文件操作
1.写数据
# open(name, mode) # name:是要打开的目标文件名的字符串(可以包含文件所在的具体路径)。 # mode:设置打开文件的模式(访问模式):只读、写入、追加等。 #1.打开文件---通道建立--申请资源 # w 模式会清空之前的内容.再次写入新的内容. # a 模式会在旧的内容之后追加写入新的内容.file = open("a.txt","a") #.2 写入内容 file.write('\nhello python') #3.关闭通道--释放资源 file.close() print('----操作结束-------')
2.读数据
#2.读取数据 # result = file.read() # 读取全部内容 # ------------------------------------- # result = file.read(10) # 读取部分数据--按照字符个数 # ---------------------------------- # result = file.readline()#读取一行 # print(result,end='') # result = file.readline()#读取二行 # print(result,end='') #-----------------------------------file = open("a.txt","a") #.2 写入内容 file.write('\nhello python') #3.关闭通道--释放资源 file.close() print('----操作结束-------')
3.路径和编码
# 路径: # 相对路径 # 绝对路径 # file = open("a.txt","a") file = open('C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\aaa.txt','w',encoding='utf-8') #.2 写入内容 file.write('hello python\n') file.write('你好') #3.关闭通道--释放资源 file.close() print('----操作结束-------')
4.文件备份
-
补充: readline()读取全部行.
#1.打开文件
file = open('a.txt','r',encoding='utf-8')
#2.读取数据
while True:
result = file.readline()#读取1行
#1.判读读取返回的结果长度为0 ,就没有内容了.break跳出循环.
# if len(result) == 0:
# break
#2.优雅: 字符串不为空转成bool值就是True
if not result:
break
print(result,end='')
#3.释放资源
file.close()-
补充:纯文本复制.
#需求: 把.a.txt 的内容复制到 b.txt 中
# 1.让程序去读取a.txt的内容.
# 2.把内容写入到b.txt
a_file = open('a.txt','r',encoding='utf-8')
b_file = open('b.txt','w',encoding='utf-8')
# 1.让程序去读取a.txt的内容.
read_info = a_file.read()
print(read_info)
# 2.把内容写入到b.txt
b_file.write(read_info)
a_file.close()
b_file.close()-
非文本文件复制
a_file = open(r"C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\aaa.png",'rb')
b_file = open("bbb.png",'wb')
while True:
con = a_file.read(1024)
#判断con如果没有数据了.我们就break跳出
if len(con) == 0:
break
b_file.write(con)
a_file.close()
b_file.close()异常处理
5.异常捕获
# 格式1: -- 缺点: 不能查看异常的原因. # try: # 可能发生异常的代码 # except: # 发生异常后的处理 #print(8 / 0) #ZeroDivisionError: division by zero # try: # print(8/0) # except: # print('发生了错误') # print('程序结束') # ---------------------------------------------------# 格式2: 优点: 可以看到异常的类型和原因. # try: # 可能发生异常的代码 # except Exception as e: # print(e) # 发生异常后的处理 try: print(8/0) except Exception as e: print('发生了错误',type(e),e)#<class 'ZeroDivisionError'> division by zero print('程序结束')
6.捕获指定类型异常
# 格式: # try: # 可能发生错误的代码 # except 异常类型: # 如果捕获到该异常类型执行的代码 try: # print('abc'.index('m')) # ValueError: substring not found # print(8 / 0) print('abc'[100]) #IndexError: string index out of range except ZeroDivisionError: print("发生了除0异常") except ValueError: print("字符串没找到") except Exception as e: print('服务器正在维护--请联系管理员',e) print('---程序结束----')
7.捕获异常完整格式
''' try: 可能发生异常的代码 except Exception as result: 发生了异常会走这里 else: print('没有异常,真开心') finally: 无论是否有异常.都会走这里. '''file = None try: file = open("F:/a.txt","a") #.2 写入内容 file.write('\nhello python') except Exception as e: print(f'发现异常:{e}') else: print('没有发生异常--文件读写完毕---') finally: # 3.关闭通道--释放资源 if file is not None: file.close() # try: # file.close() # except Exception as e: # print('释放资源出错')
8.异常传递
# 异常的传递.如果没有人进行捕获.那么最终给了主函数. # 在主函数之前捕获最合适.def aaa(): print("aaa") bbb() def bbb(): print("bbb") ccc() def ccc(): print("ccc") print(8/0) #主函数 if __name__ == '__main__': try: aaa() except Exception as e: print('出现异常了', e)
模块和包
9.模块和导入方式
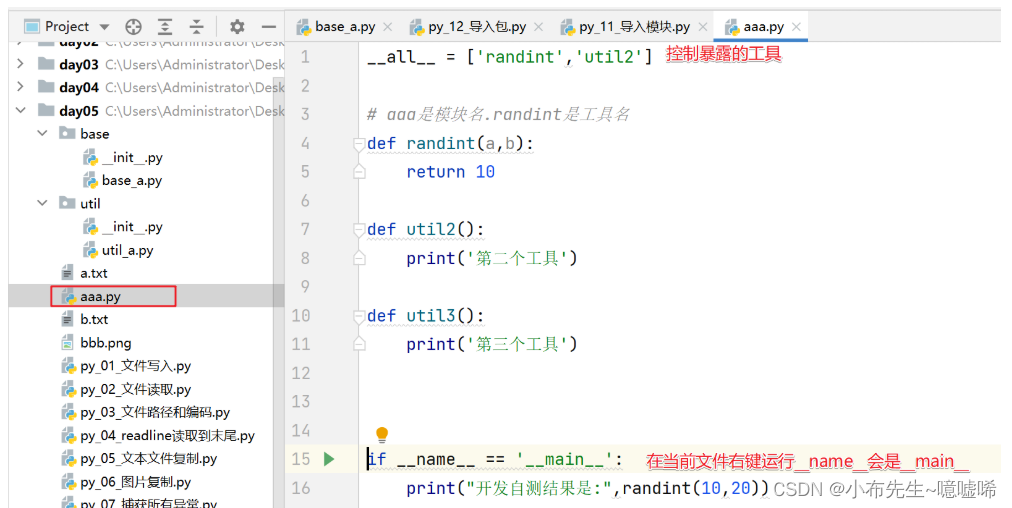
# import 模块名 # from 模块名 import 功能名 # from 模块名 import * # import 模块名 as 别名 # from 模块名 import 功能名 as 别名 # ------------------------------------# import random # 调用广泛 # print(random.randint(1, 9)) # from random import randint # 调用简单 # print(randint(1, 3)) # from random import * # *导入表示所有模块下的工具. # print(randint(1, 3)) # import random as r # 1.避免不同模块导入冲突.2.名字短容易调用. # print(r.randint(1, 4)) # from random import randint as prt # 起一个别名 # print(prt(1,5)) # from aaa import randint as mrt # print(mrt(1,6)) from aaa import * print(randint(1, 2)) util2() # util3() from aaa import util3 util3()
10.制作模块
11.包和导入方式
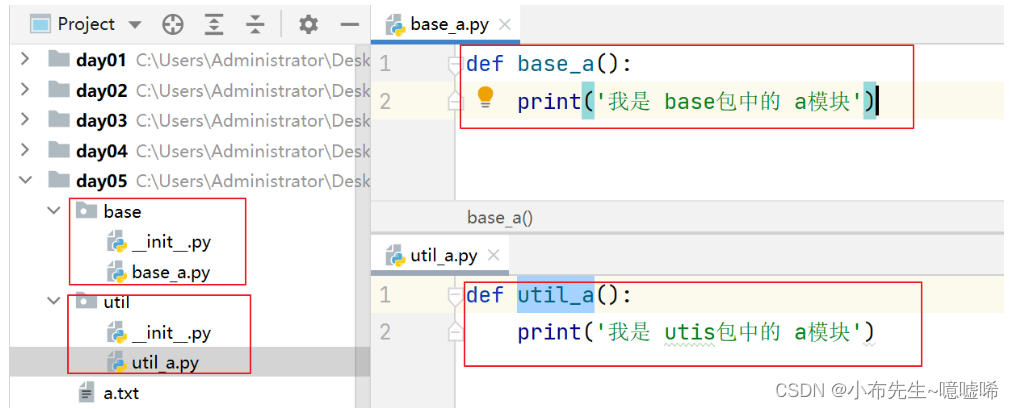
# import 包名.模块名
import base.base_a
base.base_a.base_a()
# from 包名 import 模块
from util import util_a
util_a.util_a()