Python金融入门
- 1. 加载数据与可视化
- 1.1. 加载数据
- 1.2. 折线图
- 1.3. 重采样
- 1.4. K线图 / 蜡烛图
- 1.5. 挑战1
- 2. 计算
- 2.1. 收益 / 回报
- 2.2. 绘制收益图
- 2.3. 累积收益
- 2.4. 波动率
- 2.5. 挑战2
- 3. 滚动窗口
- 3.1. 创建移动平均线
- 3.2. 绘制移动平均线
- 3.3 Challenge
- 4. 技术分析
- 4.1. OBV
- 4.2. 累积/派发指标(A/D)
- 4.3. RSI

1. 加载数据与可视化
1.1. 加载数据
# 导入所需库
from matplotlib import dates
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import yfinance as yf
# 使用Y Finance库下载S&P500数据以及2010年至2019年底的Apple数据
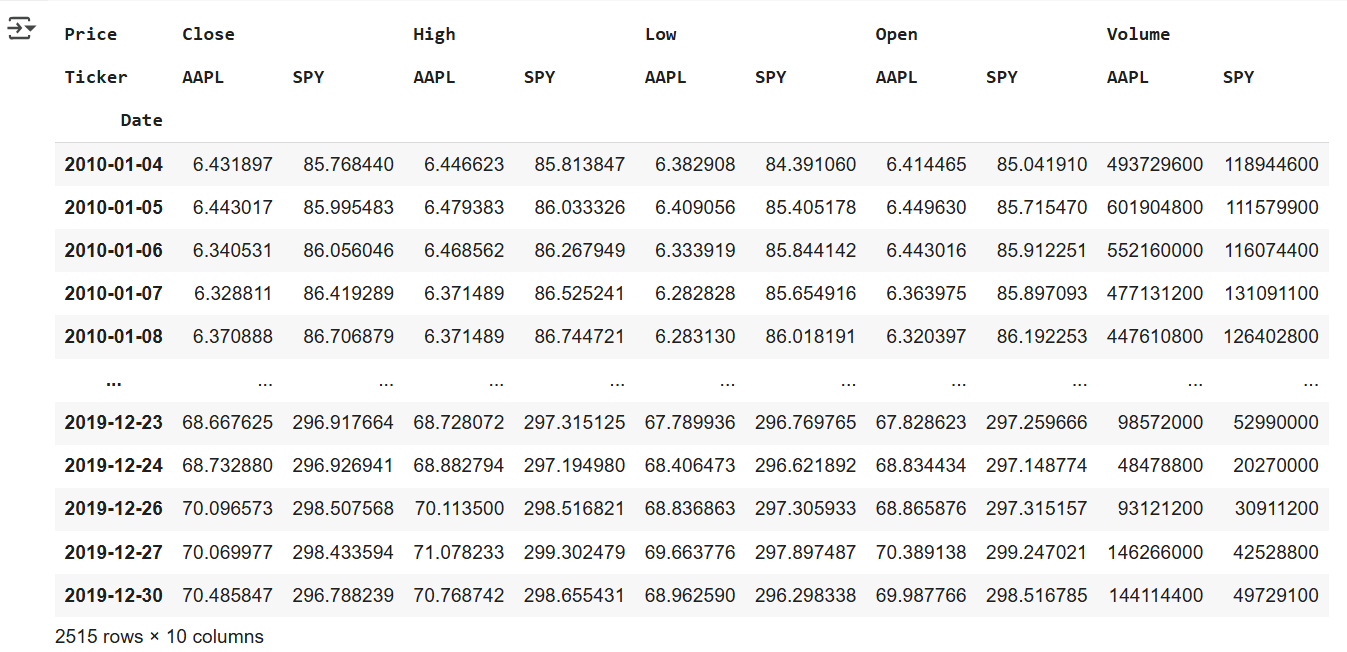
raw = yf.download('SPY AAPL', start='2010-01-01', end='2019-12-31')
raw
# Y Finance使用日期作为索引列, 每行代表一天。
# 查看列:这里有所谓的分层或多索引列,可以看到调整后的收盘价,因为我们同时要求苹果和标准普尔 500指数
# 所以我们在它下面有两个子列,可以看到收盘价、最高值、最低值、开盘价、 和Volumn
# 检查数据帧的columns属性
raw.columns

# 查看pipe的用法
raw.pipe?
import yfinance as yf
#fix_cols():重命名多层列索引为单层(只保留子列名)
def fix_cols(df):
columns = df.columns
outer = [col[0] for col in columns]
df.columns = outer
return df
# 加载与清洗逻辑封装在一个函数里,便于复用
def tweak_data():
raw = yf.download('SPY AAPL',start='2010-01-01', end='2019-12-31')
return (raw
.iloc[:,::2]
.pipe(fix_cols)) # pipe():在链式调用中插入一个自定义函数。
tweak_data()

1.2. 折线图
创建线图,并整绘图的细节(如选择列、大小等)。
(raw
.iloc[:,:-2:2] #从第0列开始,到倒数第2列,步长为2
.pipe(fix_cols)
)

(raw
.iloc[:,:-2:2]
.pipe(fix_cols)
.plot()
)

(raw
.iloc[:,:-2:2]
.pipe(fix_cols)
.Close
.plot()
)

(raw
.iloc[:,::2]
.pipe(fix_cols)
.Volume
.plot(figsize=(10,2)) # 10英寸宽,2英寸高
)

1.3. 重采样
重新采样(resampling) 是将时间序列数据的频率从一个粒度转换为另一个粒度的过程,如从每日 → 每月,Pandas 提供了.resample() 方法。
(raw
.iloc[:,::2]
.pipe(fix_cols)
.Close # 每日收盘价
.plot()
)
按月份分组:
(raw
.iloc[:,::2]
.pipe(fix_cols)
.resample('M') # offset alias
.Close
)
(raw
.iloc[:,::2]
.pipe(fix_cols)
.resample('M') # offset alias
.Close
.mean()
.plot() # 索引中有日期,列中有值,这样就可以绘制了
)
1.4. K线图 / 蜡烛图
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5))
def plot_candle(df, ax):
# wick
ax.vlines(x=df.index, ymin=df.Low, ymax=df.High, colors='k', linewidth=1)
# red - decrease
red = df.query('Open > Close')
ax.vlines(x=red.index, ymin=red.Close, ymax=red.Open, colors='r', linewidth=3)
# green - increase
green = df.query('Open <= Close')
ax.vlines(x=green.index, ymin=green.Close, ymax=green.Open, colors='g', linewidth=3)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(dates.MonthLocator())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(dates.DateFormatter('%b-%y'))
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(dates.DayLocator())
return df
(raw
.iloc[:,::2]
.pipe(fix_cols)
.resample('d')
.agg({'Open':'first', 'High':'max', 'Low':'min', 'Close':'last'})
.loc['jan 2018':'jun 2018']
.pipe(plot_candle, ax)
)

1.5. 挑战1
Plot the candles for the time period of Sep 2019 to Dec 2019. 可以做做看
2. 计算
Goal
- Explore Pandas methods like
.pct_change - Plotting with Pandas
- Refactoring to functions
2.1. 收益 / 回报
在金融中,“回报”通常指某个资产价格在两个时间点之间的相对变化。在Pandas中使用.pct_change() 方法计算百分比变化(Percentage Change),默认按前一行计算百分比变化(periods=1)。

# 使用aapl存储
aapl = (raw
.iloc[:,::2]
.pipe(fix_cols)
)
aapl
# returns
aapl.pct_change()
2.2. 绘制收益图
使用 .plot() 方法,查看回报的日常变化趋势。
# plot returns
(aapl
.pct_change()
.Close
.plot()
)
很多高频噪声,看起来像“毛毛虫”:

使用 .hist() 方法来观察回报的 分布情况(正负、极值、对称性等)。
# Histogram of Returns
(aapl
.pct_change()
.Close
.hist()
)

bins=30 表示分成 30 个区间,可以更细致地看到分布:
# Change bins
(aapl
.pct_change()
.Close
.hist(bins=30)
)

条形图用于查看一小段时间内每日的正负回报(比如最近 100 天):
# Understanding plotting in Pandas is a huge lever
# Bar Plot Returns
(aapl
.pct_change()
.Close
.iloc[-100:] # 获取最后100个值
.plot.bar()
)
Pandas 会把日期索引变成“分类变量”,导致 X 轴标签重叠、无法格式化。

即使调整标签,也会显示成 1970-01 等错误日期:
# Bar Plot of Returns
# Sadly dates are broken with Pandas bar plots
# 1970s?
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 4))
(aapl
.pct_change()
.Close
.iloc[-100:]
.plot.bar(ax=ax)
)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(dates.MonthLocator())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(dates.DateFormatter('%b-%y'))
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(dates.DayLocator())

解决办法:使用 Matplotlib 手动绘制条形图
# Returns - using matplotlib
def my_bar(ser, ax):
ax.bar(ser.index, ser)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(dates.MonthLocator())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(dates.DateFormatter('%b-%y'))
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(dates.DayLocator())
return ser
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 4))
_ = (aapl
.pct_change()
.Close
.iloc[-100:]
.pipe(my_bar, ax)
)

2.3. 累积收益
Goal:
- More complicated Pandas
- Refactoring into a function
- Explore source
- Creating new columns with
.assign - Illustrate lambda
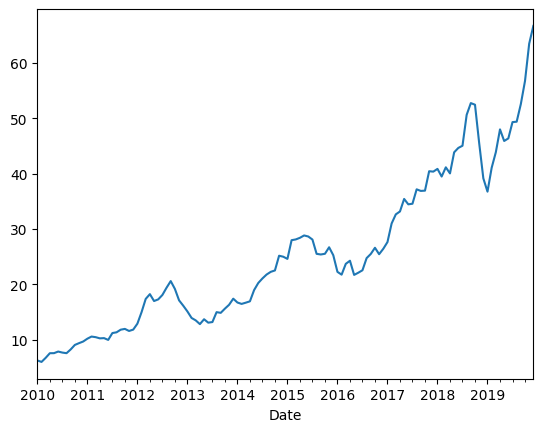
Cumulative Returns is the amount that investment has gained or lost over time:
(current_price-original_price)/original_price
(aapl
.Close
.plot()
)
逐步计算:
(aapl
.Close
.sub(aapl.Close[0]) # substract
.div(aapl.Close[0]) # divide
.plot()
)
基于日收益的累积积:
# alternatte calculation
(aapl
.Close # 取出收盘价序列
.pct_change() # 计算日收益率(百分比变化)
.add(1) # 转换为收益倍率 (1 + r)
.cumprod() # 计算累积乘积:累计收益倍率
.sub(1) # 转换为累计收益率:累计倍率 - 1
.plot() # 绘图
)
函数化重构:
# create a function for calculating
def calc_cum_returns(df,col):
ser = df[col]
return (ser
.sub(ser[0])
.div(ser[0]))
(aapl
.pipe(calc_cum_returns,'Close')
.plot()
)

# Lambda is an *anonymous function*
def get_returns(df):
return calc_cum_returns(df,'Close')
get_returns(aapl)
lambda这里我不太明白
(lambda df: get_returns(df))(aapl)
# Create a new column
(aapl
.assign(cum_returns=lambda df: calc_cum_returns(df,'Close'))
)
# Returns - using matplotlib
def my_bar(ser, ax):
ax.bar(ser.index, ser)
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(dates.MonthLocator())
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(dates.DateFormatter('%b-%y'))
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(dates.DayLocator())
return ser
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 4))
_ = (aapl
.pipe(calc_cum_returns, 'Close')
.iloc[-100:]
.pipe(my_bar, ax)
)

2.4. 波动率
Goals
- More complicated Pandas
- Learn about rolling operations
波动性(英语:volatility,又称波动率),指金融资产在一定时间段的变化性。在股票市场,以每天收市价计算的波动性称为历史波幅(Historical Volatility),以股票期权估算的未来波动性称为引申波幅(Implied Volatility)。着名的VIX指数是标准普尔500指数期权的30日引申波幅,以年度化表示。(维基百科)
(aapl
.Close
.mean()
)
(aapl
.Close
.std()
)
(aapl
.assign(pct_change_close=aapl.Close.pct_change())
.pct_change_close
.std()
)
以滑动窗口方式计算“过去 N 天”的波动性:
(aapl
.assign(close_vol=aapl.rolling(30).Close.std(),
per_vol=aapl.Close.pct_change().rolling(30).std())
.iloc[:,-2:]
.plot(subplots=True)
)

以固定周期(如每 15 天)进行分组计算标准差:
# 15 day volatility
(aapl
.assign(pct_change_close=aapl.Close.pct_change()) # 创建一个名为百分比变化的列
.resample('15D') # 15天为一个分组
.std()
)
# 15 day rolling volatility
(aapl
.assign(pct_change_close=aapl.Close.pct_change()) # 创建一个名为百分比变化的列
.rolling(window=15, min_periods=15)
.std()
)
# 15 day volatility
# note if column name conflicts with method need to use
# index access ([])
(aapl
.assign(pct_change=aapl.Close.pct_change())
.rolling(window=15, min_periods=15)
.std()
['pct_change']
.plot()
)

2.5. 挑战2
Plot the rolling volatility over 30-day sliding windows for 2015-2019。(可以参考上面的代码)
3. 滚动窗口
3.1. 创建移动平均线
对苹果公司股票(aapl)的价格数据进行三日移动平均(ma3)的计算:
(aapl
.assign(s1=aapl.Close.shift(1),
s2=aapl.Close.shift(2),
ma3=lambda df_:df_.loc[:, ['Close', 's1', 's2']].mean(axis='columns'),
ma3_builtin=aapl.Close.rolling(3).mean()
)
)
3.2. 绘制移动平均线
(aapl
.assign(s1=aapl.Close.shift(1),
s2=aapl.Close.shift(2),
ma3=lambda df_:df_.loc[:, ['Close', 's1', 's2']].mean(axis='columns'),
ma3_builtin=aapl.Close.rolling(3).mean()
)
[['Close','ma3']]
.iloc[-200:]
.plot()
)

可视化苹果公司股票的收盘价与其 50 日、200 日移动平均线(MA):
(aapl
.assign(
ma50=aapl.Close.rolling(50).mean(),
ma200=aapl.Close.rolling(200).mean(),
)
[['Close', 'ma50', 'ma200']]
.iloc[-400:]
.plot()
)
如下图可以看到:Close(原始收盘价)是日常波动最明显的一条线;ma50是比较敏感的短期趋势线;而ma200是更平滑的长期趋势线。

3.3 Challenge
Create a plot with three lines:
- AAPL close price in 2015
- Exponential moving average with alpha =. 0392
- Exponential moving average with alpha =. 00995
Hint:Use the .ewm method to create a rolling aggregator.
aapl.ewm?
(aapl
.loc['2015']
.assign(
alpha1=aapl.Close.ewm(alpha=0.0392).mean(),
alpha2=aapl.Close.ewm(alpha=0.00995).mean(),
)
[['Close', 'alpha1', 'alpha2']]
.plot()
)
alpha=0.0392:较高,表示更敏感,近期数据权重大,从而曲线更贴近原始价格;alpha=0.00995:较低,更平滑,趋势线更慢反应价格波动。

4. 技术分析
4.1. OBV
OBV(On-Balance Volume,能量潮指标),是一种常见的技术分析指标,用来结合价格走势和成交量判断趋势强度。OBV 是一个累加值:如果今日收盘价 > 昨日 → 当日成交量加到 OBV 上;如果今日收盘价 < 昨日 → 当日成交量从 OBV 中减去;如果收盘价不变 → OBV 保持不变,如下图:

下面函数的实现逻辑是对的,但是效率不高,会触发FutureWarning:
# naive
def calc_obv(df):
df = df.copy()
df["OBV"] = 0.0
# Loop through the data and calculate OBV
for i in range(1, len(df)):
# 如果该仓位的收盘价大于前一个收盘值
if df["Close"][i] > df["Close"][i - 1]:
df["OBV"][i]=df["OBV"][i - 1] + df["Volume"][i]
elif df["Close"][i] < df["Close"][i - 1]:
df["OBV"][i]=df["OBV"][i -1]-df["Volume"][i]
else:
df["OBV"][i] = df["OBV"][i - 1]
return df
calc_obv(aapl)
用 Pandas 向量化方式计算 OBV并使用 %timeit 测试:
%%timeit
# This is painful
(aapl
.assign(close_prev=aapl.Close.shift(1),
vol=0,
obv=lambda adf: adf.vol.where(cond=adf.Close == adf.close_prev,
other=adf.Volume.where(cond=adf.Close > adf.close_prev,
other =- adf.Volume.where(cond=adf.Close < adf.close_prev, other=0)
)).cumsum()
)
)
用 np.select 实现 OBV 的向量化计算:
(aapl
.assign(prev_close=aapl.Close.shift(1),
vol=np.select([aapl.Close> aapl.Close.shift(1),
aapl.Close == aapl.Close.shift(1),
aapl.Close < aapl.Close.shift(1)],
[aapl.Volume, 0, -aapl.Volume]),
obv=lambda df_:df_. vol.cumsum(),
)
)
将 OBV 的向量化计算封装成函数 calc_obv():
def calc_obv(df, close_col='Close', vol_col='Volume'):
close = df[close_col]
vol = df[vol_col]
close_shift = close.shift(1)
return (df
.assign(vol=np.select([close > close_shift,
close == close_shift,
close < close_shift],
[vol, 0, -vol]),
obv=lambda df_:df_. vol.fillna(0).cumsum()
)
['obv']
)
(aapl
.assign(obv=calc_obv)
)
4.2. 累积/派发指标(A/D)
A/D 指标(Accumulation/Distribution Line,累积/派发线)是技术分析中衡量资金流入流出的常用指标之一。
- MFM(Money Flow Multiplier):资金流动乘数,用于衡量收盘价相对当天价格区间的位置,范围在[-1, 1],越接近 1 表示更靠近高点(资金流入),越接近 -1 表示更靠近低点(资金流出)。
- Money Flow Volume(资金流动量):把价格位置信息与成交量结合起来,收盘越靠近高点,且成交量越大,说明有更多资金“流入”。
- A/D 是一个累计值,用来判断市场是否处于吸筹(Accumulation)还是派发(Distribution)。

实现逻辑:
(aapl
.assign(mfm=((aapl.Close - aapl.Low) - (aapl.High - aapl.Close))/(aapl.High - aapl.Low),
mfv=lambda df_:df_.mfm * df_.Volume, # lambda将采用数据帧的当前值
cmfv=lambda df_:df_.mfv.cumsum()
)
)

# 重构为一个函数
def calc_ad(df, close_col='Close', low_col='Low', high_col='High',vol_col='Volume'):
close = df[close_col]
low = df[low_col]
high = df[high_col]
return (df
.assign(mfm=((close - low) -(high - close))/(high - low),
mfv=lambda df_: df_. mfm * df_[vol_col],
cmfv=lambda df_: df_. mfv.cumsum())
.cmfv
)
(aapl
.assign(ad=calc_ad)
.ad
.plot()
)
 column. Relative Strength Index is a popular momentum indicator
RSI(Relative Strength Index, 相对强弱指数)是一种常用的技术分析指标,用于衡量股票或其他资产价格的近期涨跌强度,帮助判断市场是否处于超买或超卖状态。RSI 的应用意义:
- 超买区:RSI 通常高于 70,意味着价格上涨过快,可能出现回调。
- 超卖区:RSI 通常低于 30,意味着价格下跌过快,可能出现反弹。
- 趋势判断:RSI 可以帮助确认价格趋势的强度和反转信号。

(aapl
.assign(mfm=((aapl.Close - aapl.Low) - (aapl.High - aapl.Close))/(aapl.High - aapl.Low),
mfv=lambda df_:df_.mfm * df_.Volume, # lambda将采用数据帧的当前值
cmfv=lambda df_:df_.mfv.cumsum()
)
)
# prompt: Create 14-day RSI column
def rsi(df: pd.DataFrame, window: int = 14) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""
Calculates the Relative Strength Index (RSI) for a given DataFrame.
Args:
df: The input DataFrame with a 'Close' column.
window: The lookback window for RSI calculation (default is 14).
Returns:
The DataFrame with an added 'RSI' column.
"""
delta = df['Close'].diff()
up, down = delta.copy(), delta.copy()
up[up < 0] = 0
down[down > 0] = 0
# Use rolling mean
avg_gain = up.rolling(window=window).mean()
avg_loss = abs(down.rolling(window=window).mean())
rs = avg_gain / avg_loss
df['RSI'] = 100 - (100 / (1 + rs))
return df.RSI
# aapl = rsi(aapl)
# print(aapl.head(16))
(aapl
.assign(rsi_14=rsi(aapl))
.rsi_14
# .plot()
)









![[特殊字符] 深入理解 Linux 内核进程管理:架构、核心函数与调度机制](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/5a1d6f8c5cba4467ad891a42ad177176.png)


![[AI绘画]sd学习记录(二)文生图参数进阶](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/15061a8f446d09b56ab8ba527d98e766.png)