目录
- JAVA异常
- 1.初识异常
- 2.异常的处理
- 2.1 捕获异常的基本语法
- 2.2 捕获异常
- 2.3 finally的使用
- 2.4 异常的执行流程
- 2.5 抛出异常
- 3.JAVA异常体系
- 4.自定义异常类
JAVA异常
1.初识异常
异常指的就是程序在 运行时 出现错误时通知调用者的一种机制.
我们在编写代码的过程中,遇到过许多的异常,比如
1.
System.out.println(10 / 0);
// 执行结果: //0异常
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
2.
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(arr[100]);
// 执行结果 //数组越界异常
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 100
3.
int[] arr=null;
System.out.println(arr[0]);
//执行结果 //空指针异常
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
2.异常的处理
2.1 捕获异常的基本语法
try{
有可能出现异常的语句;
}[catch (异常类型 异常对象) {
} ... ]
[finally {
异常的出口
}]
| 1.try代码块中放的是可能出现异常的代码. 2.catch代码块中放的是出现异常后的处理行为. 3.finally代码块中的代码用于处理善后工作, 会在最后执行. 4.其中 catch 和 finally 都可以根据情况选择加或者不加 |
2.2 捕获异常
如果出现异常而不处理,程序会交给JVM处理,程序运行也会停止.
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println("before");
System.out.println(arr[5]);
System.out.println("after");
// 执行结果
before
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 100
使用try catch执行程序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,3,4,5};
try{
arr=null;
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("空指针异常");
}
执行结果:
空指针异常
java.lang.NullPointerException
at error.main(error.java:13)
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
try {
System.out.println("before");
arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[100]);
System.out.println("after");
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after try catch");
// 执行结果
before
after try catch
java.lang.NullPointerException at error.main(error.java:34)
catch也可以有很多个
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
try {
System.out.println("before");
arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[100]);
System.out.println("after");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("这是个数组下标越界异常");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("这是个空指针异常");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after try catch");
// 执行结果
before
这是个空指针异常
java.lang.NullPointerException
at demo02.Test.main(Test.java:12)
after try catch
也可以用一个 catch 捕获所有异常(不推荐)
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
try {
System.out.println("before");
arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[100]);
System.out.println("after");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("after try catch");
// 执行结果
before
java.lang.NullPointerException
at demo02.Test.main(Test.java:12)
after try catch
2.3 finally的使用
finally 表示最后的善后工作, 例如释放资源,无论是否存在异常, finally 中的代码一定都会执行到.
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
try {
System.out.println("before");
arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[100]);
System.out.println("after");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("finally code");
}
// 执行结果
before
java.lang.NullPointerException
at demo02.Test.main(Test.java:12)
finally code
2.4 异常的执行流程
| 1.程序先执行 try 中的代码 2.如果 try 中的代码出现异常, 就会结束 try 中的代码, 看和 catch 中的异常类型是否匹配 3.如果找到匹配的异常类型, 就会执行 catch 中的代码 4.如果没有找到匹配的异常类型, 就会将异常向上传递到上层调用者 5.无论是否找到匹配的异常类型, finally 中的代码都会被执行到(在该方法结束之前执行) 6.如果上层调用者也没有处理的了异常, 就继续向上传递 7.一直到 main 方法也没有合适的代码处理异常, 就会交给 JVM 来进行处理, 此时程序就会异常终止. |
2.5 抛出异常
除了 Java 内置的类会抛出一些异常之外,也可以手动抛出某个异常. 使用 throw 关键字完成这个操作
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(divide(10, 0));
}
public static int divide(int x, int y) {
if (y == 0) {
throw new ArithmeticException("抛出除 0 异常");
}
return x / y;
}
// 执行结果
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: 抛出除 0 异常
at demo02.Test.divide(Test.java:14)
at demo02.Test.main(Test.java:9)
3.JAVA异常体系
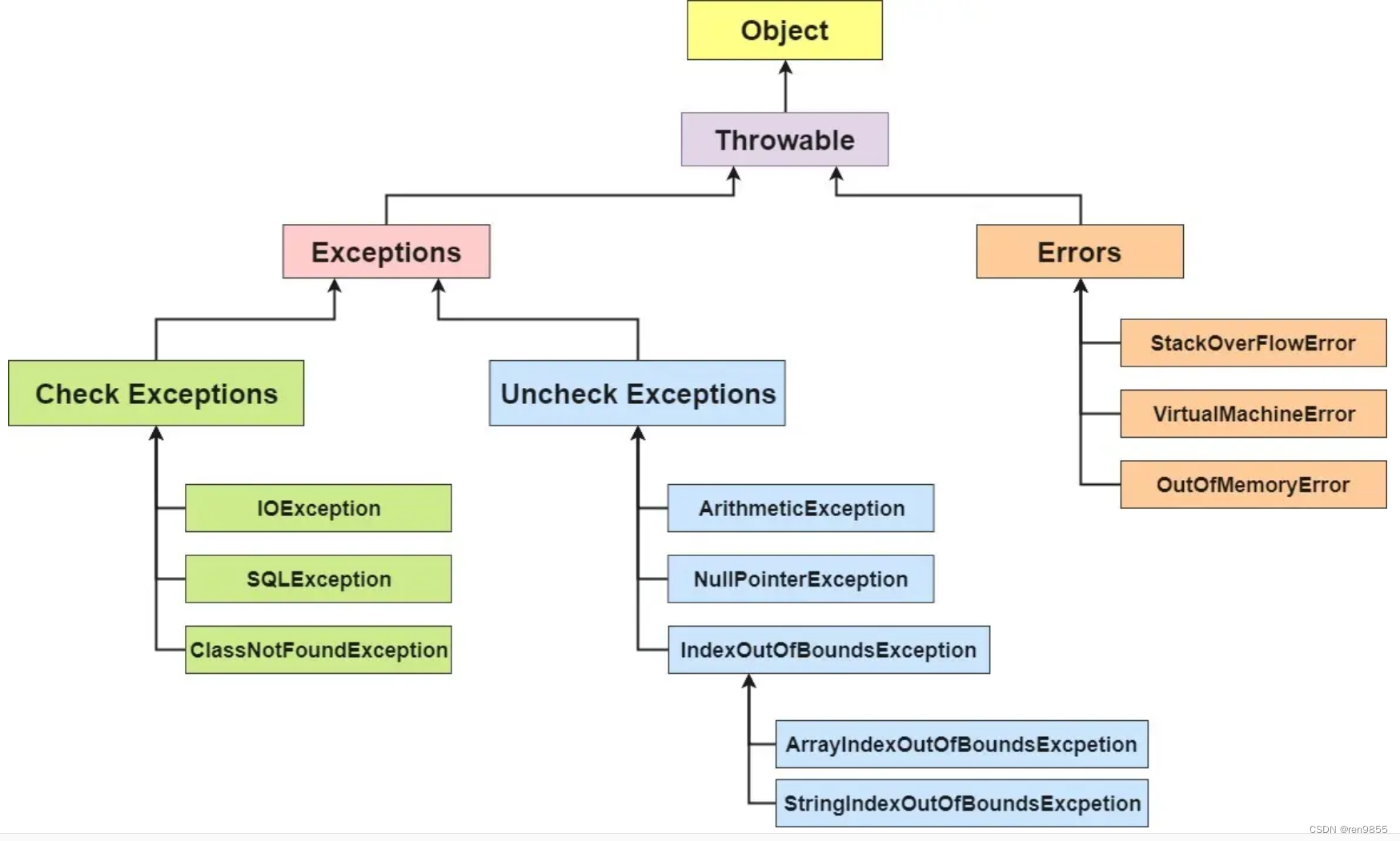
| 1.顶层类 Throwable 派生出两个重要的子类, Error 和 Exception 2.其中 Error 指的是 Java 运行时内部错误和资源耗尽错误. 应用程序不抛出此类异常. 这种内部错误一旦出现, 除了告知用户并使程序终止之外, 再无能无力. 这种情况很少出现 3.Exception 是我们程序猿所使用的异常类的父类 4.其中 Exception 有一个子类称为 RuntimeException , 这里面又派生出很多我们常见的异常NullPointerException , IndexOutOfBoundsException 等 5.Java语言规范将派生于 Error 类或 RuntimeException 类的所有异常称为 非受查异常, 所有的其他异常称为 受查 异常. |
4.自定义异常类
class UserError extends Exception {
public UserError(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
class PasswordError extends Exception {
public PasswordError(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
public class Test {
private static String userName = "admin";
private static String password = "123456";
public static void main(String[] args) {
login("admin", "123456");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
login("admin", "123456");
} catch (UserError userError) {
userError.printStackTrace();
} catch (PasswordError passwordError) {
passwordError.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void login(String userName, String password) throws UserError,
PasswordError {
if (!Test.userName.equals(userName)) {
throw new UserError("用户名错误");
}
if (!Test.password.equals(password)) {
throw new PasswordError("密码错误");
}
System.out.println("登陆成功");
}
}
![[附源码]java毕业设计疫情背景下叮当买菜管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5b87443ef4104e4a889f3f2f6d135ac9.png)