文章目录
- 一、持久层框架分析
- 1. JDBC操作数据库_问题分析
- 2. JDBC问题分析&解决思路
- (1)加载驱动,获取链接
- (2)定义sql、设置参数、执行查询
- (3)遍历查询结果集
- 3. 自定义持久层框架_思路分析
- 二、手写持久层框架
- 1.编写客户端代码
- (1)在pom.xml中引入自定义持久层框架的jar包
- (2)在sqlMapConfig.xml中配置数据库信息、引入mapper映射配置文件
- (3)编写mapper.xml
- 2.编写自定义框架代码
- (1)加载配置文件:根据配置文件的路径,加载配置文件成字节输入流,存储在内存中
- (2) 创建两个javaBean(容器对象):存放配置文件解析出来的内容
- (3)解析配置文件(使用dom4j) ,并创建SqlSession会话对象
- (4)创建SqlSessionFactory接口以及实现类DefaultSqlSessionFactory
- (5)创建SqlSession接口以及实现类DefaultSqlSession
- (6)创建Executor接口以及实现类SimpleExecutor
- (7)sql占位符解析转换工具类
- 3. 测试
- 4. 优化自定义持久层框架
- 5.手写的持久层框架结构图
一、持久层框架分析
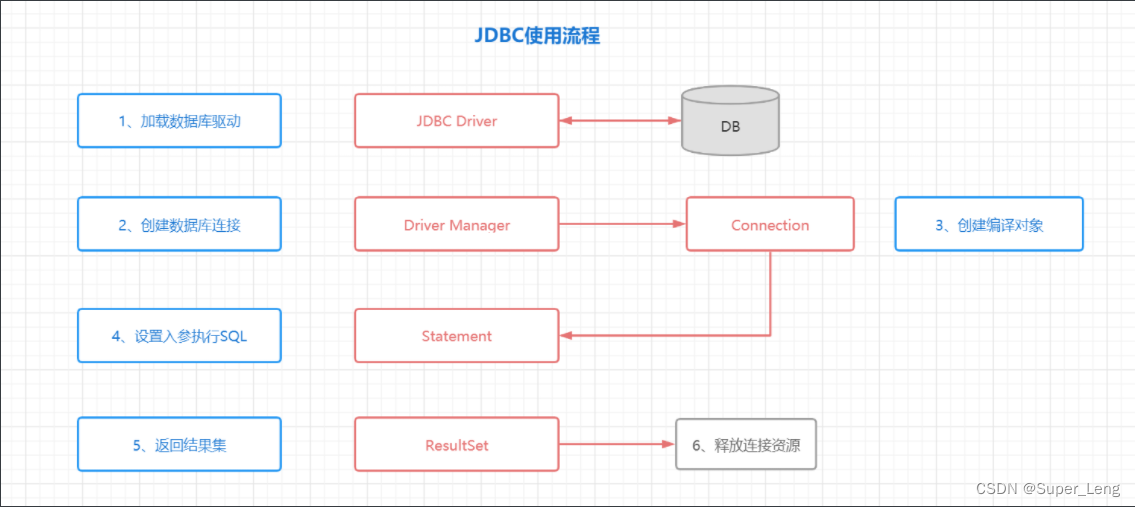
1. JDBC操作数据库_问题分析
JDBC API 允许应用程序访问任何形式的表格数据,特别是存储在关系数据库中的数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 加载数据库驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 通过驱动管理类获取数据库链接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis? characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "root");
// 定义sql语句?表示占位符
String sql = "select * from user where username = ?";
// 获取预处理statement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置参数,第一个参数为sql语句中参数的序号(从1开始),第二个参数为设置的参数值 preparedStatement.setString(1, "tom");
// 向数据库发出sql执行查询,查询出结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 遍历查询结果集
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String username = resultSet.getString("username");
// 封装User
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername(username);
System.out.println(user);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2. JDBC问题分析&解决思路
剖开代码,逐个分析:
(1)加载驱动,获取链接
// 加载数据库驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 通过驱动管理类获取数据库链接
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis? characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "root");
- 存在问题1:数据库配置信息存在硬编码问题。
优化思路:使用配置文件!- 存在问题2:频繁创建、释放数据库连接问题。
优化思路:使用数据连接池!
(2)定义sql、设置参数、执行查询
// 定义sql语句?表示占位符
String sql = "select * from user where username = ?";
// 获取预处理statement
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置参数,第一个参数为sql语句中参数的序号(从1开始),第二个参数为设置的参数值 preparedStatement.setString(1, "tom");
// 向数据库发出sql执行查询,查询出结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
- 存在问题3:SQL语句、设置参数、获取结果集参数均存在硬编码问题 。
优化思路:使用配置文件!
(3)遍历查询结果集
// 遍历查询结果集
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String username = resultSet.getString("username");
// 封装User
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername(username);
System.out.println(user);
}
- 存在问题4:手动封装返回结果集,较为繁琐
优化思路:使用Java反射、内省!
针对JDBC各个环节中存在的不足,现在,我们整理出对应的优化思路,统一汇总:
| 存在问题 | 优化思路 |
|---|---|
| 数据库配置信息存在硬编码问题 | 使用配置文件 |
| 频繁创建、释放数据库连接问题 | 使用数据连接池 |
| SQL语句、设置参数、获取结果集参数均存在硬编码问题 | 使用配置文件 |
| 手动封装返回结果集,较为繁琐 | 使用Java反射、内省 |
3. 自定义持久层框架_思路分析
- JDBC是个人作战,凡事亲力亲为,低效而高险,自己加载驱动,自己建连接,自己 …
- 而持久层框架好比是多工种协作,分工明确,执行高效,有专门负责解析注册驱动建立连接的,有专门管理数据连接池的,有专门执行sql语句的,有专门做预处理参数的,有专门装配结果集的 …
- 优化思路: 框架的作用,就是为了帮助我们减去繁重开发细节与冗余代码,使我们能更加专注于业务应用开发。
使用JDBC和使用持久层框架区别:
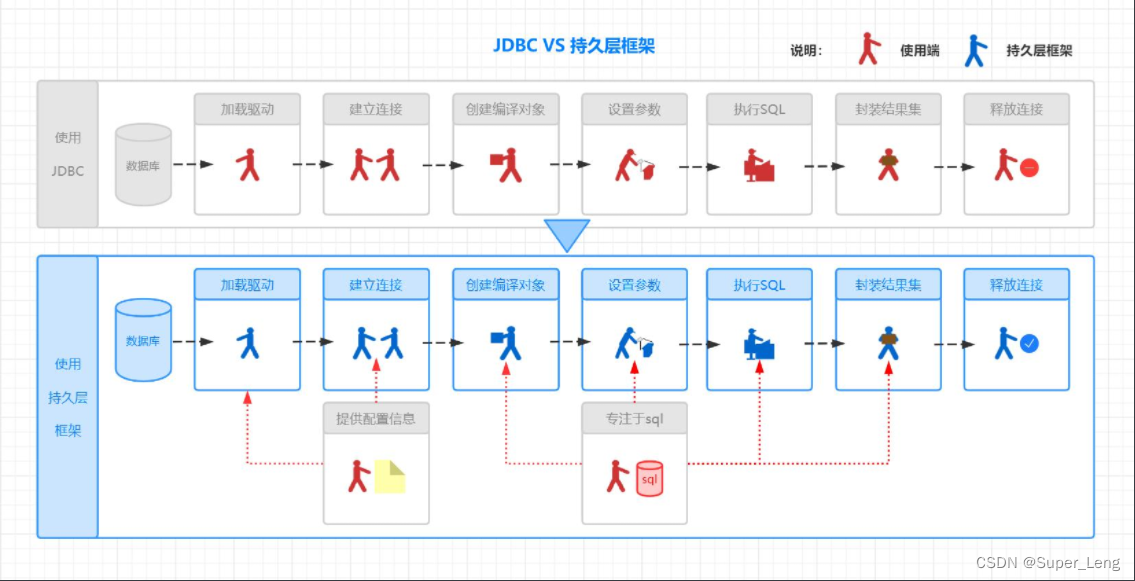
是不是发现,拥有这么一套持久层框架是如此舒适,我们仅仅需要干两件事:
- 配置数据源(地址/数据名/用户名/密码)
- 编写SQL与参数准备(SQL语句/参数类型/返回值类型)
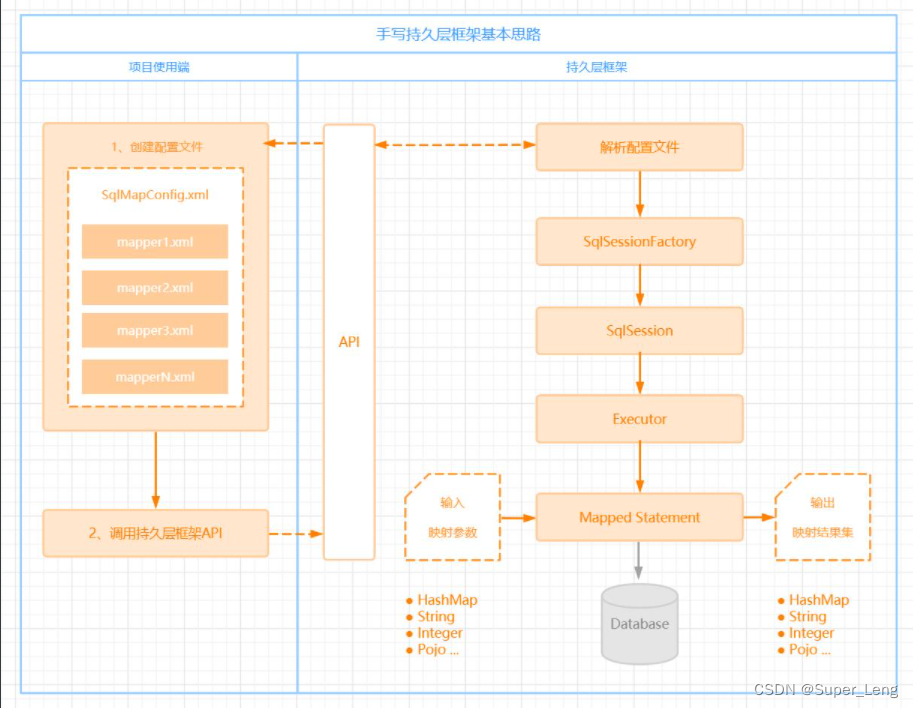
框架,除了思考本身的工程设计,还需要考虑到实际项目端的使用场景,涉及两端:
- 使用端(实际项目)
- 持久层框架本身
以上两步,我们通过一张架构图《 手写持久层框架基本思路 》来梳理清楚:

二、手写持久层框架
1.编写客户端代码
(1)在pom.xml中引入自定义持久层框架的jar包
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>ipersistent_test</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!--引入自定义持久层框架的jar包-->
<!-- 自定义的持久层框架名称叫做ipersistent -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>ipersistent</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
(2)在sqlMapConfig.xml中配置数据库信息、引入mapper映射配置文件
引入mapper映射配置文件目的是通过Resource类加载配置文件时,只需要加载一次sqlMapConfig.xml配置文件的路径就可以将
sqlMapConfig.xml和mapper.xml中的信息都获取到,而不需要再多加载一次mapper.xml的路径,这样就减少了一次IO交互
<configuration>
<!--1.配置数据库信息-->
<dataSource>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///zdy_mybatis?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</dataSource>
<!--2.引入mapper映射配置文件,即mapper.xml的全路径-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"></mapper>
</mappers>
</configuration>
(3)编写mapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.dao.IUserDao">
<!--唯一标识:namespace.id statementId-->
<!--查询所有-->
<!--
规范:接口的全路径要和namespace的值保持一致
接口中的方法名要和id的值保持一致
-->
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User">
select * from user
</select>
<!--按条件进行查询-->
<!--
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUserName("tom");
-->
<select id="findByCondition" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User" parameterType="com.itheima.pojo.User">
select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{username}
</select>
</mapper>
项目使用端:
(1)调用框架API,除了引入自定义持久层框架的jar包
(2)提供两部分配置信息:
1.sqlMapConfig.xml : 数据库配置信息(地址/数据名/用户名/密码),以及mapper.xml的全路径
2.mapper.xml : SQL配置信息,存放SQL语句、参数类型、返回值类型相关信息
2.编写自定义框架代码
(1)加载配置文件:根据配置文件的路径,加载配置文件成字节输入流,存储在内存中
创建Resources类,提供加载流方法:InputStream getResourceAsSteam(String path);
public class Resources {
/**
* 根据配置文件的路径,加载配置文件成字节输入流,存到内存中
* @param path
* @return
*/
public static InputStream getResourceAsSteam(String path){
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(path);
return resourceAsStream;
}
}
(2) 创建两个javaBean(容器对象):存放配置文件解析出来的内容
Configuration(核心配置类):存放sqlMapConfig.xml解析出来的内容
MappedStatement(映射配置类):存放mapper.xml解析出来的内容
MappedStatement(映射配置类):
/**
* 映射配置类:存放mapper.xml解析内容
*/
@Data
public class MappedStatement {
// 唯一标识 statementId:namespace.id
private String statementId;
// 返回值类型
private String resultType;
// 参数值类型
private String parameterType;
// sql语句
private String sql;
// sqlCommandType :判断当前是什么操作的一个属性
private String sqlCommandType;
}
Configuration(核心配置类):
/**
* 全局配置类:存放核心配置文件解析出来的内容
*/
@Data
public class Configuration {
// 数据源对象
private DataSource dataSource;
// key:statementId:namespace.id MappedStatement:封装好的MappedStatement对象
private Map<String,MappedStatement> mappedStatementMap = new HashMap();
}
(3)解析配置文件(使用dom4j) ,并创建SqlSession会话对象
创建 类:SqlSessionFactoryBuidler,方法:build(Inputstream in)
使用dom4j解析配置文件,将解析出来的内容封装到Configuration容器对象中
创建SqlSessionFactory对象,生成SqlSession会话对象(工厂模式)
在pom.xml中引入依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>ipersistent</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<!-- Encoding -->
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
<java.version>11</java.version>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- mysql 依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit 依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<!--作用域测试范围-->
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--dom4j 依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>1.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--xpath 依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--druid连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.21</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log日志 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
/**
* 1.解析配置文件,封装容器对象 2.创建SqlSessionFactory工厂对象
* @param inputStream
* @return
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) throws DocumentException {
// 1.解析配置文件,封装容器对象; XMLConfigBuilder:专门解析核心配置文件的解析类
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder();
Configuration configuration = xmlConfigBuilder.parse(inputStream);
// 2.创建SqlSessionFactory工厂对象
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(configuration);
}
}
XMLConfigBuilder:专门解析sqlMapConfig.xml核心配置文件的解析类
public class XMLConfigBuilder {
private Configuration configuration;
public XMLConfigBuilder() {
this.configuration = new Configuration();
}
/**
* 使用dom4j+xpath解析配置文件,封装Configuration对象
* @param inputStream
* @return
*/
public Configuration parse(InputStream inputStream) throws DocumentException {
Document document = new SAXReader().read(inputStream);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
List<Element> list = rootElement.selectNodes("//property");
// <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
Properties properties = new Properties();
for (Element element : list) {
String name = element.attributeValue("name");
String value = element.attributeValue("value");
properties.setProperty(name,value);
}
// 创建数据源对象
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName(properties.getProperty("driverClassName"));
druidDataSource.setUrl(properties.getProperty("url"));
druidDataSource.setUsername(properties.getProperty("username"));
druidDataSource.setPassword(properties.getProperty("password"));
// 创建好的数据源对象封装到Configuration对象中
configuration.setDataSource(druidDataSource);
//-----------解析映射配置文件----
// 1.获取映射配置文件的路径 2.根据路径进行映射配置文件的加载解析 3.封装到MappedStatement--》configuration里面的map集合中
// <mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"></mapper>
List<Element> mapperList = rootElement.selectNodes("//mapper");
for (Element element : mapperList) {
String mapperPath = element.attributeValue("resource");
InputStream resourceAsSteam = Resources.getResourceAsSteam(mapperPath);
// XMLMapperBuilder:专门解析映射配置文件的对象
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(configuration);
xmlMapperBuilder.parse(resourceAsSteam);
}
return configuration;
}
}
XMLMapperBuilder :专门解析mapper.xml映射配置文件的解析类
/**
* parse : 解析映射配置文件--》mappedStatement--->configuration里面的map集合中
*/
public class XMLMapperBuilder {
private Configuration configuration;
public XMLMapperBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
public void parse(InputStream resourceAsSteam) throws DocumentException {
Document document = new SAXReader().read(resourceAsSteam);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
/**
* <select id="selectOne" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.User" parameterType="com.itheima.pojo.User">
* select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{username}
* </select>
*/
List<Element> selectList = rootElement.selectNodes("//select");
String namespace = rootElement.attributeValue("namespace");
for (Element element : selectList) {
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType");
String parameterType = element.attributeValue("parameterType");
String sql = element.getTextTrim();
// 封装mappedStatement对象
MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement();
// StatementId:namespace.id
String statementId = namespace + "." + id;
mappedStatement.setStatementId(statementId);
mappedStatement.setResultType(resultType);
mappedStatement.setParameterType(parameterType);
mappedStatement.setSql(sql);
mappedStatement.setSqlCommandType("select");
// 将封装好的mappedStatement封装到configuration中的map集合中
configuration.getMappedStatementMap().put(statementId,mappedStatement);
}
}
}
(4)创建SqlSessionFactory接口以及实现类DefaultSqlSessionFactory
创建openSession()接口方法,生成sqlSession
SqlSessionFactory接口:
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
/**
* 1.生产sqlSession对象 2.创建执行器对象
* @return
*/
SqlSession openSession();
}
DefaultSqlSessionFactory :
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
// 1.创建执行器对象
Executor simpleExecutor = new SimpleExecutor();
// 2.生产sqlSession对象
DefaultSqlSession defaultSqlSession = new DefaultSqlSession(configuration,simpleExecutor);
return defaultSqlSession;
}
}
(5)创建SqlSession接口以及实现类DefaultSqlSession
定义对数据库的CRUD操作:
selectList();
selectOne();
update();
delete();
insert();
SqlSession接口:
public interface SqlSession {
/**
* 查询多个结果
* sqlSession.selectList(); :定位到要执行的sql语句,从而执行
* select * from user where username like '% ? %'
*/
<E> List<E> selectList(String statementId,Object param) throws Exception;
/**
* 查询单个结果
*/
<T> T selectOne(String statementId,Object param) throws Exception;
/**
* 清除资源
*/
void close();
/**
* 生成代理对象
*/
<T> T getMapper(Class<?> mapperClass);
}
DefaultSqlSession实现类:
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Configuration configuration;
private Executor executor;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
}
@Override // user
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statementId, Object param) throws Exception {
// 将查询操作委派给底层的执行器
// query(): 执行底层的JDBC 1.数据库配置信息 2.sql配置信息
MappedStatement mappedStatement = configuration.getMappedStatementMap().get(statementId);
List<E> list = executor.query(configuration,mappedStatement,param);
return list;
}
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statementId, Object param) throws Exception {
// 去调用selectList();
List<Object> list = this.selectList(statementId, param);
if(list.size() == 1){
return (T) list.get(0);
}else if (list.size() > 1){
throw new RuntimeException("返回结果过多");
}else {
return null;
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
executor.close();
}
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<?> mapperClass) {
// 使用JDK动态代理生成基于接口的代理对象
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(DefaultSqlSession.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{mapperClass}, new InvocationHandler() {
/*
Object:代理对象的引用,很少用
Method:被调用的方法的字节码对象
Object[]:调用的方法的参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects) throws Throwable {
// 具体的逻辑 :执行底层的JDBC
// 通过调用sqlSession里面的方法来完成方法调用
// 参数的准备:1.statementId: com.itheima.dao.IUserDao.findAll 2.param
// 问题1:无法获取现有的statementId
// findAll
String methodName = method.getName();
// com.itheima.dao.IUserDao
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
String statementId = className + "." + methodName;
// 方法调用:问题2:要调用sqlSession中增删改查的什么方法呢?
// 改造当前工程:sqlCommandType
MappedStatement mappedStatement = configuration.getMappedStatementMap().get(statementId);
// select update delete insert
String sqlCommandType = mappedStatement.getSqlCommandType();
switch (sqlCommandType){
case "select":
// 执行查询方法调用
// 问题3:该调用selectList还是selectOne?
Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
// 判断是否实现了 泛型类型参数化
if(genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
if(objects != null) {
return selectList(statementId, objects[0]);
}
return selectList(statementId, null);
}
return selectOne(statementId,objects[0]);
case "update":
// 执行更新方法调用
break;
case "delete":
// 执行delete方法调用
break;
case "insert":
// 执行insert方法调用
break;
}
return null;
}
});
return (T) proxy;
}
}
(6)创建Executor接口以及实现类SimpleExecutor
创建query(Configuration conf, MappedStatement ms, Object… params)
实际执行的是JDBC代码
Executor接口:
public interface Executor {
<E> List<E> query(Configuration configuration, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object param) throws Exception;
void close();
}
SimpleExecutor实现类:
public class SimpleExecutor implements Executor {
private Connection connection = null;
private PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
private ResultSet resultSet = null;
@Override // user
public <E> List<E> query(Configuration configuration, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object param) throws Exception {
// 1.加载驱动,获取数据库连接
connection = configuration.getDataSource().getConnection();
// 2.获取preparedStatement预编译对象
// 获取要执行的sql语句
/* 自定义的占位符
select * from user where id = #{id} and username = #{username}
替换: select * from user where id = ? and username = ?
解析替换的过程中:#{id}里面的值保存下来
*/
String sql = mappedStatement.getSql();
BoundSql boundSql = getBoundSql(sql);
String finalSql = boundSql.getFinalSql();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(finalSql);
// 3.设置参数
// com.itheima.pojo.User
String parameterType = mappedStatement.getParameterType();
if(parameterType != null ) {
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = Class.forName(parameterType);
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList = boundSql.getParameterMappingList();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappingList.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappingList.get(i);
// id || username
String paramName = parameterMapping.getContent();
// 反射
Field declaredField = parameterTypeClass.getDeclaredField(paramName);
// 暴力访问
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
Object value = declaredField.get(param);
// 赋值占位符
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,value);
}
}
// 4.执行sql,发起查询
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
// 5.处理返回结果集
ArrayList<E> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()){
// 元数据信息 包含了 字段名 字段的值
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
// com.itheima.pojo.User
String resultType = mappedStatement.getResultType();
Class<?> resultTypeClass = Class.forName(resultType);
Object o = resultTypeClass.newInstance();
for (int i = 1; i <= metaData.getColumnCount() ; i++) {
// 字段名 id username
String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
// 字段的值
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnName);
// 问题:现在要封装到哪一个实体中
// 封装
// 属性描述器:通过API方法获取某个属性的读写方法
PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor = new PropertyDescriptor(columnName, resultTypeClass);
Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();
// 参数1:实例对象 参数2:要设置的值
writeMethod.invoke(o,value);
}
list.add((E) o);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 1.#{}占位符替换成? 2.解析替换的过程中 将#{}里面的值保存下来
* @param sql
* @return
*/
private BoundSql getBoundSql(String sql) {
// 1.创建标记处理器:配合标记解析器完成标记的处理解析工作
ParameterMappingTokenHandler parameterMappingTokenHandler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler();
// 2.创建标记解析器
GenericTokenParser genericTokenParser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", parameterMappingTokenHandler);
// #{}占位符替换成? 2.解析替换的过程中 将#{}里面的值保存下来 ParameterMapping
String finalSql = genericTokenParser.parse(sql);
// #{}里面的值的一个集合 id username
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = parameterMappingTokenHandler.getParameterMappings();
BoundSql boundSql = new BoundSql(finalSql, parameterMappings);
return boundSql;
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
@Override
public void close() {
// 释放资源
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
BoundSql :
@Data
public class BoundSql {
private String finalSql;
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList;
public BoundSql(String finalSql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappingList) {
this.finalSql = finalSql;
this.parameterMappingList = parameterMappingList;
}
}
(7)sql占位符解析转换工具类
TokenHandler:
public interface TokenHandler {
String handleToken(String content);
}
ParameterMapping:
public class ParameterMapping {
// id || username
private String content;
public ParameterMapping(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
}
ParameterMappingTokenHandler :
public class ParameterMappingTokenHandler implements TokenHandler {
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = new ArrayList<ParameterMapping>();
// context是参数名称 #{id} #{username}
public String handleToken(String content) {
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
return "?";
}
private ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(String content) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = new ParameterMapping(content);
return parameterMapping;
}
public List<ParameterMapping> getParameterMappings() {
return parameterMappings;
}
public void setParameterMappings(List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings) {
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
}
}
GenericTokenParser :
public class GenericTokenParser {
private final String openToken; //开始标记
private final String closeToken; //结束标记
private final TokenHandler handler; //标记处理器
public GenericTokenParser(String openToken, String closeToken, TokenHandler handler) {
this.openToken = openToken;
this.closeToken = closeToken;
this.handler = handler;
}
/**
* 解析${}和#{}
* @param text
* @return
* 该方法主要实现了配置文件、脚本等片段中占位符的解析、处理工作,并返回最终需要的数据。
* 其中,解析工作由该方法完成,处理工作是由处理器handler的handleToken()方法来实现
*/
public String parse(String text) {
// 验证参数问题,如果是null,就返回空字符串。
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// 下面继续验证是否包含开始标签,如果不包含,默认不是占位符,直接原样返回即可,否则继续执行。
int start = text.indexOf(openToken, 0);
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
// 把text转成字符数组src,并且定义默认偏移量offset=0、存储最终需要返回字符串的变量builder,
// text变量中占位符对应的变量名expression。判断start是否大于-1(即text中是否存在openToken),如果存在就执行下面代码
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
int offset = 0;
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
// 判断如果开始标记前如果有转义字符,就不作为openToken进行处理,否则继续处理
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
//重置expression变量,避免空指针或者老数据干扰。
if (expression == null) {
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {存在结束标记时
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {//如果结束标记前面有转义字符时
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {//不存在转义字符,即需要作为参数进行处理
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
break;
}
}
if (end == -1) {
// close token was not found.
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
offset = src.length;
} else {
//首先根据参数的key(即expression)进行参数处理,返回?作为占位符
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
}
3. 测试
public class IPersistentTest {
/**
* 传统方式(不使用mapper代理)测试
*/
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
// 1.根据配置文件的路径,加载成字节输入流,存到内存中 注意:配置文件还未解析
InputStream resourceAsSteam = Resources.getResourceAsSteam("sqlMapConfig.xml");
// 2.解析了配置文件,封装了Configuration对象 2.创建sqlSessionFactory工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsSteam);
// 3.生产sqlSession 创建了执行器对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 4.调用sqlSession方法
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("tom");
/* User user2 = sqlSession.selectOne("user.selectOne", user);
System.out.println(user2);*/
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("user.selectList", null);
for (User user1 : list) {
System.out.println(user1);
}
// 5.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
}
4. 优化自定义持久层框架
通过上述我们的自定义框架,我们解决了JDBC操作数据库带来的一些问题:例如频繁创建释放数据库连接,硬编码,手动封装返回结果集等问题,但是现在我们继续来分析刚刚完成的自定义框架代码,有没有什么问题?
问题如下:
1.dao的实现类中存在重复的代码,整个操作的过程模板重复(创建sqlsession,调用sqlsession方法,关闭 sqlsession)
// 1.根据配置文件的路径,加载成字节输入流,存到内存中 注意:配置文件还未解析
InputStream resourceAsSteam = Resources.getResourceAsSteam("sqlMapConfig.xml");
// 2.解析了配置文件,封装了Configuration对象 2.创建sqlSessionFactory工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsSteam);
// 3.生产sqlSession 创建了执行器对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 4.调用sqlSession方法
// 5.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
2.dao的实现类中存在硬编码,调用sqlsession的方法时,参数statement的id硬编码
// "user.selectOne"就是硬编码
User user2 = sqlSession.selectOne("user.selectOne", user);
解决:使用代理模式来创建接口的代理对象
在sqlSession中添加getMappper()接口:
public interface SqlSession {
public <T> T getMappper(Class<?> mapperClass);
}
实现getMappper()方法:
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Configuration configuration;
private Executor executor;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
}
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<?> c) {
// 基于JDK动态代理产生接口的代理对象
Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(DefaultSqlSession.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{c}, new InvocationHandler() {
/*
o : 代理对象:很少用到
method :正在执行的方法
objects :方法的参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects) throws Throwable {
// findByCondition
String methodName = method.getName();
// com.itheima.dao.IUserDao
String className = method.getDeclaringClass().getName();
// 唯一标识:namespace.id com.itheima.dao.IUserDao.findByCondition
String statementId = className + "." +methodName;
MappedStatement mappedStatement = configuration.getMappedStatementMap().get(statementId);
String sql = mappedStatement.getSql();
// sqlcommandType select insert update delete
String sqlcommandType = mappedStatement.getSqlcommandType();
switch (sqlcommandType){
case "select":
// 查询操作 问题来了:selectList 还是selectOne?
Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
// 判断是否实现泛型类型参数化
if(genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
return selectList(statementId,objects);
}
return selectOne(statementId,objects);
case "update":
break;
// 更新操作
case "delete":
break;
// 删除操作
case "insert":
break;
// 添加操作
}
return null;
}
});
return (T) proxy;
}
测试:
/**
* mapper代理测试
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
// 1.根据配置文件的路径,加载成字节输入流,存到内存中 注意:配置文件还未解析
InputStream resourceAsSteam = Resources.getResourceAsSteam("sqlMapConfig.xml");
// 2.解析了配置文件,封装了Configuration对象 2.创建sqlSessionFactory工厂对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsSteam);
// 3.生产sqlSession 创建了执行器对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 4.调用sqlSession方法
IUserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
/* User user1 = new User();
user1.setId(1);
user1.setUsername("tom");
User user3 = userDao.findByCondition(user1);
System.out.println(user3);*/
List<User> all = userDao.findAll();
for (User user : all) {
System.out.println(user);
}
// 5.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
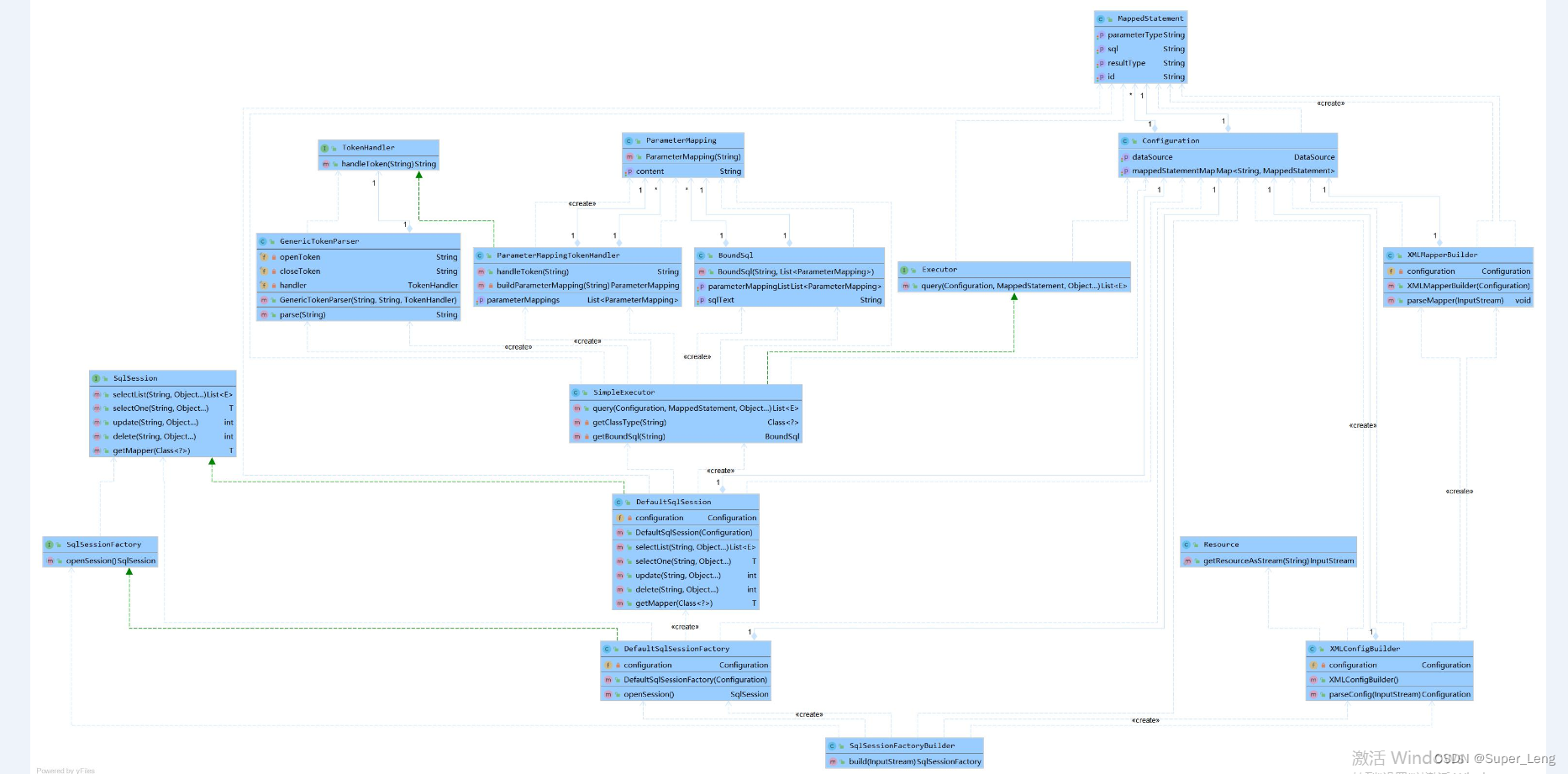
5.手写的持久层框架结构图
手写的持久层框架结构参考:
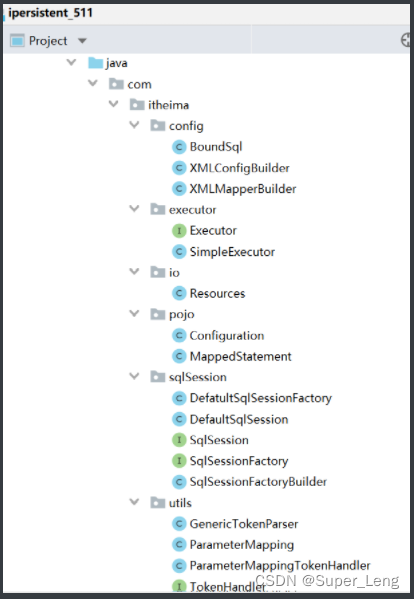
手写的持久层框架类图参考: