文章目录
- 1. 继承Tread,重写run()
- 2. 实现Runnable接口,重写run()
- 3. 使用匿名内部类,继承Thread
- 4. 使用匿名内部类,实现Runnable
- 5. 使用lambda表达式
1. 继承Tread,重写run()
示例:pandas 是基于NumPy 的一种工具,该工具是为了解决数据分析任务而创建的。
class MyTread extends Thread {
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("hello thread");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class thread{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new MyTread();
t.start();
while(true){
System.out.println("hello world");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
执行结果如下
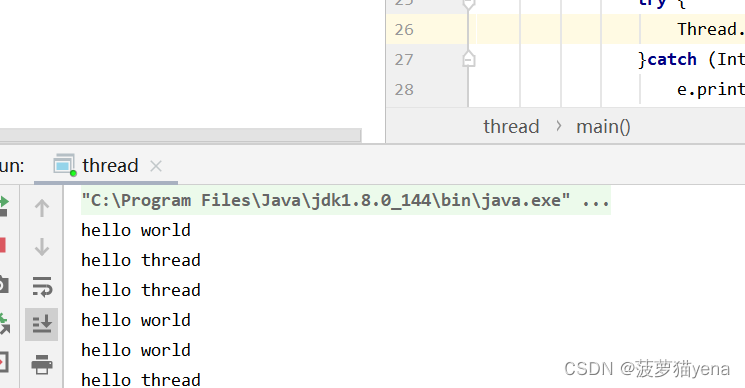
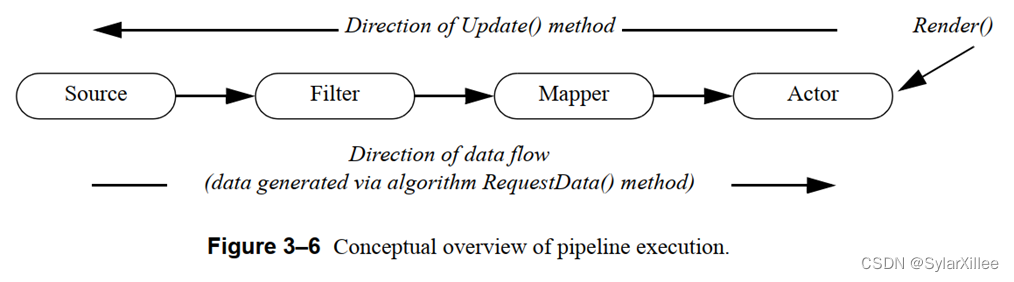
如下图,有main,t两个线程
线程执行顺序是抢占式,开始之后,只有前两条结果是固定的,之后的顺序由操作系统控制,不可预测。
t.start();创建了一个新的线程,之后新的线程调用run()方法,打印“hello thread”。
run()方法执行完毕后,线程销毁。
2. 实现Runnable接口,重写run()
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
public void run(){
while(true){
System.out.println("hello runnable");
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class UseRunnable{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r = new MyRunnable();
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();
while(true){
System.out.println("hello main");
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
执行结果如下
Thread t = new Thread(r),由线程t去完成r的任务,即执行run()方法。
3. 使用匿名内部类,继承Thread
public class InnerRunnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(){
public void run(){
while(true){
System.out.println("hello thread");
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
t.start();
while (true){
System.out.println("hello main");
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
4. 使用匿名内部类,实现Runnable
public class InnerRunnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
while(true){
System.out.println("hello runnable");
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
});
t.start();
while(true){
System.out.println("hello main");
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
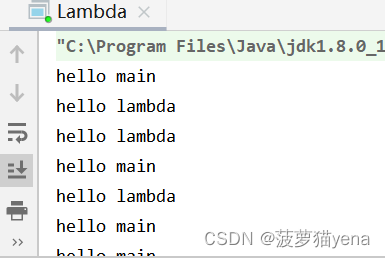
5. 使用lambda表达式
lambda指的是匿名函数
public class Lambda {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t = new Thread(() ->{
while(true){
System.out.println("hello lambda");
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t.start();
while(true){
System.out.println("hello main");
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}