gormpher
- Gormpher 介绍
- 快速开始
- WebObject 接口约定
- 查询单条数据
- 删除单条数据
- 创建单条数据
- 编辑单条数据
- 条件查询多条数据
- 进阶
- WebObject 配置项
- 动态接口函数
- Gorm 泛型函数
- Admin
- 源码
- handleEditObject
- handleQueryObject
Gormpher 介绍
gormpher 是一个轻量级的 Golang 库
- 基于 Gin 和 Gorm
- WebObject 机制:根据模型生成对应的 Restful API,一键生成平时开发中重复的 CRUD 代码
- 通用 Gorm 泛型函数
- 基于泛型的动态接口函数
- 将 WebObject 注册到 Admin,自带测试用的 Web 界面
- 完善的单元测试,覆盖率接近 80%(完善中)
gormpher github:https://github.com/restsend/gormpher
使用 gormpher 的开源项目 rabbit-admin:https://github.com/szluyu99/rabbit-admin
建议看完本文,理解 gormpher 后可以查看该开源项目,体会其在实际开发中到底能节约多少工作量
快速开始
先直观的体会一下这个项目最基础的功能是用来做什么的。
go get github.com/restsend/gormpher
示例源于 gormpher 仓库下 example/main.go:(下面是其简化版)
代码版本可能会更新,文章中不一定是最新的,可以参考上面的 example/main.go 文件获取最新用法
使用流程:
- 定义好一个结构体 struct,指定其
primarykey - 创建 gormpher 依赖的 gorm 指针 和 gin 路由对象(后续考虑适配其他 web 框架)
- 创建 gormpher 中的 WebObject 对象
- 注册 WebObject 对象到指定路由组
- (可选)将 WebObject 对象注册到 Admin 中,展示一个测试用的 Web 界面
package main
import (
"flag"
"time"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/restsend/gormpher"
"gorm.io/driver/sqlite"
"gorm.io/gorm"
)
// 1. 定义结构体,指定 primarykey
type User struct {
ID uint `json:"id" gorm:"primarykey"`
CreatedAt time.Time `json:"createdAt"`
UpdatedAt time.Time `json:"updatedAt"`
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int `json:"age"`
Enabled bool `json:"enabled"`
LastLogin *time.Time `json:"lastLogin"`
}
func main() {
var dsn string
var addr string
flag.StringVar(&dsn, "n", "", "DB DSN")
flag.StringVar(&addr, "a", ":8890", "Api Server Addr")
flag.Parse()
// 2. gorm db, gin router
db, _ := gorm.Open(sqlite.Open(dsn), nil)
db.AutoMigrate(User{})
r := gin.Default()
// 3. 创建 gormpher WebObject 对象(User 为模型对象)
objs := []gormpher.WebObject{
{
Name: "user",
Model: &User{},
SearchFields: []string{"Name", "Enabled"}, // 可模糊搜索的字段
EditFields: []string{"Name", "Age", "Enabled", "LastLogin"}, // 可编辑的字段
FilterFields: []string{"Name", "CreatedAt", "Age", "Enabled"}, // 可条件查询的字段
OrderFields: []string{"CreatedAt", "Age", "Enabled"}, // 可排序的字段
GetDB: func(ctx *gin.Context, isCreate bool) *gorm.DB { return db }, // 返回 *gorm.DB 的方法
},
}
// 4. 注册 gormpher WebObject 对象到指定路由组,生成以下 API
// PUT http://localhost:8890/api/user
// GET http://localhost:8890/api/user/:key
// PATCH http://localhost:8890/api/user/:key
// POST http://localhost:8890/api/user
// DELETE http://localhost:8890/api/user/:key
gormpher.RegisterObjects(r.Group("api"), objs)
// 5. (可选)将 WebObject 对象注册到 Admin 中,展示一个测试用的 Web 界面
// 访问 URL: http://localhost:8890/admin
gormpher.RegisterObjectsWithAdmin(r.Group("admin"), objs)
r.Run(addr)
}
运行该程序:
go run main.go
经过上面简短的代码,我们就生成了以下 API:
[GIN-debug] GET /api/user/:key --> github.com/restsend/gormpher.(*WebObject).RegisterObject.func1 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] PUT /api/user --> github.com/restsend/gormpher.(*WebObject).RegisterObject.func2 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] PATCH /api/user/:key --> github.com/restsend/gormpher.(*WebObject).RegisterObject.func3 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] DELETE /api/user/:key --> github.com/restsend/gormpher.(*WebObject).RegisterObject.func4 (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] POST /api/user --> github.com/restsend/gormpher.(*WebObject).RegisterObject.func5 (3 handlers)
目前你可能不太理解这些接口的用法,具体参数本文后面会介绍:核心约定。
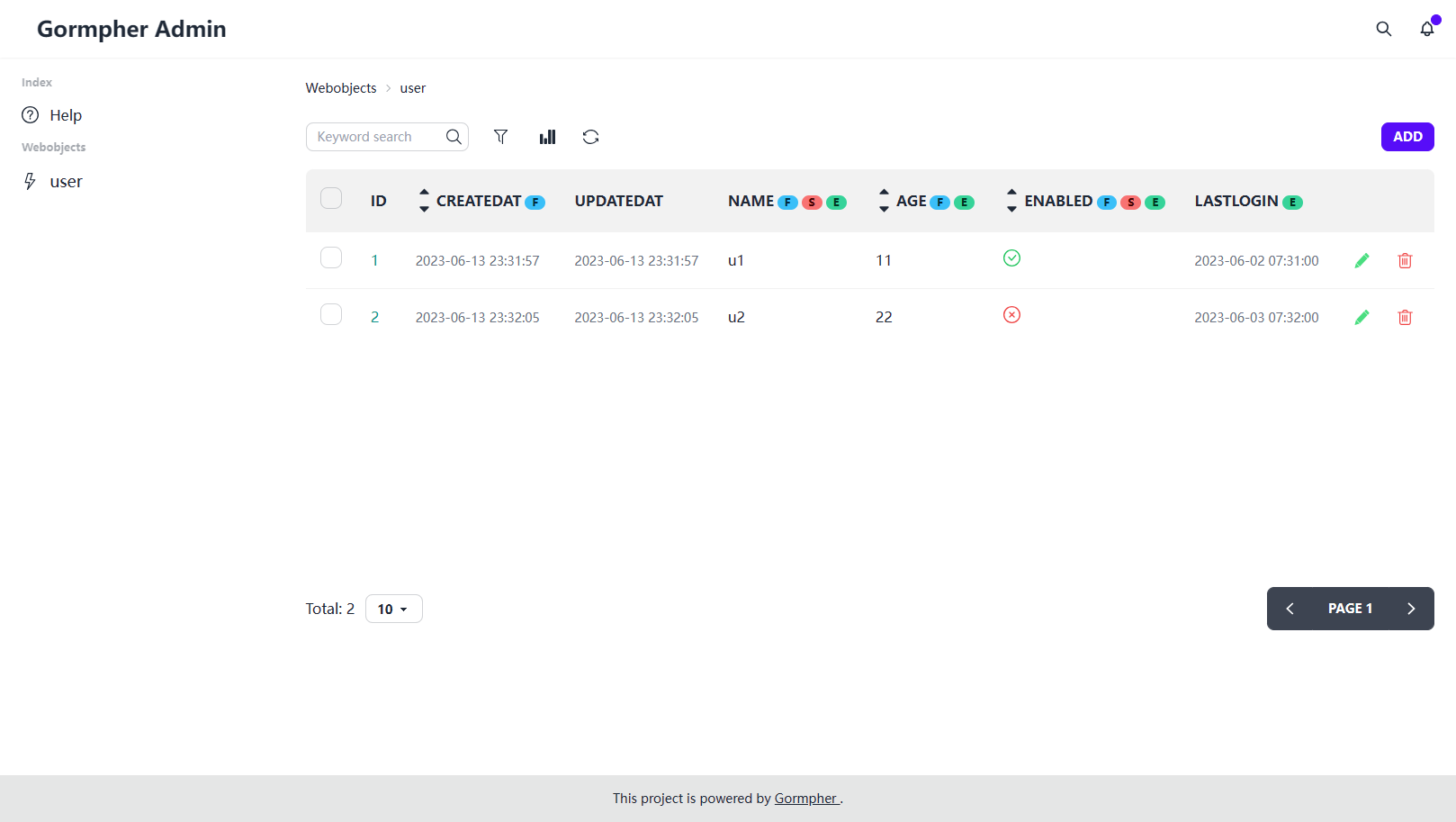
访问:http://localhost:8890/admin 查看测试用的 Web 界面
先尝试体验一下,通过上面这么简单的几行代码可以实现的接口效果。
WebObject 接口约定
平时开发中的容易重复的 CRUD 代码可以简单分为以下情况:
- 新增数据(单条)- Create
- 删除数据(单条 或 多条)- Delete
- 编辑数据(单条)- Edit
- 查询单条数据 - Get
- 条件查询多条数据(分页)- Query
概述:Gormpher 的核心思想是基于模型对象来生成其 API,例如对于一个 user 模块
- PUT /user 即创建一个 user 对象
- 请求体传递要创建的 user 对象
- DELETE /user/:key 即删除主键为
key的 user 数据 - PATCH /user/:key 即编辑主键为
key的 user 数据- 请求体传递要编辑的 user 对象
- GET /user/:key 即查询主键为
key的单个 user 数据 - POST /user 即条件查询多条 user 的信息(分页)
- 请求体传递查询参数
涉及到请求体全部使用
Content-Type: application/json传输数据
即对于 user 模块,最终我们生成的 API 如下:
GET /user/:key
PUT /user
PATCH /user/:key
DELETE /user/:key
POST /user
然后再解析一下以上的行为,并给出对应的接口请求与响应示例。
查询单条数据
GET /user/:key
- 请求参数:
- URL 路径参数:
key为数据的主键
- URL 路径参数:
# Path
GET /user/1
- 响应数据:User 对象
{
"id": 1,
"createdAt": "2023-06-13T23:43:27.590377962+08:00",
"updatedAt": "2023-06-13T23:43:27.590377962+08:00",
"name": "u1",
"age": 10,
"enabled": false,
"lastLogin": "2023-06-01T23:43:00Z"
}
删除单条数据
DELETE /user/:key
- 请求参数:
- URL 路径参数:
key为数据的主键
- URL 路径参数:
# Path
DELETE /user/1
- 响应数据:
Boolean,表示是否删除成功
true
创建单条数据
PUT /user
- 请求参数:
- 请求体参数:User 对象
# Path
PUT /user
# Request Body
{
"name": "u2",
"age": 5,
"lastLogin": "2023-06-01T23:49",
"enabled": true
}
- 响应数据:User 对象
{
"id": 2,
"createdAt": "2023-06-13T23:50:01.615012885+08:00",
"updatedAt": "2023-06-13T23:50:01.615012885+08:00",
"name": "u2",
"age": 5,
"enabled": true,
"lastLogin": "2023-06-01T23:49:00Z"
}
编辑单条数据
PATCH /user/:key
- 请求参数:
- URL 路径参数:
key为数据的主键 - 请求体参数:需要编辑的 User 对象(未传的属性不会被修改,传了的即使是空值也会被修改)
- URL 路径参数:
# Path
PATCH /user/1
# Request Body
{
"enabled" : true,
"name": "aaaa"
}
- 响应数据:
Boolean,表示是否编辑成功
true
注意:
- 并不是所有的字段都可以被前端传来的参数所编辑的
- 因此,我们将可以被编辑的字段暴露成一个配置项
EditFields - 如果前端传递了非
EditFeilds中指定的字段,则无法编辑成功
示例中指定了 user 可编辑字段为:Name、Age、Enabled、LastLogin
{
// ...
Model: &User{},
EditFields: []string{"Name", "Age", "Enabled", "LastLogin"}, // 可编辑的字段
// ...
}
条件查询多条数据
POST /user
- 请求参数:
QueryForm对象- 请求体参数:User 对象
- 响应数据:
QueryResult对象
这是一个非常重要且复杂的行为,大部分重复的代码都出自它,为抽象出一个通用规则,我们将以下字段暴露成可配置项:
SearchFields:可以被模糊搜索的字段FilterFields:可以被条件查询的字段OrderFields:可以被排序的字段
{
// ...
Model: &User{},
SearchFields: []string{"Name", "Enabled"}, // 可模糊搜索的字段
FilterFields: []string{"Name", "CreatedAt", "Age", "Enabled"}, // 可条件查询的字段
OrderFields: []string{"CreatedAt", "Age", "Enabled"}, // 可排序的字段
// ...
}
查询表单对象:QueryForm
| Name | Type | Desc | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| pos | number | 分页参数,数据查询位置 | 0 |
| limit | number | 分页参数 ,数据查询范围 | 50 |
| keyword | number | 模糊搜索关键字,字段需要配置在 SearchFields 中 | “” |
| filters | []Filter | 条件查询对象数组,字段需要配置在 FilterFields 中 | null |
| orders | []Order | 排序对象数组,字段需要配置在 OrderFields 中 | null |
Filter:
| Name | Op | Desc |
|---|---|---|
| name | string | 字段 |
| op | string | =, <>, in, not_in, >, >=, <, <= |
| value | string | 值 |
示例:检索 age > 10 且 enabled = true 的数据,请求参数如下
{
filters: [
{ "name": "age", "op": ">", "value": 10 },
{ "name": "enabled", "op": "=", "value": true }
]
}
Order:
| Name | Op | Desc |
|---|---|---|
| name | string | |
| op | string | asc, desc |
示例:检索按 age 降序排序的数据,请求参数如下
{
orders: [
{ "name": "age", op: "desc" }
]
}
请求示例:检索条件如下
- 查询开始位置 0,查询数量 10
- 模糊查询关键字为 “u”
- age > 10 且 enabled = true
- 按 age 降序排序
{
"pos": 0,
"limit": 10,
"keyword": "u",
"filters": [
{ "name": "age", "op": ">", "value": 10 },
{ "name": "enabled", "op": "=", "value": true }
],
"orders": [
{ "name": "age", op: "desc" }
]
}
查询结果:QueryResult
| Name | Type | Desc |
|---|---|---|
| pos | number | 本次查询中分页参数 |
| limit | number | 本次查询分页参数 |
| keyword | string | 本次查询模糊搜索关键字 |
| total | number | 本次查询数据总数 |
| items | []object | 本次查询数据数组 |
响应示例:
{
"total": 2,
"pos": 0,
"limit": 10,
"items": [
{
"id": 1,
"createdAt": "2023-06-13T23:43:27.590377962+08:00",
"updatedAt": "2023-06-14T00:23:36.46322106+08:00",
"name": "u1",
"age": 10,
"enabled": true,
"lastLogin": "2023-06-01T23:43:00Z"
},
{
"id": 2,
"createdAt": "2023-06-13T23:50:01.615012885+08:00",
"updatedAt": "2023-06-13T23:50:01.615012885+08:00",
"name": "u2",
"age": 5,
"enabled": true,
"lastLogin": "2023-06-01T23:49:00Z"
}
]
}
下面的内容后续完善。