今天学习了如何用c语言拷贝一个文件,一个字符一个字符的拷贝一个文件,特此记录一下。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
FILE * pfr = fopen("1.txt", "r"); //打开文件1.txt 用读的模式
if (pfr == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
FILE* pfw = fopen("2.txt", "w"); //打开文件2.txt 用写的模式
if (pfw == NULL)
{ // 如果2.txt打开失败,就把1.txt的文件关闭,指针赋空值
fclose(pfr);
pfr = NULL;
return 0;
}
char ch = 0;
while ((ch = fgetc(pfr)) != EOF) // 循环读取1.txt的指针内容,只要不是EOF文件结束 ,就一直读
{
fputc(ch, pfw); // 把读到的内容写到2.txt中。
}
fclose(pfr); //关闭文件1
pfr = NULL; //指针赋空值
fclose(pfw); //关闭文件2
pfw = NULL; //指针赋空值
}
这样就把文件1中的所有内容都拷贝到了文件2中。
1、fprintf()函数
//int main()
//{
// struct s s = { "大家好!", 999, 3.1405926 };
// FILE* pf = fopen("1.txt", "w");
// if (pf == NULL)
// {
// perror("打开文件失败!");
// return 1;
// }
//
// // fprintf是 格式化输出到指定流,也可以指定到stdio到屏幕
// fprintf(pf, "%s %d %f", s.arr, s.a, s.b);
// fclose(pf);
// pf = NULL;
//}
2、fscanf()函数
/int main()
//{
// struct s s;
// FILE* pf = fopen("1.txt", "r");
// if (pf == NULL)
// {
// perror("打开文件失败!");
// return 1;
// }
//
// // fscanf从指定流中获取数据
// fscanf(pf, "%s %d %f", s.arr, &(s.a), &(s.b));
//
// printf("%s %d %f", s.arr, s.a, s.b);
// fclose(pf);
// pf = NULL;
//
// return 0;
//}
3、fwrite()
//int main()
//{
// struct S s = { "大家好!", 999, 3.1415962f };
// FILE* pf = fopen("1.txt", "w");
// if (NULL != pf)
// {
// // fwrite()以二进制的形式写入
// fwrite(&s, sizeof(struct S), 1, pf);
// fclose(pf);
// pf = NULL;
// }
//
// return 0;
//}
4、fread()
/int main()
//{
// struct S s = { 0 };
// FILE* pf = fopen("1.txt", "r");
// if (NULL != pf)
// {
// // fread()以二进制读取
// fread(&s, sizeof(struct S), 1, pf);
// fclose(pf);
// pf = NULL;
// }
// printf("%s %d %f", s.arr, s.a, s.b);
// return 0;
//}
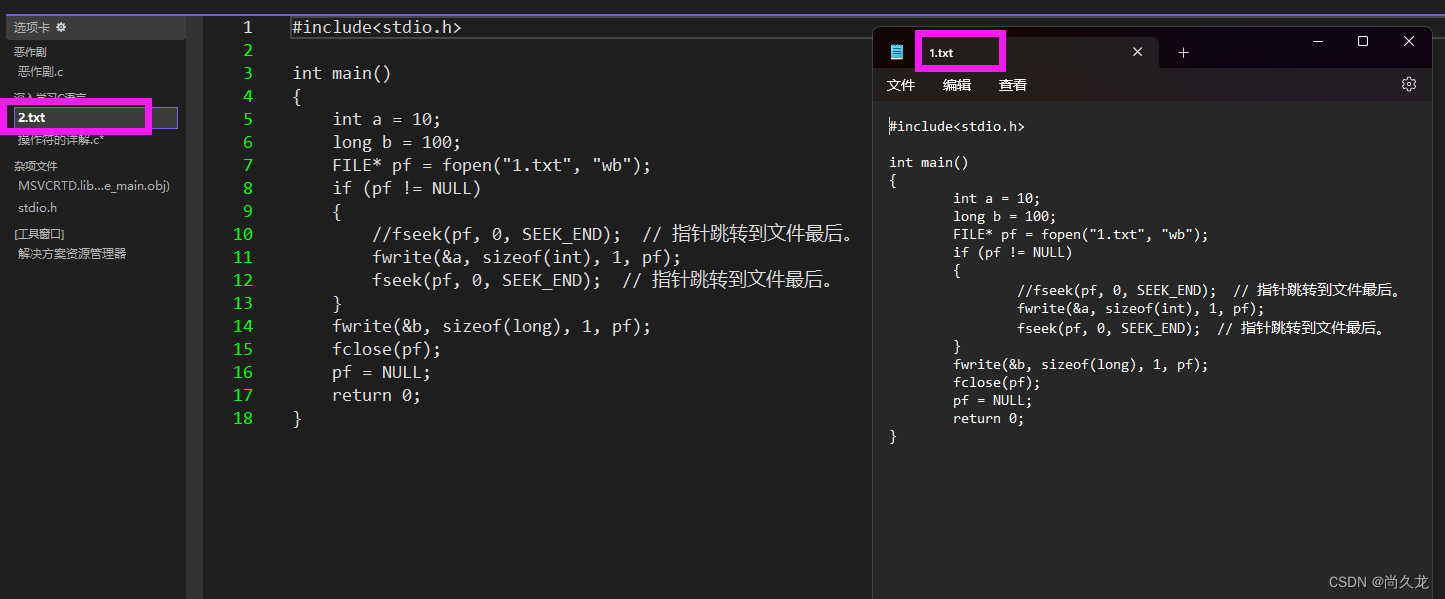
5、fseek(pf, -1, SEEK_CUR);// 重新定义文件指针的位置
6、printf("当前地址的距离文件起始位置的偏移量:%d\n", ftell(pf));
7、 rewind(pf); 让文件指针回到起始位置
8、scanf/fscanf/sscanf