观察者模式Spring之publishEvent事件处理
1.使用场景
这个一般什么时候使用,我们一般是在不同的bean直接进行信息传递,比如我们beanA的事件处理完后,需要beanB进行处理一些业务逻辑的时候这种情况就一般可以使用publish-event解决。
可用于操作日志记录
2.原理
ApplicationContext中的事件处理是通过ApplicationEvent类和ApplicationListener接口来提供的,通过ApplicationContext的publishEvent()方法发布到ApplicationListener;。
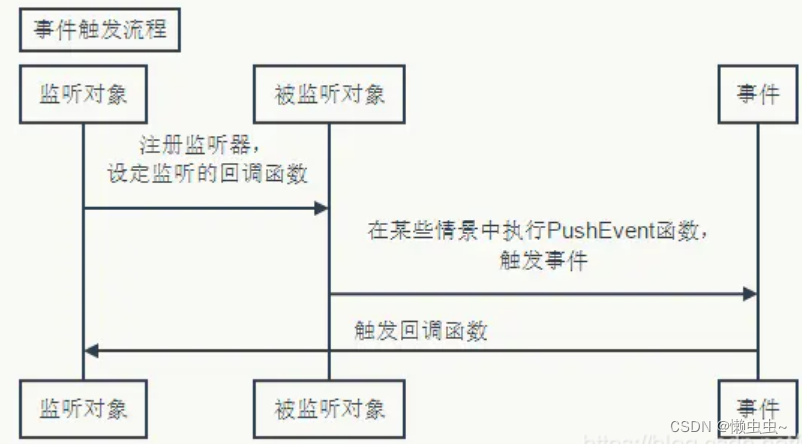
一个事件模型有三个组成部分:被监听对象source(也称为事件源),事件event和监听对象listener。事件发布者在发布事件的时候->通知事件的监听者。
首先,由监听对象注册监听回调函数(Callback),当事件源触发了事件后,监听对象会收到事件源的信息,然后决定如何对事件源进行处理,简要流程如下图所示。
3.事件触发 && 监听处理过程
(1) 使用 org.springframework.context 包下的 ApplicationContext.publishEvent(ApplicationEvent appEvent) 发布事件
(2) 使用 org.springframework.context.event 包下的 @EventListener(事件名) 监听事件并处理。
注意:
(1) ApplicationContext.publishEvent 默认是同步操作, 并非发布后不管的异步操作,发布事件后需要等 @EventListener 执行完。
(2) 如果需要开启异步操作需要在@EventListener上增加@Async 注解。
4.代码实现
(1)CustomEvent
/**
* 用户事件监听
*
* @author zhang
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class CustomEvent {
private String message;
}
(2)CustomEventListener
/**
* @author zhang
*/
@Component
public class CustomEventListener {
@EventListener(CustomEvent.class)
public void onApplicationEvent(CustomEvent customEvent) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("监听器接受消息:"+ customEvent.getMessage());
}
}
(3)CustomController
/**
* @author zhang
*/
@RestController
public class CustomController {
@Resource
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
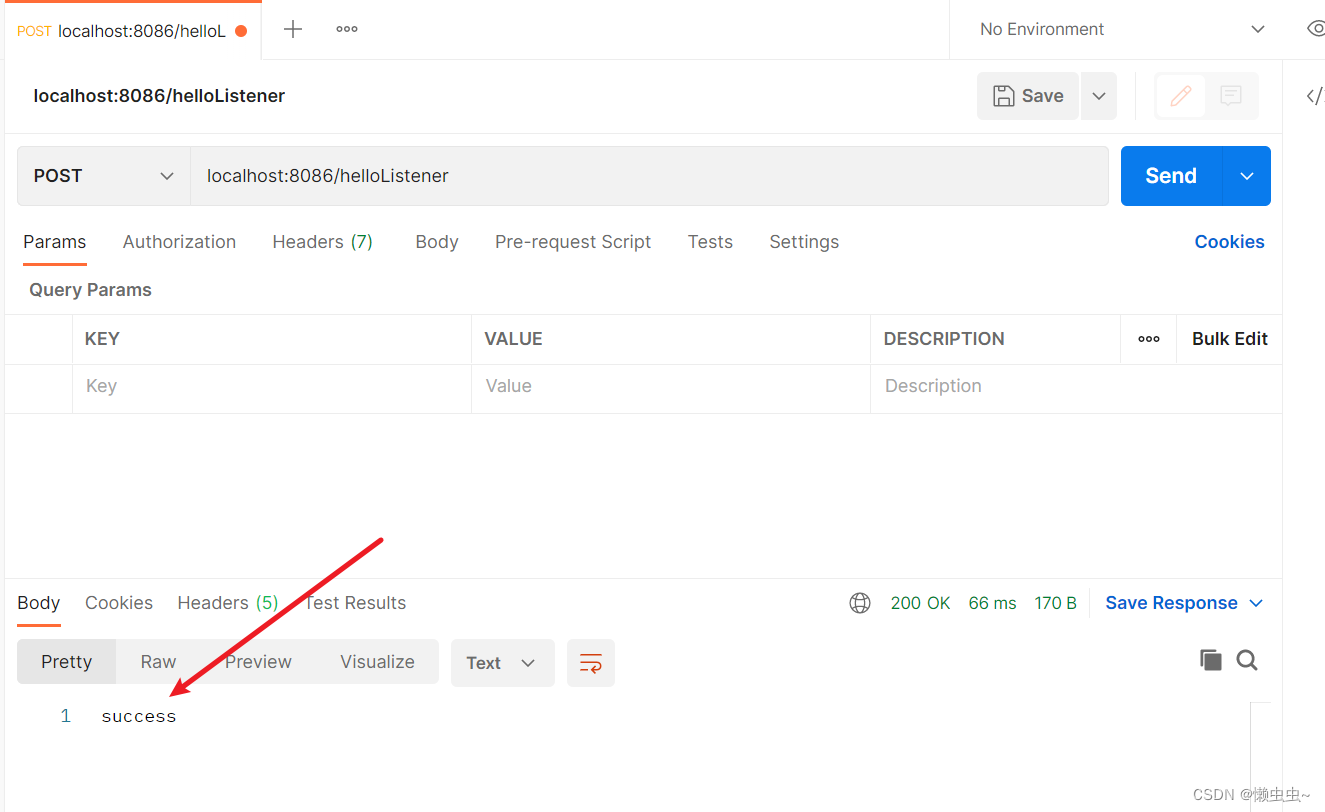
@RequestMapping("/helloListener")
public String helloListener(){
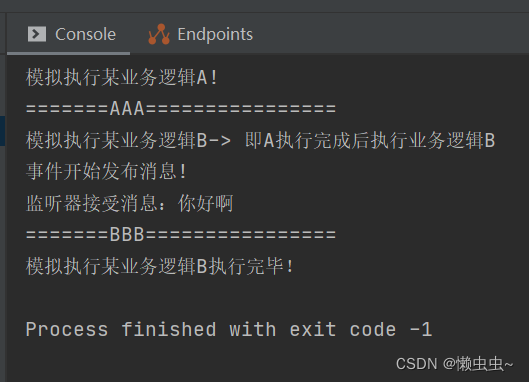
System.out.println("模拟执行某业务逻辑A!");
System.out.println("=======AAA================");
System.out.println("模拟执行某业务逻辑B-> 即A执行完成后执行业务逻辑B");
System.out.println("事件开始发布消息!");
applicationContext.publishEvent(new CustomEvent("你好啊"));
System.out.println("=======BBB================");
System.out.println("模拟执行某业务逻辑B执行完毕!");
return "success";
}
}
5.执行结果
https://blog.csdn.net/jike11231/article/details/124872298


![深度学习基础入门篇[9.3]:卷积算子:空洞卷积、分组卷积、可分离卷积、可变性卷积等详细讲解以及应用场景和应用实例剖析](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/8458852e6b0157f98825fde38279e3c2.png)