目录
一、概述
1.特点:
2.方法:
二、Set接口的使用
三、Set实现类
1.HashSet ***
(1)简单应用:
(2)存储方式
2.TreeSet
(1)红黑树
(2)使用
(3)保存数据
(4)Comparator接口
一、概述
1.特点:
无序、无下标、元素不可重复。
2.方法:
全部继承自 Collection 中的方法。
二、Set接口的使用
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 测试Set接口的使用
* 特点:无序 没有下标 不能重复
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
//1.添加数据
set.add("苹果");
set.add("小米");
set.add("Vivo");
set.add("OPPO");
System.out.println("数据个数:"+set.size());
System.out.println(set.toString());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
//2.删除数据
set.remove("Vivo");
System.out.println(set.toString());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
//3.遍历
//(1)增强for
for (String string : set){
System.out.println(string);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
//(2)使用迭代器
Iterator<String> it = set.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
//4.判断
System.out.println(set.isEmpty());
System.out.println(set.contains("OPPO"));
}
}
三、Set实现类
1.HashSet ***
基于HashCode实现元素不重复
当存入元素的哈希码相同时,会调用equals进行确认,如结果为true,则拒绝后者存入。
(1)简单应用:
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* HashSet集合的使用
* 无序
* 存储结构:哈希表 (数组+链表+红黑树)
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//新建集合
HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<String>();
//1.添加元素
hashSet.add("E");
hashSet.add("B");
hashSet.add("C");
hashSet.add("D");
hashSet.add("E"); //出现重复的,最后也只会显示一个
System.out.println("元素个数:"+hashSet.size());
System.out.println(hashSet.toString());
//2.删除数据
hashSet.remove("E");
System.out.println("删除之后:"+hashSet.size());
System.out.println("-------------------");
//3.遍历操作
//(1)增强for循环
for (String string : hashSet){
System.out.println(string);
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
//(2)迭代器
Iterator<String> it =hashSet.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
//4.判断
System.out.println(hashSet.isEmpty());
System.out.println(hashSet.contains("K"));
}
}
(2)存储方式
添加数据:
Person p1= new Person("张三",22);
Person p2= new Person("张",2);
Person p3= new Person("三",12);
Person p4= new Person("张 三",20);
hashSet.add(p1);
hashSet.add(p2);
hashSet.add(p3);
hashSet.add(p4);
当添加数据 hashset.add(new Person("张三",22)); 时,数据仍会被添加进去。为什么呢?
存储结构:哈希表(数组+链表+红黑树)
存储过程:
(1)根据hashcode计算保存位置,如果此位置为空,则直接保存,如果不为空执行第二步。

(2)再执行equals方法,如果equals方法为true,则认为是重复;否则,形成链表。
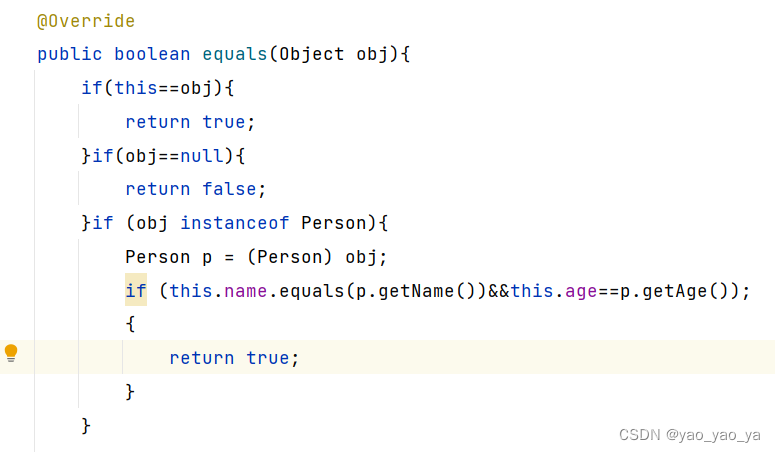
完整代码 重在注释 重在注释 重在注释
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
Person类:
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Person [name=" + name + ",age=" + age + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode(){
int n1 = this.name.hashCode();
int n2 = this.age;
return n1+n2;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(this==obj){
return true;
}if(obj==null){
return false;
}if (obj instanceof Person){
Person p = (Person) obj;
if (this.name.equals(p.getName())&&this.age==p.getAge());
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
Test测试类:
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* HashSet集合的使用
* 无序
* 存储结构:哈希表 (数组+链表+红黑树)
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//新建集合
HashSet<Person> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
//1.添加数据
Person p1= new Person("张三",22);
Person p2= new Person("张",2);
Person p3= new Person("三",12);
Person p4= new Person("张 三",20);
hashSet.add(p1);
hashSet.add(p2);
hashSet.add(p3);
hashSet.add(p4);
hashSet.add(new Person("张三",22));
System.out.println("元素个数:" +hashSet.size());
System.out.println(hashSet.toString());
//2.删除数据
hashSet.remove(p2);
hashSet.remove(new Person("张三",22));//重写hashCode才能用这种方式删除
System.out.println("删除之后:"+hashSet.size());
System.out.println("-------------------");
//3.遍历操作
//(1)增强for循环
for (Person person : hashSet){
System.out.println(person);
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
//(2)迭代器
Iterator<Person> it =hashSet.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
System.out.println("-------------------");
//4.判断
System.out.println(hashSet.isEmpty());
System.out.println(hashSet.contains("K"));
}
}
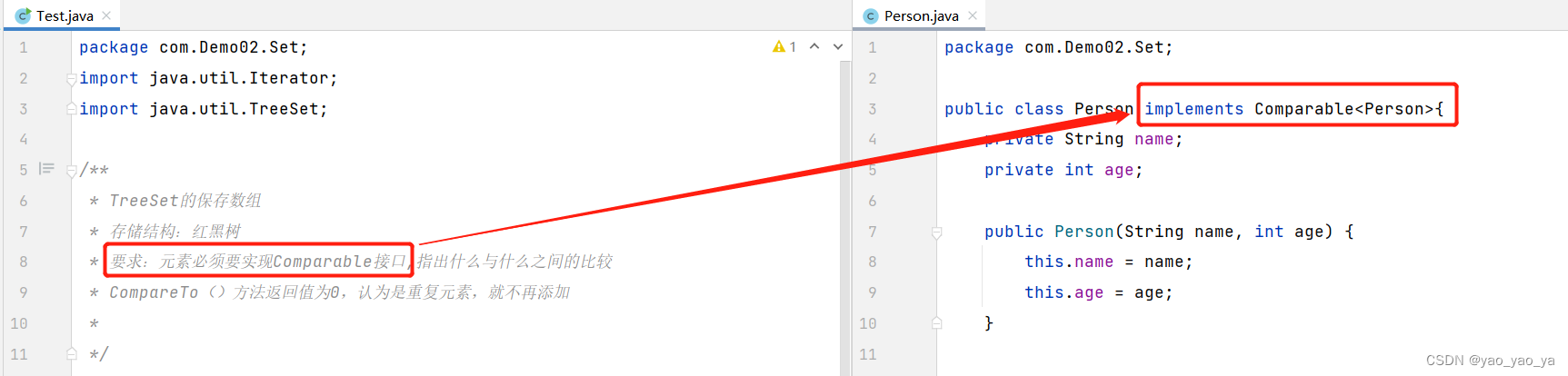
2.TreeSet
基于排列顺序实现元素不重复。
实现了SortedSet接口,对集合元素自动排列。
元素对象的类型必须实现Compareable接口,指定排序规则。
通过CompareTo方法确定是否为重复元素。
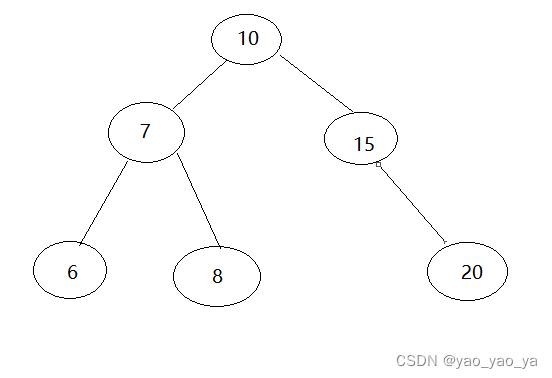
(1)红黑树
红黑树是在二叉树的基础上加了颜色。(保持平衡)
二叉树:每个节点有两个分支,从上到下依次列出,数字大小 左小右大。
(2)使用
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* TreeSet的使用
* 存储结构:红黑树
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
//1、添加元素
treeSet.add("rgre");
treeSet.add("esf");
treeSet.add("rgewfgre");
treeSet.add("rgrgre");
System.out.println("元素个数:"+treeSet.size());
System.out.println(treeSet.toString());
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//2.删除元素
treeSet.remove("esf");
System.out.println("删除之后的个数:" + treeSet.size());
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//3.遍历
//(1)增强for
for (String str : treeSet){
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//(2)迭代器
Iterator<String> it = treeSet.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
System.out.println("--------------------------");
//4.判断
System.out.println(treeSet.contains("wfef"));
System.out.println(treeSet.isEmpty());
}
}
(3)保存数据
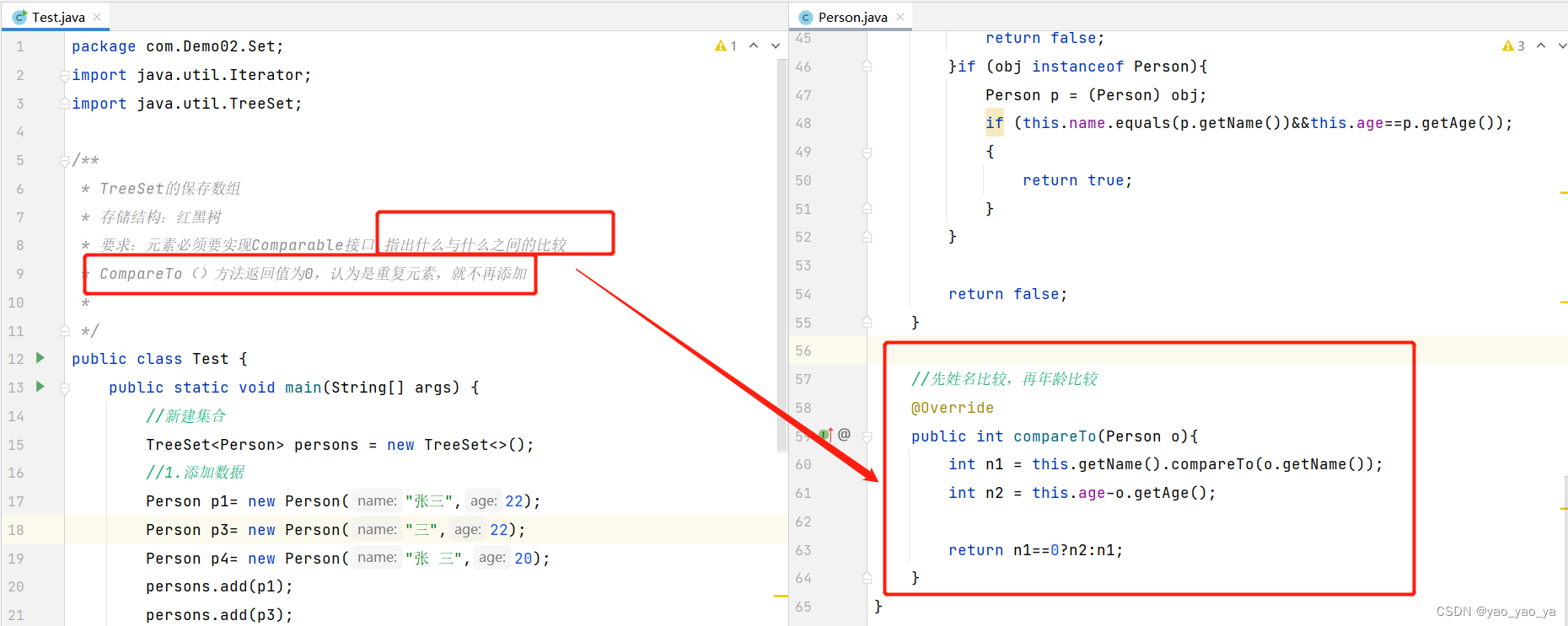
其他方法和HashCode一样。
(4)Comparator接口
import com.Demo02.Set.Person;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
/**
* TreeSet集合的使用
* Comparator:实现定制比较(比较器)
*/
public class TreeSet1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合,并制定比较规则
TreeSet<Person> persons = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
int n1 = o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
int n2 = o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
return n1==0?n2:n1;
}
});
Person p1 = new Person("ewfe",21);
Person p2 = new Person("few",11);
Person p3 = new Person("ewrvgfe",11);
Person p4 = new Person("gtrh", 22);
persons.add(p1);
persons.add(p2);
persons.add(p3);
persons.add(p4);
System.out.println(persons.toString());
}
}
重在理解!!
感谢ლ(°◕‵ƹ′◕ლ)!!!