
目录
115. 不同的子序列 Distinct Subsequences 🌟🌟🌟
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 Populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node 🌟🌟
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II Populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii 🌟🌟
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏 🌟
Golang每日一练 专栏
Python每日一练 专栏
C/C++每日一练 专栏
Java每日一练 专栏
二叉树专题(8)第115题除外
115. 不同的子序列 Distinct Subsequences
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串 t ,计算在 s 的子序列中 t 出现的个数。
字符串的一个 子序列 是指,通过删除一些(也可以不删除)字符且不干扰剩余字符相对位置所组成的新字符串。(例如,"ACE" 是 "ABCDE" 的一个子序列,而 "AEC" 不是)
题目数据保证答案符合 32 位带符号整数范围。
示例 1:
输入:s = "rabbbit", t = "rabbit"
输出:3
解释:如下图所示, 有 3 种可以从 s 中得到 "rabbit" 的方案。
rabbbit
rabbbit
rabbbit
示例 2:
输入:s = "babgbag", t = "bag"
输出:5
解释:如下图所示, 有 5 种可以从 s 中得到 "bag" 的方案。
babgbag
babgbag
babgbag
babgbag
babgbag
提示:
0 <= s.length, t.length <= 1000s和t由英文字母组成
代码1: 暴力枚举
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func numDistinct(s string, t string) int {
var ans int
var dfs func(int, int)
dfs = func(i, j int) {
if j == len(t) {
ans++
return
}
if i == len(s) {
return
}
if s[i] == t[j] {
dfs(i+1, j+1) // 匹配
}
dfs(i+1, j) // 不匹配
}
dfs(0, 0)
return ans
}
func main() {
s := "rabbbit"
t := "rabbit"
fmt.Println(numDistinct(s, t))
s = "babgbag"
t = "bag"
fmt.Println(numDistinct(s, t))
}
输出:
3
5
代码2: 记忆化搜索
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func numDistinct(s string, t string) int {
memo := make([][]int, len(s))
for i := range memo {
memo[i] = make([]int, len(t))
for j := range memo[i] {
memo[i][j] = -1
}
}
var dfs func(int, int) int
dfs = func(i, j int) int {
if j == len(t) {
return 1
}
if i == len(s) {
return 0
}
if memo[i][j] != -1 {
return memo[i][j]
}
ans := dfs(i+1, j)
if s[i] == t[j] {
ans += dfs(i+1, j+1)
}
memo[i][j] = ans
return ans
}
return dfs(0, 0)
}
func main() {
s := "rabbbit"
t := "rabbit"
fmt.Println(numDistinct(s, t))
s = "babgbag"
t = "bag"
fmt.Println(numDistinct(s, t))
}
代码3: 动态规则
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func numDistinct(s string, t string) int {
m, n := len(s), len(t)
dp := make([][]int, m+1)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int, n+1)
}
for i := 0; i <= m; i++ {
dp[i][0] = 1
}
for i := 1; i <= m; i++ {
for j := 1; j <= n; j++ {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]
if s[i-1] == t[j-1] {
dp[i][j] += dp[i-1][j-1]
}
}
}
return dp[m][n]
}
func main() {
s := "rabbbit"
t := "rabbit"
fmt.Println(numDistinct(s, t))
s = "babgbag"
t = "bag"
fmt.Println(numDistinct(s, t))
}
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 Populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node
给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。
二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
示例 1:
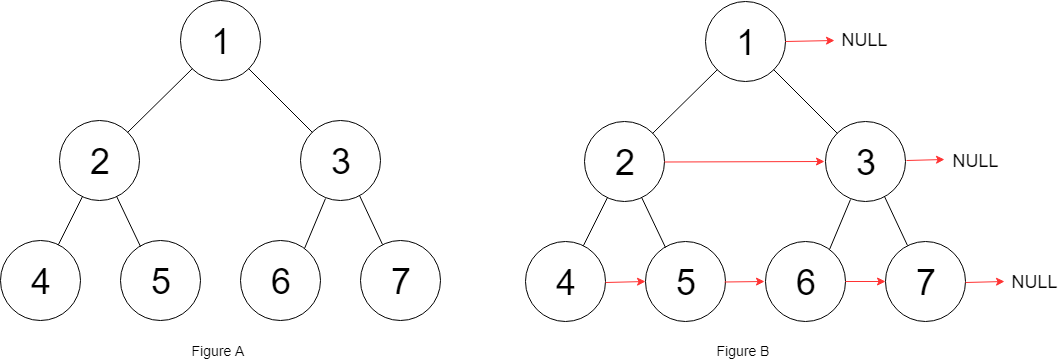
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] 输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#] 解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。序列化的输出按层序遍历排列,同一层节点由 next 指针连接,'#' 标志着每一层的结束。
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 2^12 - 1]范围内 -1000 <= node.val <= 1000
进阶:
- 你只能使用常量级额外空间。
- 使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
代码1: 递归
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
const null = -1 << 31
type Node struct {
Val int
Left *Node
Right *Node
Next *Node
}
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
if root.Left != nil {
root.Left.Next = root.Right
}
if root.Right != nil {
if root.Next != nil {
root.Right.Next = root.Next.Left
}
}
connect(root.Left)
connect(root.Right)
return root
}
func buildTree(nums []int) *Node {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return nil
}
root := &Node{Val: nums[0]}
Queue := []*Node{root}
idx := 1
for idx < len(nums) {
node := Queue[0]
Queue = Queue[1:]
if nums[idx] != null {
node.Left = &Node{Val: nums[idx]}
Queue = append(Queue, node.Left)
}
idx++
if idx < len(nums) && nums[idx] != null {
node.Right = &Node{Val: nums[idx]}
Queue = append(Queue, node.Right)
}
idx++
}
return root
}
func (root *Node) LevelOrder() string {
if root == nil {
return "[]"
}
var arr []int
Queue := []*Node{root}
for len(Queue) > 0 {
cur := Queue[0]
Queue = Queue[1:]
arr = append(arr, cur.Val)
if cur.Left != nil {
Queue = append(Queue, cur.Left)
}
if cur.Right != nil {
Queue = append(Queue, cur.Right)
}
if cur.Next == nil {
arr = append(arr, null)
}
}
size := len(arr)
for size > 0 && arr[size-1] == null {
arr = arr[:size-1]
size = len(arr)
}
result := "["
for i, n := range arr {
if n == null {
result += "#"
} else {
result += strconv.FormatInt(int64(n), 10)
}
if i < size-1 {
result += ","
} else {
result += ",#]"
}
}
return result
}
func main() {
nums := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
root := buildTree(nums)
fmt.Println(connect(root).LevelOrder())
}
输出:
[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
代码2: 迭代
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
const null = -1 << 31
type Node struct {
Val int
Left *Node
Right *Node
Next *Node
}
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
queue := []*Node{root}
for len(queue) > 0 {
n := len(queue)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
node := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if i < n-1 {
node.Next = queue[0]
}
if node.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Right)
}
}
}
return root
}
func buildTree(nums []int) *Node {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return nil
}
root := &Node{Val: nums[0]}
Queue := []*Node{root}
idx := 1
for idx < len(nums) {
node := Queue[0]
Queue = Queue[1:]
if nums[idx] != null {
node.Left = &Node{Val: nums[idx]}
Queue = append(Queue, node.Left)
}
idx++
if idx < len(nums) && nums[idx] != null {
node.Right = &Node{Val: nums[idx]}
Queue = append(Queue, node.Right)
}
idx++
}
return root
}
func (root *Node) LevelOrder() string {
if root == nil {
return "[]"
}
var arr []int
Queue := []*Node{root}
for len(Queue) > 0 {
cur := Queue[0]
Queue = Queue[1:]
arr = append(arr, cur.Val)
if cur.Left != nil {
Queue = append(Queue, cur.Left)
}
if cur.Right != nil {
Queue = append(Queue, cur.Right)
}
if cur.Next == nil {
arr = append(arr, null)
}
}
size := len(arr)
for size > 0 && arr[size-1] == null {
arr = arr[:size-1]
size = len(arr)
}
result := "["
for i, n := range arr {
if n == null {
result += "#"
} else {
result += strconv.FormatInt(int64(n), 10)
}
if i < size-1 {
result += ","
} else {
result += ",#]"
}
}
return result
}
func main() {
nums := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
root := buildTree(nums)
fmt.Println(connect(root).LevelOrder())
}
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II Populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii
给定一个二叉树
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
进阶:
- 你只能使用常量级额外空间。
- 使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
示例:
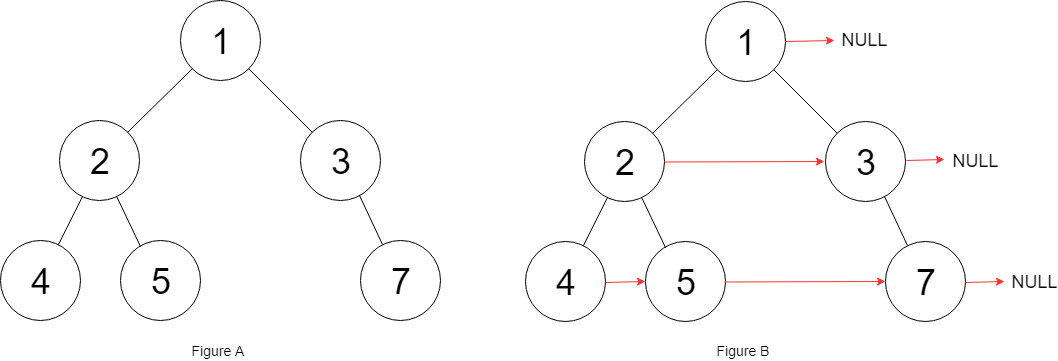
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7] 输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#] 解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。序列化输出按层序遍历顺序(由 next 指针连接),'#' 表示每层的末尾。
提示:
- 树中的节点数小于
6000 -100 <= node.val <= 100
代码1: 递归
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
const null = -1 << 31
type Node struct {
Val int
Left *Node
Right *Node
Next *Node
}
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
if root.Left != nil {
if root.Right != nil {
root.Left.Next = root.Right
} else {
root.Left.Next = getNext(root.Next)
}
}
if root.Right != nil {
root.Right.Next = getNext(root.Next)
}
connect(root.Right)
connect(root.Left)
return root
}
func getNext(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
if root.Left != nil {
return root.Left
}
if root.Right != nil {
return root.Right
}
return getNext(root.Next)
}
func buildTree(nums []int) *Node {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return nil
}
root := &Node{Val: nums[0]}
Queue := []*Node{root}
idx := 1
for idx < len(nums) {
node := Queue[0]
Queue = Queue[1:]
if nums[idx] != null {
node.Left = &Node{Val: nums[idx]}
Queue = append(Queue, node.Left)
}
idx++
if idx < len(nums) && nums[idx] != null {
node.Right = &Node{Val: nums[idx]}
Queue = append(Queue, node.Right)
}
idx++
}
return root
}
func (root *Node) LevelOrder() string {
if root == nil {
return "[]"
}
var arr []int
Queue := []*Node{root}
for len(Queue) > 0 {
cur := Queue[0]
Queue = Queue[1:]
arr = append(arr, cur.Val)
if cur.Left != nil {
Queue = append(Queue, cur.Left)
}
if cur.Right != nil {
Queue = append(Queue, cur.Right)
}
if cur.Next == nil {
arr = append(arr, null)
}
}
size := len(arr)
for size > 0 && arr[size-1] == null {
arr = arr[:size-1]
size = len(arr)
}
result := "["
for i, n := range arr {
if n == null {
result += "#"
} else {
result += strconv.FormatInt(int64(n), 10)
}
if i < size-1 {
result += ","
} else {
result += ",#]"
}
}
return result
}
func main() {
nums := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
root := buildTree(nums)
fmt.Println(connect(root).LevelOrder())
}
输出:
[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,6,7,#]
代码2: 迭代
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
const null = -1 << 31
type Node struct {
Val int
Left *Node
Right *Node
Next *Node
}
func connect(root *Node) *Node {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
queue := []*Node{root}
for len(queue) > 0 {
n := len(queue)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
node := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if i < n-1 {
node.Next = queue[0]
}
if node.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Right)
}
}
}
return root
}
func buildTree(nums []int) *Node {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return nil
}
root := &Node{Val: nums[0]}
Queue := []*Node{root}
idx := 1
for idx < len(nums) {
node := Queue[0]
Queue = Queue[1:]
if nums[idx] != null {
node.Left = &Node{Val: nums[idx]}
Queue = append(Queue, node.Left)
}
idx++
if idx < len(nums) && nums[idx] != null {
node.Right = &Node{Val: nums[idx]}
Queue = append(Queue, node.Right)
}
idx++
}
return root
}
func (root *Node) LevelOrder() string {
if root == nil {
return "[]"
}
var arr []int
Queue := []*Node{root}
for len(Queue) > 0 {
cur := Queue[0]
Queue = Queue[1:]
arr = append(arr, cur.Val)
if cur.Left != nil {
Queue = append(Queue, cur.Left)
}
if cur.Right != nil {
Queue = append(Queue, cur.Right)
}
if cur.Next == nil {
arr = append(arr, null)
}
}
size := len(arr)
for size > 0 && arr[size-1] == null {
arr = arr[:size-1]
size = len(arr)
}
result := "["
for i, n := range arr {
if n == null {
result += "#"
} else {
result += strconv.FormatInt(int64(n), 10)
}
if i < size-1 {
result += ","
} else {
result += ",#]"
}
}
return result
}
func main() {
nums := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
root := buildTree(nums)
fmt.Println(connect(root).LevelOrder())
}
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏 🌟
✨ 持续,努力奋斗做强刷题搬运工!
👍 点赞,你的认可是我坚持的动力!
🌟 收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向!
✎ 评论,你的意见是我进步的财富!
☸ 主页:https://hannyang.blog.csdn.net/
 | Golang每日一练 专栏 |
 | Python每日一练 专栏 |
 | C/C++每日一练 专栏 |
 | Java每日一练 专栏 |








![[Python工匠]输出③容器类型](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/26100ccda1774af5839e97f6ac5f5047.png)