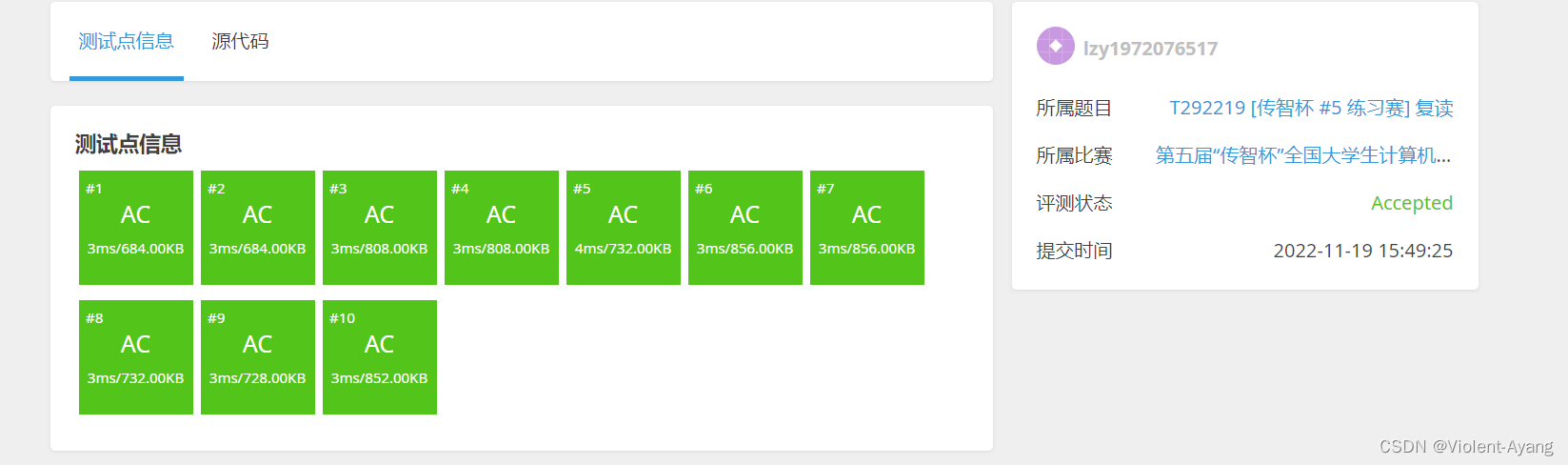
[传智杯 #5 练习赛] 复读
题目描述
给定若干个字符串,不定数量,每行一个。有些字符串可能出现了多次。如果读入一个字符串后,发现这个字符串以前被读入过,则这个字符串被称为前面相同的字符串的复读,这个字符串被称为复读字符串。相应的,每个首次出现的字符串就是非复读字符串。
举个例子,
abc
def
abc
abc
abc
第
1
,
3
,
4
,
5
1,3,4,5
1,3,4,5 行是字符串 abc,那么
3
,
4
,
5
3,4,5
3,4,5 行的字符串会被称为“复读”。
请你把所有的非复读字符串,按照行号从小到大的顺序,依次拼接为一个长串并输出。
输入格式
多个字符串,每行一个,含义见题目描述。
注意:如果这个字符串是 0,说明所有字符串都读完了。这个 0 不认为是一个“非复读字符串”。
输出格式
共一行,表示所有非复读字符串,按照行号从小到大依次连接的结果。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
cc
b
a
cc
0
样例输出 #1
ccba
提示
【数据范围】
字符串的个数不超过
500
500
500 个,字符串总长度不超过
50000
50000
50000,每个字符串中只包含小写字母、数字、 . 、! 和 &,不包含空格等特殊符号。
题解
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(){
char stringAll[501][1000];
int len = 0;
char tmp[1000];
scanf("%s",&tmp);
while(strcmp(tmp,"0") != 0){
strcpy(stringAll[len],tmp);
len++;
int flag = 0;
for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++){
if(strcmp(tmp,stringAll[i]) == 0){
flag = 1;
}
}
if(!flag){
printf("%s",tmp);
}
scanf("%s",&tmp);
}
return 0;
}
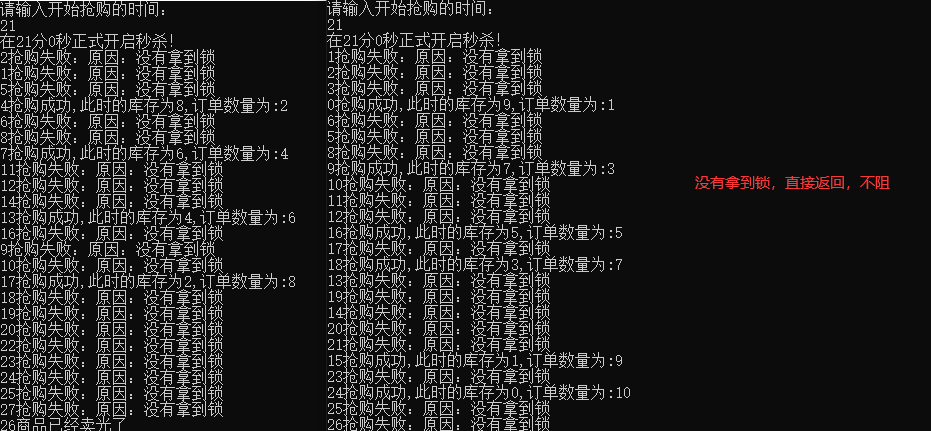




![[附源码]java毕业设计乒乓球俱乐部管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5951e63798284ee1a8ca88ad1878b918.png)