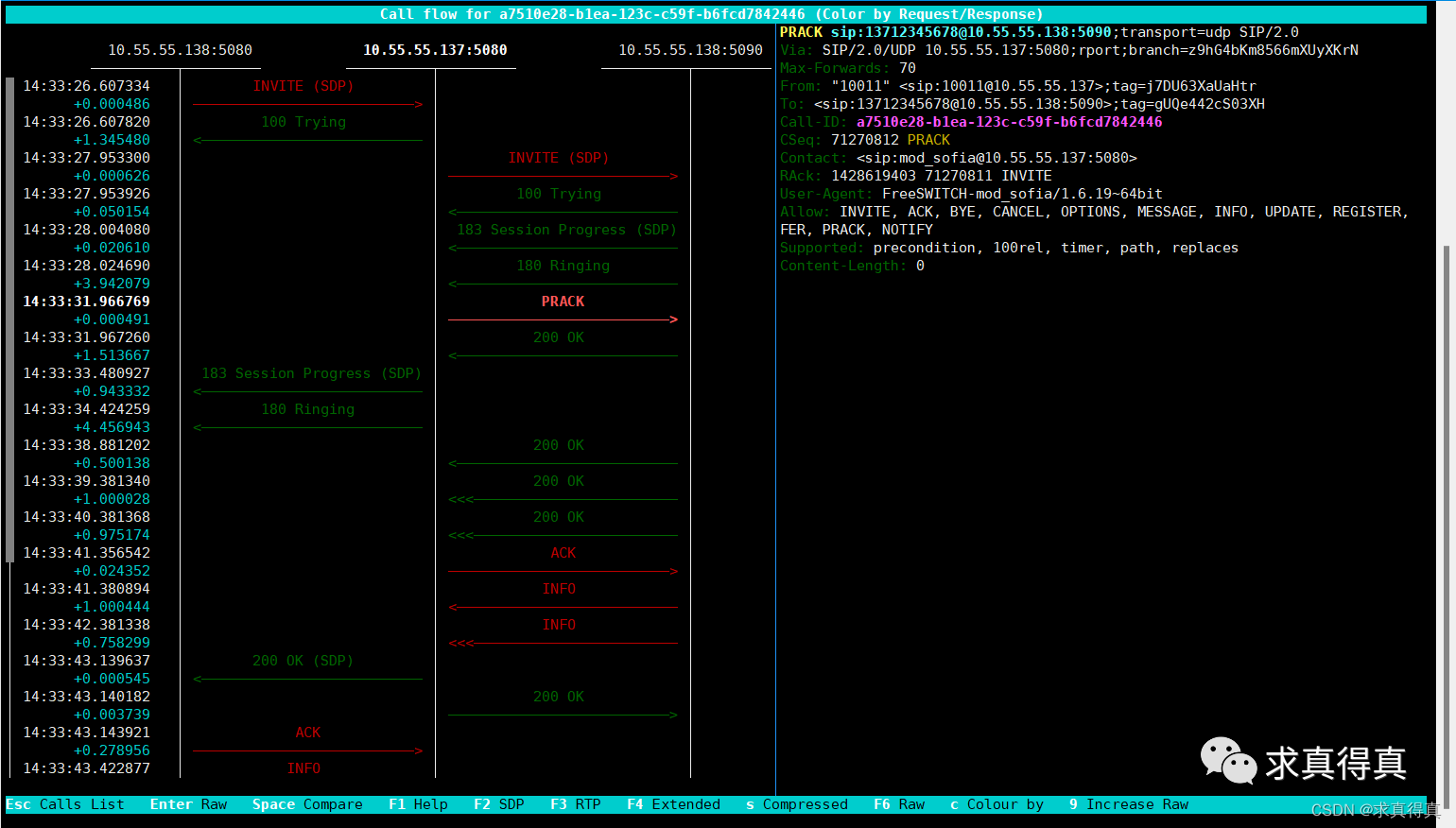
栈和队列
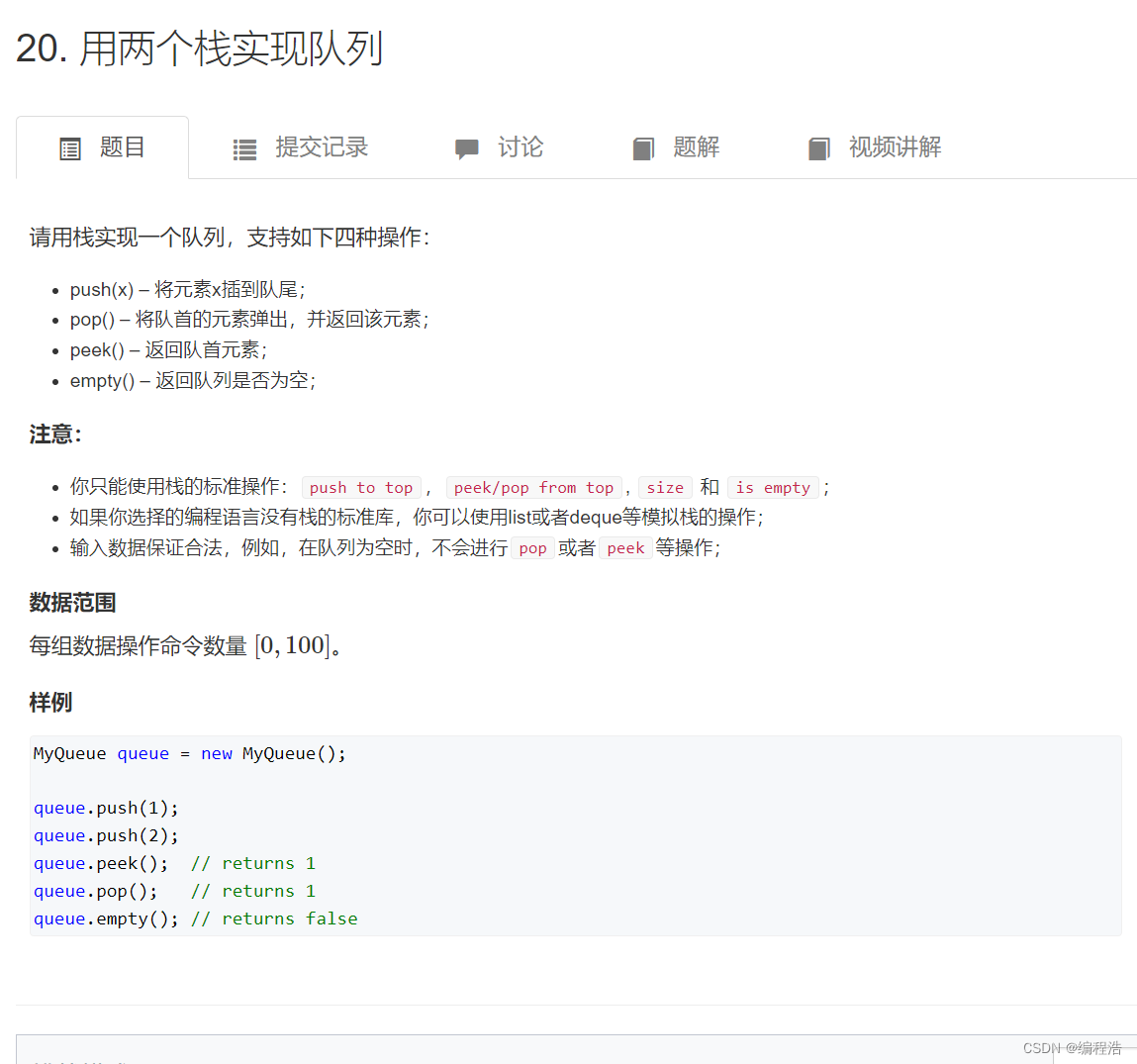
1. 用两个栈实现队列
原题链接
补充:copy(a,b) 把a赋值给b

class MyQueue {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
stack<int> stk, cache;
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
stk.push(x);
}
void copy(stack<int> &a, stack<int> &b) {
while (a.size()) {
b.push(a.top());
a.pop();
}
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
copy(stk, cache);
int res = cache.top();
cache.pop();
copy(cache, stk);
return res;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
copy(stk, cache);
int res = cache.top();
copy(cache, stk);
return res;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return stk.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* bool param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> inStack;
Stack<Integer> outStack;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
inStack = new Stack<>();
outStack = new Stack<>();
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
inStack.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
while(!inStack.isEmpty()){
outStack.push(inStack.pop());
}
int tmp = outStack.pop();
while(!outStack.isEmpty()){
inStack.push(outStack.pop());
}
return tmp;
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
while(!inStack.isEmpty()){
outStack.push(inStack.pop());
}
int res = outStack.peek();
while(!outStack.isEmpty()){
inStack.push(outStack.pop());
}
return res;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return inStack.isEmpty() && outStack.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
2. 包含min函数的栈
原题链接
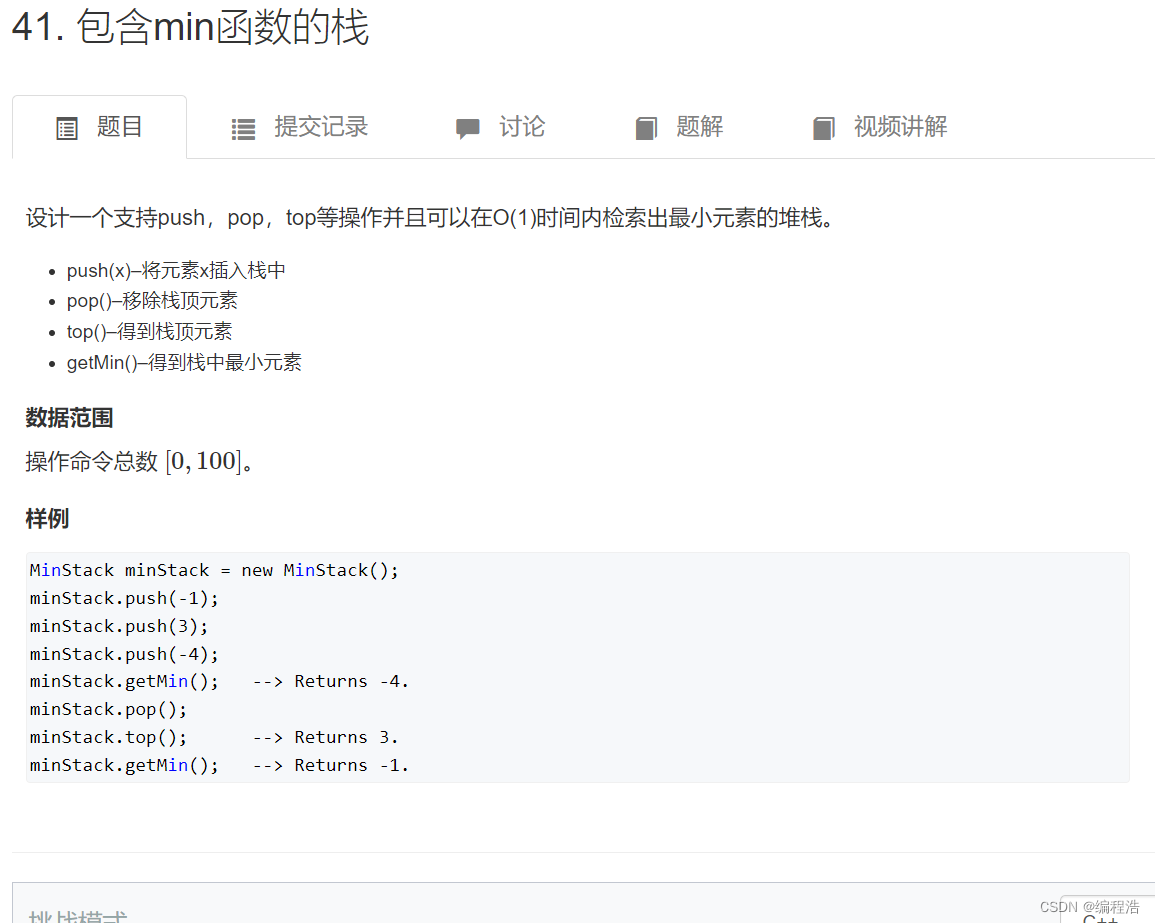
本题我们用样例说话
- 比如是 1 2 3 4 5
那么对应的最小栈就是 1 - 如果是 5 4 3 2 1
对应就是 5 4 3 2 1 - 如果是 3 1 2 4 5
对应是 3 1
所以我们创建一个最小栈
如果入栈的值 小于 栈顶的值
就入最小栈
否则只入栈,不入最小栈
当最小栈和普通栈的栈顶一样时 出栈
class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
stack<int> stackValue;
stack<int> stackMin;
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
stackValue.push(x);
if (stackMin.empty() || stackMin.top() >= x)
stackMin.push(x);
}
void pop() {
if (stackMin.top() == stackValue.top()) stackMin.pop();
stackValue.pop();
}
int top() {
return stackValue.top();
}
int getMin() {
return stackMin.top();
}
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(x);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.getMin();
*/
3. 栈的压入、弹出序列
原题链接

class Solution {
public:
bool isPopOrder(vector<int> pushV,vector<int> popV) {
if(popV.size() != pushV.size())
{
return false;
}
if(pushV.size()==0 && popV.size()==0)
return true;
stack<int> st;
for(int i = 0,j = 0; i < popV.size(); i++)
{
if(popV[j]!=pushV[i])
{
st.push(pushV[i]);
}
else
{
st.push(pushV[i]);
while(st.size() && j < popV.size() && st.top() == popV[j])
{
st.pop();
j++;
}
}
}
if(st.size()==0)
return true;
return false;
}
};
class Solution {
public boolean isPopOrder(int [] pushV,int [] popV) {
// 如果两个数组为空, 直接返回true, 两个数组长度不等, 返回false
if(pushV == null && popV == null){
return true;
}
if(pushV.length != popV.length){
return false;
}
// 新建一个栈, 将push一个一个放入, 并判断
// 如果元素与popV的top元素相等, 则弹出popV, 否则继续在stack里放元素
// 如果顺序正确的话, PopV应该会为空值
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i< popV.length; i++){
stack.push(pushV[i]);
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == popV[index]){
stack.pop();
index++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
4. 数据流中的中位数( 大根堆 + 小根堆 )
原题链接
class Solution {
public:
priority_queue<int> maxheap;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > minheap;
void insert(int x){
maxheap.push(x);
if(minheap.size() && maxheap.top() > minheap.top()) // **1
{
int maxe = maxheap.top(), mine = minheap.top();
maxheap.pop(), minheap.pop();
maxheap.push(mine), minheap.push(maxe);
}
if(maxheap.size() > minheap.size() + 1)
{
minheap.push(maxheap.top());
maxheap.pop();
}
}
double getMedian(){
if((maxheap.size() + minheap.size()) & 1) return maxheap.top();
else return (maxheap.top() + minheap.top()) / 2.0;
}
};
//这里填你的代码^^
//注意代码要放在两组三个点之间,才可以正确显示代码高亮哦~
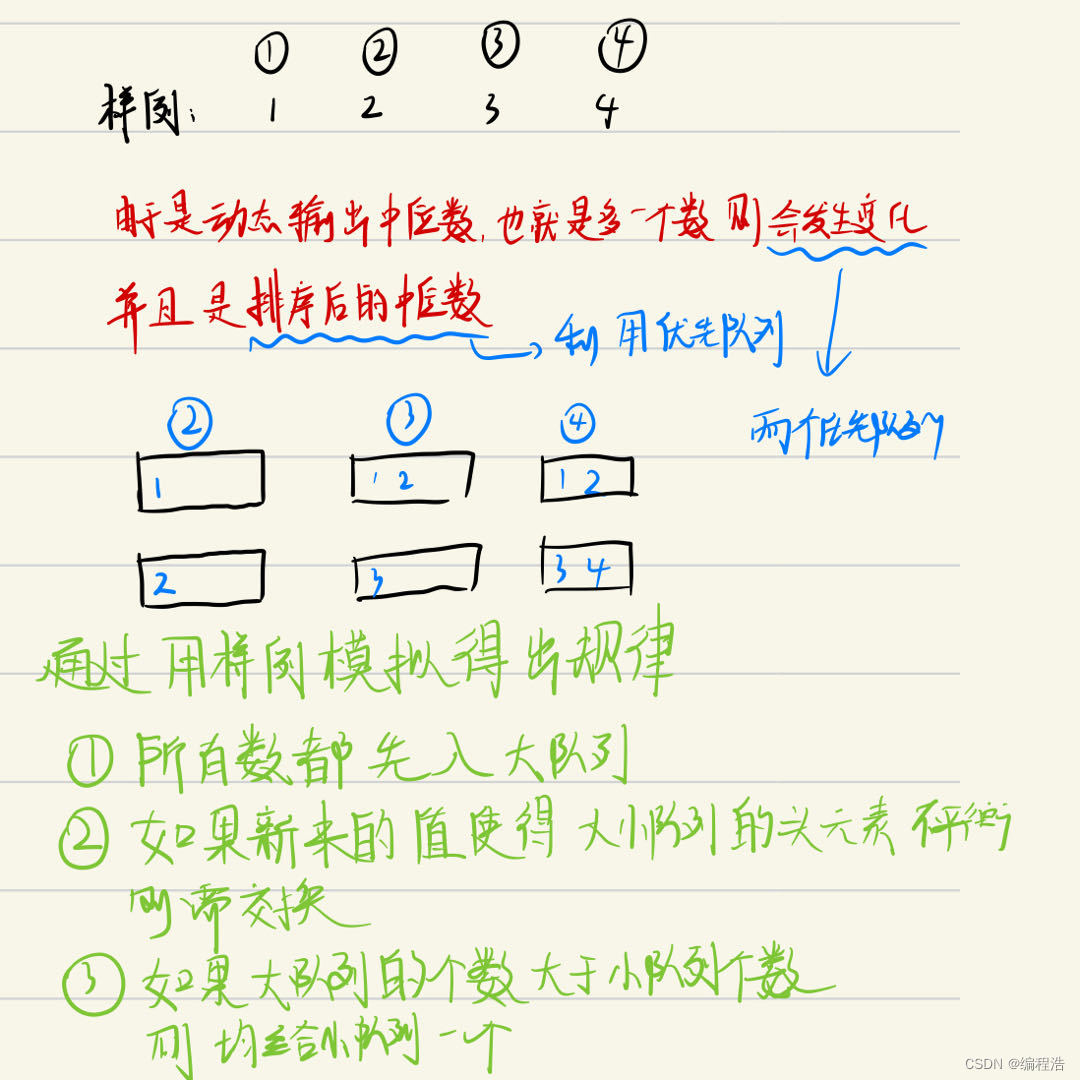
/*
最大堆保存左半部分,即较小一半
最小堆保存右半部分,即较大一半
但是新插入数据可能会比最大堆中最大的数字要小,
也可能会比最小堆中最小的数字要大,
因此先将数字放入最大堆,然后将最大堆中最大的数字放入最小堆
(也可先将数字放入最小堆,然后将最小堆中最小的数字放入最大堆)
这样始终保持,最大堆中最大的数字,比最小堆最小的数字还要小。
同时控制数字数量,保证最大堆的容量与最小堆的容量差距不超过1
这样最终如果最大堆的容量较大,则直接返回最大堆顶,
否则两个堆顶数字相加除以2.0(返回double)
*/
class Solution {
Queue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->b-a);
Queue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
public void insert(Integer num) {
maxHeap.add(num);
minHeap.add(maxHeap.poll());
if(maxHeap.size() < minHeap.size()){
maxHeap.add(minHeap.poll());
}
}
public Double getMedian() {
return maxHeap.size() > minHeap.size()
? maxHeap.peek()
: (maxHeap.peek() + minHeap.peek()) / 2.0;
}
}
5. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字【全部入队列】
原题链接
直接维护一个队列来做:
每走过一步,就把队首元素放到队列的后面,每走完m步把队列头元素删除
直到进行完n-1次迭代
class Solution {
public:
int lastRemaining(int n, int m){
queue<int> q;
for(int i = 0;i < n; i++) q.push(i);
int cnt = 0;
int s = q.size();
while(cnt < n - 1){
int curr = 0;//curr表示当前走了多少步
while(curr < m - 1){ //每次从0开始走m-1步
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
q.push(t);
curr ++;
}//循环结束说明当前走到了第m个元素
q.pop();//把第m个元素删掉
cnt ++;
}
return q.front();//删完n-1个元素,队列里剩下的就是最后一个元素,返回它
}
};





![java八股文面试[JVM]——JVM内存结构2](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/337de420415c4aa8b1347b5cd9dee5a3.png)