1. 内容安排说明
二叉树在前面C数据结构阶段已经讲过,本节取名二叉树进阶是因为:
1. map和set特性需要先铺垫二叉搜索树,而二叉搜索树也是一种树形结构
2. 二叉搜索树的特性了解,有助于更好的理解map和set的特性
3. 二叉树中部分面试题稍微有点难度,在前面讲解大家不容易接受,且时间长容易忘
4. 有些OJ题使用C语言方式实现比较麻烦,比如有些地方要返回动态开辟的二维数组,非常麻 烦。 因此本节借二叉树搜索树,对二叉树部分进行收尾总结。
2. 二叉搜索树实现
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
1若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
2若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
3它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树

2.1二叉搜索树操作
接下来我们对于搜索二叉树的分析都是基于这个树来进行的

1二叉树的搜索
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
if (_root->_key == key)
{
return _root;
}
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return cur;
}
}
return nullptr;
}2二叉树的构建
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
//先找到符合的位置,再进行插入
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return false;//搜索二叉树不允许重复
}
}
//这时候找到位置了进行链接
cur = new Node(key);
if (prev->_key < key)
{
prev->_right = cur;
}
else
{
prev->_left = cur;
}
return true;
}3二叉树的删除
这里的删除分为三个场景
1删除的节点为叶子节点(没有子节点)(这里直接删除就行了)
2删除的节点有一个子节点
3删除的节点有两个子节点
这里就要用到替换法(左树的最大节点或者右树的最小节点)
具体代码:
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
//这里要保留parent 就不复用Find函数了
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else//找到了
{
//接下来根据各个场景依次判断
//如果左右其中一个为空,那么属于第一类,直接将空的另一边连接到parent
//左为空
if (cur->_left == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)//防止parent为空
{
_root = cur->_right;
}
else
{
if (parent->_key < cur->_key)
{
parent->_right = cur->_right;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
}//右为空
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)
{
if (cur == _root)//防止parent为空
{
_root = cur->_left;
}
else
{
if (parent->_key < cur->_key)
{
parent->_right = cur->_left;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
}
}
else//左右都不为空,我们找左树最大的来替代
{
parent = cur;//防止parent 为空
Node* LeftMax = cur->_left;
while (LeftMax->_right)
{
parent = LeftMax;
LeftMax = LeftMax->_right;
}
//找到最大的就替换
cur->_key = LeftMax->_key;
//再将这个节点删除,这个节点可能有左树
if (LeftMax == cur->_left)
{
parent->_left = LeftMax->_left;
}
else//这时候要特殊处理
{
parent->_right = LeftMax->_left;
}
cur = LeftMax;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
}
//没找到
return false;
}接下来我们用递归实现二叉搜索树的递归版本
1查找
public:
//递归版本的查找
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
private:
Node* _FindR(Node* root,const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
if (root->_key == key)
{
return root;
}
else if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
}2插入
插入这里就要讲的很多了,这里_InsertR用的是引用返回(这是指针和引用的结合),这就给我们省下了很多力气,因为不用再去判断这个节点是parent 的左树还是右树

public:
//递归版本的插入
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
private:
bool _InsertR(Node* &root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
//这时候要注意,指针加引用很厉害
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
_InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
_InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}3删除
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
//要转化为子问题分置
if (root->_key < key)
{
_EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
_EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else //找到了
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)
{
root = root->_left;
}
else //3左右都不为空
{
Node* leftMax = root->_left ;
while (leftMax->_right)
{
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}
swap(leftMax->_key, root->_key);
//这一步很精髓
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
这里一定是返回了,不然还会走下面删除,就删除多了
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
这里最后_EraseR的时候不能传leftMax,因为传leftMax有些情况删不掉
以上三个基本的完成了,剩下的destory走一个后续删除就可以了
3.二叉树搜索树应用分析
二叉搜索树在实际应用当中很常见
有两个模型
1key的搜索模型:快速判断不在的场景
门禁系统,小区车辆出入系统
2,key.value的搜索模型:通过一个值,去找另外一个值
商场的车辆出入系统模型(车牌号和入场时间联系起来)
4. 二叉树进阶面试题
606. 根据二叉树创建字符串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
这一题根本就是前序
要注意
1当左树为空,右树为空,都不加括号
2左树不为空,右树为空,右树不加括号
3左树为空,右树不为空,左树加括号
class Solution {
public:
string tree2str(TreeNode* root) {
if(root==nullptr)
{
return "";
}
string str=to_string(root->val);
if(root->left || root->right)
{
str+="(";
str+=tree2str(root->left);
str+=")";
}
if(root->right)
{
str+="(";
str+=tree2str(root->right);
str+=")";
}
return str;
}
};236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public:
bool Find(TreeNode* root,int val)
{
if(root==nullptr)
return false;
if(root->val==val)
return true;
return Find(root->left,val) || Find(root->right,val);
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root==nullptr)
return nullptr;
if(p==root || q == root)
{
return root;
}
bool pleft,pright,qleft,qright;
pleft = Find(root->left,p->val);
pright = !pleft;
qleft = Find(root->left,q->val);
qright = !qleft;
if(pleft && qleft)
{
return lowestCommonAncestor( root->left, p, q);
}
else if(pright && qright)
{
return lowestCommonAncestor( root->right, p, q);
}
else
{
return root;
}
}
};这里的解法就是暴力求解,我们可以优化解法让它达到O(N)
就是如果能倒着走,就可以转化为链表相交
这里就用一个栈来实现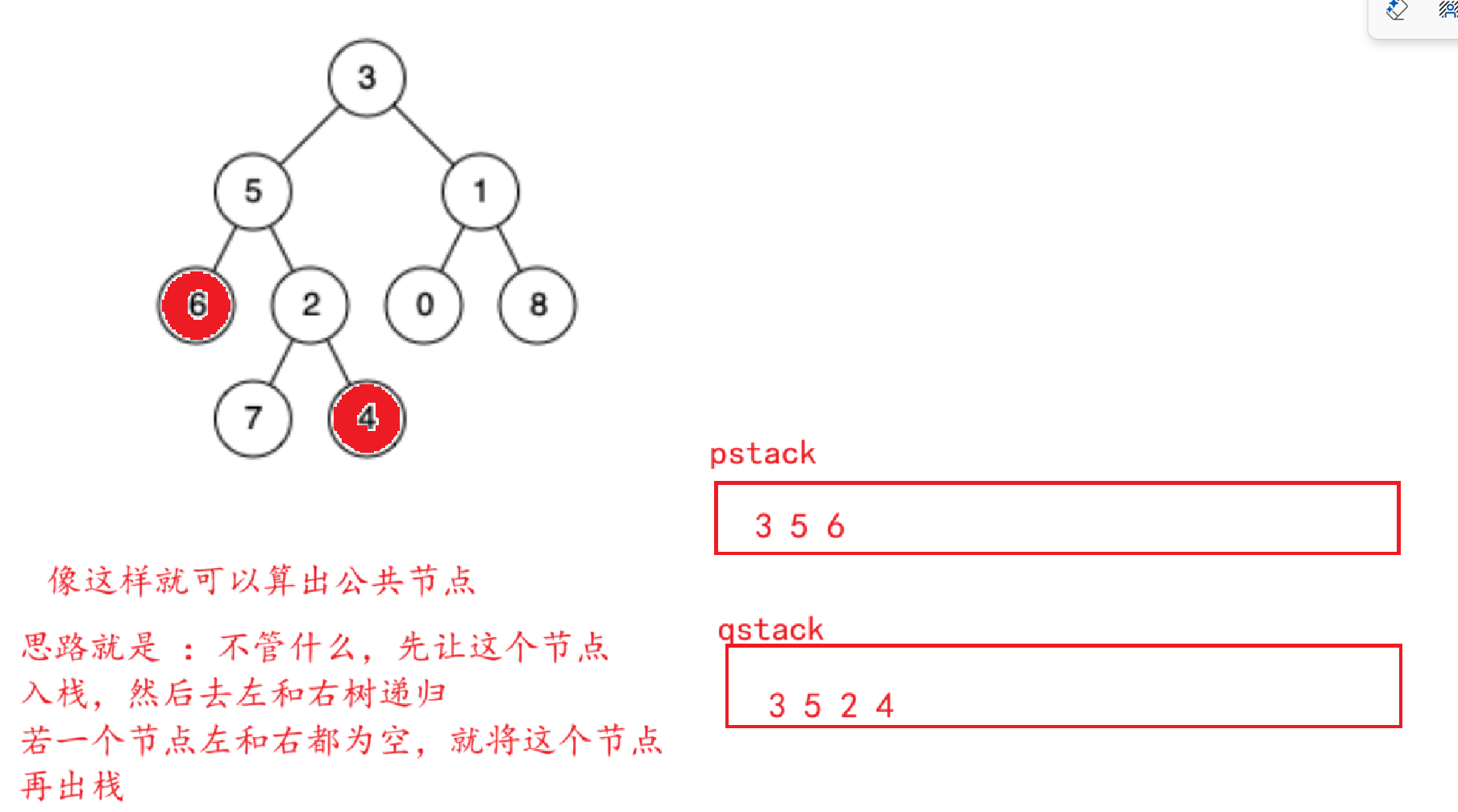
class Solution {
public:
bool CreatStack(TreeNode* root,stack<TreeNode*>& st,TreeNode* x)
{
if(root==nullptr)
return false;
st.push(root);
if(root==x)
{
return true;
}
//左右两边找到了就返回
if(CreatStack(root->left,st,x))
return true;
if(CreatStack(root->right,st,x))
return true;
st.pop();
return false;
}
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
stack<TreeNode*> pstack,qstack;
CreatStack(root,pstack,p);
CreatStack(root,qstack,q);
while(pstack.size()>qstack.size())
{
pstack.pop();
}
while(pstack.size()<qstack.size())
{
qstack.pop();
}
while(pstack.top()!=qstack.top())
{
pstack.pop();
qstack.pop();
}
return pstack.top();
}
};二叉搜索树与双向链表_牛客题霸_牛客网
这种写法是实在写不出来就这样写
class Solution {
public:
void Inorder(TreeNode* root,vector<TreeNode*> &v)
{
if(root==nullptr)
{
return ;
}
Inorder(root->left,v);
v.push_back(root);
Inorder(root->right,v);
}
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
vector<TreeNode*> vt;
Inorder(pRootOfTree,vt);
TreeNode* root = vt[0];
TreeNode* end = vt[vt.size()-1];
root->right = vt[1];
end->left = vt[vt.size()-2];
for(size_t i = 1;i<vt.size()-1;i++)
{
vt[i]->left = vt[i-1];
vt[i]->right = vt[i+1];
}
root->left = nullptr;
end->right = nullptr;
return root;
}
};这个才是正解
class Solution {
public:
void _Convert(TreeNode* cur,TreeNode* &prev)
{
if(cur==nullptr)
{
return ;
}
_Convert(cur->left,prev);
//中序
cur->left = prev;
if(prev)
{
prev->right = cur;
}
prev = cur;
_Convert(cur->right,prev);
}
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree ==nullptr)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* head = pRootOfTree;
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
while(head->left)
{
head = head->left;
}
_Convert(pRootOfTree, prev);
head->left==nullptr;
return head;
}
};
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
前序:根 左子树 右子树
中序:左子树 根 右子树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder,
int& i,int begin,int end)
{
if(begin>end)
{
return nullptr;
}
//建立根节点
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(preorder[i]);
//查找根节点位置,分出左右区间
int rooti = begin;
while(rooti<=end)
{
if(preorder[i]==inorder[rooti])
{
break;
}
rooti++;
}
i++;
//区间就是[begin,rooti-1]rooti[rooti+1,end]
root->left = _buildTree(preorder,inorder,i,begin,rooti-1);
root->right = _buildTree(preorder,inorder,i,rooti+1,end);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int i = 0;
int begin = 0;
int end = inorder.size()-1;
TreeNode* root = _buildTree(preorder,inorder,i,begin,end);
return root;
}
};106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
这两题就差不多,就是后续的时候倒着遍历posorder
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* _buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder,int& posi,int begin ,int end)
{
if(begin>end)
{
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(postorder[posi]);
int rooti = begin;
while(rooti<=end)
{
if(inorder[rooti]==postorder[posi])
break;
rooti++;
}
posi--;
root->right = _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posi,rooti+1,end);
root->left = _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posi,begin,rooti-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
int posi = postorder.size()-1;
int begin = 0;
int end = inorder.size()-1;
TreeNode* root = _buildTree(inorder,postorder,posi,begin,end);
return root;
}
};144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
这个要求是非递归实现,这就与我们之前搞的不同了,递归实现很简单,非递归就是用迭代的方式来实现
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode* cur = root;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
vector<int> v;
while(cur || !st.empty())
{
//1先访问左树节点
while(cur)
{
st.push(cur);
v.push_back(cur->val);
cur = cur->left;
}
//这里左树为空了
cur = st.top();
st.pop();
//以子问题的方式访问右树
cur = cur->right;
}
return v;
}
};94. 二叉树的中序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
这一题复制上一题的模板,就是在将要访问右树的时候在push_back;
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode* cur = root;
stack<TreeNode*> st;
TreeNode* prev = nullptr;
vector<int> v;
while(cur || !st.empty())
{
//1先访问左树节点
while(cur)
{
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
//cur是指要取访问的节点
//top取出来判断后决定cur的指向
TreeNode* top = st.top();
if(top->right==nullptr || top->right == prev)
{
//这时候不用访问
prev = top;
v.push_back(top->val);
st.pop();
}
else
{
cur =top->right;
}
}
return v;
}
};








![[春秋云镜] Brute4Road 仿真场景](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c9178adb040a474dbc0ca735e851daed.png)