目录
一、概念
二、接口
2.1、 集合接口
2.2、 Set 接口
2.2.1 zise方法
2.2.2 isEmpty 方法
2.2.3 contains 方法
2.2.4 Iterator 方法
2.2.5 toArray 方法
2.2.6 add 方法
2.2.7 remove 方法
2.2.8 containsAll 方法
2.2.9 containsAll 方法
2.2.10 retainAll 方法
2.2.11 removeAll 方法
2.2.12 containsAll 方法
2.2.13 spliterator 方法
2.3、 List 接口
2.3.1、get 方法
2.3.2、set 方法
2.3.3、add 方法
2.3.4、remove 方法
2.3.5、indexOf 方法
2.3.6、lastIndexOf 方法
2.3.7、listIterator 方法
2.3.8、subList 方法
2.4、 Queue 接口
2.4.1 add 方法
2.4.2 offer 方法
2.4.3 remove 方法
2.4.4 poll 方法
2.4.5 element 方法
2.4.6 peek 方法
2.5、 Deque 接口
2.5.1 addFirst 方法
2.5.2 addLast 方法
2.5.3 offerFirst 方法
2.5.4 offerLast 方法
2.5.5 removeFirst 方法
2.5.6 removeLast 方法
2.5.7 pollFirst 方法
2.5.8 pollLast 方法
2.5.9 getFirst 方法
2.5.10 getLast 方法
2.5.11 peekFirst 方法
2.5.12 peekLast 方法
2.5.13 removeFirstOccurrence 方法
2.5.14 removeLastOccurrence 方法
2.5.15 descendingIterator 方法
2.6、 SortedSet 接口
2.6.1 comparator 方法
2.6.2 subSet 方法
2.6.3 headSet 方法
2.6.4 tailSet 方法
2.6.5 first 方法
2.6.6 last 方法
2.7、 Map 接口
2.7.1 size 方法
2.7.1 isEmpty 方法
2.7.2 containsKey 方法
2.7.3 containsValue 方法
2.7.4 get 方法
2.7.5 put 方法
2.7.6 remove 方法
2.7.7 putAll 方法
2.7.8 clear方法
2.7.9 keySet 方法
2.7.10 values 方法
2.7.11 entrySet 方法
2.7.12 getOrDefault 方法
2.7.13 forEach 方法
2.7.14 replaceAll 方法
2.7.15 putIfAbsent 方法
2.7.16 remove 方法
2.7.17 replace 方法
2.7.18 computeIfAbsent 方法
2.7.19 computeIfPresent 方法
2.7.20 compute 方法
2.7.21 merge方法
2.8、 SortedMap 接口
2.8.1 comparator 方法
2.8.2 subMap 方法
2.8.3 headMap方法
2.8.4 tailMap 方法
2.8.5 firstKey 方法
2.8.6 lastKey方法
三、接口实现
一、概念
集合(有时称为容器):将多个元素分组为单个单元的对象。集合用于存储、查找和通信聚合数据。
集合框架是表示和操作集合的同一体系结构。集合框架有如下内容:
接口:这些是表示集合抽象数据类型。接口允许独立于集合表示的细节来操作集合。
实现:这些都是接口的具体实现。本质上,他们是可以重用的数据结构。
算法:这些方法在实现集合接口的对象上执行高效的计算。比如查找和排序。这些算法被认为是多态的,也就是说,相同的方法可以在不同实现类去实现。本质上算法是可以重用的功能。
Java 集合框架有如下优点:
1、减少编程工作量。通过提供高效的数据结构和算法,集合框架可以使编程人员将精力集中在程序的业务部分,而不是编程工作所需的代码底层。
2、提高程序的速度和质量。集合框架为高效的数据结构和算法提供高性能和高质量的实现。集合框架提供集合之间互相转换功能,简单易用,可以用编程人员更多的时间去改进程序的质量和性能。
3、允许不相关 API 之间的互相操作性。换句话来说,就是在不同包中的 API 将无缝地互相操作。
4、减少和学习新 API 的学习工作量。一般 API 都有自己规范,需要花时间去了解和学习。随着标准集合框架的出现。这个问题就消失了。
5、 软件重用。符合标准的集合接口的新数据结构上是可重用的。对实现这些接口的对象进行操作的新算法也是如此。
二、接口
2.1、 集合接口
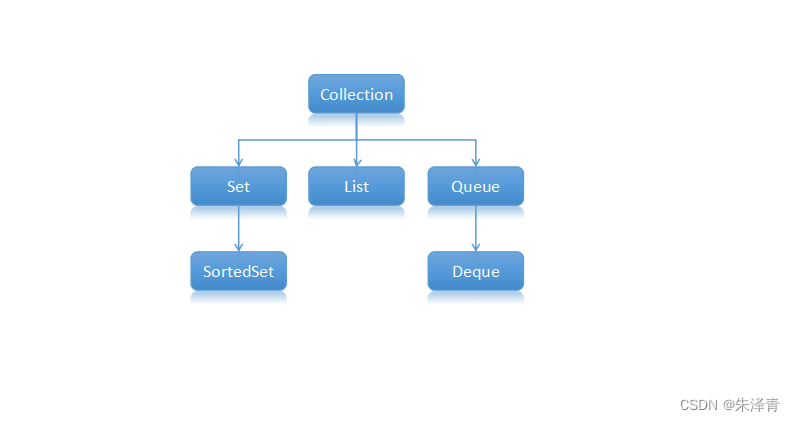
Collection:集合层次的根。
Set:不包含重复元素的集合。
List:有序集合。列表包含重复的元素。
Queue:队列,是一种操作受限的线性表,只允许在表的一端进行插入,而表的另外一端进行删除。先进先出(First in First Out,FIFO)。
SortedSet:默认按升序维护其元素的集合。
Deque:双向队列,可以先进先出,也可以先进后出。
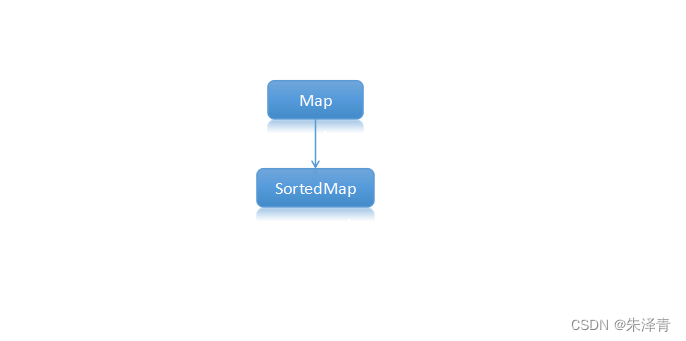
Map:将键映射到值的对象。一个 Map 不能包含重复的键,每个键最多只能映射到一个值。
SortedMap:默认按升序维护映射的集合。
2.2、 Set 接口
Set 集合不能包含重复元素的集合。
Set 接口只包含从 Collection 继承的方法,并扩展了禁止重复元素的限制。Set 还在 equals 和 HashCode 操作的行为添加了更强的契约,允许对 Set 实例进行有意义的比较,即使他们的实现类型不同。如果两个 Set 实例包含相同的元素,则他们相等。
Java 平台包含三种通用 Set 实现:HashSet 、TreeSet 和 LinkedHashSet。HashSet 将其元素存储在哈希表中,是性能最好的实现,但是不能保证迭代的顺序。TreeSet 将元素存储在红黑树中。根据元素的值对其进行排,它比 HashSet 慢很多。LinkedHashSet 实现为一个哈希表,并且是链表的数据结构,根据元素插入集合的顺序(插入顺序)对其元素进行排序。
示例:假设有个集合,需要去除重复元素。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.add("a");
arrayList.add("b");
arrayList.add("a");
System.out.println("没有去除重复之前:"+arrayList);
// JDK1.8或者以上
Set<String> noDups = (Set<String>) arrayList.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println("去除重复后:"+noDups);
}
}控制台显示
没有去除重复之前:[a, b, a]
去除重复后:[a, b]Set 接口方法如下:
| 方法 | 描述 |
| size() | 返回集合元素大小 |
| isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
| contains() | 判断集合是否包含某个元素 |
| iterator() | 遍历集合元素 |
| toArray() | 集合转数组 |
| add() | 插入元素 |
| remove() | 删除某个元素 |
| containsAll() | 判断集合是否包含某个集合全部元素 |
| addAll() | 集合添加某个集合所有元素 |
| retainAll() | 返回集合交集 |
| removeAll() | 集合中删除某个集合全部元素 |
| clear() | 清空集合所有元素 |
| equals() | 判断对象和集合是否相等 |
| hashCode() | 返回集合哈希码值 |
| spliterator() | 集合拆分器 |
查看JDK为JDK1.8。
2.2.1 zise方法
返回集合大小。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
// 集合大小
System.out.println("size() : "+set.size());
}
}2.2.2 isEmpty 方法
判断集合是否为空。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
// 判断集合是否为空
System.out.println("isEmpty() : " + set.isEmpty());
}
}2.2.3 contains 方法
判断集合是否包含某个元素。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
// 判断集合是否包含1这个元素
System.out.println("contains() : " + set.contains(1));
}
}2.2.4 Iterator 方法
集合遍历。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
// 集合遍历
Iterator i = set.iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
System.out.println("iterator() : " + i.next());
}
}
}2.2.5 toArray 方法
集合转数组。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
// 集合转换成数组
Object[] arr = set.toArray();
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
System.out.print("toArray() : "+arr[j]+" ");
}
}
}<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);重载方法,参数是一个数组类型。
2.2.6 add 方法
插入元素。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
// 集合插入元素
set.add(1);
}
}
2.2.7 remove 方法
集合删除元素。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
// 集合删除元素
set.remove(1);
}
}2.2.8 containsAll 方法
集合是否包含某个集合的全部元素。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<Integer>();
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
// set集合是否包含set1,set与set1为空都为空,返回true
boolean result = set.containsAll(set1);
System.out.println(result);
}
}2.2.9 containsAll 方法
集合添加某个集合的全部元素。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<Integer>();
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
// set集合添加set1全部元素
boolean result = set.addAll(set1);
System.out.println(set);
}
}2.2.10 retainAll 方法
返回两个集合交集。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<Integer>();
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
// 返回set、set1集合的交集
boolean result = set.retainAll(set1);
System.out.println(set);
}
}2.2.11 removeAll 方法
集合删除某个集合中包含的全部元素。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
set.add(1);
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<Integer>();
set1.add(1);
set1.add(2);
// set集合中删除包含set1集合元素
boolean result = set.removeAll(set1);
System.out.println(set);
}
}2.2.12 containsAll 方法
集合清空所有元素。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
// 清空集合全部元素
set.clear();
}
}2.2.13 spliterator 方法
集合拆分器,JDK1.8或者以上可以使用。
示例
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Spliterator;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
// 集合插入元素
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(3);
// 集合拆分器使用
Spliterator spliterator = set.spliterator();
spliterator.forEachRemaining((n)->
System.out.println(n)
);
}
}2.3、 List 接口
List 是一个有序的集合。列表可以包含重复元素。除了继承 Collction 继承操作方法之外,List 接口扩展了自己特有方法。
List 接口包含如下几点操作:
1、位置范围,基于元素在列表的数值位置操作元素。例如 get 、set 、add、addAll等。
2、查找,在列表查找指定对象并返回其数值的位置。例如 indexOf 和LastIndexOf
3、遍历,扩展迭代器。
4、范围视图,子列表方法在列表上执行任意范围操作。
List 扩展方法如下:
| 方法 | 描述 |
| get() | 通过索引值获取集合元素 |
| set() | 根据索引值替换集合元素 |
| add() | 根据位置插入集合元素 |
| remove() | 根据索引值删除集合元素 |
| indexOf() | 返回集合元素索引值 |
| lastIndexOf() | 返回集合元素在集合中最后出现的位置 |
| listIterator() | 遍历集合中的元素 |
| subList(); | 根据开始位置与结束位置返回一个子集合 |
2.3.1、get 方法
通过索引值获取集合元素。
示例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("1");
// 通过索引值获取集合元素
System.out.println("get() : "+list .get(0));
}
}2.3.2、set 方法
根据索引值替换集合元素。
示例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(1);
// 通过索引值获取集合元素
System.out.println("get() : "+list .get(0));
// 根据索引值替换集合元素
list .set(0,2);
System.out.println(list .get(0));
}
}2.3.3、add 方法
根据位置插入集合元素。
示例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
// 根据位置插入集合元素
list.add(1);
}
}2.3.4、remove 方法
根据索引值删除集合元素。
示例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
// 根据位置插入集合元素
list.add(1);
// 根据索引值删除集合元素
list.remove(0);
}
}2.3.5、indexOf 方法
返回集合元素索引值。
示例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
// 根据位置插入集合元素
list.add(1);
// 返回集合元素索引值
System.out.println(list.indexOf(1));
}
}2.3.6、lastIndexOf 方法
返回集合元素在集合中最后出现的位置。
示例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
// 根据位置插入集合元素
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(1);
// 返回集合元素在集合中最后出现的位置
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1));
}
}2.3.7、listIterator 方法
遍历集合中的元素。
示例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
// 根据位置插入集合元素
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(1);
// 遍历集合中的元素
ListIterator l = list.listIterator();
while (l.hasNext()){
System.out.print(l.next()+" ");
}
}
}2.3.8、subList 方法
根据开始位置与结束位置返回一个子集合。
示例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
// 根据位置插入集合元素
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(1);
// 遍历集合中的元素
List list1 = list.subList(0,2);
System.out.println(list1); // [0,2) 结果[1, 2]
}
}2.4、 Queue 接口
Queue 队列,是一种操作受限的线性表,只允许在表的一端进行插入,而表的另外一端进行删除。先进先出(First in First Out,FIFO)。
Queue扩展方法如下:
| 方法 | 描述 |
| add() | 添加元素到队列,相当于进入队尾排队,如果队列已满,抛出异常 |
| offer() | 添加元素到队列,相当于进入队尾排队 |
| remove() | 移除队头元素,如果为空,抛出异常 |
| poll() | 移除队头元素,如果为空,返回null |
| element() | 获取但不移除队列头的元素,如果为空,抛出异常 |
| peek() | 获取但不移除队列头的元素,如果为空,返回null |
2.4.1 add 方法
添加元素到队列,相当于进入队尾排队,如果队列已满,抛出异常。
示例
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue q = new ArrayBlockingQueue(1);
q.add(1);
/***
* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
* at java.util.AbstractQueue.add(AbstractQueue.java:98)
* at java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue.add(ArrayBlockingQueue.java:312)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:13)
*/
q.add(2);
}
}因为集合大小设置为1,当队列已满,还在添加元素,使用 add 方法 会抛出不合法状态异常
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
at java.util.AbstractQueue.add(AbstractQueue.java:98)
at java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue.add(ArrayBlockingQueue.java:312)
at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:13)如果是正常插入元素,返回插入结果 true 或者 false。
2.4.2 offer 方法
添加元素到队列,相当于进入队尾排队。
示例
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue q = new ArrayBlockingQueue(1);
q.offer(1);
/**
* 因为队列已经满了,不能插入失败,不会抛出异常
*/
q.offer(2);
}
}虽然集合大小为 1 ,当队列已满,使用 offer 方法添加元素前会判断集合是否已满,已满的话,直接返回 false。
JDK1.8 ArrayBlockingQueue 类的 offer 方法 部分源码
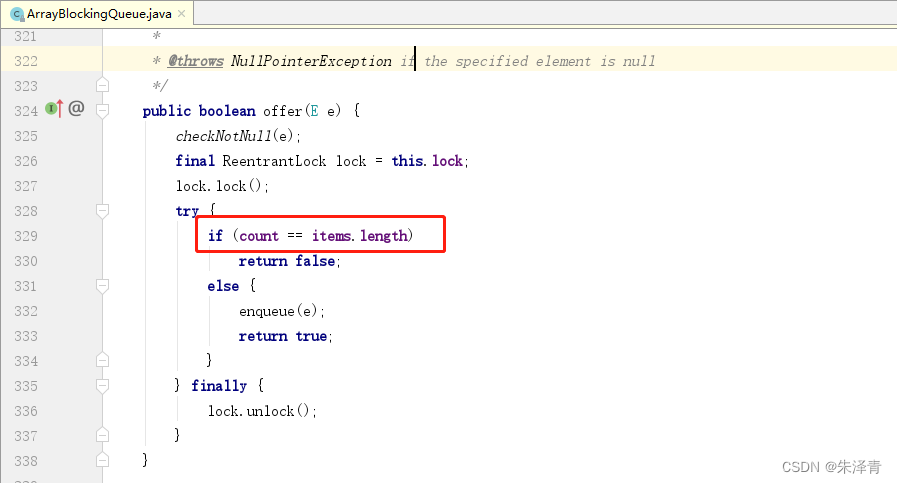
如果集合没有满,count 添加一个元素自增1,统计元素的个数。this.items就是容器大小。
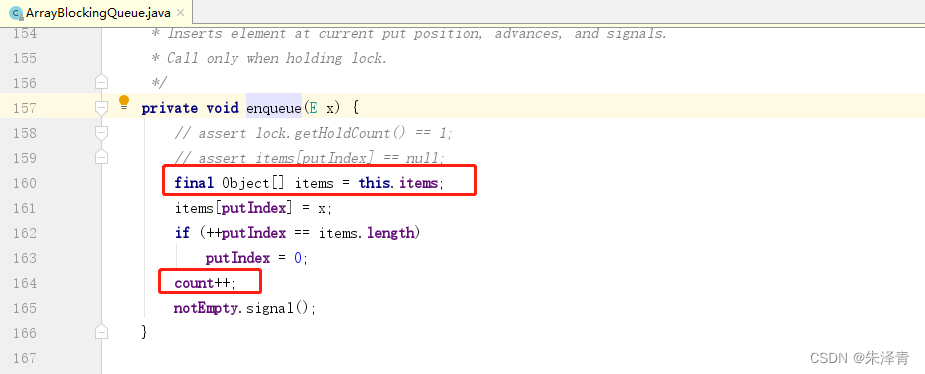
如果是正常插入元素,返回插入结果 true 或者 false。添加 null 会抛出异常。
2.4.3 remove 方法
移除队头元素,如果为空,抛出异常。
示例
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue q = new ArrayBlockingQueue(1);
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException
* at java.util.AbstractQueue.remove(AbstractQueue.java:117)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:11)
*/
q.remove();
}
}因为 ArrayBlockingQueue 类结构
public class ArrayBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable如果为空,抛出异常部分源码
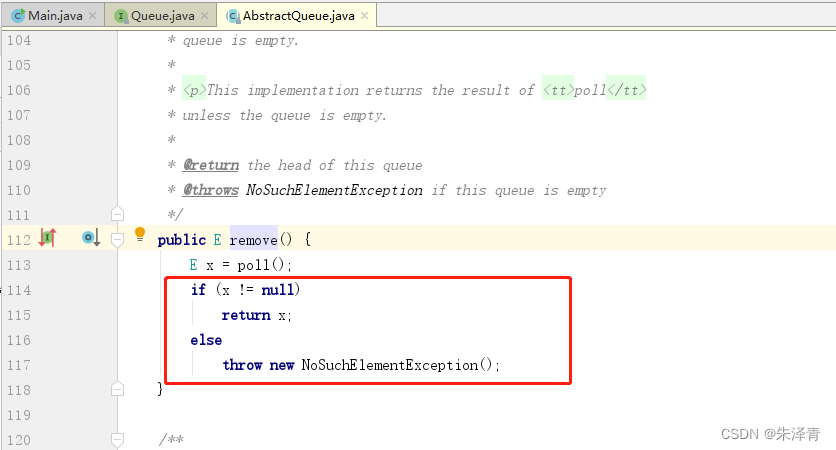
2.4.4 poll 方法
移除队头元素,如果为空,返回null。
示例
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue q = new ArrayBlockingQueue(1);
// 移除队头元素,如果为空,返回null
System.out.println(q.poll());
}
}JDK1.8 ArrayBlockingQueue 类的 poll 方法 部分源码,如果没有元素,返回null。
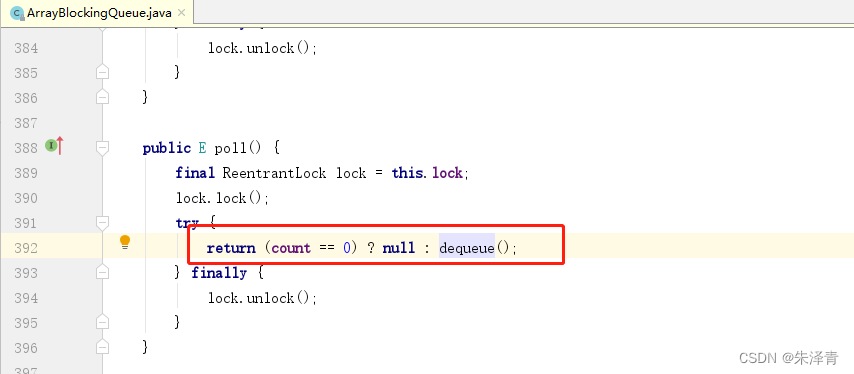
2.4.5 element 方法
获取但不移除队列头的元素,如果为空,抛出异常。
示例
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue q = new ArrayBlockingQueue(1);
q.element();
}
}JDK1.8 ArrayBlockingQueue 类的 element 方法 部分源码,如果为空,抛出异常。
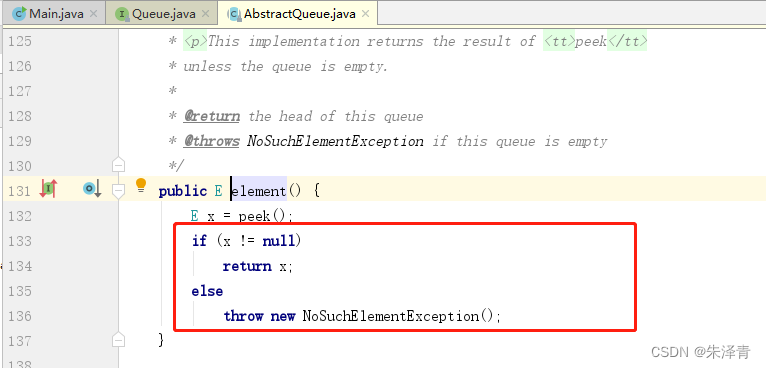
2.4.6 peek 方法
获取但不移除队列头的元素,如果为空,返回null。
示例
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue q = new ArrayBlockingQueue(1);
System.out.println(q.peek());// null
}
}JDK1.8 ArrayBlockingQueue 类的 peek 方法 部分源码,如果为空,返回 null。
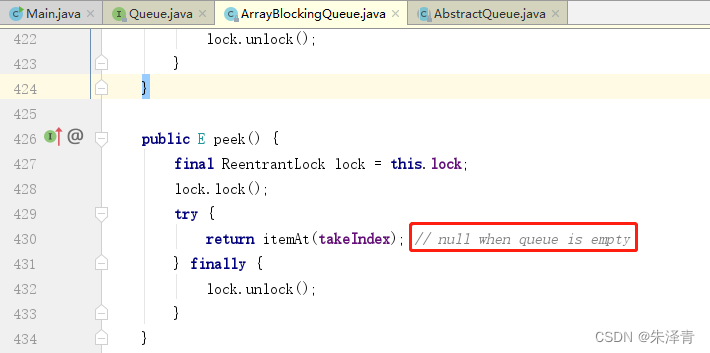
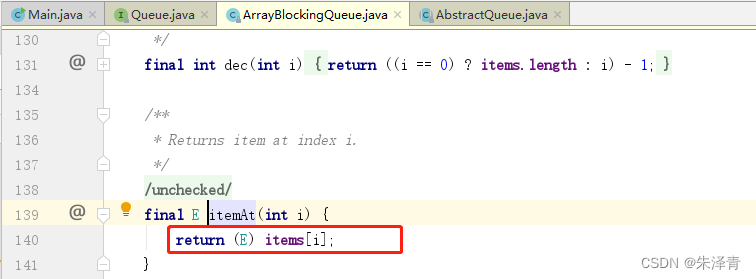
items 对象数组初始化之后值为 null 。
2.5、 Deque 接口
双向队列是元素的线性集合,支持两个端点插入与删除元素。
LinkedBlockingDeque 类简图如下:
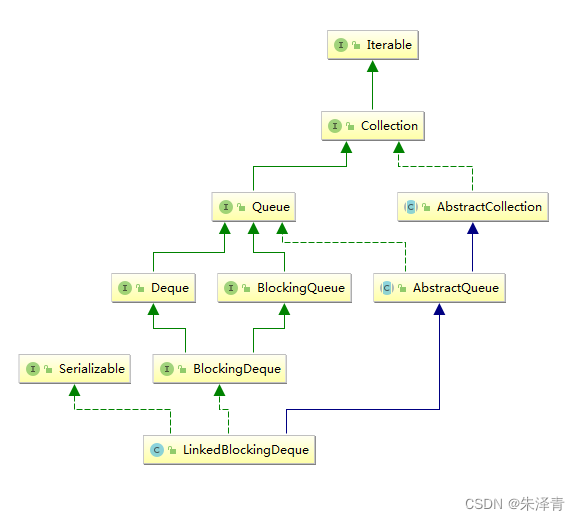
Deque扩展方法如下:
| 方法 | 描述 |
| addFirst() | 添加元素到头部 |
| addLast() | 添加元素到尾部 |
| offerFirst() | 添加元素到头部 |
| offerLast() | 添加元素到尾部 |
| removeFirst() | 删除头部元素 |
| removeLast() | 删除头尾元素 |
| pollFirst() | 删除头部元素 |
| pollLast() | 删除头尾元素 |
| getFirst() | 获取头部元素 |
| getLast() | 获取尾部元素 |
| peekFirst() | 获取头部元素 |
| peekLast() | 获取尾部元素 |
| removeFirstOccurrence() | 删除头部匹配的第一个元素 |
| removeLastOccurrence() | 删除尾部匹配的第一个元素 |
| descendingIterator() | 遍历集合中元素 |
2.5.1 addFirst 方法
添加元素到头部,如果实现类集合有大小限制,超过限制抛出IllegalStateException异常。添加 null ,将会抛出空指针异常。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Deque full
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.addFirst(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:326)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:16)
*/
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1);
//q.addFirst(1);
//q.addFirst(2);
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.offerLast(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:357)
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.addLast(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:334)
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.add(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:633)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:23)
*/
q.add(null);
}
}2.5.2 addLast 方法
添加元素到尾部,如果实现类集合有大小限制,超过限制抛出IllegalStateException异常。添加 null ,将会抛出空指针异常。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Deque full
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.addLast(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:335)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:17)
*/
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1);
// q.addLast (1);
//q.addLast (2);
/**
*Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.offerLast(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:357)
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.addLast(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:334)
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.add(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:633)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:26)
*/
q.add(null);
}
}2.5.3 offerFirst 方法
添加元素到头部,成功返回 true ,没有成功返回 false。添加 null ,将会抛出空指针异常。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.offerFirst(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:342)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:12)
*/
//System.out.println(q.offerFirst(null));
System.out.println(q.offerFirst(1)); // true
System.out.println(q.offerFirst(2)); // false
}
}2.5.4 offerLast 方法
添加元素到尾部,成功返回 true ,没有成功返回 false。添加 null ,将会抛出空指针异常。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.offerLast(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:357)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:15)
*/
// System.out.println(q.offerLast(null));
System.out.println(q.offerLast(1)); // true
System.out.println(q.offerLast(2)); // false
}
}2.5.5 removeFirst 方法
删除头部元素,成功返回删除对象,没有删除的元素抛出没有删除对象异常。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.removeFirst(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:453)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:15)
*/
System.out.println(q.removeFirst()); // 抛出异常
//q.offer(1);
//System.out.println(q.removeFirst()); // 返回1
}
}2.5.6 removeLast 方法
删除尾部元素,成功返回删除对象,没有删除的元素抛出没有删除对象异常。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.removeLast(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:462)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:17)
*/
//System.out.println(q.removeLast ()); // 抛出异常
q.offer(1);
System.out.println(q.removeLast ()); // 返回1
}
}2.5.7 pollFirst 方法
删除头部元素,如果集合中没有元素,返回 null , 如果有删除的元素返回删除元素。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
System.out.println(q.pollFirst()); // 如果没有元素可以删除,返回 null
q.offer(1);
System.out.println(q.pollFirst ()); // 返回1
}
}2.5.8 pollLast 方法
删除尾部元素,如果集合中没有元素,返回 null , 如果有删除的元素返回删除元素。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
System.out.println(q.pollLast ()); // 如果没有元素可以删除,返回 null
q.offer(1);
System.out.println(q.pollLast ()); // 返回1
}
}2.5.9 getFirst 方法
获取头部元素。如果集合没有元素,抛出没有元素异常。有元素返回头部元素。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.getFirst(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:553)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:12)
*/
// System.out.println(q.getFirst ()); // 如果没有元素抛出异常
q.offer(1);
System.out.println(q.getFirst ()); // 返回1
}
}2.5.10 getLast 方法
获取尾部元素。如果集合没有元素,抛出没有元素异常。有元素返回头部元素。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
/**
* Exception in thread "main" java.util.NoSuchElementException
* at java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque.getLast(LinkedBlockingDeque.java:562)
* at com.example.demo1.Main.main(Main.java:13)
*/
//System.out.println(q.getLast ()); // 如果没有元素抛出异常
q.offer(1);
System.out.println(q.getLast ()); // 返回1
}
}2.5.11 peekFirst 方法
获取头部元素。如果集合没有元素,返回 null,有元素返回头部元素。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
System.out.println(q.peekFirst()); // 返回null 。如果没有元素返回 null,有元素返回头部元素
q.offer(1);
System.out.println(q.peekFirst()); // 返回1
}
}2.5.12 peekLast 方法
获取尾部元素。如果集合没有元素,返回 null,有元素返回头部元素。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
System.out.println(q.peekLast()); // 返回null 。如果没有元素返回 null,有元素返回头部元素
q.offer(1);
System.out.println(q.peekLast()); // 返回1
}
}2.5.13 removeFirstOccurrence 方法
删除头部匹配的第一个元素。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
System.out.println(q.removeFirstOccurrence(1)); // 删除头部匹配的第一个元素,成功返回true, 反之返回false
}
}2.5.14 removeLastOccurrence 方法
删除尾部匹配的第一个元素。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
System.out.println(q.removeLastOccurrence(1)); // 删除未部匹配的第一个元素,成功返回true, 反之返回false
}
}2.5.15 descendingIterator 方法
遍历集合。
示例
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque q = new LinkedBlockingDeque(1); // 设置大小1
q.offer(1);
// 遍历集合
Iterator it = q.descendingIterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
}2.6、 SortedSet 接口
SortedSet 是一个默认按升序维护元素的Set集合。根据元素的自然排序或根据 SortedSet 创建时提供的 Comparator 进行排序。
SortedSet 接口包含如下几点操作:
1、范围视图,允许对排序集合元素任意范围操作。
2、查找,返回已排序集合中第一个元素或最后一个元素
3、比较器访问,返回用于对集合排序的比较器(如果有比较器)
SortedSet 扩展了如下方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
| comparator() | 获取比较器 |
| subSet() | 获取子集合 |
| headSet() | 返回小于某个值的子集合 |
| tailSet() | 返回大于等于某个值的子集合 |
| first() | 返回排序顺序的第一个元素 |
| last() | 返回排序顺序的最后一个元素 |
2.6.1 comparator 方法
获取比较器。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedSet sortedSet = new TreeSet(Collections.reverseOrder());
sortedSet.add(1);
sortedSet.add(2);
sortedSet.add(3);
/**
* comparator() 方法
* 获取比较器
*/
Comparator comparator = sortedSet.comparator();
System.out.println(comparator);// java.util.Collections$ReverseComparator@2626b418
}
}2.6.2 subSet 方法
获取子集合。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedSet sortedSet = new TreeSet();
sortedSet.add(1);
sortedSet.add(2);
sortedSet.add(3);
/**
* subSet 方法
* 获取子集subSet[开始位置,结束位置),开始位置从1开始,开始位置是闭区间,结束位置是开区间。
*/
SortedSet s = sortedSet.subSet(1,3);
System.out.println(s); // [1, 2]
}
}2.6.3 headSet 方法
返回小于当前元素的集合。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedSet sortedSet = new TreeSet();
sortedSet.add(1);
sortedSet.add(2);
sortedSet.add(3);
/**
* headSet 方法
* 返回小于当前元素的集合( 新的SortedSet)
*/
SortedSet s1 = sortedSet.headSet(2);
System.out.println(s1); // [1]
}
}2.6.4 tailSet 方法
返回大于等于当前元素的集合
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedSet sortedSet = new TreeSet();
sortedSet.add(1);
sortedSet.add(2);
sortedSet.add(3);
/**
* tailSet 方法
* 返回大于等于当前元素的集合( 新的SortedSet)
*/
SortedSet s2 = sortedSet.tailSet(2);
System.out.println(s2); // [2, 3]
}
}2.6.5 first 方法
返回排序顺序的第一个元素 。如果集合为空,会抛出 NoSuchElementException异常。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedSet sortedSet = new TreeSet();
sortedSet.add(1);
sortedSet.add(2);
sortedSet.add(3);
/**
* first 方法
* 返回排序顺序的第一个元素 。如果集合为空,会抛出 NoSuchElementException异常
*/
System.out.println(sortedSet.first());
}
}2.6.6 last 方法
返回排序顺序的最后一个元素 。如果集合为空,会抛出 NoSuchElementException异常。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedSet sortedSet = new TreeSet();
sortedSet.add(1);
sortedSet.add(2);
sortedSet.add(3);
/**
* last 方法
* 返回排序顺序的最后一个元素 。如果集合为空,会抛出 NoSuchElementException异常
*/
System.out.println(sortedSet.last());
}
}2.7、 Map 接口
Map 是一个将键映射到值的对象。映射不能包含重复的键,每个键最多映射一个值。Map 接口用于基本操作有 put、get、remove、containsKey、containsValue、size、empty、批量操作(putAll、clear)和集合视图(keySet、entrySet、values)等方法。
Java 平台包含三种通用 Map 实现: HashMap、treeMap 和 LinkedHashMap。他们的性能和方法类似于 HashSet、TreeSet 和 LinkedHashSet。
Map 接口方法如下:
| 方法 | 描述 |
| size() | 获取集合元素大小 |
| isEmpty() | 判断集合是否为空 |
| containsKey() | 判断集合是否包含某个key |
| containsValue() | 判断集合是否包含某个value |
| get() | 根据 key 获取集合 value 值 |
| put() | 集合添加元素 |
| remove() | 根据 key 删除元素 |
| putAll() | 集合中添加某个集合的全部元素 |
| clear() | 清空集合元素 |
| keySet() | 获取集合所有 key |
| values() | 获取集合所有 value |
| entrySet() | 返回 Map 集合映射实体 |
| getOrDefault() | 根据 key或者 value。如果 key 不存在,则返回默认值 |
| forEach() | 遍历集合 |
| replaceAll() | 替换方法 |
| putIfAbsent() | 根据key,不存在就添加,有了就不添加 |
| remove() | 根据 key 删除元素 |
| replace() | 集合替换操作 |
| computeIfAbsent() | 计算元素操作,如果存在不计算操作,不存在就执行操作计算 |
| computeIfPresent() | 计算元素操作,如果存在计算操作,不存在不执行操作计算 |
| compute() | 计算函数 |
| merge() | 集合合并操作 |
2.7.1 size 方法
获取集合大小。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
// 获取集合大小
System.out.println(map.size());
}
}2.7.1 isEmpty 方法
判断集合是否为空。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
// 判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(map.isEmpty ());
}
}2.7.2 containsKey 方法
判断集合是否包含某个key。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","张三");
// 判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(map.containsKey("name"));// true
}
}2.7.3 containsValue 方法
判断集合是否包含某个值。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","张三");
System.out.println(map.containsValue ("张三"));// true
}
}2.7.4 get 方法
根据 key 获取集合 value 值。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","张三");
System.out.println(map.get ("name"));// 张三
}
}2.7.5 put 方法
集合添加元素。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","张三");
}
}2.7.6 remove 方法
根据 key 删除元素。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","张三");
System.out.println("删除前集合大小: " + map.size()); // 1
map.remove("name");
System.out.println("删除后集合大小: " + map.size()); // 0
}
}2.7.7 putAll 方法
集合中添加某个集合的全部元素。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","张三");
Map map1 = new HashMap();
map1.putAll(map);
}
}2.7.8 clear方法
清空集合元素。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","张三");
System.out.println("清空前集合大小: " + map.size()); // 1
// 集合清空操作
map.clear();
System.out.println("清空后集合大小: " + map.size()); // 0
}
}2.7.9 keySet 方法
获取集合所有 key。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","张三");
map.put("age",18);
// 获取集合所有 key
Set keys = map.keySet();
// 遍历集合key
Iterator it = keys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next()+" "); // name age
}
}
}2.7.10 values 方法
获取集合所有 value 。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","张三");
map.put("age",18);
// 获取集合所有 values
Collection values = map.values();
// 遍历集合 value
Iterator it = values.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next()+" "); // 张三 18
}
}
}2.7.11 entrySet 方法
返回 Map 集合映射实体。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name","张三");
map.put("age",18);
Iterator<Map.Entry> it= map.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry entry = it.next();
/**
* name 张三
* age 18
*/
System.out.println(entry.getKey() +" "+ entry.getValue());
}
}
}2.7.12 getOrDefault 方法
根据 key或者 value。如果 key 不存在,则返回默认值。
getOrDefault 方法 第一参数是 key。第二个参数是 key 不存在的时候,返回 value 的默认值。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", "张三");
map.put("age", 18);
System.out.println(map.getOrDefault("name","默认值")); // 张三 ,因为存在key
System.out.println(map.getOrDefault("notExistkey","默认值")); // 默认值,key 不存在,返回自己设置的默认值
}
}2.7.13 forEach 方法
遍历集合。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", "张三");
map.put("age", 18);
// 遍历
map.forEach((key,value) -> {
System.out.println("key:"+key+" value:"+value);
});
}
}2.7.14 replaceAll 方法
替换方法。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", "zhuzq");
// 把value替换成大写
map.replaceAll((key,value) ->{
return value.toString().toUpperCase();
});
map.forEach((key,value) ->{
System.out.println("key:"+key+" value:"+value); // key:name value:ZHUZQ
});
}
}2.7.15 putIfAbsent 方法
根据key,不存在就添加,有了就不添加。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", "zhuzq");
/**
*
*/
map.forEach((key,value) ->{
System.out.println("最开始 key:"+key+" value:"+value);
});
// 覆盖value 旧值
map.put("name", "lisi");
map.forEach((key,value) ->{
System.out.println("覆盖value key:"+key+" value:"+value);
});
// 根据key,不存在就添加,有了就不添加
map.putIfAbsent("name","wangwu");
map.putIfAbsent("age","18"); // 不存在,添加成功
map.forEach((key,value) ->{
System.out.println("putIfAbsent方法操作后 key:"+key+" value:"+value);
});
}
}控制台显示
最开始 key:name value:zhuzq
覆盖value key:name value:lisi
putIfAbsent方法操作后 key:name value:lisi
putIfAbsent方法操作后 key:age value:18
2.7.16 remove 方法
根据 key 删除元素。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", "zhuzq");
map.put("age", "18");
// 删除 key = name 操作
map.remove("name");
/**
* 控制台显示 key:age value:18
*/
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
}
}2.7.17 replace 方法
集合替换操作。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", "zhuzq");
map.put("age", "18");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("替换前 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
// 替换操作
map.replace("name","lishi");
// 替换重载方法,第一个参数 key 第二个参数旧值 第三个参数 新值
map.replace("age", "18","20");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("替换后 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
}
控制显示
替换前 key:name value:zhuzq
替换前 key:age value:18
替换后 key:name value:lishi
替换后 key:age value:20
2.7.18 computeIfAbsent 方法
计算元素操作,如果存在不计算操作,不存在就执行操作计算。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", "zhuzq");
map.put("age", "18");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("操作前 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
map.computeIfAbsent("name", key -> "lishi");
map.computeIfAbsent("comeFrom", key -> "深圳");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("computeIfAbsent方法操作后 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
}
}控制台显示
操作前 key:name value:zhuzq
操作前 key:age value:18
computeIfAbsent方法操作后 key:comeFrom value:深圳
computeIfAbsent方法操作后 key:name value:zhuzq
computeIfAbsent方法操作后 key:age value:18
2.7.19 computeIfPresent 方法
计算元素操作,如果存在计算操作,不存在不执行操作计算。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", "zhuzq");
map.put("age", "18");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("操作前 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
map.computeIfPresent("name", (key, value) -> "lishi");
map.computeIfPresent("comeFrom", (key, value) -> "深圳");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("computeIfPresent操作之后 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
}
}控制台显示
操作前 key:name value:zhuzq
操作前 key:age value:18
computeIfPresent操作之后 key:name value:lishi
computeIfPresent操作之后 key:age value:182.7.20 compute 方法
计算函数。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("comeFrom", null);
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("操作前 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
map.compute("comeFrom", (k, v) -> v == null ? "深圳" : v);
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("compute 操作之后 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
}
}2.7.21 merge方法
集合合并操作。
示例
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", "zhangsan");
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("操作前 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
map.merge("age","18" ,(old,new_) -> old.toString()+ new_);
map.merge("name","zhangsan" ,(old,new_) -> old.toString()+" "+ new_);
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("merge 操作之后 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
}
}2.8、 SortedMap 接口
SortedMap 默认按升序维护元素的集合。根据自然顺序或根据创建SortedMap时提供的Comparator 进行排序。
SortedMap 包含如下操作:
1、范围视图操作,在排序的映射上执行范围操作。
2、端点操作,返回已排序映射中的第一个或者最后一个键
3、Comparator访问,如果有,返回用于对映射进行排序的Comparator。
SortedMap扩展方法如下
| 方法 | 描述 |
| comparator() | 获取比较器 |
| subMap() | 返回子集合 |
| headMap() | 返回小于Key集合 |
| tailMap() | 返回大于等于Key集合 |
| firstKey() | 返回集合第一个key |
| lastKey() | 返回集合最后一个key |
2.8.1 comparator 方法
获取比较器。
示例
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedMap sortedMap = new TreeMap(Collections.reverseOrder());
// 获取比较器
Comparator c = sortedMap.comparator();
System.out.printf(c.toString());//java.util.Collections$ReverseComparator@64c64813
}
}
2.8.2 subMap 方法
返回子集合。
示例
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedMap sortedMap = new TreeMap();
sortedMap.put(1,1);
sortedMap.put(2,2);
sortedMap.put(3,3);
SortedMap sortedMap1 = sortedMap.subMap(1,2); // [开始位置,结束位置 )
sortedMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("sortedMap 集合 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
sortedMap1.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("sortedMap1 集合 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
}
}控制台显示
sortedMap 集合 key:1 value:1
sortedMap 集合 key:2 value:2
sortedMap 集合 key:3 value:3
sortedMap1 集合 key:1 value:12.8.3 headMap方法
返回小于Key集合。
示例
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedMap sortedMap = new TreeMap();
sortedMap.put(1,1);
sortedMap.put(2,2);
sortedMap.put(3,3);
// 返回小于Key集合
SortedMap sortedMap1 = sortedMap.headMap(3);
sortedMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("sortedMap 集合 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
sortedMap1.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("sortedMap1 集合 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
}
}控制台
sortedMap 集合 key:1 value:1
sortedMap 集合 key:2 value:2
sortedMap 集合 key:3 value:3
sortedMap1 集合 key:1 value:1
sortedMap1 集合 key:2 value:22.8.4 tailMap 方法
返回大于等于Key集合。
示例
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedMap sortedMap = new TreeMap();
sortedMap.put(1,1);
sortedMap.put(2,2);
sortedMap.put(3,3);
SortedMap sortedMap1 = sortedMap.tailMap (2);
sortedMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("sortedMap 集合 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
sortedMap1.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("sortedMap1 集合 key:" + key + " value:" + value);
});
}
}2.8.5 firstKey 方法
返回集合第一个key。
示例
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedMap sortedMap = new TreeMap();
sortedMap.put(1,1);
sortedMap.put(2,2);
System.out.printf(sortedMap.firstKey().toString()); //1
}
}
2.8.6 lastKey方法
返回集合最后一个key。
示例
import java.util.SortedMap;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedMap sortedMap = new TreeMap();
sortedMap.put(1,1);
sortedMap.put(2,2);
System.out.printf(sortedMap.lastKey().toString()); //2
}
}
三、接口实现
通用实现如下表
| Interfaces | Hash table Implementations | Resizable array Implementations | Tree Implementations | Linked list Implementations | Hash table + Linked list Implementations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Set | HashSet | TreeSet | LinkedHashSet | ||
List | ArrayList | LinkedList | |||
Queue | |||||
Deque | ArrayDeque | LinkedList | |||
Map | HashMap | TreeMap | LinkedHashMap |
Java集合框架提供了几个核心接口的通用实现:
对于Set接口,HashSet是最常用的实现。
对于List接口,ArrayList是最常用的实现。
对于Map接口,HashMap是最常用的实现。
对于Queue接口,LinkedList是最常用的实现。
对于Deque接口,ArrayDeque是最常用的实现。





![[附源码]java毕业设计在线二手车交易信息管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/06da7ba9f0464ec9bdc8344f25b001d9.png)