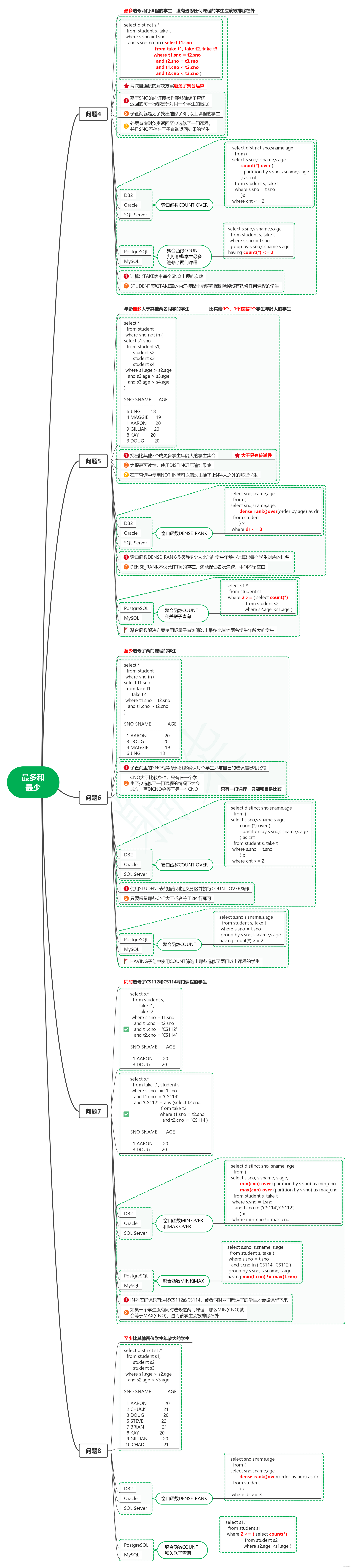
1. 问题4
1.1. 最多选修两门课程的学生,没有选修任何课程的学生应该被排除在外
1.2. sql
select distinct s.*
from student s, take t
where s.sno = t.sno
and s.sno not in ( select t1.sno
from take t1, take t2, take t3
where t1.sno = t2.sno
and t2.sno = t3.sno
and t1.cno < t2.cno
and t2.cno < t3.cno )
1.3. 两次自连接的解决方案避免了聚合运算
1.4. 基于SNO的内连接操作能够确保子查询返回的每一行都是针对同一个学生的数据
1.5. 子查询就是为了找出选修了3门以上课程的学生
1.6. 外层查询则负责返回至少选修了一门课程,并且SNO不存在于子查询返回结果的学生
1.7. DB2
1.8. Oracle
1.9. SQL Server
1.10. 窗口函数COUNT OVER
1.10.1. sql
select distinct sno,sname,age
from (
select s.sno,s.sname,s.age,
count(*) over (
partition by s.sno,s.sname,s.age
) as cnt
from student s, take t
where s.sno = t.sno
)x
where cnt <= 2
1.11. PostgreSQL
1.12. MySQL
1.13. 聚合函数COUNT判断哪些学生最多选修了两门课程
1.13.1. sql
select s.sno,s.sname,s.age
from student s, take t
where s.sno = t.sno
group by s.sno,s.sname,s.age
having count(*) <= 2
1.14. 计算出TAKE表中每个SNO出现的次数
1.15. STUDENT表和TAKE表的内连接操作能够确保剔除掉没有选修任何课程的学生
2. 问题5
2.1. 年龄最多大于其他两名同学的学生
2.1.1. 比其他0个、1个或者2个学生年龄大的学生
2.2. sql
select *
from student
where sno not in (
select s1.sno
from student s1,
student s2,
student s3,
student s4
where s1.age > s2.age
and s2.age > s3.age
and s3.age > s4.age
)
SNO SNAME AGE
--- ---------- ---
6 JING 18
4 MAGGIE 19
1 AARON 20
9 GILLIAN 20
8 KAY 20
3 DOUG 20
2.3. 找出比其他3个或更多学生年龄大的学生集合
2.3.1. 大于具有传递性
2.4. 为提高可读性,使用DISTINCT压缩结果集
2.5. 在子查询中使用NOT IN就可以筛选出除了上述4人之外的那些学生
2.6. DB2
2.7. Oracle
2.8. SQL Server
2.9. 窗口函数DENSE_RANK
2.9.1. sql
select sno,sname,age
from (
select sno,sname,age,
dense_rank()over(order by age) as dr
from student
) x
where dr <= 3
2.10. 窗口函数DENSE_RANK根据有多少人比当前学生年龄小计算出每个学生对应的排名
2.11. DENSE_RANK不仅允许Tie的存在,还能保证名次连续,中间不留空白
2.12. PostgreSQL
2.13. MySQL
2.14. 聚合函数COUNT和关联子查询
2.14.1. sql
select s1.*
from student s1
where 2 >= ( select count(*)
from student s2
where s2.age <s1.age )
2.15. 聚合函数解决方案使用标量子查询筛选出最多比其他两名学生年龄大的学生
3. 问题6
3.1. 至少选修了两门课程的学生
3.2. sql
select *
from student
where sno in (
select t1.sno
from take t1,
take t2
where t1.sno = t2.sno
and t1.cno > t2.cno
)
SNO SNAME AGE
--- ---------- ----------
1 AARON 20
3 DOUG 20
4 MAGGIE 19
6 JING 18
3.3. 子查询里的SNO相等条件能够确保每个学生只与自己的选课信息相比较
3.4. CNO大于比较条件,只有在一个学生至少选修了一门课程的情况下才会成立,否则CNO会等于另一个CNO
3.4.1. 只有一门课程,只能和自身比较
3.5. DB2
3.6. Oracle
3.7. SQL Server
3.8. 窗口函数COUNT OVER
3.8.1. sql
select distinct sno,sname,age
from (
select s.sno,s.sname,s.age,
count(*) over (
partition by s.sno,s.sname,s.age
) as cnt
from student s, take t
where s.sno = t.sno
) x
where cnt >= 2
3.9. 使用STUDENT表的全部列定义分区并执行COUNT OVER操作
3.10. 只要保留那些CNT大于或者等于2的行即可
3.11. PostgreSQL
3.12. MySQL
3.13. 聚合函数COUNT
3.13.1. sql
select s.sno,s.sname,s.age
from student s, take t
where s.sno = t.sno
group by s.sno,s.sname,s.age
having count(*) >= 2
3.14. HAVING子句中使用COUNT筛选出那些选修了两门以上课程的学生
4. 问题7
4.1. 同时选修了CS112和CS114两门课程的学生
4.2. sql
select s.*
from student s,
take t1,
take t2
where s.sno = t1.sno
and t1.sno = t2.sno
and t1.cno = 'CS112'
and t2.cno = 'CS114'
SNO SNAME AGE
--- ---------- ----
1 AARON 20
3 DOUG 20
4.3. sql
select s.*
from take t1, student s
where s.sno = t1.sno
and t1.cno = 'CS114'
and 'CS112' = any (select t2.cno
from take t2
where t1.sno = t2.sno
and t2.cno != 'CS114')
SNO SNAME AGE
--- ---------- ----
1 AARON 20
3 DOUG 20
4.4. DB2
4.5. Oracle
4.6. SQL Server
4.7. 窗口函数MIN OVER和MAX OVER
4.7.1. sql
select distinct sno, sname, age
from (
select s.sno, s.sname, s.age,
min(cno) over (partition by s.sno) as min_cno,
max(cno) over (partition by s.sno) as max_cno
from student s, take t
where s.sno = t.sno
and t.cno in ('CS114','CS112')
) x
where min_cno != max_cno
4.8. PostgreSQL
4.9. MySQL
4.10. 聚合函数MIN和MAX
4.10.1. sql
select s.sno, s.sname, s.age
from student s, take t
where s.sno = t.sno
and t.cno in ('CS114','CS112')
group by s.sno, s.sname, s.age
having min(t.cno) != max(t.cno)
4.11. IN列表确保只有选修CS112或CS114,或者同时两门都选了的学生才会被保留下来
4.12. 如果一个学生没有同时选修这两门课程,那么MIN(CNO)就会等于MAX(CNO),进而该学生会被排除在外
5. 问题8
5.1. 至少比其他两位学生年龄大的学生
5.2. sql
select distinct s1.*
from student s1,
student s2,
student s3
where s1.age > s2.age
and s2.age > s3.age
SNO SNAME AGE
--- ---------- ----------
1 AARON 20
2 CHUCK 21
3 DOUG 20
5 STEVE 22
7 BRIAN 21
8 KAY 20
9 GILLIAN 20
10 CHAD 21
5.3. DB2
5.4. Oracle
5.5. SQL Server
5.6. 窗口函数DENSE_RANK
5.6.1. sql
select sno,sname,age
from (
select sno,sname,age,
dense_rank()over(order by age) as dr
from student
) x
where dr >= 3
5.7. PostgreSQL
5.8. MySQL
5.9. 聚合函数COUNT和关联子查询
5.9.1. sql
select s1.*
from student s1
where 2 <= ( select count(*)
from student s2
where s2.age <s1.age )