main()
{
cin>>n;
cin>>start>>last;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[start][last]==1)
{
cout<<"yes";
return 0;
}
}
}
cout<<"no";
}
1065: 无向图的连通分量计算
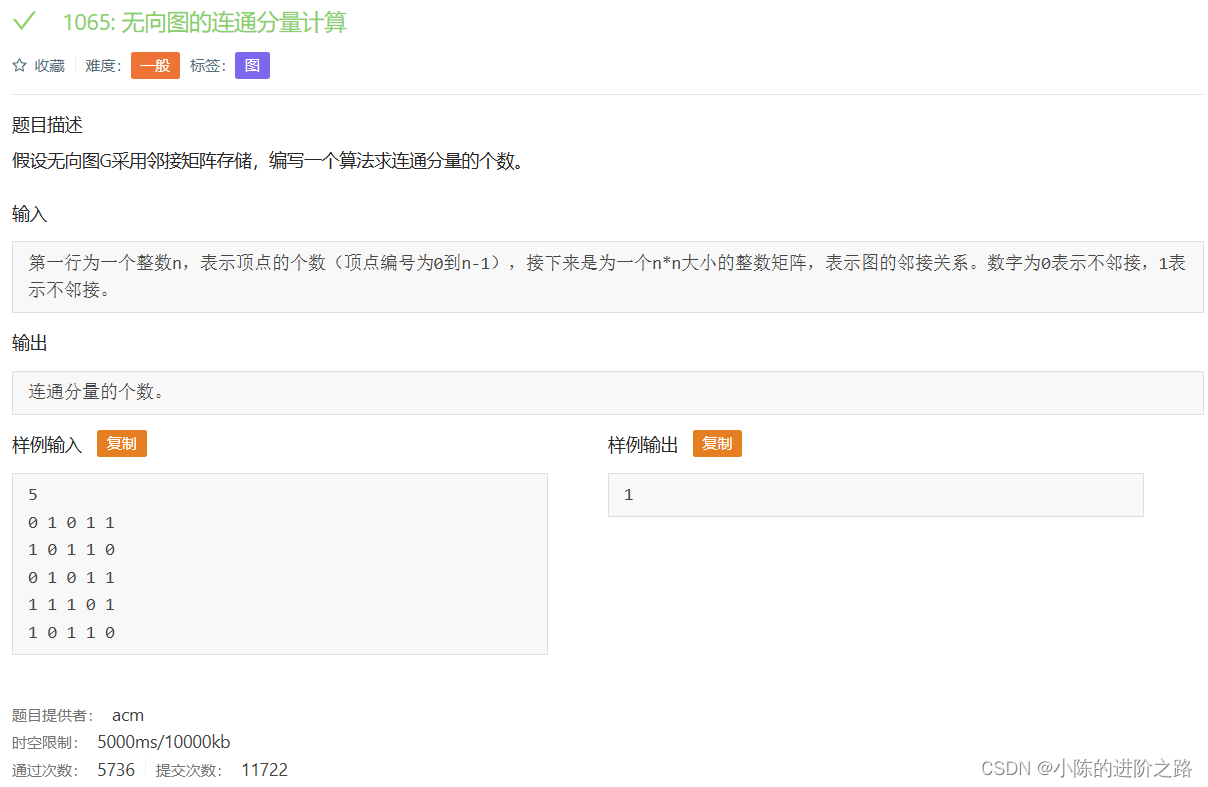
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
#include"cstring"
#include"stdio.h"
int n;
int a[100][100];
int separte;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
}
}
int sum=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int separte=0;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]==1)
{
separte=1;
break;
}
}
if(separte==0) sum++;
}
cout<<sum;
}
1076: 判断给定有向图是否存在回路
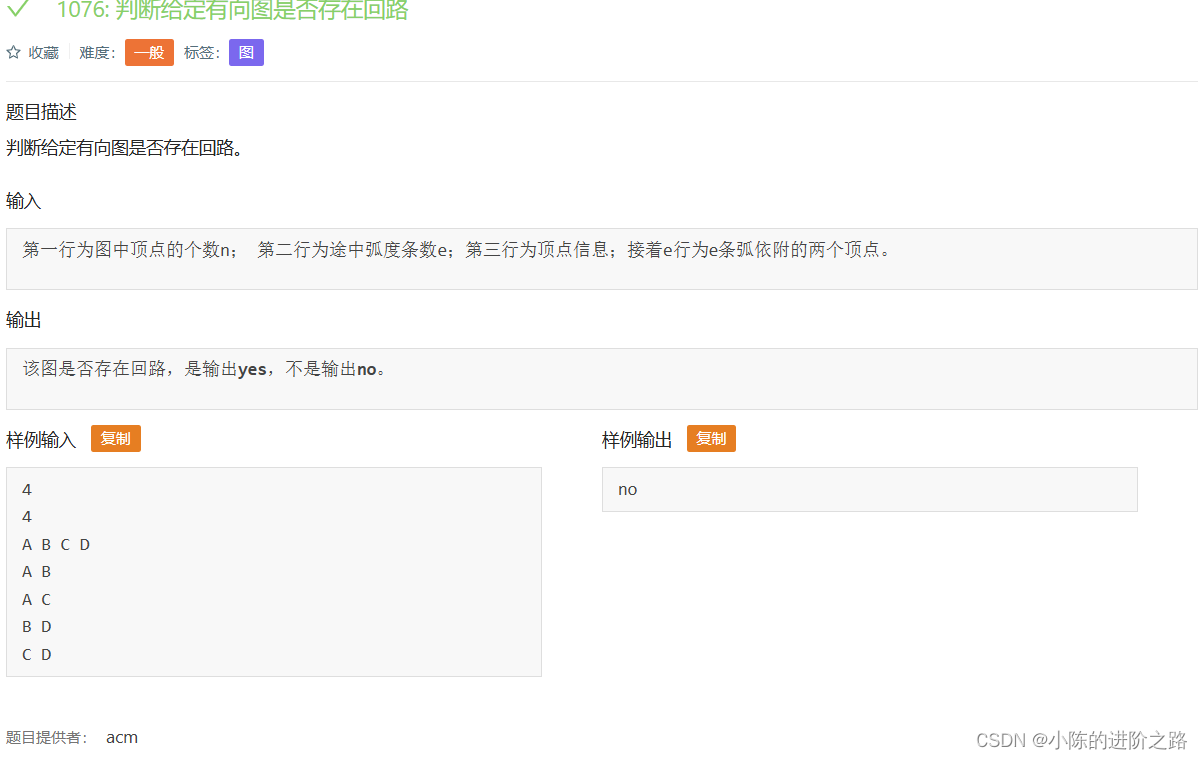
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
int n;
int e;
char s[100];
char str,last;
int visited[100];
int flag;
int a[100][100];
void bfs(int j,int start)
{
if(visited[j]==0)
{
if(j==start)
{
flag=1;
return;
}
visited[j]=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[j][i]!=0&&visited[i]==0)
{
bfs(i,start);
}
}visited[j]=0;
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
cin>>e;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>s[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<e;i++)
{
cin>>str>>last;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(s[j]==str)
{
for(int k=0;k<n;k++)
{
if(s[k]==last)
{
a[j][k]=1;
}
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]!=0)
{
bfs(j,i);
}
}
}
if(flag==1) cout<<"yes";
else cout<<"no";
}
1075: 求最小生成树(Prim算法)
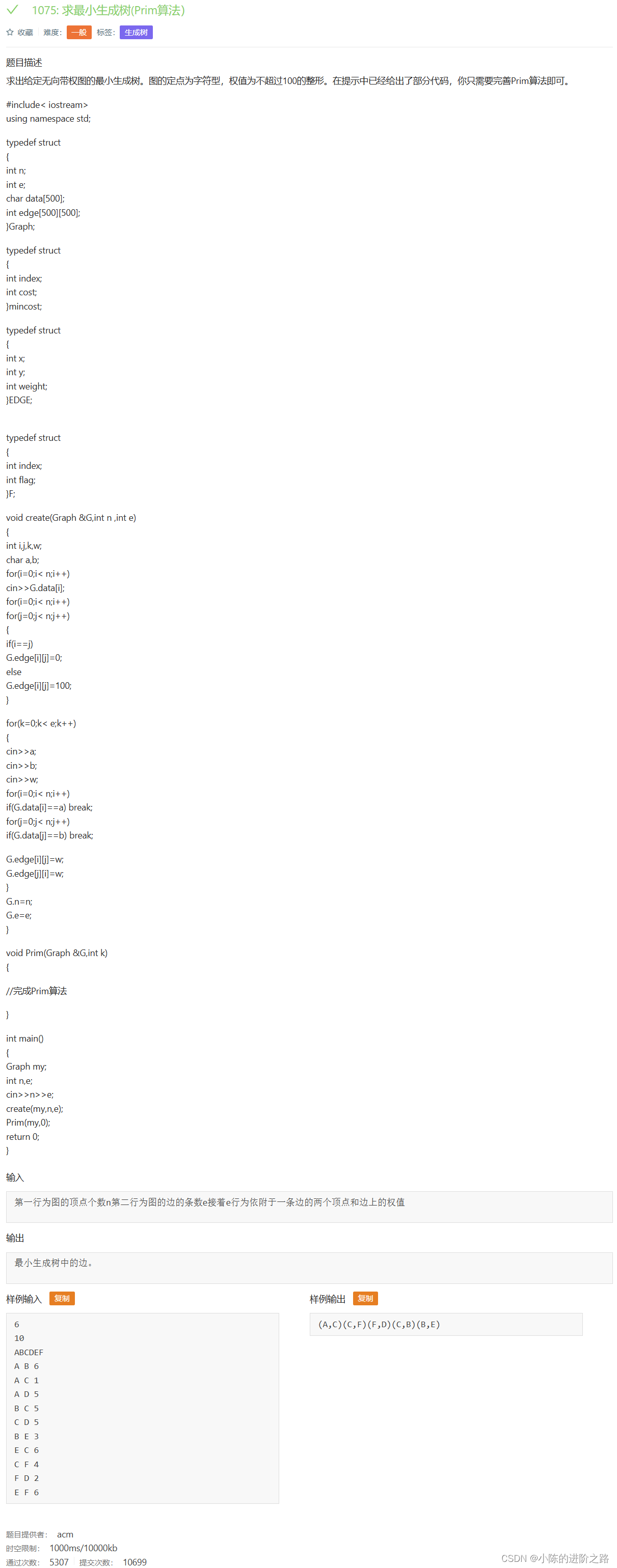
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100;
const int INF = 101;
typedef struct
{
int n;
int e;
char data[500];
int edge[500][500];
}Graph;
typedef struct
{
int index;
int cost;
}mincost;
typedef struct
{
int x;
int y;
int weight;
}EDGE;
typedef struct
{
int index;
int flag;
}F;
void create(Graph &G,int n ,int e)
{
int i,j,k,w;
char a,b;
for(i=0;i< n;i++)
cin>>G.data[i];
for(i=0;i< n;i++)
for(j=0;j< n;j++)
{
if(i==j)
G.edge[i][j]=0;
else
G.edge[i][j]=100;
}
for(k=0;k< e;k++)
{
cin>>a;
cin>>b;
cin>>w;
for(i=0;i< n;i++)
if(G.data[i]==a) break;
for(j=0;j< n;j++)
if(G.data[j]==b) break;
G.edge[i][j]=w;
G.edge[j][i]=w;
}
G.n=n;
G.e=e;
}
void Prim(Graph& G,int k)
{
int pe[maxn];
int pn[maxn];
int MIN;
int v;
for(int i=0;i<G.n;i++)
{
pe[i]=G.edge[k][i];
pn[i]=k;
}
for(int i=1;i<G.n;i++)
{
MIN=INF;
for(int j=0;j<G.n;j++)
{
if(pe[j]!=0&&pe[j]<MIN)
{
MIN=pe[j];
v=j;
}
}
cout<<"("<<G.data[pn[v]]<<','<<G.data[v]<<")";
pe[v]=0;
for(int j=0;j<G.n;j++)
{
if(pe[j]!=0&&G.edge[v][j]<pe[j])
{
pe[j]=G.edge[v][j];
pn[j]=v;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
Graph my;
int n,e;
cin>>n>>e;
create(my,n,e);
Prim(my,0);
return 0;
}
1067: 有向图的邻接表存储强连通判断
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
int n;
int e;
int str;
int last;
int a[100][100];
int main()
{
cin>>n;
cin>>e;
for(int i=0;i<e;i++)
{
cin>>str>>last;
a[str][last]=1;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
for(int k=0;k<n;k++)
{
if(a[j][i]==1&&a[i][k]==1)
{
a[j][k]=1;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]==0)
{
cout<<"no";
return 0;
}
}
}
cout<<"yes";
}
1012: 哈希表(链地址法处理冲突)
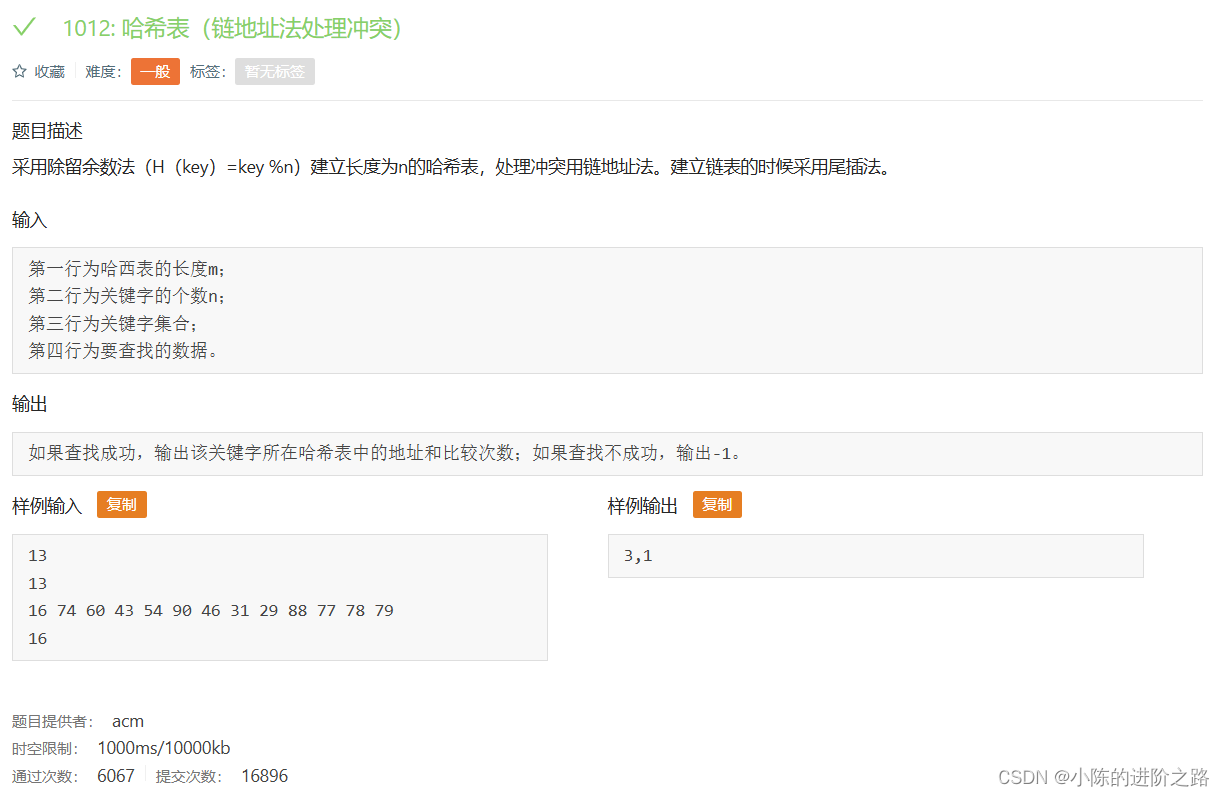
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
int n;
int m;
int a[100][100];
int b[100];
int key;
int data;
int main()
{
cin>>m;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>data;
a[data%m][++(b[data%m])]=data;
}
int cnt=0;
cin>>key;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[key%m][i]==key)
{
cout<<key%m<<','<<cnt;
return 0;
}
else
{
cnt++;
}
}
cout<<"-1";
}
1013: 哈希表(开放定址法处理冲突)
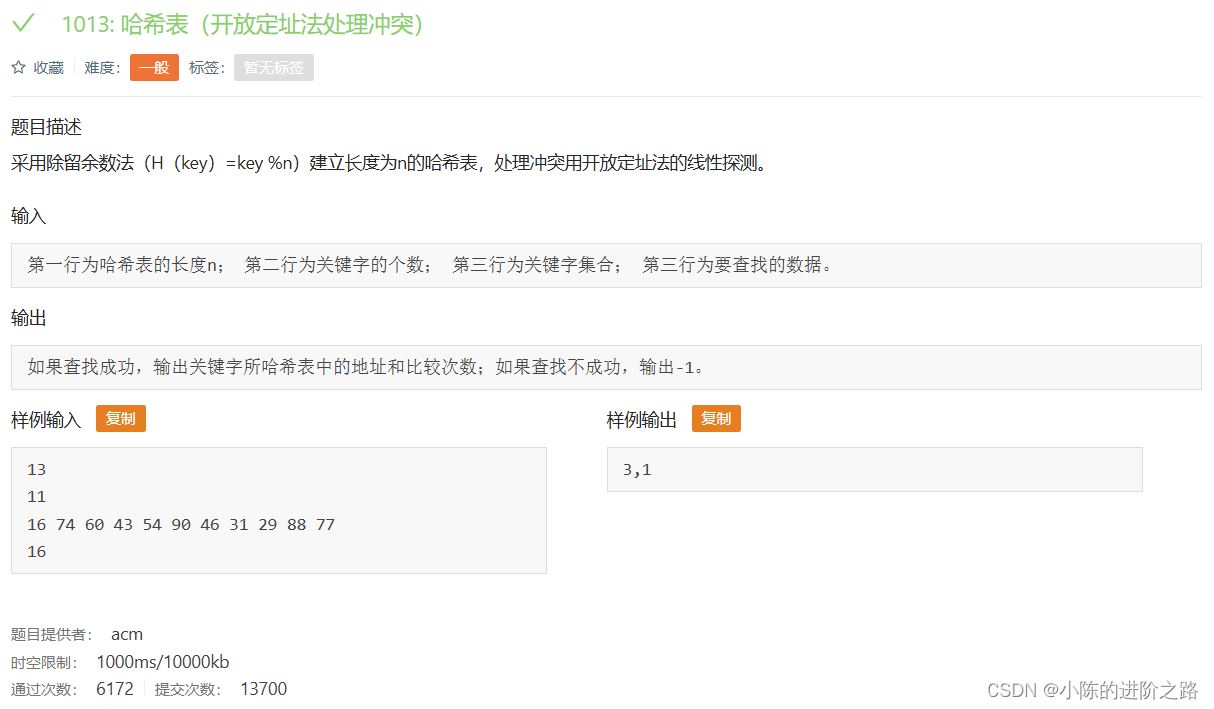
#include"iostream"
#include"cstring"
using namespace std;
const int N=200003,null=0x3f3f3f3f;
int h[N];
int n;
int m;
int a[100];
int key;
int cnt;
int find(int x,int size)
{
cnt=1;
int t=x%size;
while(h[t]!=x&&h[t]!=null)
{
cnt++;
t++;
if(t==size) t=0;
}
return t;
}
int main()
{
memset(h,0x3f,sizeof h);
cin>>n;
int data=0;
cin>>m;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>data;
h[find(data,n)]=data;
}
cin>>key;
if(h[find(key,n)]==null) cout<<"-1";
else cout<<find(key,n)<<','<<cnt;
}
1011: 二叉排序树的实现和查找
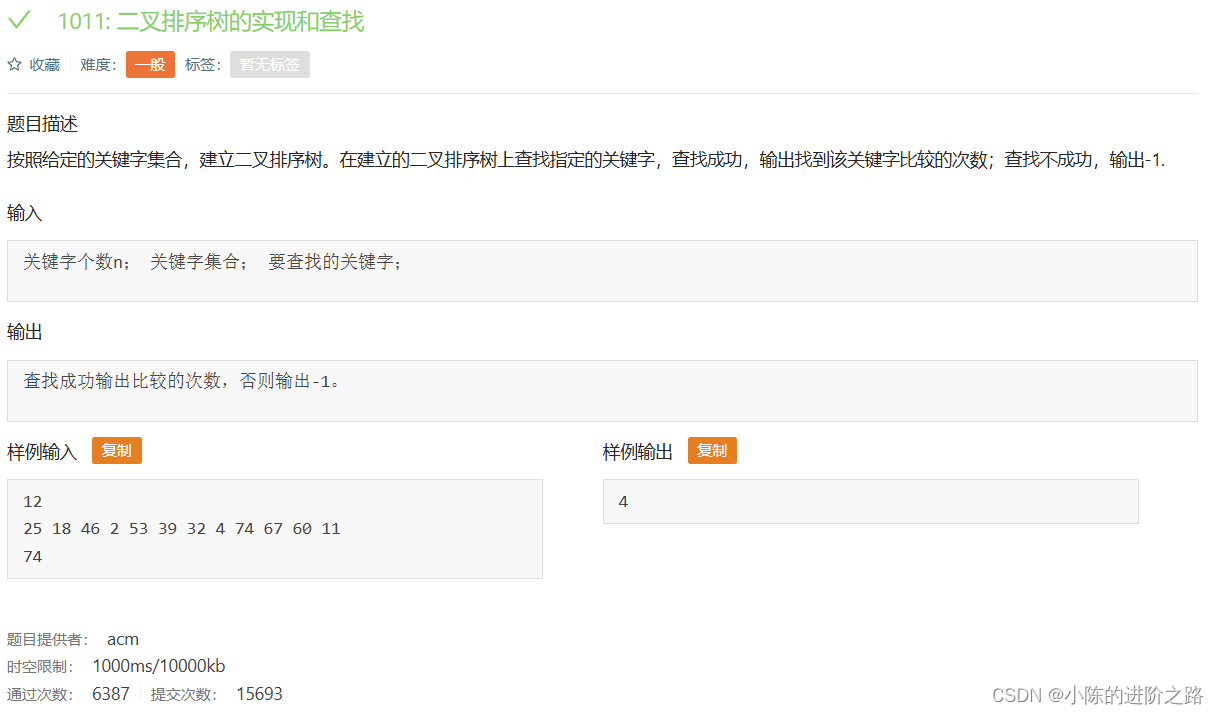
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
int a[100];
int n;
typedef struct tree
{
struct tree* left,*right;
char data;
}tree;
tree* buynode(char ch)
{
tree* root=(tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree));
root->data=ch;
root->left=root->right=NULL;
return root;
}
tree* insert(tree* root,int x)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
root=buynode(x);
return root;
}
if(root->data<x)
{
root->right=insert(root->right,x);
}
if(root->data>x)
{
root->left=insert(root->left,x);
}
return root;
}
void create(tree*& root,int a[])
{
root=NULL;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
root=insert(root,a[i]);
}
}
int cnt=0;
tree* find(tree* root,int key)
{
if(root==NULL) return NULL;
if(key<root->data)
{
cnt++;
return find(root->left,key);
}
if(root->data<key)
{
cnt++;
return find(root->right,key);
}
if(root->data==key)
{
return root;
}
}
int key;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
cin>>key;
tree* root=NULL;
create(root,a);
if(find(root,key)==NULL) cout<<"-1";
else cout<<cnt+1;
}
1016: 插入排序算法实现
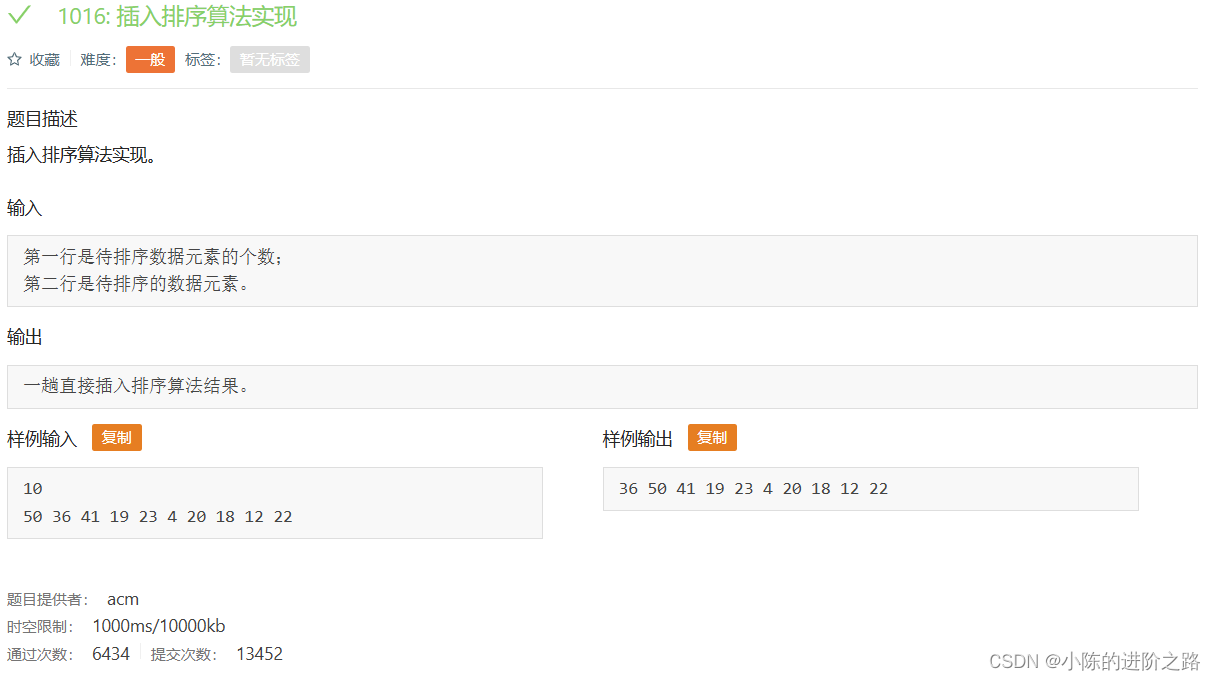
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
int n;
int x;
int b[100];
int a[100];
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int end=i;
int tmp=a[end];
while(end-1>=0)
{
if(a[end-1]>tmp)
{
a[end]=a[end-1];
end-=1;
}
}
a[end]=tmp;
break;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
}
1099: 希尔排序算法实现
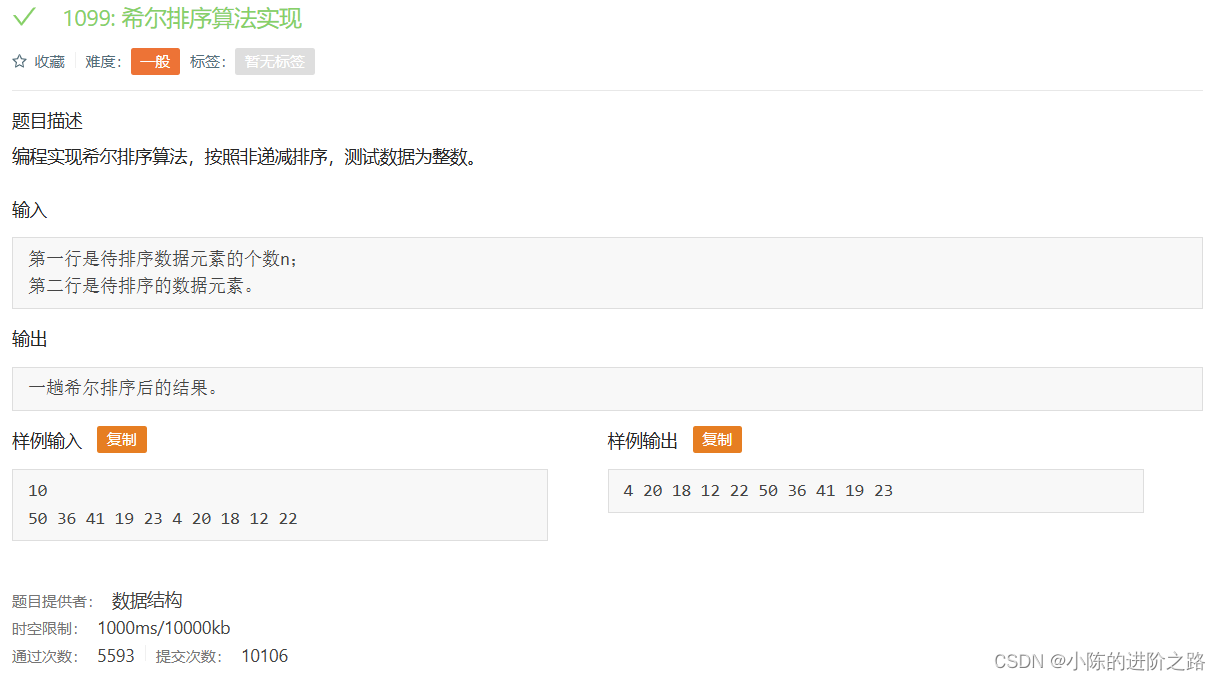
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
char s[100];
#include"cstring"
int n;
int a[100];
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
int gap=5;
for(int i=0;i<gap;i++)
{
int end=i;
int tmp=a[end+gap];
while(end>=0)
{
if(a[end]>tmp)
{
a[end+gap] =a[end];
end-=gap;
}
}
a[end+gap]=tmp;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
}
980: 输出利用先序遍历创建的二叉树的层次遍历序列
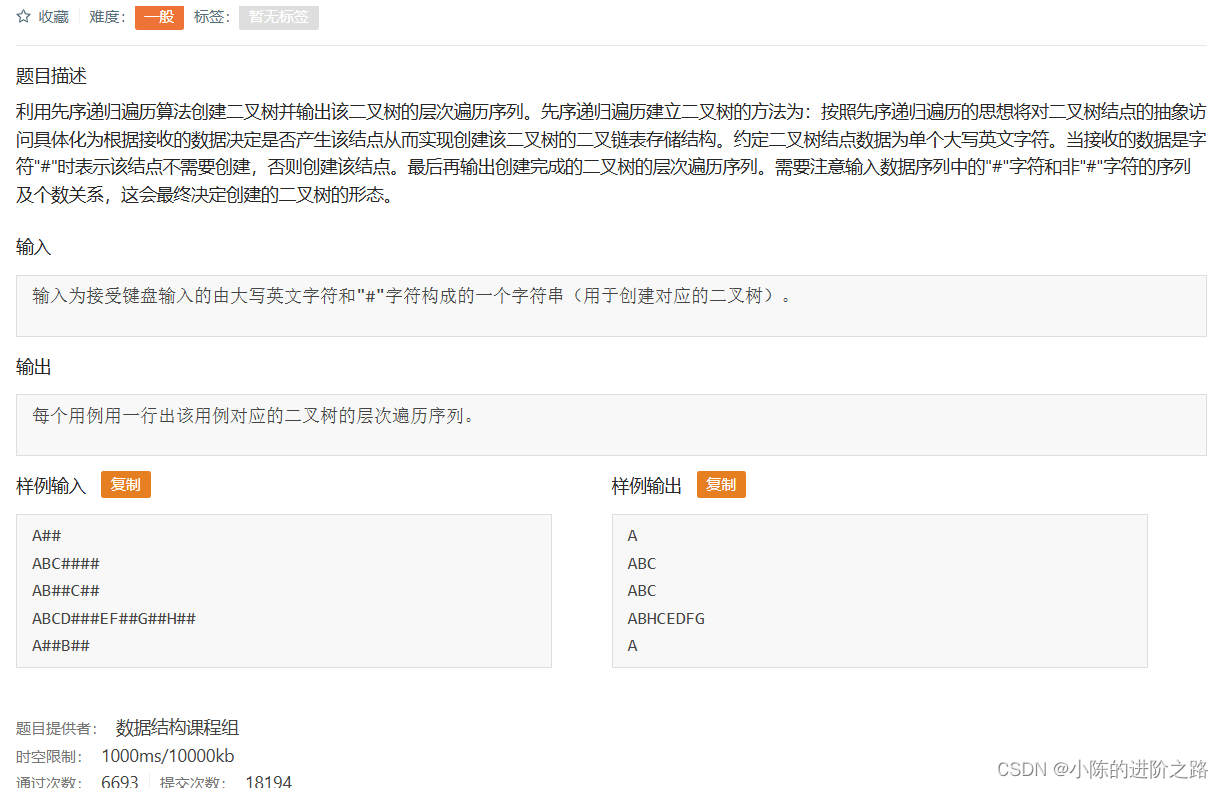
#include"iostream"
#include"queue"
using namespace std;
typedef struct node
{
struct node* left,*right;
char data;
}node,*tree;
tree create()
{
tree t;
char ch;
cin>>ch;
if(ch=='#')
{
return NULL;
}
else
{
t=new node;
t->data=ch;
t->left=create();
t->right=create();
}
return t;
}
void f(tree t)
{
queue<tree>q;
q.push(t);
tree p;
p=q.front();
while(!q.empty())
{
cout<<q.front()->data;
p=q.front();
q.pop();
if(p->left!=NULL)
{
q.push(p->left);
}
if(p->right!=NULL)
{
q.push(p->right);
}
}
}
int main()
{
tree t=create();
f(t);
}
987: 输出用先序遍历创建的二叉树是否为完全二叉树的判定结果
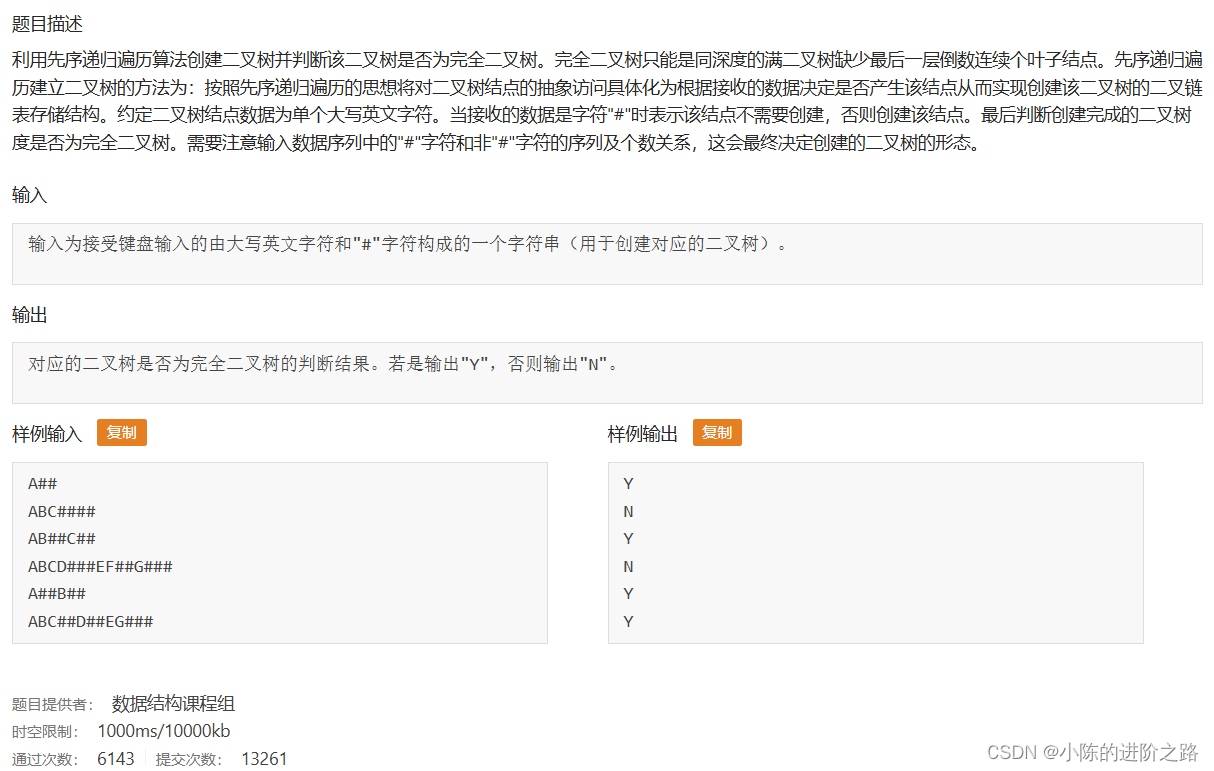
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
char s[100];
#include"queue"
typedef struct node
{
struct node*left,*right;
char data;
}node,*tree;
tree create()
{
tree t;
char ch;
cin>>ch;
if(ch=='#')
{
return NULL;
}
else
{
t=new node;
t->data=ch;
t->left=create();
t->right=create();
}
return t;
}
bool f(tree t)
{
queue<tree>q;
tree p;
q.push(t);
p=q.front();
int flag=0;
while(!q.empty())
{
p=q.front();
q.pop();
if(p->left!=NULL)
{
q.push(p->left);
}
else
{
flag=1;
}
if(p->right!=NULL&&flag==0)
{
q.push(p->right);
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main()
{
tree t=create();
if(f(t)==1) cout<<"Y";
else cout<<"N";
}
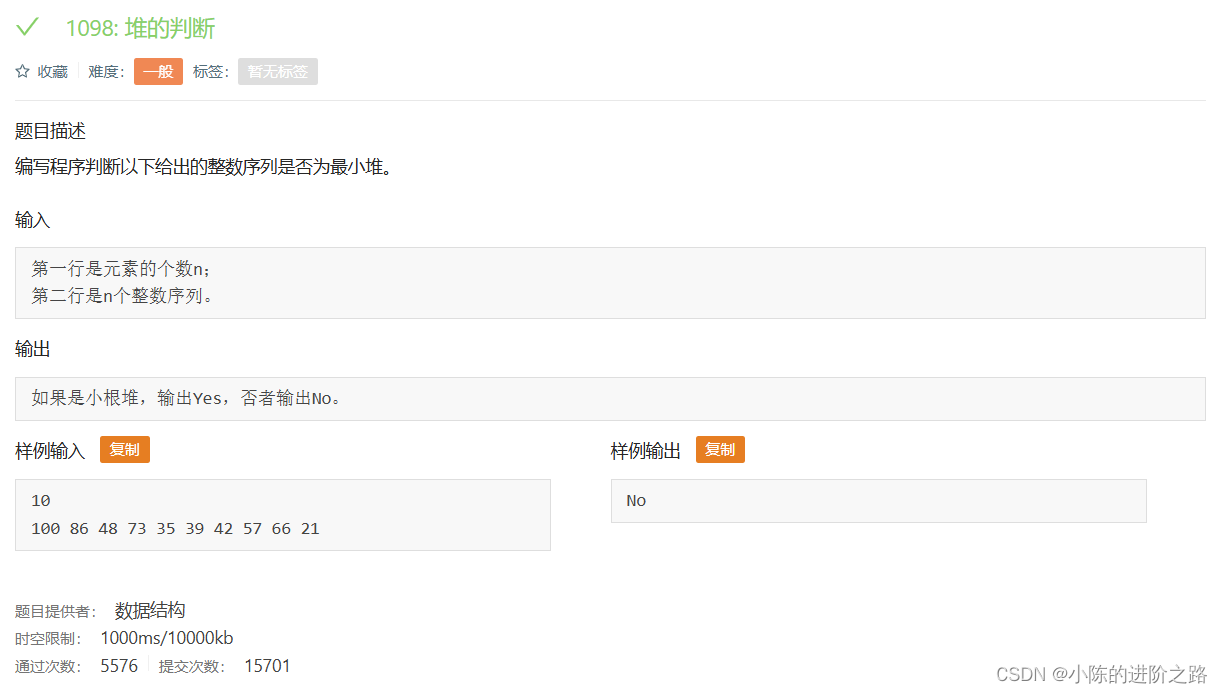
1098: 堆的判断
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
char s[100];
#include"cstring"
int n;
int a[100];
int judge(int parent,int n)
{
int child=parent*2;
if(child<=n)
{
if(child<n)
{
if(a[child+1]<a[child])
child++;
}
if(a[parent]<a[child])
return 1;
else return 0;
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=n/2;i>=1;i--)
{
if(judge(i,n)==0)
{
cout<<"No";
return 0;
}
}
cout<<"Yes";
}
1015: 堆排序算法
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
int a[100];
int n;
void sort(int parent,int n)
{
int child=parent*2;
int top=a[parent];
while(child<=n)
{
if(child<n)
{
if(a[child+1]<a[child])
{
child++;
}
}
if(a[child]<top)
{
a[parent]=a[child];
parent=child;
child=parent*2;
}
}
a[parent]=top;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=n/2;i>=1;i--)
{
sort(i,n);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
}
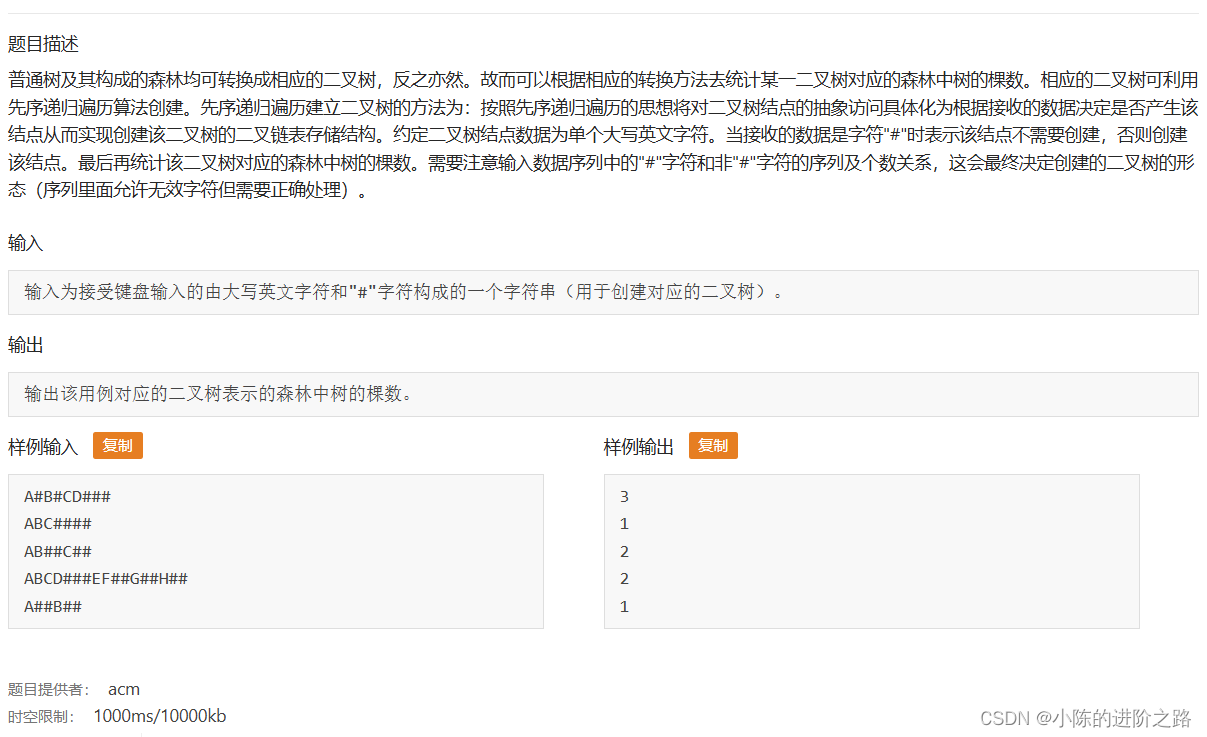
981: 统计利用二叉树存储的森林中树的棵数
#include"iostream"
#include"queue"
using namespace std;
typedef struct tree
{
struct tree* left,*right;
char data;
}tree;
tree* buynode(char ch)
{
tree* root=(tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree));
root->data=ch;
root->left=root->right=NULL;
return root;
}
tree* create(char s[],int* data)
{
if(s[*data]=='#'||s[*data]=='\0')
{
(*data)++;
return NULL;
}
tree* root=buynode(s[*data]);
(*data)++;
root->left=create(s,data);
root->right=create(s,data);
return root;
}
int forest(tree* root)
{
int count=0;
if(root==NULL) return 0;
if(root->right==NULL) return 0;
if(root->right!=NULL) count=1;
return forest(root->right)+count;
}
int main()
{
char s[100];
while(scanf("%s",s)!=EOF)
{
int data=0;
tree* root=create(s,&data);
cout<<forest(root)+1;
}
}
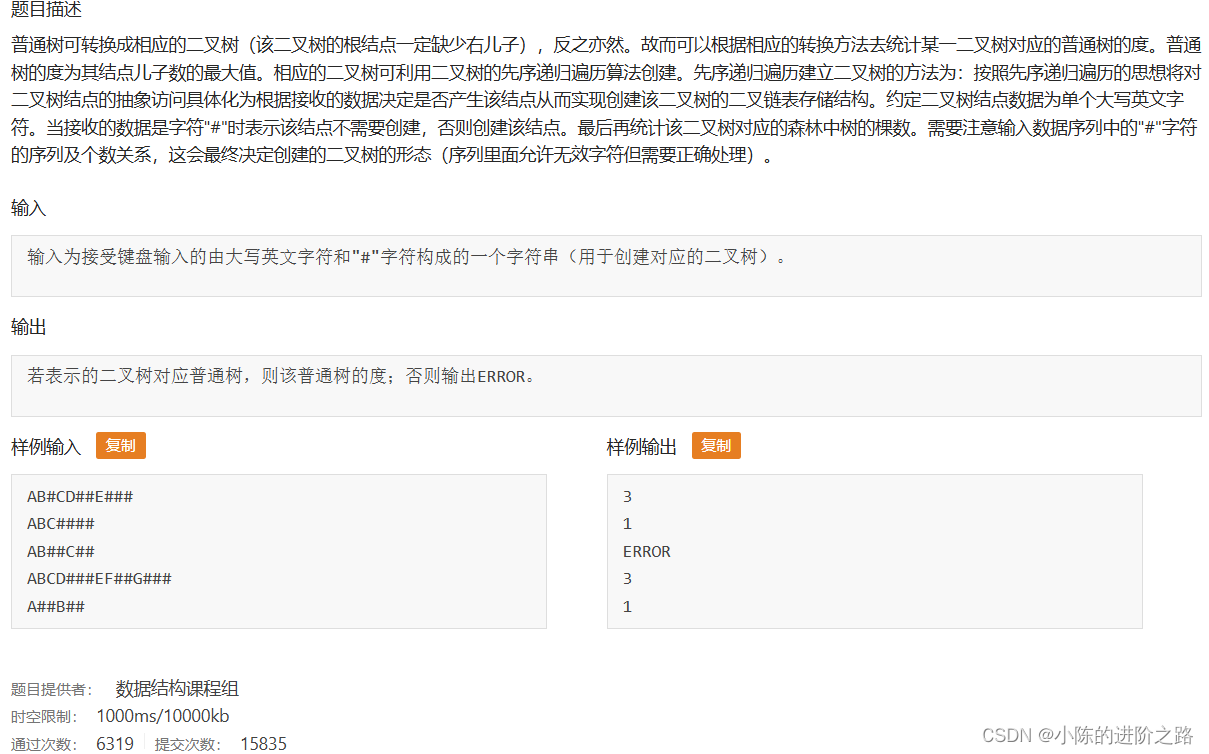
982: 输出利用二叉树存储的普通树的度
#include"iostream"
#include"queue"
using namespace std;
typedef struct tree
{
struct tree* left,*right;
char data;
}tree;
tree* buynode(char ch)
{
tree* root=(tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree));
root->data=ch;
root->left=root->right=NULL;
return root;
}
tree* create(char s[],int*data)
{
if(s[*data]=='#'||s[*data]=='\0')
{
(*data)++;
return NULL;
}
tree* root=buynode(s[*data]);
(*data)++;
root->left=create(s,data);
root->right=create(s,data);
return root;
}
int lf(tree* root)
{
int count=0;
if(root==NULL) return NULL;
if(root->right!=NULL) count=1;
return lf(root->right)+count;
}
int forest(tree* root)
{
if(root==NULL) return 0;
if(root->right!=NULL) return 0;
tree* lrof=root->left;
lf(lrof);
return lf(lrof)+1;
}
int main()
{
char s[100];
while(scanf("%s",s)!=EOF)
{
int data=0;
tree* root=create(s,&data);
if(forest(root)==0) cout<<"ERROR";
else cout<<forest(root);
}
}
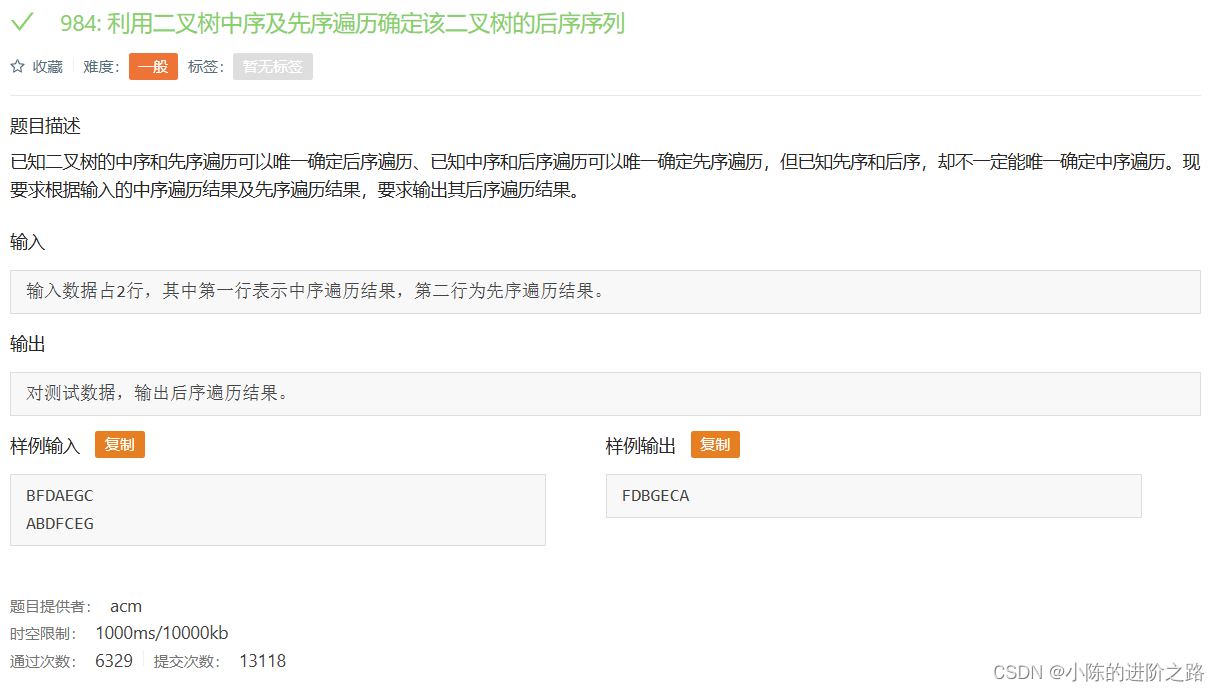
984: 利用二叉树中序及先序遍历确定该二叉树的后序序列
#include"iostream"
#include"queue"
#include"string.h"
using namespace std;
typedef struct tree
{
struct tree* left,*right;
char data;
}tree;
tree* buynode(char ch)
{
tree* root=(tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree));
root->data=ch;
root->left=root->right=NULL;
return root;
}
tree* later(char* prder,char* order,int x)
{
if(x==0) return NULL;
char *p=NULL;
int t=0;
for(p=order;p<order+x;p++)
{
if(*p==prder[0])
{
break;
}
else
{
t++;
}
}
tree* root=buynode(prder[0]);
root->left=later(prder+1,order,t);
root->right=later(prder+1+t,order+t+1,x-t-1);
return root;
}
void print(tree* root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
print(root->left);
print(root->right);
cout<<root->data;
}
}
int main()
{
char order[100];
char prder[100];
cin>>order;
cin>>prder;
tree*root=later(prder,order,strlen(prder));
print(root);
}
986: 哈夫曼译码
const int maxvalue=100;
const int maxbit=100;
const int maxn=100;
#include "iostream"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
using namespace std;
struct haffnode
{
char ch;
int weight;
int flag;
int parent;
int leftchild;
int rightchild;
};
struct code
{
int bit[maxn];
int start;
int weight;
char ch;
};
void haffman(int weight[],char text[],int n,haffnode hafftree[])
{
int j,m1,m2,x1,x2,i;
for(i=0;i< 2*n-1;i++)
{
if(i < n)
{
hafftree[i].weight=weight[i];
hafftree[i].
ch=text[i];
}
else
{
hafftree[i].weight=0;
hafftree[i].ch='#';
}
hafftree[i].parent=0;
hafftree[i].flag=0;
hafftree[i].leftchild=-1;
hafftree[i].rightchild=-1;
}
for(i=0;i< n-1;i++)
{
m1=m2=maxvalue;
x1=x2=0;
for(j=0;j< n+i;j++)
{
if(hafftree[j].weight< m1&&hafftree[j].flag==0)
{
m2=m1;
x2=x1;
m1=hafftree[j].weight;
x1=j;
}
else if(hafftree[j].weight< m2&&hafftree[j].flag==0)
{
m2=hafftree[j].weight; x2=j;
}
}
hafftree[x1].parent=n+i;
hafftree[x2].parent=n+i;
hafftree[x1].flag=1;
hafftree[x2].flag=1;
hafftree[n+i].weight=hafftree[x1].weight+hafftree[x2].weight;
hafftree[n+i].leftchild=x1; hafftree[n+i].rightchild=x2;
}
}
void haffmancode(haffnode hafftree[],int n,code haffcode[])
{
code cd; int i,j; int child,parent;
for( i=0;i< n;i++)
{
cd.start=n-1;
cd.weight=hafftree[i].weight;
cd.ch=hafftree[i].ch;
child=i;
parent=hafftree[child].parent;
while(parent!=0)
{
if(hafftree[parent].leftchild==child)
cd.bit[cd.start]=0;
else cd.bit[cd.start]=1;
cd.start--;
child=parent;
parent=hafftree[child].parent;
}
for(j=cd.start+1;j< n;j++)
haffcode[i].bit[j]=cd.bit[j];
haffcode[i].start=cd.start;
haffcode[i].weight=cd.weight;
haffcode[i].ch=cd.ch;
}
}
#include"string.h"
void ccode(haffnode hafftree[],int n)
{
char str[100];
cin>>str;
int treenode=n*2-2;
int len=strlen(str);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(str[i]=='0')
{
treenode=hafftree[treenode].leftchild;
}
if(str[i]=='1')
{
treenode=hafftree[treenode].rightchild;
}
if(hafftree[treenode].leftchild==-1||hafftree[treenode].rightchild==-1)
{
cout<<hafftree[treenode].ch;
treenode=n*2-2;
}
}
}
int main( )
{
int n=8;
int weight[]={5,29,7,8,14,23,3,11};
char text[]={'a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h'};
haffnode myhafftree[maxvalue];
code myhaffcode[maxvalue];
haffman(weight,text,n,myhafftree);
haffmancode(myhafftree,n,myhaffcode);
ccode(myhafftree,n);
return 0;
}
1105: 交换二叉树的孩子结点
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
char s[100];
typedef struct tree
{
struct tree* left,*right;
char data;
}tree;
tree* buynode(char ch)
{
tree* root=(tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree));
root->data=ch;
root->left=root->right=NULL;
return root;
}
tree* create(char s[],int*data)
{
if(s[*data]=='#'||s[*data]=='\0')
{
(*data)++;
return NULL;
}
tree* root=buynode(s[*data]);
(*data)++;
root->left=create(s,data);
root->right=create(s,data);
return root;
}
void order(tree* root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
order(root->right);
cout<<root->data;
order(root->left);
}
}
void prder(tree* root)
{
if(root!=NULL)
{
cout<<root->data;
prder(root->right);
prder(root->left);
}
}
int main()
{
cin>>s;
int data=0;
tree* root=create(s,&data);
order(root);
cout<<endl;
prder(root);
}
1077: 平衡二叉树的判定
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
char s[100];
#include"cstring"
typedef struct tree
{
struct tree* left,*right;
char data;
}tree;
tree* buynode(char ch)
{
tree* root=(tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree));
root->data=ch;
root->left=root->right=NULL;
return root;
}
tree* create(char s[],int* data)
{
if(s[*data]=='#'||s[*data]=='\0')
{
(*data)++;
return NULL;
}
tree* root=buynode(s[*data]);
(*data)++;
root->left=create(s,data);
root->right=create(s,data);
return root;
}
int depth(tree* root)
{
if(root==NULL) return 0;
int left=depth(root->left);
int right=depth(root->right);
return left>right?left+1:right+1;
}
bool balance(tree* root)
{
if(root==NULL) return 1;
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL) return 1;
int left=depth(root->left);
int right=depth(root->right);
return abs(left-right)<=1&&balance(root->left)
&&balance(root->right);
}
int main()
{
cin>>s;
int data=0;
tree* root=create(s,&data);
if(balance(root)==1) cout<<"yes!";
else cout<<"no!";
}
1014: 交换排序算法的设计与实现——冒泡排序
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
int a[100];
int n;
int main()
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
for(int j=i;j<n-i-1;j++)
{
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
{
int tmp=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=a[j];
a[j]=tmp;
}
}
break;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
}
1053: 输出利用先序遍历创建的二叉树中的指定结点的度
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
int a[100];
int n;
char s[100];
typedef struct tree
{
struct tree* left,*right;
char data;
}tree;
tree* buynode(char ch)
{
tree* root=(tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree));
root->data=ch;
root->left=root->right=NULL;
return root;
}
tree* create(char s[],int*data)
{
if(s[*data]=='#'||s[*data]=='\0')
{
(*data)++;
return NULL;
}
tree* root=buynode(s[*data]);
(*data)++;
root->left=create(s,data);
root->right=create(s,data);
return root;
}
int find(tree* root,char* key)
{
if(root==NULL) return 0;
if(root->data==*key)
{
if(root->left!=NULL&&root->right!=NULL) return 2;
else if(root->left!=NULL||root->right!=NULL) return 1;
else return 0;
}
int left=find(root->left,key);
int right=find(root->right,key);
if(left>0||right>0)
return 1;
}
int main()
{
cin>>s;
char key;
cin>>key;
int data=0;
tree* root=create(s,&data);
cout<<find(root,&key);
}
1010: 折半查找的实现
#include"iostream"
using namespace std;
int a[100];
int main()
{
int n=0;
cin>>n;
int data=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
int key=0;
cin>>key;
int left=0;
int right=n-1;
int cnt=0;
while(left<=right)
{
int mid=(left+right)/2;
if(a[mid]<key)
{
left=mid+1;
cnt++;
}
if(a[mid]>key)
{
right=mid-1;
cnt++;
}
if(a[mid]==key)
{
cout<<mid<<endl<<cnt;
return 0;
}
}
cout<<"-1"<<endl<<cnt;
}




































![[Android] 青木扫描全能文档3.0,支持自动扫描功能](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/6c0892c8f11746db8fba79f7ed7eac30.png)