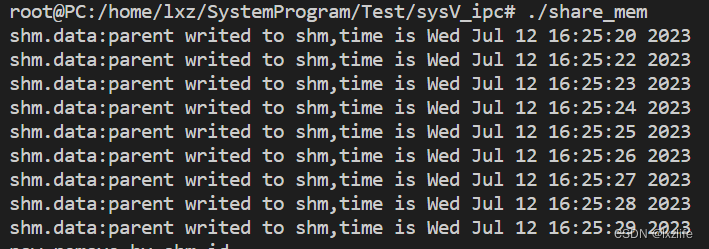
note
1.使用shmget将在内核创建一个共享内存区
2.使用shmctl才可以删除内核创建的共享内存区
3.使用shmat给当前进程开辟与内核共享内存对应的内存区p,用户态对p的操作会作用到内核共享内存区
code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int shm_id = -1; // 共享内存实例(内核实例),由父进程管理
const size_t shm_len = 1024; // 共享内存字节数
struct mm { // 父子进程通信数据协议
int flag; /* 父进程写状态111 or 子进程读状态222*/
char data[1020];
};
static void remove_shm(void) {
int ret = -1;
if (shm_id != -1) {
fprintf(stdout, "now remove by shm_id\n");
ret = shmctl(shm_id, IPC_RMID, NULL);
if (ret == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "shmctl error,%s\n", strerror(errno));
}
shm_id = -1;
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
key_t key = 0;
pid_t pid = 0;
char *pathname = argv[0];
int proj_id = 0x11; // 盐值
struct mm* shm = NULL;
key = ftok(pathname, proj_id); // key由当前程序名和盐值生成
if (key == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "ftok error,%s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
shm_id = shmget(key, shm_len, IPC_CREAT|666);
if (shm_id == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "shmget error,%s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 把共享内存映射到当前父进程空间
shm = shmat(shm_id, NULL, 0); // 0:可读可写
if (shm == (void*)(-1)) {
fprintf(stderr, "shmat error,%s\n", strerror(errno));
remove_shm();
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
shm->flag = 111; //父进程先初始化共享内存读写标志
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "fork error,%s\n", strerror(errno));
shmdt(shm); // 父进程解除共享内存映射
remove_shm(); // 父进程销毁共享内存(内核实例)
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (pid == 0) { // 子进程
int i = 0;
shm = shmat(shm_id, NULL, 0); // 把共享内存映射到当前子进程空间
if (shm == (void*)(-1)) {
fprintf(stderr, "fork error,%s\n", strerror(errno));
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (shm->flag == 222) {
fprintf(stdout, "shm.data:%s", shm->data);
shm->flag = 111;
}
sleep(1);
}
shmdt(shm); // 子进程解除共享内存映射
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else if (pid > 0) { // 父进程
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (shm->flag == 111) {
memset(shm->data, 0, shm_len);
time_t t;
time(&t);
sprintf(shm->data, "parent writed to shm,time is %s", ctime(&t));
shm->flag = 222;
}
sleep(1);
}
wait(NULL); // 父进程等待子进程资源回收完成
shmdt(shm); // 父进程解除共享内存映射
remove_shm(); // 父进程删除共享内存实例(内核实例)
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
return 0;
}test




![数据结构05:树与二叉树[C++][并查集]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/166187d9fbcc4ec9966414466e83b30e.png)