文章目录
- mysql操作
- pymysql操作
- 导入数据并启动
- 使用pandas导入MySQL
- 数据库连接引擎
- 使用to_sql方法
- pandas读取sql
- read_sql_table
- read_sql_query
mysql操作
创建数据库test和table
create database test;
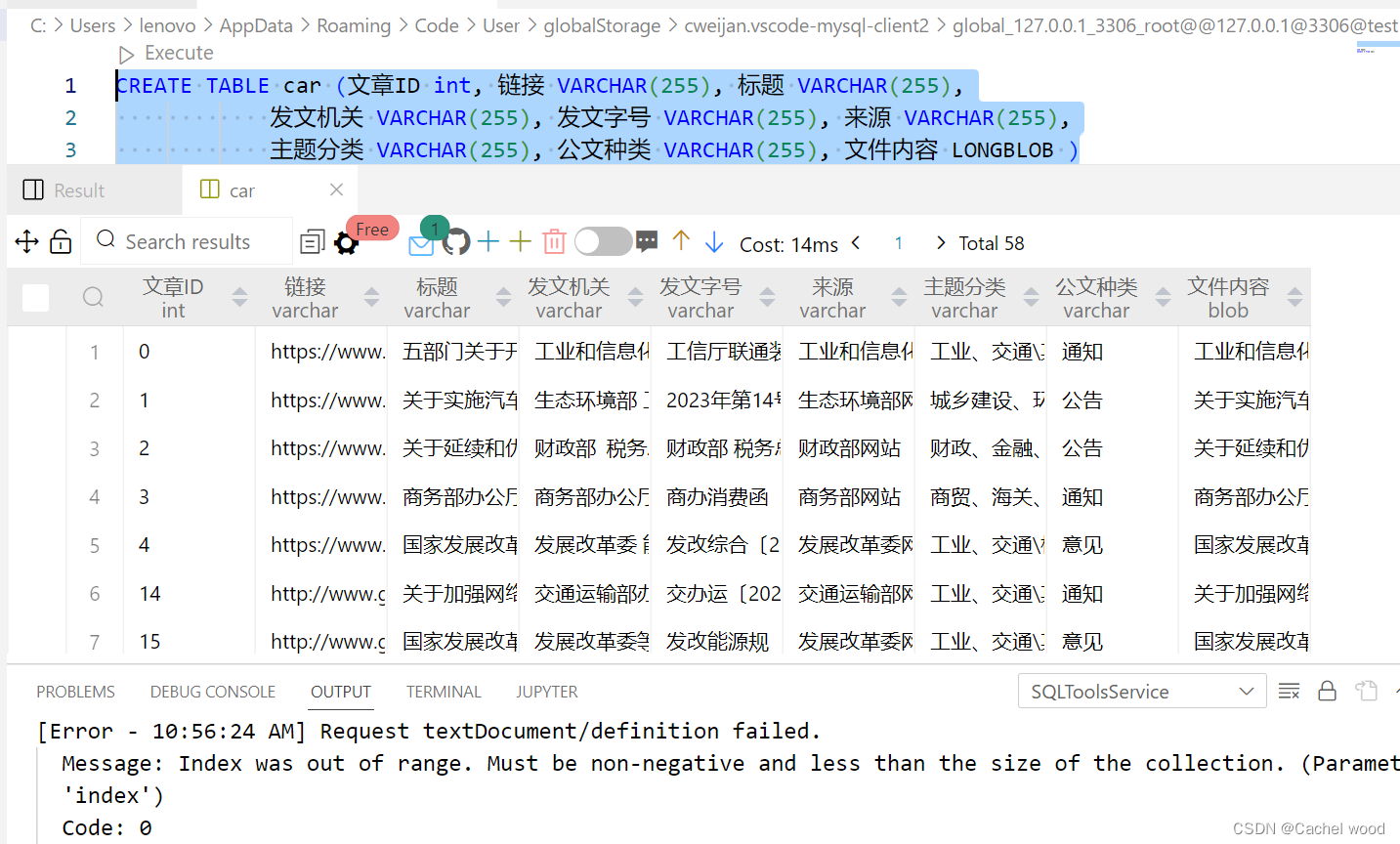
CREATE TABLE car (文章ID int, 链接 VARCHAR(255), 标题 VARCHAR(255),
发文机关 VARCHAR(255), 发文字号 VARCHAR(255), 来源 VARCHAR(255),
主题分类 VARCHAR(255), 公文种类 VARCHAR(255), 文件内容 LONGBLOB )

pymysql操作
- python安装pymysql
- pymysql连接数据库
connect = pymysql.connect(
host=self.MYSQL_HOST,
db=self.MYSQL_DB,
port=3306,
user=self.MYSQ_USER,
passwd=self.MYSQL_PWD,
charset='utf8',
use_unicode=False
)
- 创建游标
cursor = connect.cursor()
- 插入数据
def insert_mysql(self, data_json):
"""
数据插入mysql
:param data_json:
:return:
"""
sql = "insert into {}(文章ID,链接,标题,发文机关,发文字号,来源,主题分类,公文种类,文件内容) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)".format(mysql_table)
try:
self.cursor.execute(sql, (data_json['文章ID'], data_json['链接'], data_json['标题'],data_json['发文机关'],
data_json['发文字号'],data_json['来源'],data_json['主题分类'],data_json['公文种类'],data_json['文件内容']))
self.connect.commit()
print('数据插入成功')
except Exception as e:
print('e= ', e)
print('数据插入错误')
- 完整代码
import pymysql
import pandas as pd
mysql_host = 'localhost'
mysql_db = 'test'
mysql_user = 'root'
mysql_pwd = 'root'
mysql_table = 'car'
class MYSQL:
def __init__(self):
# MySQL
self.MYSQL_HOST = mysql_host
self.MYSQL_DB = mysql_db
self.MYSQ_USER = mysql_user
self.MYSQL_PWD = mysql_pwd
self.connect = pymysql.connect(
host=self.MYSQL_HOST,
db=self.MYSQL_DB,
port=3306,
user=self.MYSQ_USER,
passwd=self.MYSQL_PWD,
charset='utf8',
use_unicode=False
)
print(self.connect)
self.cursor = self.connect.cursor()
def create_table(self):
self.cursor.execute("""CREATE TABLE car (文章ID int, 链接 VARCHAR(255), 标题 VARCHAR(255),
发文机关 VARCHAR(255), 发文字号 VARCHAR(255), 来源 VARCHAR(255),
主题分类 VARCHAR(255), 公文种类 VARCHAR(255), 文件内容 LONGBLOB )""")
def insert_mysql(self, data_json):
"""
数据插入mysql
:param data_json:
:return:
"""
sql = "insert into {}(文章ID,链接,标题,发文机关,发文字号,来源,主题分类,公文种类,文件内容) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)".format(mysql_table)
try:
self.cursor.execute(sql, (data_json['文章ID'], data_json['链接'], data_json['标题'],data_json['发文机关'],
data_json['发文字号'],data_json['来源'],data_json['主题分类'],data_json['公文种类'],data_json['文件内容']))
self.connect.commit()
print('数据插入成功')
except Exception as e:
print('e= ', e)
print('数据插入错误')
导入数据并启动
def main():
mysql = MYSQL()
df = pd.read_excel('汽车行业政策文本研究.xlsx')
print(df.columns)
# orient='records', 表示将DataFrame的数据转换成我想要的json格式
data_json = df.to_dict(orient='records')
for dt in data_json:
print(dt)
mysql.insert_mysql(dt)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
使用pandas导入MySQL
数据库连接引擎
‘mysql+pymysql://[user]:[pwd]@localhost:3306/[database]?charset=utf8’
import pymysql
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://root:root@localhost:3306/test?charset=utf8')
使用to_sql方法
name: str
Name of SQL table.con: sqlalchemy.engine.(Engine or Connection) or sqlite3.Connectionschema: str, optional
Specify the schema (if database flavor supports this). If None, use default schema.if_exists: {‘fail’, ‘replace’, ‘append’}, default ‘fail’
How to behave if the table already exists.fail: Raise a ValueError.replace: Drop the table before inserting new values.append: Insert new values to the existing table.
index: bool, default True
Write DataFrame index as a column. Uses index_label as the column name in the table.index_label: str or sequence, default None
Column label for index column(s). If None is given (default) and index is True, then the index names are used. A sequence should be given if the DataFrame uses MultiIndex.chunksize: int, optional
Specify the number of rows in each batch to be written at a time. By default, all rows will be written at once.dtype: dict or scalar, optional
Specifying the datatype for columns. If a dictionary is used, the keys should be the column names and the values should be the SQLAlchemy types or strings for the sqlite3 legacy mode. If a scalar is provided, it will be applied to all columns.method: {None, ‘multi’, callable}, optional
Controls the SQL insertion clause used:
Raises
ValueError
When the table already exists and if_exists is ‘fail’ (the default).
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_excel('汽车行业政策文本研究.xlsx')
#将data写入数据库,如果表存在就替换,将data的index也写入数据表,写入字段名称为id_name
df.to_sql('qiche',con=engine,schema='test',chunksize=10000,index=False,if_exists='replace')
pandas读取sql
read_sql_table
pd.read_sql_table可以直接读取数据库的整个table
pd.read_sql_table('car',con=engine,schema='test')
read_sql_query
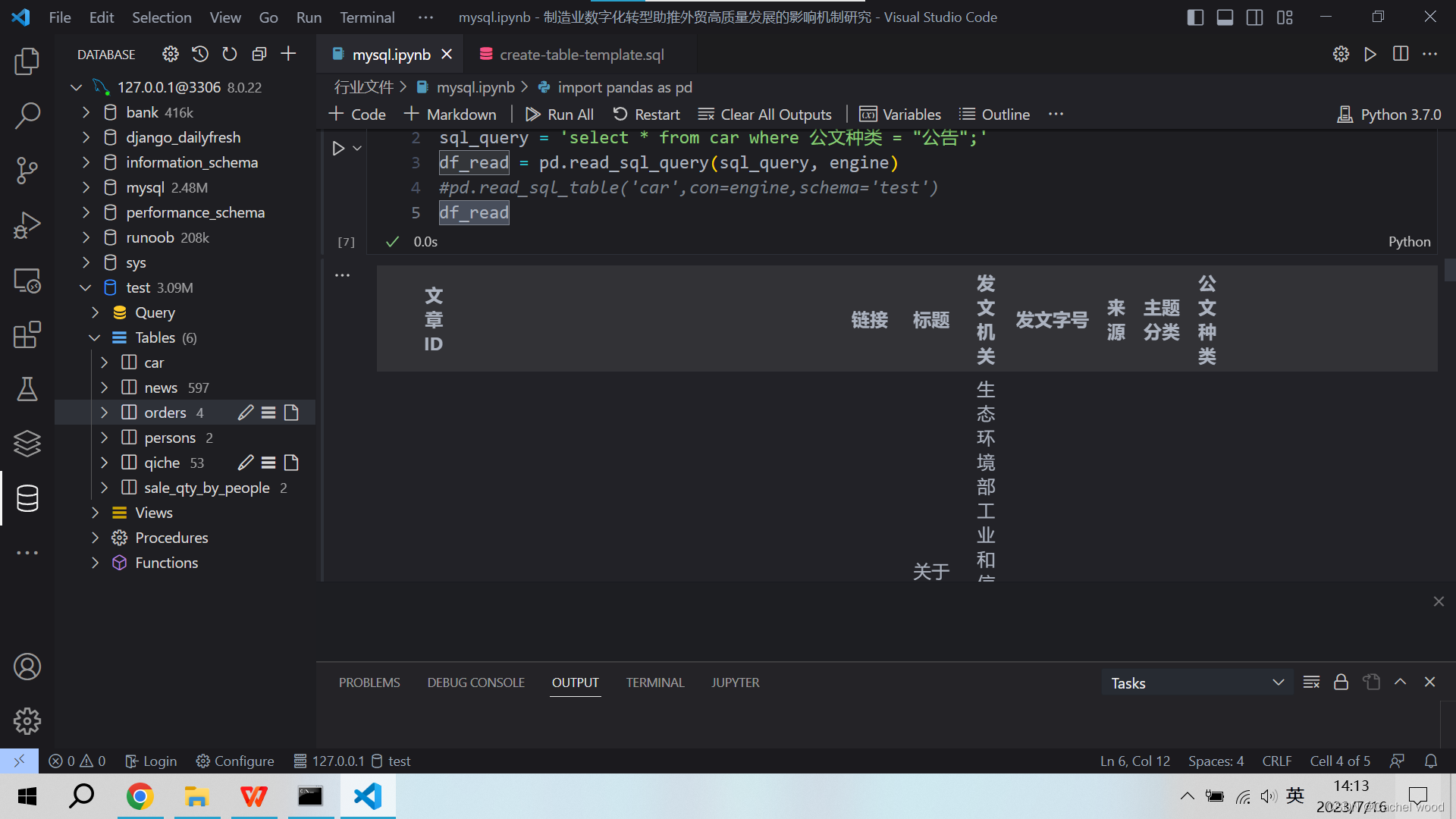
pd.read_sql_query通过执行sql_query来读取部分表格内容
#sql_query = 'select * from car;'
sql_query = 'select * from car where 公文种类 = "公告";'
df_read = pd.read_sql_query(sql_query, engine)
df_read