前言
为什么这一章节要细分之前的解析xml处理逻辑,原因是违反了单一原则设计,职责并不明确,将Sql语句、参数、返回值等等一切都进行解析,那么这种的需要拆开,为了后面可维护可扩展,例如Mapper级别的有mapper解析,Sql语句有Sql语句的解析,因为Sql也是脚本,需要对脚本进行动态处理,也会延伸一些脚本类来处理对应语句
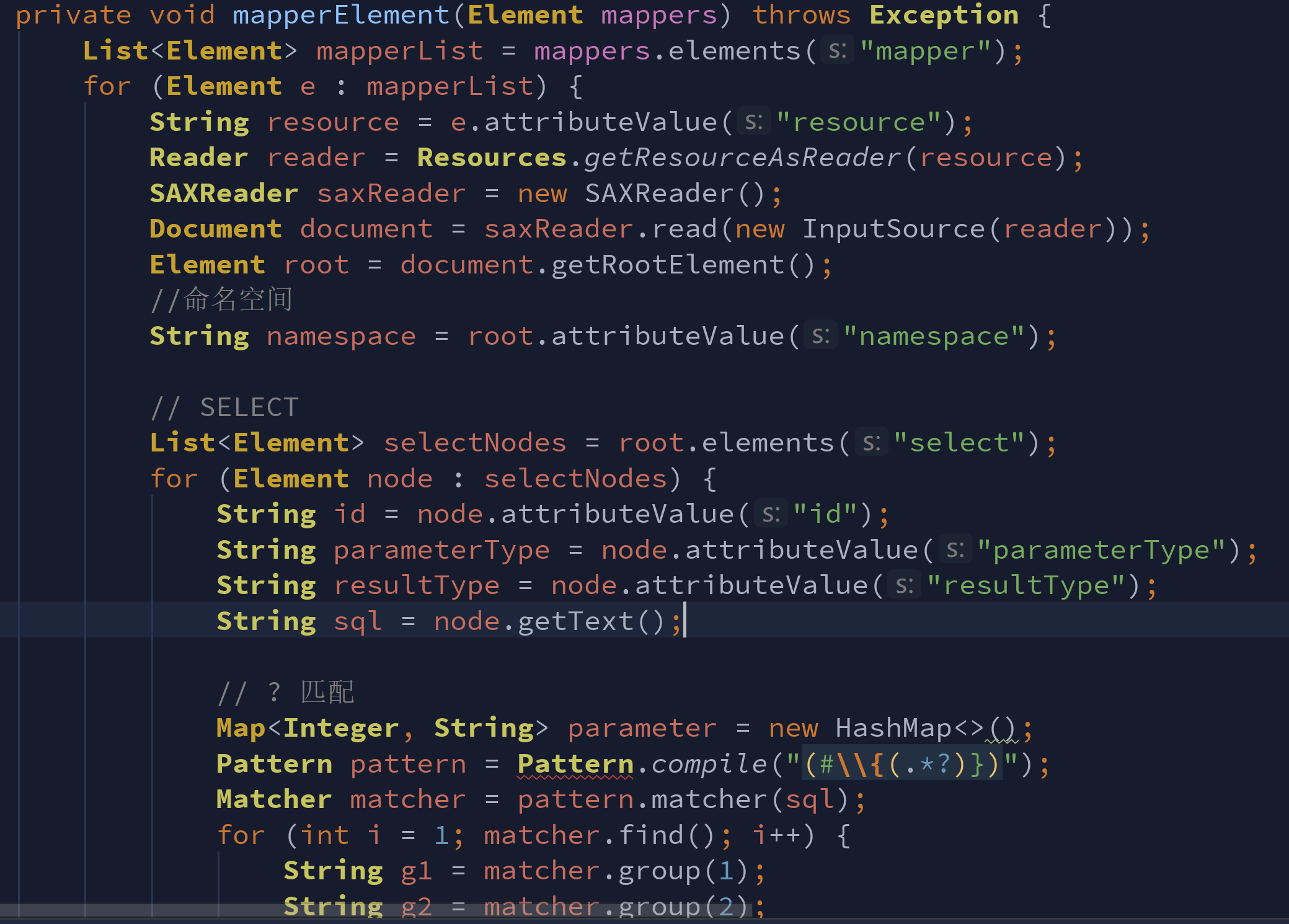
图一,全部职责混到一个类里一个方法里
2. UML类图
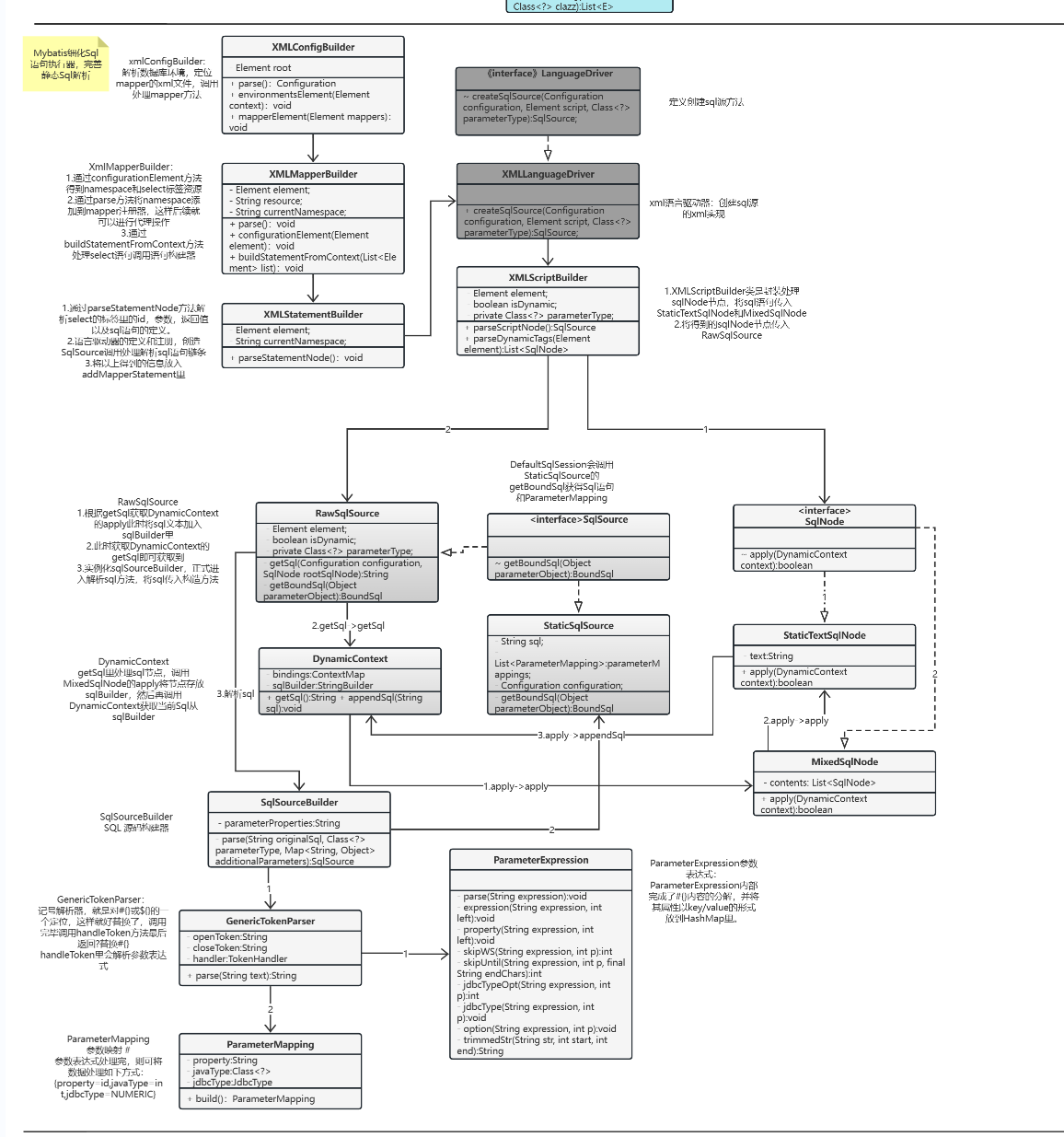
按照设计原则,需要各功能满模块满足单一原则,而每一个具体的实现上采用迪米特原则(关联类只关联"朋友",不应该"关联陌生人"),而显然,在mapper解析时没有职责明确,全部写到一个方法里处理,现在就要优化这部分内容。
XMLConfigBuilder:Xml配置构建器(名字起的多见名之意啊,ps:赞美之情)
此类构建Xml的环境,如开发环境的jdbc,测试环境等等,也扩展了Mapper映射器包装,整个解析以此类为入口进行串联调用。
XMLMapperBuilder:XmlMapper构建器
此类解析Mapper数据,对mapper的namespace进行绑定映射,扩展语句构建器包装
XMLStatementBuilder:语句构建器
此类处理select、update....标签上的id,参数类型、返回类型、包装语言驱动器用来得到处理过的Sql语句,最终绑定到MapperStatement。
LanguageDriver:语言驱动器接口,定义创建SqlSource方法
XMLLanguageDriver:语言驱动器实现类,
此类在Configuration中配置为默认实现的语言驱动器,包装调用脚本构建器。
LanguageDriverRegistry:语言驱动器注册器,在Configuration中配置默认将XMLLanguageDriver注册到map里
XMLScriptBuilder:脚本构建器
此类处理静态语言Sql和动态语言Sql,所以和SqlNode节点、SqlSource打交道
SqlNode:sql节点接口,主要是描述文件配置中Sql的信息,定义了apply方法。
StaticTextSqlNode:静态文本Sql节点,
实现SqlNode,描述Xml配置中不带标签的信息,即静态文本内容。
MixedSqlNode:混合Sql节点
实现SqlNode,最终由MixedSqlNode将所有的SqlNode实现串起来执行,也看作责任。
SqlSource:Sql源接口,定义获取BoundSql方法。
RawSqlSource:原始Sql源
此类实现了SqlSource接口,得到了Sql语句,将Sql语句传给Sql源进行解析处理。
SqlSourceBuilder:SQL 源构建器,此类主要完成以下两个操作
一方面是解析Sql中的#{}占位符定义的属性,如jdbcType、javaType(使用较少)
一方面是把#{}占位符替换成?占位符
ParameterMappingTokenHandler:SqlSourceBuilder内部类,处理Sql中的#{}占位符定义的属性
GenericTokenParser:普通记号解析器,完成对#{}标记的内容定位,并用?替换参数
StaticSqlSource:静态Sql源,将处理的sql语句和参数以构造方式传入进来,提供了获取boundSql方法,供其他的SqlSource使用。
总共涉及的就是这些类,最终流转回XmlStateMentBuilder中,将所有的信息存储到addMapperStatement,就可以供sql执行器基础信息。
以上的类解说也都是根据一步步流程梳理下来的,大家可以好好看下理解下,对照uml图看下
3. 代码实现及分析
3.1 Xml构建器(XMLConfigBuilder)
包:package df.middleware.mybatis.builder.xml
此类中其他地方没有变动,只有mapperElement有变动,将循环去XMLMapperBuilder取出每一个mapper信息。
此类中其他信息在下面链接里有具体代码,本节就不展示没有改动的了,新来的小伙伴可以看下
手敲Mybatis-Mapper的XML解析自动注册使用_渣渣洒泪成长记的博客-CSDN博客
/*
* <mappers>
* <mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
* <mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/BlogMapper.xml"/>
* <mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/PostMapper.xml"/>
* </mappers>
*/
// 将xml中的配置解析出来存储到对应的实体类中
// 处理mapper的方法,mapper里有多个sql语句,所以需要List
private void mapperElement(Element mappers) throws Exception {
// 得到mybatis-config-datasource.xml的mappers标签里的mapper
List<Element> mapperList = mappers.elements("mapper");
for (Element e : mapperList) {
String resource = e.attributeValue("resource");
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 在for循环里每个mapper都重新new一个XMLMapperBuilder,来解析
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource);
mapperParser.parse();
}
}3.2 XmlMapper构建器(XMLMapperBuilder)
我们将Mapper映射的部分解构出来放入此类中,在parse方法中,isResourceLoaded方法主要是判断资源是否加载重复,不重复开始解析配置,解析namespace,循环调用语句处理要解析语句,最后将namespce绑定mapper中。
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private Element element;
private String resource;
private String currentNamespace;
public XMLMapperBuilder(InputStream inputStream, Configuration configuration, String resource) throws DocumentException {
this(new SAXReader().read(inputStream), configuration, resource);
}
public XMLMapperBuilder(Document document, Configuration configuration,String resource) {
super(configuration);
this.element=document.getRootElement();
this.resource=resource;
}
/**
* 解析
* 绑定namespace
* 找到mapper下的所有select标签
*/
public void parse() throws ClassNotFoundException {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)){
configurationElement(element);
// 标记resource已被加载过
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 绑定映射器nameSpace
configuration.addMapper(Resources.classForName(currentNamespace));
}
}
// 配置mapper元素
// <mapper namespace="org.mybatis.example.BlogMapper">
// <select id="selectBlog" parameterType="int" resultType="Blog">
// select * from Blog where id = #{id}
// </select>
// </mapper>
// 找到mapper的namespace以及select的sql语句
private void configurationElement(Element element){
// 配置namespace
currentNamespace=element.attributeValue("namespace");
if (currentNamespace.equals("")) {
throw new RuntimeException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// select
buildStatementFromContext(element.elements("select"));
}
// 配置select|insert|update|delete
// 多个select需要list
// 并调用语句处理器
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<Element> list){
for(Element element:list){
// 解析语句
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser=new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration,element, currentNamespace);
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
}
}
}
Configuration中判断是否资源已加载,并缓存资源操作
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<>();
public boolean isResourceLoaded(String resource) {
return loadedResources.contains(resource);
}
public void addLoadedResource(String resource) {
loadedResources.add(resource);
}
3.3XML语句构建器 (XMLStatementBuilder)
在parseStatementNode方法中解析Select标签的id,参数返回值等,以及用默认语言驱动器处理Sql语句,最终将处理好的Sql语句和参数放入addmapperStateMent供DefaultSqlSession使用
设计的还是蛮清晰的每个类都有自己的职责,而且这里对Xml配置的构建都采用建造器模式,一步一步将所需要数据进行组合构建最终拿到想要的整体,我们在日常使用中有类似场景可以借鉴下。
当前解析呢我们先只解析SELECT标签下的。
public class XMLStatementBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private Element element;
private String currentNamespace;
public XMLStatementBuilder(Configuration configuration, Element element, String currentNamespace) {
super(configuration);
this.element = element;
this.currentNamespace = currentNamespace;
}
// 开始解析select标签的id,参数,返回值,并调用语言驱动器
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
// 参数类型
String parameterType = element.attributeValue("parameterType");
// 获取参数类型
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveAlias(parameterType);
// 结果
String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType");
// 获取结果类型
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveAlias(resultType);
// 获取命令类型(select|insert|update|delete)
String nodeName = element.getName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
Class<?> langClass = configuration.getLanguageRegistry().getDefaultDriverClass();
LanguageDriver langDriver = configuration.getLanguageRegistry().getDriver(langClass);
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, element, parameterTypeClass);
MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, currentNamespace + "." + id, sqlCommandType, sqlSource, resultTypeClass).build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(mappedStatement);
}
}3.4 语言驱动器(LanguageDriver)
包 package df.middleware.mybatis.scripting
语言驱动器接口,定义了创建Sql源。
public interface LanguageDriver {
SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, Element script, Class<?> parameterType);
}3.4.1 Xml语言驱动器(XMLLanguageDriver)
包:package df.middleware.mybatis.scripting.xmltags
语言驱动器实现类,主要调用Xml脚本构建器,在Configuration中注册为默认语言驱动器
public class XMLLanguageDriver implements LanguageDriver {
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, Element script, Class<?> parameterType) {
// 用XML脚本构建解析
XMLScriptBuilder xmlScriptBuilder = new XMLScriptBuilder(configuration, script, parameterType);
return xmlScriptBuilder.parseScriptNode();
}
}Configuration中又添加了注册Xml语句驱动器
protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry=new LanguageDriverRegistry();
public Configuration() {
// 注册xml语言驱动器
languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class);
}
public LanguageDriverRegistry getLanguageRegistry() {
return languageRegistry;
}3.4.2 语言驱动器注册器(LanguageDriverRegistry)
包:package df.middleware.mybatis.scripting.xmltags
提供了注册驱动器,以及注册默认驱动器方法,主要就是缓存操作,将驱动器存储map中
public class LanguageDriverRegistry {
// map
private final Map<Class<?>, LanguageDriver> LANGUAGE_DRIVER_MAP = new HashMap<Class<?>, LanguageDriver>();
private Class<?> defaultDriverClass = null;
public void register(Class<?> cls) {
if (cls == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("null is not a valid Language Driver");
}
if (!LanguageDriver.class.isAssignableFrom(cls)) {
throw new RuntimeException(cls.getName() + " does not implements " + LanguageDriver.class.getName());
}
// 如果没注册过,再去注册
LanguageDriver driver = LANGUAGE_DRIVER_MAP.get(cls);
if (driver == null) {
try {
//单例模式,即一个Class只有一个对应的LanguageDriver
driver = (LanguageDriver) cls.newInstance();
LANGUAGE_DRIVER_MAP.put(cls, driver);
}catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to load language driver for " + cls.getName(), ex);
}
}
}
public LanguageDriver getDriver(Class<?> cls) {
return LANGUAGE_DRIVER_MAP.get(cls);
}
public Class<?> getDefaultDriverClass() {
return defaultDriverClass;
}
public void setDefaultDriverClass(Class<?> defaultDriverClass) {
register(defaultDriverClass);
this.defaultDriverClass = defaultDriverClass;
}
}
4. Xml脚本构建器(XMLScriptBuilder)
包:package df.middleware.mybatis.scripting.xmltags
话说回来,从语言驱动器调用脚本构建器,处理解析脚本节点,此类处理静态和动态的Sql,不过本次只实现静态的Sql,待后续完善,首先parseDynamicTags通过其方法将Sql文本信息放入了Sql节点里,最终通过parseScriptNode方法将Sql节点信息放入混合节点里,再创建RawSqlSource将混合节点传入,后续RawSqlSource准备解析Sql。
/**
* @Author df
* @Date 2022/12/5 15:36
* @Version 1.0
* XML脚本构建器
* 封装sql
*/
public class XMLScriptBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private Element element;
private boolean isDynamic;
private Class<?> parameterType;
public XMLScriptBuilder(Configuration configuration, Element element, Class<?> parameterType) {
super(configuration);
this.element = element;
this.parameterType = parameterType;
}
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
// 将所有的Sql内容存储Sql节点里
List<SqlNode> contents = parseDynamicTags(element);
// 再将其放入混合节点
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = new MixedSqlNode(contents);
// 创建源Sql进行解析
return new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
public List<SqlNode> parseDynamicTags(Element element) {
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
// 得到sql语句文本
String data = element.getText();
// 将sql内容放入静态文本Sql节点,并存储List集合
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
return contents;
}
}5. SQL节点(SqlNode)
包:package df.middleware.mybatis.scripting.xmltags
SqlNode节点接口,定义了apply方法
/**
* @Author df
* @Date 2022/12/5 15:44
* @Version 1.0
* Sql节点,描述Mapper文件中配置的SQL信息
*/
public interface SqlNode {
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}5.1 静态文本Sql节点(StaticTextSqlNode)
实现SqlNode节点接口,处理静态文本Sql信息
/**
* @Author df
* @Date 2022/12/5 15:48
* @Version 1.0
* 静态文本SQL节点
* 描述XML或者注解中不带有任何标签的配置信息,即静态文本内容
*/
public class StaticTextSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private String text;
public StaticTextSqlNode(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
//将文本加入context
context.appendSql(text);
return true;
}
}5.2 混合Sql节点(MixedSqlNode)
实现SqlNode节点接口,混合Sql节点,其实就是不同的SqlNode都可以加载进来,到时统一调用不同实现类的SqlNode。
/**
* @Author df
* @Date 2022/12/5 15:50
* @Version 1.0
* 混合Sql节点,最终由MixedSqlNode将所有的SqlNode实现串起来执行,也看作责任链模式
* 1.将一组SqlNode对象进行串联执行,通常多个SqlNode对象才能联合表述一个SQL信息,所以就需要借助MixedSqlNode来将其进行串联,最终形成一个完整的SQL信息
*/
public class MixedSqlNode implements SqlNode {
//组合模式,拥有一个SqlNode的List
private List<SqlNode> contents;
public MixedSqlNode(List<SqlNode> contents) {
this.contents = contents;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 依次调用list里每个元素的apply
contents.forEach(node -> node.apply(context));
return true;
}
}
6. SQL源(SqlSource)
包:package df.middleware.mybatis.mapping
SQL源接口,定义了一个获取绑定的Sql方法。
/**
* @Author df
* @Date 2022/12/5 14:24
* @Version 1.0
* SQL源,主要作用创建一个Sql语句
*/
public interface SqlSource {
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}6.1 原Sql源(RawSqlSource)
包:package df.middleware.mybatis.scripting.defaults
此类处理#{}或者没有标签的纯文本Sql信息。
/**
* @Author df
* @Date 2022/12/5 15:52
* @Version 1.0
* 原始SQL源码,比 DynamicSqlSource 动态SQL处理快
* 存储的是只有“#{}”或者没有标签的纯文本sql信息
*/
public class RawSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private final SqlSource sqlSource;
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode, Class<?> parameterType) {
this(configuration, getSql(configuration, rootSqlNode), parameterType);
}
// 数据sql解析
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
// Sql源构建器
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
// 解析最终可执行的Sql
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<>());
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 获取已绑定过的Sql
return sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
// 获取Sql
private static String getSql(Configuration configuration, SqlNode rootSqlNode) {
DynamicContext dynamicContext = new DynamicContext(configuration, null);
// 将Sql信息存入dynamicContext的sqlBuilder里
rootSqlNode.apply(dynamicContext);
// 从dynamicContext的sqlBuilder里得到Sql文本
return dynamicContext.getSql();
}
}
6.2 StaticSqlSource
包:package df.middleware.mybatis.builder
在目录8最后一阶段返回的时候使用,结合目录8一起看。
/**
* @Author df
* @Date 2022/12/14 17:41
* @Version 1.0
* 主要创建BoundSql,供其他的SqlSource实现类使用,一个中间状态
*/
public class StaticSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private String sql;
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
private Configuration configuration;
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql) {
this(configuration, sql, null);
}
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
return new BoundSql(configuration, sql, parameterMappings, parameterObject);
}
}
7. DynamicContext
此类在RawSqlSource中使用,对传入的parameterObject对象进行“map”化处理,并且提供存储和获取Sql方法。
public class DynamicContext {
// 在编写映射文件时, '${parameter}','${databaseId}'分别可以取到当前用户传入的参数, 以及当前执行的数据库类型
public static final String PARAMETER_OBJECT_KEY = "_parameter";
// _databaseId可以指定不同的数据库支持
public static final String DATABASE_ID_KEY = "_databaseId";
private final StringBuilder sqlBuilder = new StringBuilder();
private final ContextMap bindings;
// 构造函数, 对传入的parameterObject对象进行“map”化处理;
// 也就是说,你传入的pojo对象,会被当作一个键值对数据来源来进行处理,读取这个pojo对象的接口,依然是Map对象(依然是以Map接口方式来进行读取)。
public DynamicContext(Configuration configuration, Object parameterObject) {
/*
* 在DynamicContext的构造函数中,可以看到:
* 1. 根据传入的参数对象是否为Map类型,有两个不同构造ContextMap的方式。
* 2. 而ContextMap作为一个继承了HashMap的对象,作用就是用于统一参数的访问方式:用Map接口方法来访问数据。具体来说:
* 2.1 当传入的参数对象不是Map类型时,Mybatis会将传入的POJO对象用MetaObject对象来封装,
* 2.2 当动态计算sql过程需要获取数据时,用Map接口的get方法包装 MetaObject对象的取值过程。
* 2.3 ContextMap覆写的get方法正是为了上述目的.具体参见下面的`ContextMap`覆写的get方法里的详细解释.
*/
if (parameterObject != null && !(parameterObject instanceof Map)) {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
bindings = new ContextMap(metaObject);
} else {
bindings = new ContextMap(null);
}
// 向刚构造出来的ContextMap实例中推入用户本次传入的参数parameterObject.
bindings.put(PARAMETER_OBJECT_KEY, parameterObject);
// 向刚构造出来的ContextMap实例中推入用户配置的DatabaseId.
bindings.put(DATABASE_ID_KEY, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
// 追加Sql
public void appendSql(String sql) {
sqlBuilder.append(sql);
sqlBuilder.append(" ");
}
// 获取Sql语句
public String getSql() {
return sqlBuilder.toString().trim();
}
// 上下文map,静态内部类
static class ContextMap extends HashMap<String, Object> {
private MetaObject parameterMetaObject;
public ContextMap(MetaObject parameterMetaObject) {
this.parameterMetaObject = parameterMetaObject;
}
}
}
8. SQL源构造器(SqlSourceBuilder)
包:package df.middleware.mybatis.builder
此类调用解析Sql标签将得到的最终的Sql语句、以及封装的参数类型创建并传递给了StaticSqlSource,而StaticSqlSource最终提供getBoundSql供DefaultSqlSesison使用。
/**
* @Author df
* @Date 2022/12/7 16:32
* @Version 1.0
* SQL 源构建器,此类主要完成以下两个操作
* 1.一方面是解析Sql中的#{}占位符定义的属性,如jdbcType、javaType(使用较少)
* 2.一方面是把#{}占位符替换成?占位符
*/
public class SqlSourceBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private static final String parameterProperties = "javaType,jdbcType,mode,numericScale,resultMap,typeHandler,jdbcTypeName";
public SqlSourceBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
super(configuration);
}
public SqlSource parse(String originSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
// 将Sql中#{}替换?,并把#{}内容转变为ParameterMapping对象
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
// 定位标签#{}并与ParameterMappingTokenHandler合作替换?
GenericTokenParser genericTokenParser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
// 得到处理后可执行的Sql
String sql = genericTokenParser.parse(originSql);
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
/**
*
* ParameterMappingTokenHandler的作用是配合着GenericTokenParaser完成Mybatis的占位符#{}格式的处理。它的处理方式是将每个#{}的内容,使用?进行替换,并且将#{}里的内容转变成ParameterMapping对象。
* */
public static class ParameterMappingTokenHandler extends BaseBuilder implements TokenHandler {
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = new ArrayList<>();
private Class<?> parameterType;
private MetaObject metaParameters;
public ParameterMappingTokenHandler(Configuration configuration, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
super(configuration);
this.parameterType = parameterType;
this.metaParameters = configuration.newMetaObject(additionalParameters);
}
public List<ParameterMapping> getParameterMappings() {
return parameterMappings;
}
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
return "?";
}
public ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(String content) {
// 解析参数映射
Map<String, String> parameterMap = new ParameterExpression(content);
String property = parameterMap.get("property");
Class<?> propertyType = parameterType;
ParameterMapping.Builder builder = new ParameterMapping.Builder(configuration, property, propertyType);
return builder.build();
}
}
}
8.1 普通记号解析器(GenericTokenParser)
包:package df.middleware.mybatis.parsing
此类主要是定位#{}标记,并协助handler返回?拼接成想要的Sql数据
/**
* @Author df
* @Date 2022/12/7 17:50
* @Version 1.0
* 普通记号解析器,处理#{}和${}参数
* GenericTokenParser的作用是完成对字符窜中${}和#{}的内容定位,每次定位完成后,调用TokenHandler进行内容替换。
*/
public class GenericTokenParser {
// 有一个开始和结束记号
private final String openToken;
private final String closeToken;
// 记号处理器
private final TokenHandler handler;
public GenericTokenParser(String openToken, String closeToken, TokenHandler handler) {
this.openToken = openToken;
this.closeToken = closeToken;
this.handler = handler;
}
// 解析#{} 为具体的?
public String parse(String text) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
if (text != null && text.length() > 0) {
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
int start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
// #{favouriteSection,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
// 这里是循环解析参数,参考GenericTokenParserTest,比如可以解析${first_name} ${initial} ${last_name} reporting.这样的字符串,里面有3个${}
while (start > -1) {
//判断一下 ${ 前面是否是反斜杠,这个逻辑在老版的mybatis中(如3.1.0)是没有的
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// the variable is escaped. remove the backslash.
// 新版已经没有调用substring了,改为调用如下的offset方式,提高了效率
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, start);
if (end == -1) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
offset = src.length;
} else {
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
String content = new String(src, offset, end - offset);
// 得到一对大括号里的字符串后,调用handler.handleToken,比如替换变量这种功能
builder.append(handler.handleToken(content));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
}
return builder.toString();
}
}9. ParameterMapping
/**
* @Author df
* @Date 2022/12/7 16:57
* @Version 1.0
* 参数映射 #{property,javaType=int,jdbcType=NUMERIC}
*/
public class ParameterMapping {
private Configuration configuration;
// property
private String property;
// javaType = int
private Class<?> javaType = Object.class;
// jdbcType=NUMERIC
private JdbcType jdbcType;
public static class Builder {
private ParameterMapping parameterMapping = new ParameterMapping();
public Builder(Configuration configuration, String property, Class<?> javaType) {
parameterMapping.configuration = configuration;
parameterMapping.property = property;
parameterMapping.javaType = javaType;
}
public Builder javaType(Class<?> javaType) {
parameterMapping.javaType = javaType;
return this;
}
public ParameterMapping build() {
return parameterMapping;
}
}
}
10. DefaultSqlSession调整点
这里的调整并不多,主要是获取Sql调整为ms.getSqlSource().getBoundSql(parameter),通过sqlSource进行获取Sql
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
List<T> list = executor.query(ms, parameter, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER, ms.getSqlSource().getBoundSql(parameter));
//connection.close();
return list.get(0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}MappedStatement里添加了SqlSource的使用
public class MappedStatement {
private Configuration configuration;
private String id;
private SqlCommandType sqlCommandType;
private SqlSource sqlSource;
Class<?> resultType;
//public MappedStatement(){}
public static class Builder {
private MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement();
public Builder(Configuration configuration, String id, SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
SqlSource sqlSource,Class<?> resultType) {
mappedStatement.configuration = configuration;
mappedStatement.id = id;
mappedStatement.sqlCommandType = sqlCommandType;
mappedStatement.sqlSource = sqlSource;
mappedStatement.resultType = resultType;
}
public MappedStatement build() {
assert mappedStatement.configuration != null;
assert mappedStatement.id != null;
return mappedStatement;
}
}
public Configuration getConfiguration() {
return configuration;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public SqlCommandType getSqlCommandType() {
return sqlCommandType;
}
public void setConfiguration(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
public void setSqlCommandType(SqlCommandType sqlCommandType) {
this.sqlCommandType = sqlCommandType;
}
public SqlSource getSqlSource() {
return sqlSource;
}
public Class<?> getResultType() {
return resultType;
}
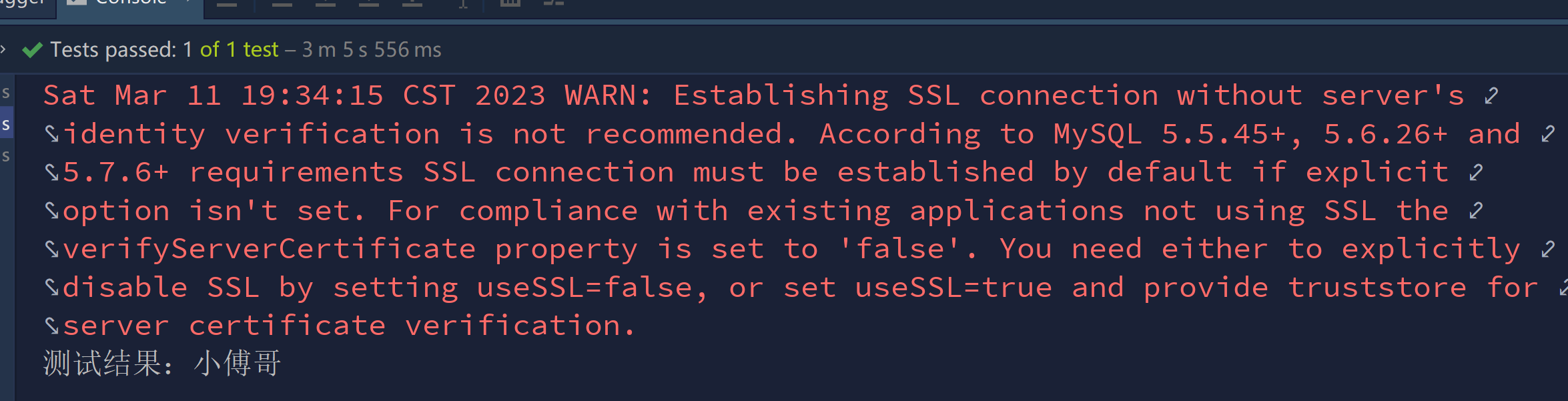
}单元测试下(单元测试以及准备工作都没有变动,可查看之前Mybatis的章节复制),打断点所有的信息都有了。
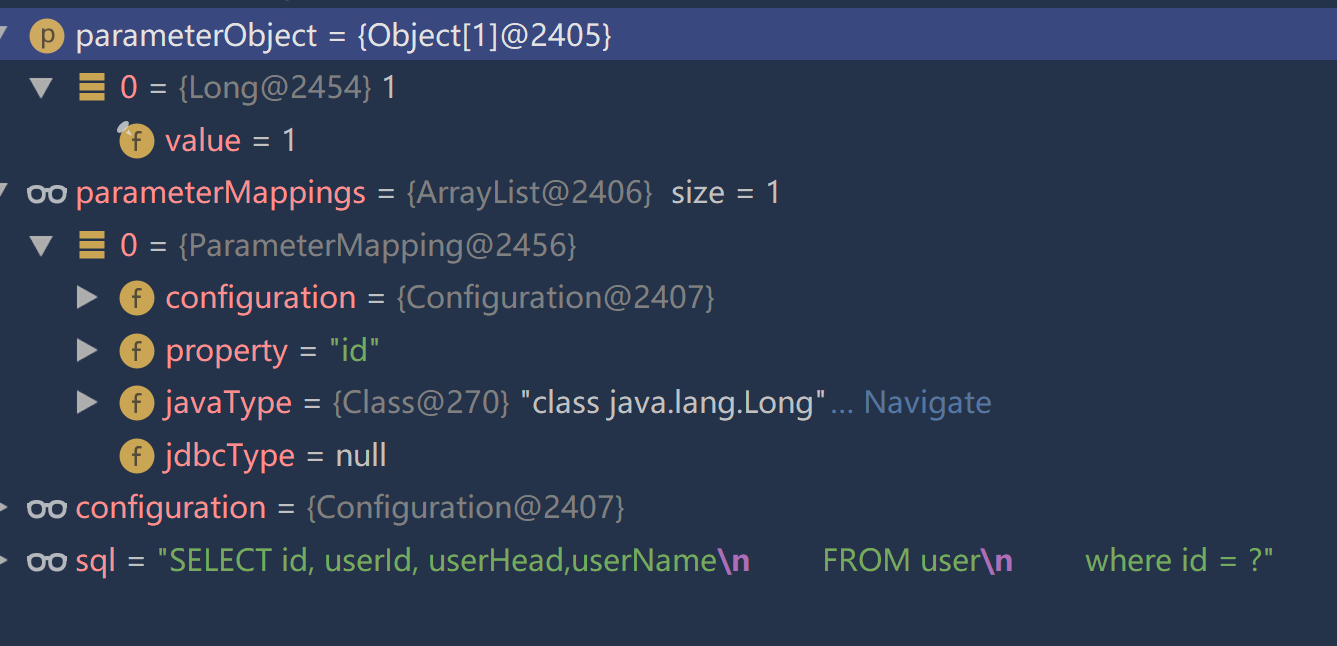
结果,能够查询到数据,可以使用
本节涉及的内容也比较多,如果大家在手写过程中缺少一些内容可以来私信我要呀,我会随时关注的。