目录
一、Math类
1、Math类中的方法
1.1 圆周率:PI
1.2 绝对值:abs()
1.3 返回最小近似值:ceil()
1.4 返回最大近似值
1.5 四舍五入:round()
1.6 最大值和最小值:max()/min()
1.7 求指定次幂 :pow()
1.8 随机数:random()
二、Random类
1、Random类构造方法
2、Random中的方法
3、代码演示
4、同种子 (参数相同)
三、String类
1、String类的常用方法
2、拼接字符串:concat(String string)
3、字符串提取和查询
四、StringBuffer
1、StringBuffer类的构造方法
2、StringBuffer类常用方法
五、StringBuilder类
六、String类、StringBuffer类和StringBuilder类异同
一、Math类
Math类是被关键字final修饰的类,不能被继承

1、Math类中的方法
Math类中的方法有很多,都是用于数学计算的,我们就随便看几个
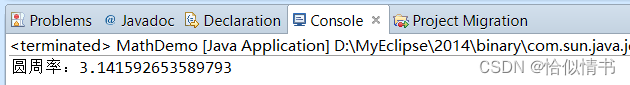
1.1 圆周率:PI
public static void main(String[] args) {
double pi = Math.PI;
System.out.println("圆周率:"+pi);
} 
1.2 绝对值:abs()
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = Math.abs(-100);
System.out.println("-100的绝对值为:"+num);
}
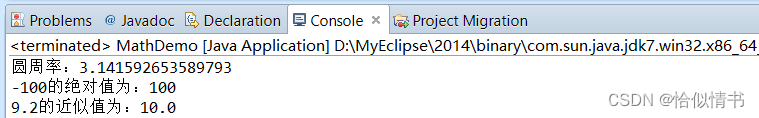
1.3 返回最小近似值:ceil()
返回比参数大的最小整数

public static void main(String[] args) {
double ceil = Math.ceil(9.2);
System.out.println("9.2的近似值为:"+ceil);
}
1.4 返回最大近似值
返回比参数小的最大整数
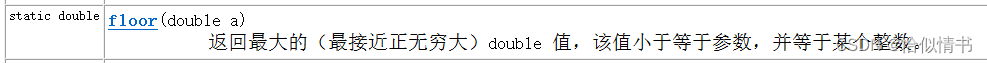
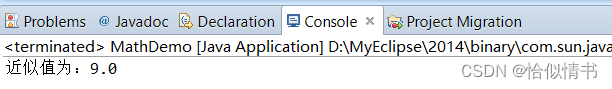
public static void main(String[] args) {
double floor = Math.floor(9.2);
System.out.println("近似值为:"+floor);
}
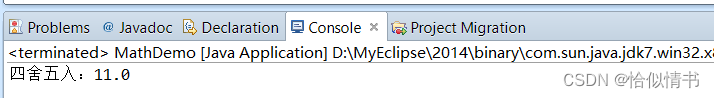
1.5 四舍五入:round()
public static void main(String[] args) {
double round = Math.round(10.6);
System.out.println("四舍五入:"+round);
}
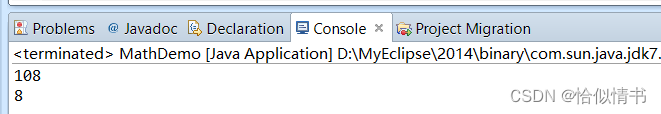
1.6 最大值和最小值:max()/min()
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.max(108, 8));
System.out.println(Math.min(108, 8));
}
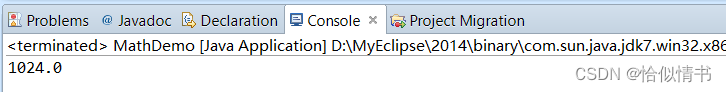
1.7 求指定次幂 :pow()
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 10));
}
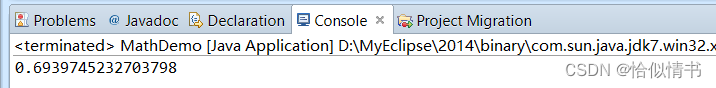
1.8 随机数:random()
Math.random();返回一个[0.0,1.0]之间的double类型的数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
double random01 = Math.random();
System.out.println(random01);
}
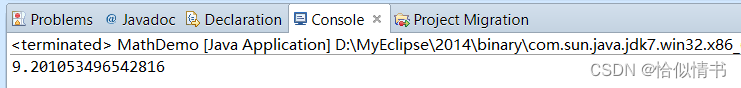
Math.random()*10;返回一个[0.0,10.0]之间的double类型的数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
double random02 = Math.random()*10;
System.out.println(random02);
}
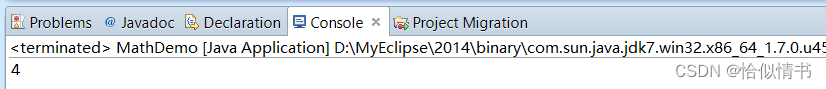
(int)(Math.random()*10);返回[0.0,10.0]之间的int类型的数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
int random03 = (int)(Math.random()*10);
System.out.println(random03);
}
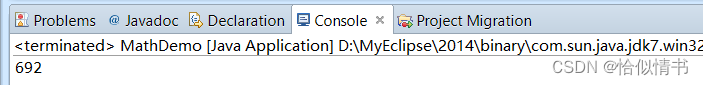
(int)(Math.random()*(num2-num1)+num1);输出num1到num2之间的整数
lic class MathDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//输出一个1-999之间的随机数
int random04 = (int)(Math.random()*(998-1)+1);
System.out.println(random04);
}
二、Random类
在java.util包中;
此类的实例用于生成伪随机数流,就是生成随机数
1、Random类构造方法

2、Random中的方法
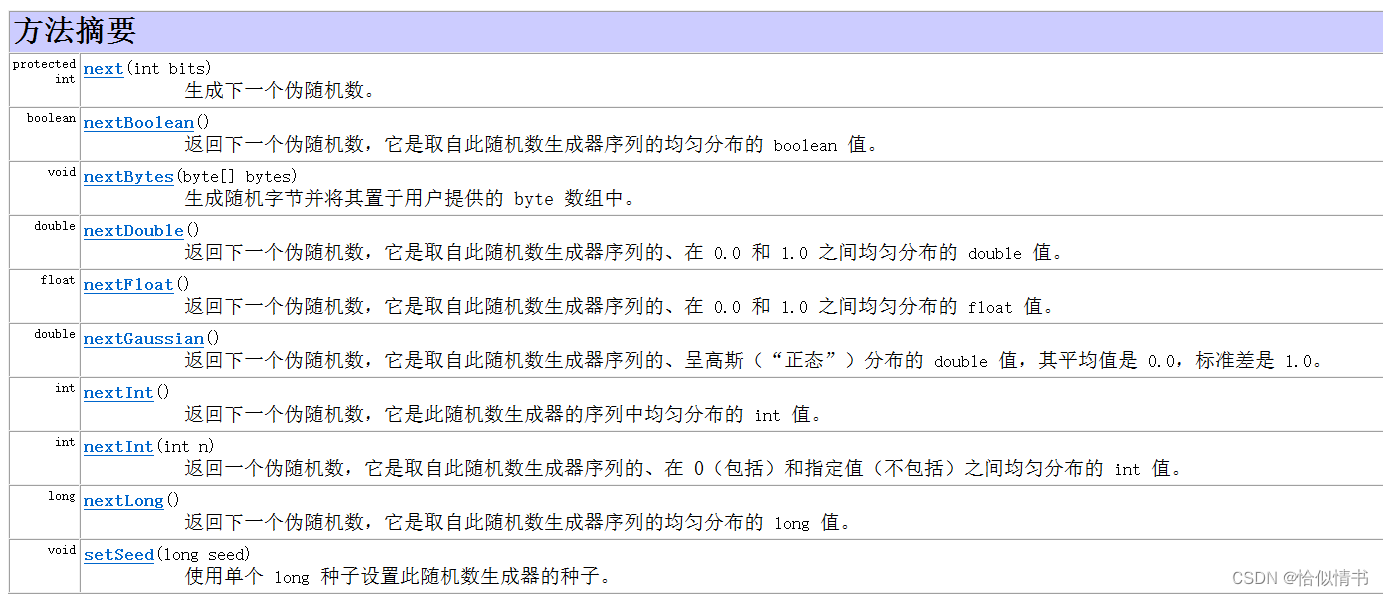
3、代码演示
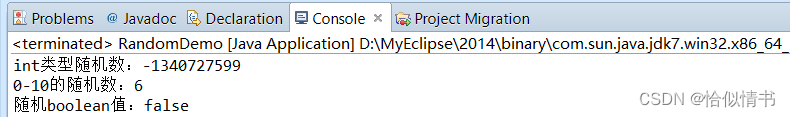
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Random类对象
Random random = new Random();
//获取int类型的随机数
int num1 = random.nextInt();
System.out.println("int类型随机数:"+num1);
//产生的数可能性为int类型的取值范围
//生成指定范围的随机数
int num2 = random.nextInt(10);
System.out.println("0-10的随机数:"+num2);
//随机boolean值
System.out.println("随机boolean值:"+random.nextBoolean());
}
4、同种子 (参数相同)
如果用相同的种子创建两个
Random实例,则对每个实例进行相同的方法调用序列,它们将生成并返回相同的数字序列。为了保证此属性的实现,为类Random指定了特定的算法。为了 Java 代码的完全可移植性,Java 实现必须让类Random使用此处所示的所有算法。但是允许Random类的子类使用其他算法,只要其符合所有方法的常规协定即可。
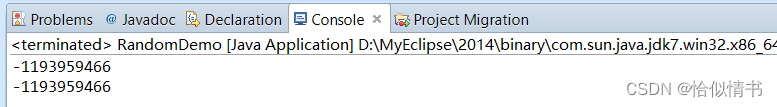
public static void main(String[] args) {
//如果用相同的种子创建两个 Random 实例,则对每个实例进行相同的方法调用序列,它们将生成并返回相同的数字序列
Random r1 = new Random(100);
Random r2 = new Random(100);
System.out.println(r1.nextInt());
System.out.println(r2.nextInt());
}
三、String类
我们在前面已经对String类已经有过了解,今天我们看一下String类中常用方法
1、String类的常用方法
(1)获取字符串长度:length();
(2)获取指定索引的字符:charAt();
(3)字符串的比较:equals();
(4)字符串大写转小写:toLowerCase();
(5)字符串小写转大写:toUpperCase();
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建String类对象
String str1 = new String("yfgtetwyubfuy");
String str2 = "fhubuyfd";
//获取字符串的长度:length()
int lengthStr1 = str1.length();
System.out.println("字符串str1的长度为:"+lengthStr1);
int lengthStr2= str2.length();
System.out.println("字符串str2的长度为:"+lengthStr2);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//获取指定索引的字符:charAt()
char str1Char = str1.charAt(5);
System.out.println("字符串str1的第六个字符是:"+str1Char);
System.out.println("字符串str2的第三个字符是:"+str2.charAt(2));
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//字符串的比较:equals()
boolean result1 = str1.equals(str2);
System.out.println("字符串str1与str2是否相同:"+result1);
System.out.println("字符串str2是否与fhubuyfd相同:"+str2.equals("fhubuyfd"));
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//字符串大写转小写:toLowerCase();
String str3 = "JDIUGNRLasd";
String str4 = str3.toLowerCase();
System.out.println("将字符串str3转为小写为:"+str4);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//字符串小写转大写:toUpperCase();
String str5 = "keriolkJUHNU";
String str6 = str5.toUpperCase();
System.out.println("将字符串str5转换大写:"+str6);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
}2、拼接字符串:concat(String string)
第一种方式:
使用拼接符号"+"拼接
第二种方式:
使用concat(String string)方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "qwerty";
String str2 = "asdfghj";
//使用"+"实现拼接
//输出[q,w,e,r,t,y]
for(int i = 0;i <str1.length();i++){
if(i == 0){
System.out.print("["+str1.charAt(i)+",");
}else if(i > 0 && i <str1.length()-1){
System.out.print(str1.charAt(i)+",");
}else{
System.out.println(str1.length()+"]");
}
}
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//调用concat(String string)实现拼接
String str3 = str1+"nfdiugnriun";
System.out.println(str3);
String str4 = str1.concat(str2);
System.out.println(str4);
}
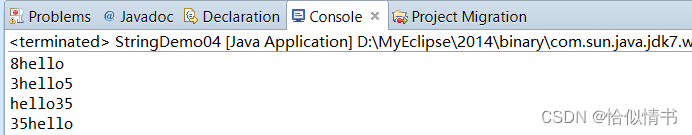
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(3+5+"hello");
System.out.println(3+"hello"+5);
System.out.println("hello"+3+5);
System.out.println(3+""+5+"hello");
}
程序不仅是从上到下执行,还要遵循从左到右执行
3、字符串提取和查询
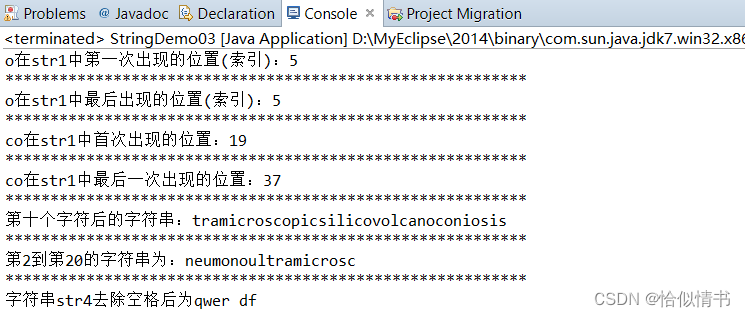
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis";
//返回第一个o出现的位置
int numStr1 = str1.indexOf(111);
System.out.println("o在str1中第一次出现的位置(索引):"+numStr1);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//返回最后一个o的索引
int numStr2 = str1.lastIndexOf(111);
System.out.println("o在str1中最后出现的位置(索引):"+numStr1);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//返回第一次出现字符串co的索引
int numStr3 = str1.indexOf("co");
System.out.println("co在str1中首次出现的位置:"+numStr3);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//返回最后一次出现字符串co的索引
int numStr4 = str1.lastIndexOf("co");
System.out.println("co在str1中最后一次出现的位置:"+numStr4);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//返回第十个字符后的所有字符
String str2 = str1.substring(10);
System.out.println("第十个字符后的字符串:"+str2);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//返回第2到第20个字符
String str3 = str1.substring(1,20);
System.out.println("第2到第20的字符串为:"+str3);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//去除字符串前后的空格
String str4 = " qwer df ";
String str5 = str4.trim();
System.out.println("字符串str4去除空格后为"+str5);
}
4、String类实用方法
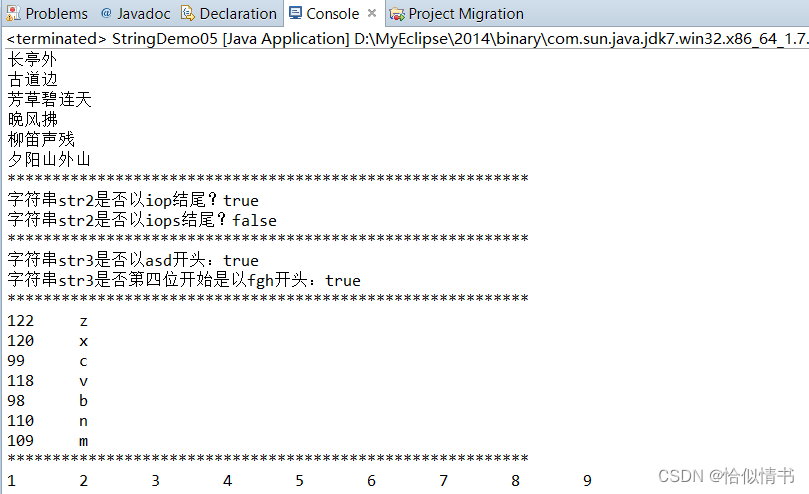
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "长亭外 古道边 芳草碧连天 晚风拂 柳笛声残 夕阳山外山";
//String[] split(String regex) 根据给定正则表达式的匹配拆分此字符串
//按空格来拆分字符串,返回的是一个字符数组
String[] strs1 = str1.split(" ");
for(String string:strs1){
System.out.println(string);
}
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//boolean endsWith(String suffix)测试此字符串是否以指定的后缀结束
String str2 = "qwertyuiop";
boolean result1 = str2.endsWith("iop");
System.out.println("字符串str2是否以iop结尾?"+result1);
boolean result2 = str2.endsWith("iops");
System.out.println("字符串str2是否以iops结尾?"+result2);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
// boolean startsWith(String prefix,int toffset)测试此字符串从指定索引开始的子字符串是否以指定前缀开始
String str3 = "asdfghjkl";
boolean result3 = str3.startsWith("asd");
System.out.println("字符串str3是否以asd开头:"+result3);
boolean result4 = str3.startsWith("fgh",3);
System.out.println("字符串str3是否第四位开始是以fgh开头:"+result4);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//byte[] getBytes()使用平台的默认字符集将此String编码为byte序列,并将结果存储到一个新的byte数组中
String str4 = "zxcvbnm";
byte[] bytes = str4.getBytes();
for(byte strBytes:bytes){
System.out.print(strBytes+"\t");
System.out.println((char)strBytes);
}
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//char[] toCharArray() 将此字符串转换为一个新的字符数组
String str5 = "123456789";
char[] chars = str5.toCharArray();
for(char strChar:chars){
System.out.print(strChar+"\t");
}
}
四、StringBuffer
StringBuffer类位于java.util包中,是String类的增强类。是线程安全的可变字符序列。一个类似于String的字符串缓冲区,但不能修改。
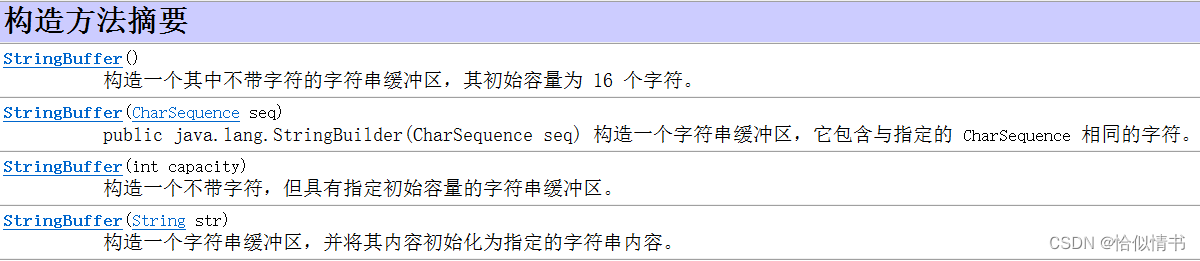
1、StringBuffer类的构造方法
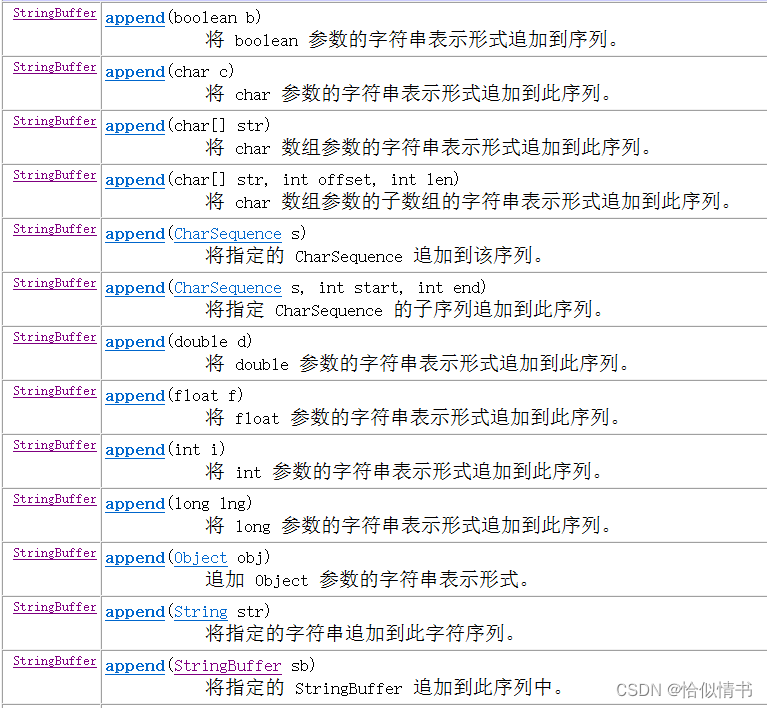
2、StringBuffer类常用方法
append(Type type):将字符串表示形式添加到序列
StringBuffer delete(int start, int end):移除此序列的子字符串中的字符
insert(int offset,Type type):插入
reverse():字符串反转

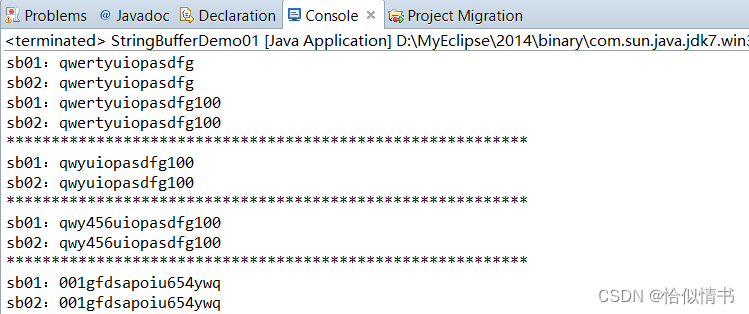
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建StringBuffer类对象
StringBuffer sb01 = new StringBuffer("qwertyuiop");
//append(Type type)将字符串表示形式添加到序列
StringBuffer sb02 = sb01.append("asdfg");
System.out.println("sb01:"+sb01);
System.out.println("sb02:"+sb02);
sb01.append(100);
System.out.println("sb01:"+sb01);
System.out.println("sb02:"+sb02);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
// StringBuffer delete(int start, int end)移除此序列的子字符串中的字符。
sb02.delete(2,5);
System.out.println("sb01:"+sb01);
System.out.println("sb02:"+sb02);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//insert(int offset,Type type)插入
sb02.insert(3, 456);
System.out.println("sb01:"+sb01);
System.out.println("sb02:"+sb02);
System.out.println("**********************************************************");
//reverse():字符串反转
sb01.reverse();
System.out.println("sb01:"+sb01);
System.out.println("sb02:"+sb02);
}
五、StringBuilder类
(1)java.lang.StringBuilder是JDK 5.0版本新增的类,它是一个可变的字符序列。
(2)一个可变的字符序列。此类提供一个与
StringBuffer兼容的 API,但不保证同步。该类被设计用作StringBuffer的一个简易替换,用在字符串缓冲区被单个线程使用的时候(这种情况很普遍)。如果可能,建议优先采用该类,因为在大多数实现中,它比StringBuffer要快。在
StringBuilder上的主要操作是append和insert方法,可重载这些方法,以接受任意类型的数据。每个方法都能有效地将给定的数据转换成字符串,然后将该字符串的字符追加或插入到字符串生成器中。append方法始终将这些字符添加到生成器的末端;而insert方法则在指定的点添加字符。(3)使用StringBuilder类处理字符串的方法与StringBuffer类基本一样。
六、String类、StringBuffer类和StringBuilder类异同
(1)String类:字符串常量
String是不可变的对象,在每次对String类型进行改变时其实都等同于生成了一个新的String对象,然后指向新的String对象,所以经常改变内容的字符串最好不要用String类型,因为每次生成对象都会对系统性能产生影响。
(2)StringBuffer类:字符串变量
StringBuffer是可变的字符串,在每次对StringBuffer对象进行改变时,会对StringBuffer对象本身进行操作,而不是生成新的对象,再改变对象引用。所以,在字符串对象经常改变的情况下,推荐使用StringBuffer类。
(3)StringBuilder类:字符串变量
JDK 5.0版本以后提供了StringBuilder类,它和StringBuffer类等价,区别在于StringBuffer类是线程安全的,StringBuilder类是单线程的,不提供同步,理论上效率更高。

![[附源码]计算机毕业设计JAVA乒乓球俱乐部管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a7e7adfe53ab4b419541e442423d2666.png)