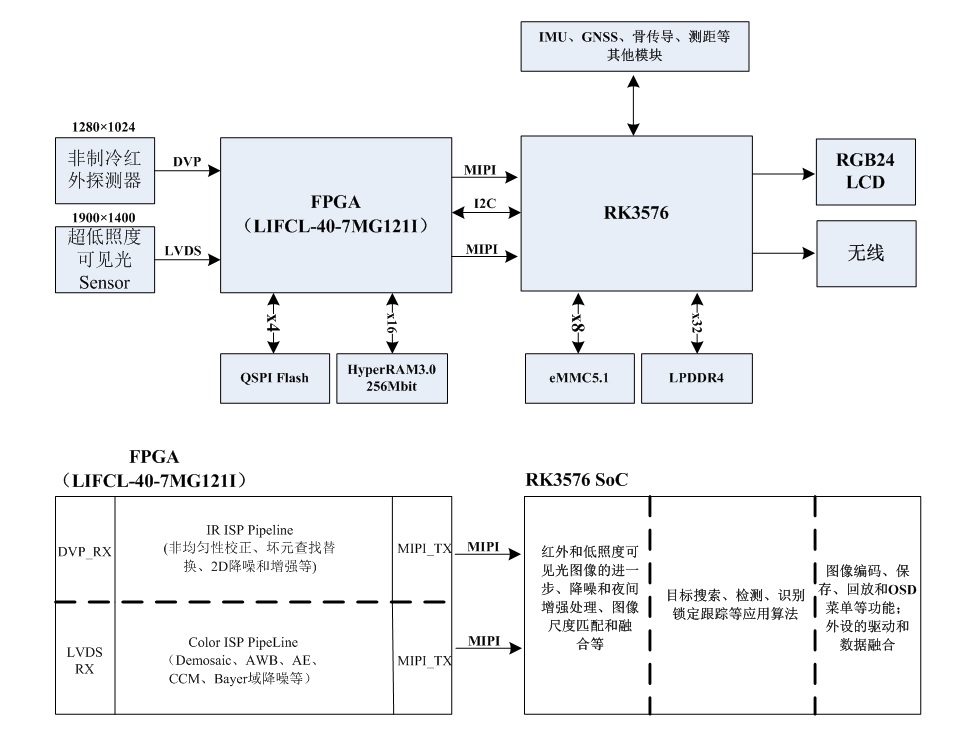
青少年编程与数学 02-020 C#程序设计基础 12课题、使用控件
- 一、控件
- 二、控件的分类
- 1. 按功能分类
- 2. 按可见性分类
- 三、控件的核心特性
- (一) 属性(Properties) - 控件的"状态描述"
- 1. 外观属性
- 2. 布局属性
- 3. 行为属性
- 4. 数据绑定属性
- (二) 方法(Methods) - 控件的"行为能力"
- 1. 布局方法
- 2. 焦点控制
- 3. 更新与刷新
- 4. 容器操作
- (三) 事件(Events) - 控件的"响应机制"
- 1. 鼠标事件
- 2. 键盘事件
- 3. 焦点事件
- 4. 数据事件
- (四) 高级特性
- 1. 控件继承
- 2. 双缓冲技术
- 3. 设计时特性
- (五) 最佳实践
- 1. 属性设置顺序:
- 2. 事件处理优化:
- 3. 线程安全调用:
- 四、常用控件
- (一)基础输入控件
- 1. Button(按钮)
- 2. TextBox(文本框)
- (二)选择控件
- 3. ComboBox(下拉框)
- 4. CheckBox(复选框) & RadioButton(单选按钮)
- (三)数据显示控件
- 5. DataGridView(数据表格)
- (四)容器控件
- 6. Panel & GroupBox
- 7. TabControl(选项卡)
- (五)高级控件
- 8. ListView(列表视图)
- 9. TreeView(树形视图)
- (六)菜单和工具栏
- 10. MenuStrip(菜单栏)
- 11. ToolStrip(工具栏)
- (七)对话框控件
- 12. 通用对话框
- (八)最佳实践建议
- 五、控件的关系结构
- (一)继承体系结构
- 1. 核心继承链
- 2. 关键基类解析
- (二)容器-控件关系
- 1. 父子关系模型
- 2. 关键属性和方法
- 3. 容器控件的特殊行为
- (三)控件集合管理
- 1. ControlCollection 特性
- 2. 动态控件管理示例
- (四)可视化树结构
- 1. 遍历控件树
- 2. 查找特定控件
- (五)焦点管理机制
- 1. 焦点层次结构
- 2. 焦点相关成员
- 3. 焦点事件序列
- (六)设计时与运行时关系
- 1. 设计器生成的代码
- 2. 设计时特性
- (七)高级关系模式
- 1. 控件聚合模式
- 2. 可视化继承
- 六、编程方式使用控件
- (一)基础创建流程
- 1. 基本创建步骤
- 2. 控件属性设置最佳实践
- (二)不同类型控件的创建示例
- 1. 创建数据绑定控件
- 2. 创建复杂容器控件
- (三)高级编程技巧
- 1. 控件工厂模式
- 2. 动态控件的事件处理
- 3. 使用SuspendLayout/ResumeLayout优化性能
- (四)控件生命周期管理
- 1. 动态移除控件
- 2. 控件持久化技巧
- (五)实际应用案例
- 1. 动态表单生成器
- 2. 动态菜单系统
- (六)调试与问题解决
- 1. 常见问题处理
- 2. 设计时支持
- 七、控件的设计时支持
- (一)设计时基础架构
- 1. 设计时与运行时区别
- 2. 核心设计时组件
- (二)设计时特性(Attributes)详解
- 1. 外观控制特性
- 2. 属性控制特性
- 3. 集合编辑器特性
- (三)自定义设计器实现
- 1. 基本设计器类
- 2. 设计时行为控制
- (四)高级设计时功能
- 1. 自定义属性编辑器
- 2. 智能标签(Smart Tag)实现
- (五)设计时序列化机制
- 1. 序列化控制
- 2. 自定义序列化
- (六)调试设计时行为
- 1. 设计时调试技巧
- 2. 常见问题解决
- (七)完整设计时控件示例
- 八、综合示例
- (一)主窗体设计 (MainForm.cs)
- (二)、员工信息编辑窗体 (EmployeeForm.cs)
- (三)数据模型 (Employee.cs)
- (四)应用程序入口 (Program.cs)
- (五)功能扩展建议
- 总结
摘要:本文详细介绍了C# WinForms控件的使用,涵盖控件的基本概念、分类、核心特性及编程方式。通过综合示例,展示了如何在实际项目中应用多种控件,实现数据展示、表单输入、菜单导航等功能,并提供了功能扩展建议。
关键词:C#程序设计、WinForms控件、控件分类、核心特性、编程方式、综合示例、功能扩展
AI助手:Kimi、DeepSeek
一、控件
在Windows窗体(WinForms)应用程序开发中,控件是可视化用户界面(UI)的基本构建块,它们是封装了特定功能和外观的可重用组件。
-
可视化元素:控件是用户界面上可见的交互元素,如按钮、文本框等
-
功能封装:每个控件封装了特定的功能和行为
-
对象实例:在代码中,控件是类的实例,继承自System.Windows.Forms.Control基类
-
属性-方法-事件模型:
属性:控制外观和行为
方法:定义可以执行的操作
事件:响应用户交互
二、控件的分类
1. 按功能分类
| 类别 | 示例控件 | 用途说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 基本输入 | TextBox, Button, CheckBox | 用户输入和交互 |
| 数据显示 | DataGridView, ListView | 显示和操作数据集合 |
| 容器控件 | Panel, GroupBox, TabControl | 组织其他控件的布局 |
| 菜单和工具栏 | MenuStrip, ToolStrip | 提供命令和功能访问 |
| 对话框 | OpenFileDialog, ColorDialog | 与用户进行特定交互 |
2. 按可见性分类
可视化控件:有可见界面(如Button, Label)
非可视化组件:无界面但提供功能(如Timer, BackgroundWorker)
三、控件的核心特性
控件(Control)是WinForms应用程序的基本构建单元,其核心特性可分为三大类:属性(Properties)、方法(Methods)和事件(Events)。以下是深度解析:
(一) 属性(Properties) - 控件的"状态描述"
1. 外观属性
| 属性名 | 类型 | 说明 | 示例值 |
|---|---|---|---|
BackColor | Color | 背景色 | Color.White, Color.Red |
ForeColor | Color | 前景色(文本颜色) | Color.Black |
Font | Font | 字体设置 | new Font("Arial", 12) |
Text | string | 显示的文本内容 | “确定”, “用户名:” |
Image | Image | 显示的图像 | Image.FromFile("1.png") |
Visible | bool | 是否可见 | true/false |
2. 布局属性
| 属性名 | 说明 | 重要值 |
|---|---|---|
Location | 控件相对于容器的位置(X,Y坐标) | new Point(100, 50) |
Size | 控件的宽度和高度 | new Size(200, 30) |
Dock | 停靠方式(填充父容器某侧) | DockStyle.Fill, DockStyle.Top |
Anchor | 锚定到父容器的哪些边(窗体缩放时保持相对位置) | `AnchorStyles.Left |
Margin | 控件与相邻控件的外边距 | new Padding(5) |
Padding | 控件内容与边框的内边距 | new Padding(10) |
3. 行为属性
| 属性名 | 说明 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|
Enabled | 是否启用(灰色不可用状态) | 表单验证未通过时禁用提交按钮 |
TabIndex | Tab键切换焦点的顺序 | 优化表单填写流程 |
TabStop | 是否可通过Tab键获得焦点 | 跳过不需要交互的显示性控件 |
Cursor | 鼠标悬停时的指针形状 | Cursors.Hand(手型指针) |
ContextMenuStrip | 右键菜单 | 添加快捷操作菜单 |
4. 数据绑定属性
// 数据绑定示例
textBox1.DataBindings.Add("Text", dataSource, "CustomerName");
(二) 方法(Methods) - 控件的"行为能力"
1. 布局方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
BringToFront() | 将控件置于Z顺序的前端(显示在最上层) |
SendToBack() | 将控件置于Z顺序的底层 |
Show() | 显示控件(设置Visible=true) |
Hide() | 隐藏控件(设置Visible=false) |
2. 焦点控制
// 焦点控制示例
if (!textBox1.Focus())
{
MessageBox.Show("无法获取焦点");
}
3. 更新与刷新
| 方法 | 区别 |
|---|---|
Refresh() | 强制立即重绘控件 |
Update() | 使控件重绘无效区域 |
Invalidate() | 标记控件需要重绘(异步) |
4. 容器操作
// 动态添加控件
Panel panel = new Panel();
panel.Controls.Add(new Button() { Text = "动态按钮" });
this.Controls.Add(panel);
(三) 事件(Events) - 控件的"响应机制"
1. 鼠标事件
| 事件 | 触发时机 |
|---|---|
MouseClick | 鼠标点击(完整的按下+释放) |
MouseDown | 鼠标按钮按下 |
MouseUp | 鼠标按钮释放 |
MouseMove | 鼠标指针移动 |
MouseEnter | 鼠标进入控件区域 |
MouseLeave | 鼠标离开控件区域 |
MouseHover | 鼠标悬停(停留一段时间) |
2. 键盘事件
// 键盘事件处理示例
textBox1.KeyPress += (s, e) => {
if (!char.IsDigit(e.KeyChar) e.Handled = true; // 只允许数字输入
};
3. 焦点事件
| 事件 | 触发顺序 | 典型应用 |
|---|---|---|
Enter | 获取焦点前 | 准备输入状态 |
GotFocus | 获取焦点后 | 高亮当前输入框 |
Leave | 失去焦点前 | 验证输入内容 |
LostFocus | 失去焦点后 | 保存输入结果 |
Validating | 验证期间 | 实现复杂验证逻辑 |
Validated | 验证通过后 | 确认有效输入 |
4. 数据事件
// 数据绑定事件
bindingSource1.DataSourceChanged += (s, e) => {
label1.Text = $"共 {bindingSource1.Count} 条记录";
};
(四) 高级特性
1. 控件继承
// 创建自定义按钮
public class MyButton : Button
{
protected override void OnPaint(PaintEventArgs e)
{
base.OnPaint(e);
// 自定义绘制逻辑
}
}
2. 双缓冲技术
// 减少闪烁
public class SmoothPanel : Panel
{
public SmoothPanel()
{
this.DoubleBuffered = true;
}
}
3. 设计时特性
// 为自定义控件添加设计时支持
[DefaultProperty("Text")]
[ToolboxBitmap(typeof(Button))]
public class MyControl : Control
{
// ...
}
(五) 最佳实践
1. 属性设置顺序:
// 正确的属性设置顺序
Button btn = new Button
{
Name = "btnSubmit", // 先设置名称
Location = new Point(10, 10), // 再设置位置
Size = new Size(80, 30), // 然后设置尺寸
Text = "提交", // 最后设置内容相关属性
TabIndex = 0
};
2. 事件处理优化:
// 使用事件处理方法减少内存泄漏
void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
button1.Click += Button1_Click;
}
void Form1_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
button1.Click -= Button1_Click;
}
3. 线程安全调用:
// 跨线程更新UI
void UpdateStatus(string message)
{
if (label1.InvokeRequired)
{
label1.Invoke(new Action(() => label1.Text = message));
}
else
{
label1.Text = message;
}
}
理解这些核心特性后,您将能够:
- 更高效地配置控件行为
- 创建更复杂的交互逻辑
- 开发自定义控件
- 优化界面性能和用户体验
四、常用控件
以下是 Visual Studio WinForms 开发中最常用的控件及其详细解析,包括核心属性、方法和典型应用场景。
(一)基础输入控件
1. Button(按钮)
核心属性:
Text:按钮显示文本Image/ImageAlign:按钮图像及对齐方式FlatStyle:按钮样式(Flat, Popup, Standard 等)DialogResult:设置对话框结果(用于模式对话框)
关键事件:
Click:点击事件(最常用)MouseEnter/MouseLeave:实现悬停效果
代码示例:
btnSubmit.FlatStyle = FlatStyle.Flat;
btnSubmit.BackColor = Color.SteelBlue;
btnSubmit.ForeColor = Color.White;
btnSubmit.FlatAppearance.BorderSize = 0;
btnSubmit.Cursor = Cursors.Hand;
2. TextBox(文本框)
核心属性:
MaxLength:最大输入长度Multiline:是否多行PasswordChar:密码掩码字符(如*)ReadOnly:只读模式ScrollBars:滚动条显示
验证技巧:
// 只允许数字输入
textBox1.KeyPress += (s, e) => {
if (!char.IsControl(e.KeyChar) && !char.IsDigit(e.KeyChar))
e.Handled = true;
};
(二)选择控件
3. ComboBox(下拉框)
数据绑定方式:
// 简单绑定
comboBox1.Items.AddRange(new[] { "选项1", "选项2", "选项3" });
// 对象绑定
class Item {
public string Text { get; set; }
public int Value { get; set; }
}
comboBox1.DisplayMember = "Text";
comboBox1.ValueMember = "Value";
comboBox1.DataSource = new List<Item> {
new Item { Text = "北京", Value = 1 },
new Item { Text = "上海", Value = 2 }
};
重要事件:
SelectedIndexChanged:选择项变化时触发
4. CheckBox(复选框) & RadioButton(单选按钮)
区别:
- CheckBox:多选(独立选项)
- RadioButton:单选(同一容器内互斥)
分组技巧:
// 使用Panel或GroupBox容器分组
groupBox1.Controls.Add(radioButton1);
groupBox1.Controls.Add(radioButton2);
(三)数据显示控件
5. DataGridView(数据表格)
核心功能:
// 数据绑定
dataGridView1.DataSource = dataTable;
// 列配置
dataGridView1.Columns["Salary"].DefaultCellStyle.Format = "C2"; // 货币格式
dataGridView1.Columns["BirthDate"].DefaultCellStyle.Format = "yyyy-MM-dd";
// 自定义列
DataGridViewButtonColumn btnCol = new DataGridViewButtonColumn();
btnCol.Name = "Operation";
btnCol.Text = "删除";
dataGridView1.Columns.Add(btnCol);
重要事件:
CellClick:单元格点击CellValueChanged:值修改后触发DataError:数据处理错误
(四)容器控件
6. Panel & GroupBox
对比:
| 特性 | Panel | GroupBox |
|---|---|---|
| 边框 | 默认无边框 | 默认有边框和标题 |
| 滚动条 | 支持AutoScroll | 不支持 |
| 性能 | 更轻量 | 稍重 |
| 典型用途 | 布局管理 | 逻辑分组 |
7. TabControl(选项卡)
使用技巧:
// 动态添加选项卡
TabPage newPage = new TabPage("新页面");
newPage.Controls.Add(new Button { Text = "示例按钮" });
tabControl1.TabPages.Add(newPage);
// 美化选项卡
tabControl1.Appearance = TabAppearance.FlatButtons;
tabControl1.ItemSize = new Size(80, 24);
(五)高级控件
8. ListView(列表视图)
视图模式:
listView1.View = View.Details; // 详细视图
listView1.Columns.Add("文件名", 200);
listView1.Columns.Add("大小", 100);
listView1.Columns.Add("修改日期", 150);
// 添加项
ListViewItem item = new ListViewItem("document.txt");
item.SubItems.Add("125 KB");
item.SubItems.Add(DateTime.Now.ToString());
listView1.Items.Add(item);
9. TreeView(树形视图)
构建层次结构:
TreeNode root = new TreeNode("公司部门");
root.Nodes.Add("技术部");
root.Nodes.Add("市场部");
root.Nodes[0].Nodes.Add("开发组");
root.Nodes[0].Nodes.Add("测试组");
treeView1.Nodes.Add(root);
重要事件:
AfterSelect:节点选择后触发NodeMouseDoubleClick:双击节点
(六)菜单和工具栏
10. MenuStrip(菜单栏)
创建步骤:
- 拖拽MenuStrip到窗体
- 直接在设计器输入菜单项文本
- 设置快捷键:
文件(&F)表示Alt+F访问
11. ToolStrip(工具栏)
高级功能:
// 添加组合框
ToolStripComboBox combo = new ToolStripComboBox();
combo.Items.AddRange(new[] { "选项1", "选项2" });
toolStrip1.Items.Add(combo);
// 添加分隔符
toolStrip1.Items.Add(new ToolStripSeparator());
(七)对话框控件
12. 通用对话框
| 对话框 | 用途 | 关键属性/方法 |
|---|---|---|
| OpenFileDialog | 打开文件 | Filter, FileName |
| SaveFileDialog | 保存文件 | AddExtension, OverwritePrompt |
| FolderBrowserDialog | 选择文件夹 | SelectedPath |
| ColorDialog | 选择颜色 | Color, FullOpen |
| FontDialog | 选择字体 | Font, ShowColor |
使用模式:
if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
string filePath = openFileDialog1.FileName;
// 处理文件...
}
(八)最佳实践建议
-
命名规范:
- btnSubmit(按钮)
- txtUserName(文本框)
- cmbCountry(下拉框)
- dgvOrders(数据表格)
-
布局原则:
- 使用Anchor/Dock实现响应式布局
- 合理使用TableLayoutPanel进行网格布局
- 保持一致的Margin/Padding设置
-
性能优化:
// 批量操作时暂停绘制 myControl.SuspendLayout(); // 执行大量控件更新... myControl.ResumeLayout(true); -
可访问性:
- 设置
TabIndex保证键盘导航合理 - 为重要控件添加
AccessibleDescription - 使用
Control.TabIndex管理焦点顺序
- 设置
掌握这些控件的特性和使用技巧,可以显著提升WinForms开发效率和用户体验质量。实际开发中应根据具体场景选择合适的控件组合。
五、控件的关系结构
WinForms 控件体系采用层次化的对象模型,理解这种关系结构对于高效开发复杂界面至关重要。以下是控件关系结构的全面分析:
(一)继承体系结构
1. 核心继承链
System.Object
└─ System.MarshalByRefObject
└─ System.ComponentModel.Component
└─ System.Windows.Forms.Control
├─ System.Windows.Forms.ScrollableControl
│ └─ System.Windows.Forms.ContainerControl
│ └─ System.Windows.Forms.Form
├─ System.Windows.Forms.ButtonBase
│ ├─ System.Windows.Forms.Button
│ ├─ System.Windows.Forms.CheckBox
│ └─ System.Windows.Forms.RadioButton
└─ System.Windows.Forms.TextBoxBase
└─ System.Windows.Forms.TextBox
2. 关键基类解析
Control类(所有控件的基类):
- 提供基础功能:位置、大小、绘制、事件处理
- 包含150+个核心成员
- 实现IDropTarget接口(拖放支持)
ScrollableControl类:
- 添加滚动支持
AutoScroll属性控制滚动行为- 典型派生:Panel, ContainerControl
ContainerControl类:
- 焦点管理和子控件激活
- 表单类(Form)的直系父类
(二)容器-控件关系
1. 父子关系模型
// 典型父子关系建立
Form mainForm = new Form();
Panel panel = new Panel();
Button button = new Button();
panel.Controls.Add(button); // button的Parent变为panel
mainForm.Controls.Add(panel); // panel的Parent变为mainForm
2. 关键属性和方法
| 成员 | 说明 |
|---|---|
Controls | 子控件集合(ControlCollection类型) |
Parent | 获取或设置父容器 |
FindForm() | 查找控件所在的顶级窗体 |
HasChildren | 指示是否包含子控件 |
GetChildAtPoint() | 获取指定位置的子控件 |
3. 容器控件的特殊行为
Z轴顺序规则:
- 后添加的控件显示在上层
- 可通过
BringToFront()/SendToBack()调整
坐标系统:
// 坐标转换示例
Point screenPos = button1.PointToScreen(new Point(0, 0));
Point formPos = this.PointToClient(screenPos);
(三)控件集合管理
1. ControlCollection 特性
- 实现ICollection, IEnumerable接口
- 提供索引器访问:
panel.Controls[0] - 常用方法:
controls.Add/AddRange() // 添加 controls.Remove/RemoveAt/Clear() // 移除 controls.Contains() // 检查存在 controls.IndexOf() // 获取索引
2. 动态控件管理示例
// 动态创建并管理控件
void CreateDynamicControls()
{
FlowLayoutPanel flowPanel = new FlowLayoutPanel
{
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
AutoScroll = true
};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
var textBox = new TextBox
{
Tag = i, // 使用Tag存储自定义数据
Width = 200
};
flowPanel.Controls.Add(textBox);
}
this.Controls.Add(flowPanel);
// 查找特定控件
var target = flowPanel.Controls
.OfType<TextBox>()
.FirstOrDefault(t => (int)t.Tag == 5);
}
(四)可视化树结构
1. 遍历控件树
// 递归遍历所有子控件
void TraverseControls(Control parent)
{
foreach (Control child in parent.Controls)
{
Console.WriteLine(child.Name + " - " + child.GetType().Name);
if (child.HasChildren)
TraverseControls(child);
}
}
// 使用示例
TraverseControls(this);
2. 查找特定控件
// 通过名称查找
public Control FindControl(Control parent, string name)
{
if (parent.Name == name) return parent;
foreach (Control child in parent.Controls)
{
Control found = FindControl(child, name);
if (found != null) return found;
}
return null;
}
// LINQ方式查找
var allTextBoxes = this.Controls
.OfType<TextBox>()
.Where(t => t.Enabled);
(五)焦点管理机制
1. 焦点层次结构
- 窗体必须激活才能接收输入
- 容器控件管理内部焦点切换
TabIndex属性控制Tab键顺序
2. 焦点相关成员
| 成员 | 说明 |
|---|---|
Focused | 指示控件是否有输入焦点 |
CanFocus | 判断控件能否接收焦点 |
Select() | 激活控件 |
SelectNextControl | 按Tab顺序选择下一个控件 |
3. 焦点事件序列
Enter → GotFocus → (用户操作) → Leave → Validating → Validated → LostFocus
(六)设计时与运行时关系
1. 设计器生成的代码
// Form1.Designer.cs 中的典型结构
partial class Form1
{
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.button1 = new System.Windows.Forms.Button();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// button1
//
this.button1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(100, 50);
this.button1.Name = "button1";
this.button1.Text = "Click";
//
// Form1
//
this.Controls.Add(this.button1);
this.ResumeLayout(false);
}
private Button button1;
}
2. 设计时特性
DesignMode属性:判断是否处于设计时LicenseManager.UsageMode:检测运行模式- 设计器序列化机制:通过
InitializeComponent()重建界面
(七)高级关系模式
1. 控件聚合模式
// 自定义组合控件
public class AddressControl : UserControl
{
private TextBox txtStreet;
private TextBox txtCity;
public AddressControl()
{
// 初始化内部控件
txtStreet = new TextBox { Dock = DockStyle.Top };
txtCity = new TextBox { Dock = DockStyle.Top };
this.Controls.AddRange(new Control[] { txtCity, txtStreet });
}
// 暴露聚合属性
public string FullAddress => $"{txtStreet.Text}, {txtCity.Text}";
}
2. 可视化继承
// 基窗体
public class BaseForm : Form
{
protected Button btnOK;
protected Button btnCancel;
public BaseForm()
{
btnOK = new Button { Text = "OK", DialogResult = DialogResult.OK };
btnCancel = new Button { Text = "Cancel", DialogResult = DialogResult.Cancel };
this.AcceptButton = btnOK;
this.CancelButton = btnCancel;
}
}
// 派生窗体
public class DerivedForm : BaseForm
{
public DerivedForm()
{
// 自动继承基窗体的控件和布局
btnOK.Location = new Point(100, 100);
}
}
理解WinForms控件的这种层次化关系结构,可以帮助开发者:
- 更高效地组织和查找控件
- 实现复杂的界面布局
- 创建可重用的自定义控件
- 优化界面渲染性能
- 正确处理焦点和用户交互流程
实际开发中应善用Controls集合管理和可视化树遍历技术,这对动态界面生成和复杂表单处理尤为重要。
六、编程方式使用控件
在WinForms开发中,除了使用设计器拖拽控件外,掌握以编程方式动态创建和使用控件是开发灵活、响应式界面的关键技能。以下是详细的技术实现方法:
(一)基础创建流程
1. 基本创建步骤
// 1. 实例化控件对象
Button dynamicButton = new Button();
// 2. 配置属性
dynamicButton.Name = "btnDynamic";
dynamicButton.Text = "点击我";
dynamicButton.Location = new Point(50, 50);
dynamicButton.Size = new Size(100, 30);
// 3. 添加事件处理
dynamicButton.Click += (sender, e) => {
MessageBox.Show("动态按钮被点击!");
};
// 4. 添加到容器
this.Controls.Add(dynamicButton);
2. 控件属性设置最佳实践
// 使用对象初始化器简化代码
TextBox dynamicTextBox = new TextBox {
Name = "txtInput",
Location = new Point(50, 100),
Size = new Size(200, 20),
MaxLength = 50,
Tag = "userInput" // 使用Tag存储自定义数据
};
(二)不同类型控件的创建示例
1. 创建数据绑定控件
// 创建DataGridView
DataGridView dgv = new DataGridView {
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
AllowUserToAddRows = false,
AutoGenerateColumns = false
};
// 添加列
dgv.Columns.Add(new DataGridViewTextBoxColumn {
HeaderText = "ID",
DataPropertyName = "Id",
Width = 50
});
// 绑定数据
dgv.DataSource = GetProducts(); // 假设返回List<Product>
this.Controls.Add(dgv);
2. 创建复杂容器控件
// 创建带布局的面板
Panel containerPanel = new Panel {
Dock = DockStyle.Top,
Height = 150,
BackColor = Color.LightGray,
AutoScroll = true
};
// 使用FlowLayoutPanel自动排列
FlowLayoutPanel flowPanel = new FlowLayoutPanel {
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
FlowDirection = FlowDirection.LeftToRight,
WrapContents = true
};
// 动态添加多个控件
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
flowPanel.Controls.Add(new Button {
Text = $"按钮 {i + 1}",
Margin = new Padding(5),
Tag = i
});
}
containerPanel.Controls.Add(flowPanel);
this.Controls.Add(containerPanel);
(三)高级编程技巧
1. 控件工厂模式
public static Control CreateStyledButton(string text, EventHandler handler)
{
Button btn = new Button {
Text = text,
FlatStyle = FlatStyle.Flat,
BackColor = Color.SteelBlue,
ForeColor = Color.White,
Cursor = Cursors.Hand,
Margin = new Padding(5)
};
btn.FlatAppearance.BorderSize = 0;
btn.Click += handler;
// 悬停效果
btn.MouseEnter += (s, e) => btn.BackColor = Color.LightBlue;
btn.MouseLeave += (s, e) => btn.BackColor = Color.SteelBlue;
return btn;
}
// 使用示例
this.Controls.Add(CreateStyledButton("保存", (s,e) => SaveData()));
2. 动态控件的事件处理
// 为动态创建的多个控件共享事件处理
void CreateDynamicControlsWithSharedHandler()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
TextBox txt = new TextBox {
Name = $"txtDynamic_{i}",
Tag = i,
Width = 100
};
// 共享文本改变事件
txt.TextChanged += DynamicTextBox_TextChanged;
this.Controls.Add(txt);
}
}
private void DynamicTextBox_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
TextBox txt = sender as TextBox;
int index = (int)txt.Tag;
Console.WriteLine($"文本框{index}内容变为: {txt.Text}");
}
3. 使用SuspendLayout/ResumeLayout优化性能
// 批量添加控件时优化性能
this.SuspendLayout();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
this.Controls.Add(new Label {
Text = $"标签 {i}",
Location = new Point(10, 20 * i)
});
}
}
finally {
this.ResumeLayout(true); // 参数表示是否立即执行布局逻辑
}
(四)控件生命周期管理
1. 动态移除控件
// 按名称查找并移除
Control toRemove = this.Controls.Find("btnRemoveMe", true).FirstOrDefault();
if (toRemove != null) {
toRemove.Dispose(); // 释放资源
// 或 this.Controls.Remove(toRemove);
}
// 移除所有特定类型控件
var buttons = this.Controls.OfType<Button>().ToList();
foreach (Button btn in buttons) {
btn.Dispose();
}
2. 控件持久化技巧
// 保存动态控件状态
Dictionary<string, string> SaveControlStates()
{
return this.Controls.OfType<TextBox>()
.ToDictionary(t => t.Name, t => t.Text);
}
// 恢复状态
void RestoreControlStates(Dictionary<string, string> states)
{
foreach (var kvp in states) {
Control[] found = this.Controls.Find(kvp.Key, true);
if (found.Length > 0 && found[0] is TextBox txt) {
txt.Text = kvp.Value;
}
}
}
(五)实际应用案例
1. 动态表单生成器
public void GenerateFormFields(List<FieldDefinition> fields)
{
int yPos = 10;
foreach (var field in fields) {
// 创建标签
this.Controls.Add(new Label {
Text = field.Label,
Location = new Point(10, yPos),
AutoSize = true
});
// 创建输入控件
Control inputControl = field.FieldType switch {
FieldType.Text => new TextBox {
Name = $"txt_{field.Name}",
Location = new Point(120, yPos),
Size = new Size(200, 20)
},
FieldType.Checkbox => new CheckBox {
Name = $"chk_{field.Name}",
Location = new Point(120, yPos)
},
_ => throw new NotSupportedException()
};
this.Controls.Add(inputControl);
yPos += 30;
}
}
// 使用示例
GenerateFormFields(new List<FieldDefinition> {
new FieldDefinition("UserName", "用户名", FieldType.Text),
new FieldDefinition("AgreeTerms", "同意条款", FieldType.Checkbox)
});
2. 动态菜单系统
public void BuildContextMenu(Control targetControl, MenuItemConfig[] items)
{
ContextMenuStrip menu = new ContextMenuStrip();
foreach (var item in items) {
ToolStripMenuItem menuItem = new ToolStripMenuItem(item.Text);
if (item.SubItems != null) {
foreach (var subItem in item.SubItems) {
menuItem.DropDownItems.Add(subItem.Text, null, (s,e) => ExecuteMenuCommand(subItem.Command));
}
}
else {
menuItem.Click += (s,e) => ExecuteMenuCommand(item.Command);
}
menu.Items.Add(menuItem);
}
targetControl.ContextMenuStrip = menu;
}
// 使用示例
BuildContextMenu(this.dataGridView1, new[] {
new MenuItemConfig("编辑", "EDIT", new[] {
new MenuItemConfig("复制", "COPY"),
new MenuItemConfig("粘贴", "PASTE")
}),
new MenuItemConfig("删除", "DELETE")
});
(六)调试与问题解决
1. 常见问题处理
// 检查控件是否已释放
if (dynamicButton.IsDisposed) {
// 重新创建控件
}
// 处理跨线程访问
void UpdateControlText(Control control, string text)
{
if (control.InvokeRequired) {
control.Invoke(new Action(() => control.Text = text));
}
else {
control.Text = text;
}
}
2. 设计时支持
// 创建可在设计时使用的自定义控件
[Designer("System.Windows.Forms.Design.ControlDesigner, System.Design")]
public class DynamicPanel : Panel
{
// 实现自定义逻辑
}
掌握这些编程方式创建和使用控件的技术,您将能够:
- 实现高度动态的界面
- 根据运行时条件生成UI
- 创建可配置的表单系统
- 优化复杂界面的性能
- 构建更灵活的应用程序架构
实际开发中,建议结合设计时创建和运行时动态生成的方式,在保证开发效率的同时获得最大的灵活性。
七、控件的设计时支持
设计时支持(Design-Time Support)是WinForms控件开发中的关键特性,它决定了控件在Visual Studio设计器中的行为表现和开发体验。以下是控件设计时支持的全面解析:
(一)设计时基础架构
1. 设计时与运行时区别
| 特性 | 设计时(Design-Time) | 运行时(Run-Time) |
|---|---|---|
| 环境 | Visual Studio设计器 | 编译后的应用程序 |
| 代码执行 | 部分代码不执行(如构造函数) | 全部代码执行 |
| 目的 | 可视化编辑界面 | 实际功能运行 |
| 检测方式 | DesignMode属性或LicenseManager.UsageMode | 正常执行流程 |
2. 核心设计时组件
System.ComponentModel.Design
├─ ComponentDesigner - 组件设计器基类
├─ ControlDesigner - 控件设计器基类
└─ IDesigner - 设计器接口
System.Drawing.Design
└─ UITypeEditor - 属性编辑器基类
(二)设计时特性(Attributes)详解
1. 外观控制特性
[ToolboxBitmap(typeof(MyControl), "Resources.MyControl.bmp")] // 工具箱图标
[Designer(typeof(MyControlDesigner))] // 指定自定义设计器
[Description("这是一个自定义控件的描述")] // 属性窗口显示描述
[DefaultProperty("Text")] // 指定默认属性
[DefaultEvent("Click")] // 指定默认事件
public class MyControl : Control { /*...*/ }
2. 属性控制特性
[Category("Appearance")] // 属性分类
[Browsable(true)] // 是否在属性窗口显示
[DefaultValue("默认文本")] // 默认值
[Editor(typeof(MultilineStringEditor), typeof(UITypeEditor))] // 使用多行文本编辑器
[TypeConverter(typeof(ExpandableObjectConverter))] // 可展开对象转换器
public string CustomText { get; set; }
3. 集合编辑器特性
[DesignerSerializationVisibility(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Content)]
[Editor(typeof(CollectionEditor), typeof(UITypeEditor))]
public List<MyItem> Items { get; } = new List<MyItem>();
(三)自定义设计器实现
1. 基本设计器类
public class MyControlDesigner : ControlDesigner
{
public override void Initialize(IComponent component)
{
base.Initialize(component);
// 启用智能标签
this.EnableDesignMode(((MyControl)component).InnerPanel, "InnerPanel");
}
protected override void PostFilterProperties(IDictionary properties)
{
base.PostFilterProperties(properties);
// 隐藏不需要设计的属性
properties.Remove("InternalState");
}
}
2. 设计时行为控制
// 禁止在设计时调整大小
public override SelectionRules SelectionRules
=> base.SelectionRules & ~SelectionRules.AllSizeable;
// 添加设计时动词命令(右键菜单)
public override DesignerVerbCollection Verbs
{
get
{
return new DesignerVerbCollection {
new DesignerVerb("重置配置", OnResetConfig)
};
}
}
private void OnResetConfig(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MyControl ctrl = (MyControl)Component;
ctrl.ResetConfig();
}
(四)高级设计时功能
1. 自定义属性编辑器
public class ColorSchemeEditor : UITypeEditor
{
// 指定编辑样式(模态/下拉)
public override UITypeEditorEditStyle GetEditStyle(ITypeDescriptorContext context)
=> UITypeEditorEditStyle.Modal;
// 实现编辑逻辑
public override object EditValue(ITypeDescriptorContext context,
IServiceProvider provider,
object value)
{
if (provider != null)
{
IWindowsFormsEditorService editorService =
provider.GetService(typeof(IWindowsFormsEditorService))
as IWindowsFormsEditorService;
if (editorService != null)
{
ColorSchemeDialog dialog = new ColorSchemeDialog();
if (dialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
return dialog.SelectedScheme;
}
}
}
return value;
}
}
// 使用自定义编辑器
[Editor(typeof(ColorSchemeEditor), typeof(UITypeEditor))]
public ColorScheme Scheme { get; set; }
2. 智能标签(Smart Tag)实现
public class SmartTagDesigner : ControlDesigner
{
private DesignerActionListCollection _actionLists;
public override DesignerActionListCollection ActionLists
{
get
{
if (_actionLists == null)
{
_actionLists = new DesignerActionListCollection {
new MyControlActionList(this.Component)
};
}
return _actionLists;
}
}
}
public class MyControlActionList : DesignerActionList
{
public MyControlActionList(IComponent component) : base(component) { }
public string Title
{
get => ((MyControl)Component).Title;
set => SetProperty("Title", value);
}
public override DesignerActionItemCollection GetSortedActionItems()
{
return new DesignerActionItemCollection {
new DesignerActionHeaderItem("外观"),
new DesignerActionPropertyItem("Title", "标题文本", "外观"),
new DesignerActionMethodItem(this, "ResetDefaults", "重置默认值")
};
}
public void ResetDefaults()
{
((MyControl)Component).ResetToDefaults();
}
private void SetProperty(string name, object value)
{
PropertyDescriptor prop = TypeDescriptor.GetProperties(Component)[name];
prop.SetValue(Component, value);
}
}
(五)设计时序列化机制
1. 序列化控制
[DesignerSerializationVisibility(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Hidden)] // 完全隐藏
[DesignerSerializationVisibility(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Visible)] // 默认可见
[DesignerSerializationVisibility(DesignerSerializationVisibility.Content)] // 序列化内容而非引用
public object ComplexProperty { get; set; }
2. 自定义序列化
[TypeConverter(typeof(MyConverter))]
public class CustomData
{
public string Value { get; set; }
private class MyConverter : TypeConverter
{
public override bool CanConvertTo(ITypeDescriptorContext context, Type destType)
=> destType == typeof(string);
public override object ConvertTo(ITypeDescriptorContext context,
CultureInfo culture,
object value,
Type destType)
{
return ((CustomData)value).Value;
}
public override bool CanConvertFrom(ITypeDescriptorContext context, Type srcType)
=> srcType == typeof(string);
public override object ConvertFrom(ITypeDescriptorContext context,
CultureInfo culture,
object value)
{
return new CustomData { Value = value.ToString() };
}
}
}
(六)调试设计时行为
1. 设计时调试技巧
// 检测设计时模式
if (LicenseManager.UsageMode == LicenseUsageMode.Designtime)
{
Debug.WriteLine("当前处于设计时模式");
}
// 附加设计器调试
#if DEBUG
System.Diagnostics.Debugger.Launch();
#endif
2. 常见问题解决
- 设计器加载失败:检查控件构造函数和
InitializeComponent逻辑 - 属性不显示:确认
Browsable特性设置正确 - 序列化异常:检查复杂属性的类型转换支持
- 可视化不一致:确保
DesignMode属性被正确处理
(七)完整设计时控件示例
[Designer(typeof(EnhancedButtonDesigner))]
[ToolboxBitmap(typeof(EnhancedButton), "Resources.EnhancedButton.bmp")]
[Description("带悬停效果的高级按钮")]
[DefaultEvent("Click")]
[DefaultProperty("Text")]
public class EnhancedButton : Button
{
[Category("Appearance")]
[Description("按钮悬停时的颜色")]
[DefaultValue(typeof(Color), "LightBlue")]
public Color HoverColor { get; set; } = Color.LightBlue;
[Category("Behavior")]
[Description("是否启用动画效果")]
[DefaultValue(true)]
public bool EnableAnimation { get; set; } = true;
protected override void OnMouseEnter(EventArgs e)
{
if (!DesignMode && EnableAnimation)
this.BackColor = HoverColor;
base.OnMouseEnter(e);
}
protected override void OnMouseLeave(EventArgs e)
{
if (!DesignMode && EnableAnimation)
this.BackColor = SystemColors.Control;
base.OnMouseLeave(e);
}
}
public class EnhancedButtonDesigner : ControlDesigner
{
private DesignerActionListCollection _actionLists;
public override DesignerActionListCollection ActionLists
{
get
{
if (_actionLists == null)
{
_actionLists = new DesignerActionListCollection {
new EnhancedButtonActionList(this.Component)
};
}
return _actionLists;
}
}
protected override void PostFilterProperties(IDictionary properties)
{
base.PostFilterProperties(properties);
properties.Remove("Cursor"); // 隐藏基类Cursor属性
}
}
public class EnhancedButtonActionList : DesignerActionList
{
public EnhancedButtonActionList(IComponent component) : base(component) { }
public Color HoverColor
{
get => ((EnhancedButton)Component).HoverColor;
set => SetProperty("HoverColor", value);
}
public bool EnableAnimation
{
get => ((EnhancedButton)Component).EnableAnimation;
set => SetProperty("EnableAnimation", value);
}
public override DesignerActionItemCollection GetSortedActionItems()
{
return new DesignerActionItemCollection {
new DesignerActionHeaderItem("行为"),
new DesignerActionPropertyItem("EnableAnimation", "启用动画", "行为"),
new DesignerActionHeaderItem("外观"),
new DesignerActionPropertyItem("HoverColor", "悬停颜色", "外观"),
new DesignerActionMethodItem(this, "ResetDefaults", "重置默认值")
};
}
public void ResetDefaults()
{
((EnhancedButton)Component).HoverColor = Color.LightBlue;
((EnhancedButton)Component).EnableAnimation = true;
}
private void SetProperty(string name, object value)
{
PropertyDescriptor prop = TypeDescriptor.GetProperties(Component)[name];
prop.SetValue(Component, value);
}
}
掌握这些设计时支持技术,您可以:
- 创建专业级的可视化设计体验
- 提供直观的属性配置界面
- 控制设计器序列化行为
- 增强控件的易用性
- 提高开发效率
良好的设计时支持是区分普通控件和专业控件的重要标志,也是提升开发体验的关键因素。
八、综合示例
下面是一个完整的WinForms应用程序示例,综合展示了多种控件的协同使用,包括数据展示、表单输入、菜单导航和对话框交互等功能。
(一)主窗体设计 (MainForm.cs)
public class MainForm : Form
{
private DataGridView dataGridView;
private ToolStrip toolStrip;
private StatusStrip statusStrip;
private MenuStrip menuStrip;
private Panel detailPanel;
public MainForm()
{
InitializeComponents();
LoadEmployees();
}
private void InitializeComponents()
{
// 窗体基本设置
this.Text = "员工信息管理系统";
this.WindowState = FormWindowState.Maximized;
this.StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterScreen;
// 1. 菜单栏
menuStrip = new MenuStrip();
var fileMenu = new ToolStripMenuItem("文件(&F)");
fileMenu.DropDownItems.Add("导出Excel", null, OnExportExcel);
fileMenu.DropDownItems.Add(new ToolStripSeparator());
fileMenu.DropDownItems.Add("退出(&X)", null, (s,e) => Application.Exit());
var editMenu = new ToolStripMenuItem("编辑(&E)");
editMenu.DropDownItems.Add("新增员工", null, OnAddEmployee);
editMenu.DropDownItems.Add("编辑选中", null, OnEditEmployee);
editMenu.DropDownItems.Add("删除选中", null, OnDeleteEmployee);
menuStrip.Items.AddRange(new[] { fileMenu, editMenu });
this.Controls.Add(menuStrip);
this.MainMenuStrip = menuStrip;
// 2. 工具栏
toolStrip = new ToolStrip();
toolStrip.Items.Add(new ToolStripButton("新增", Resources.AddIcon, OnAddEmployee) {
ToolTipText = "新增员工"
});
toolStrip.Items.Add(new ToolStripButton("编辑", Resources.EditIcon, OnEditEmployee));
toolStrip.Items.Add(new ToolStripButton("删除", Resources.DeleteIcon, OnDeleteEmployee));
toolStrip.Items.Add(new ToolStripSeparator());
var searchBox = new ToolStripTextBox();
searchBox.TextChanged += (s,e) => FilterEmployees(searchBox.Text);
toolStrip.Items.Add(new ToolStripLabel("搜索:"));
toolStrip.Items.Add(searchBox);
this.Controls.Add(toolStrip);
// 3. 数据表格
dataGridView = new DataGridView {
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
AllowUserToAddRows = false,
AllowUserToDeleteRows = false,
ReadOnly = true,
SelectionMode = DataGridViewSelectionMode.FullRowSelect,
MultiSelect = false,
RowHeadersVisible = false
};
// 4. 详细信息面板 (初始隐藏)
detailPanel = new Panel {
Dock = DockStyle.Right,
Width = 300,
BackColor = SystemColors.ControlLight,
Visible = false
};
InitializeDetailPanel();
// 5. 状态栏
statusStrip = new StatusStrip();
statusStrip.Items.Add(new ToolStripStatusLabel("就绪"));
this.Controls.Add(statusStrip);
// 使用SplitContainer组织主布局
SplitContainer splitContainer = new SplitContainer {
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
Orientation = Orientation.Horizontal,
SplitterDistance = 70 // 工具栏高度
};
splitContainer.Panel1.Controls.Add(toolStrip);
SplitContainer mainSplit = new SplitContainer {
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
Orientation = Orientation.Vertical
};
mainSplit.Panel1.Controls.Add(dataGridView);
mainSplit.Panel2.Controls.Add(detailPanel);
splitContainer.Panel2.Controls.Add(mainSplit);
this.Controls.Add(splitContainer);
// 调整控件层次顺序
this.Controls.SetChildIndex(menuStrip, 0);
this.Controls.SetChildIndex(statusStrip, 1);
this.Controls.SetChildIndex(splitContainer, 2);
}
private void InitializeDetailPanel()
{
detailPanel.SuspendLayout();
Label lblTitle = new Label {
Text = "员工详细信息",
Dock = DockStyle.Top,
TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleCenter,
Font = new Font(Font.FontFamily, 12, FontStyle.Bold),
Height = 40
};
PropertyGrid propGrid = new PropertyGrid {
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
ToolbarVisible = false,
HelpVisible = false
};
Button btnClose = new Button {
Text = "关闭",
Dock = DockStyle.Bottom,
Height = 30
};
btnClose.Click += (s,e) => detailPanel.Visible = false;
detailPanel.Controls.AddRange(new Control[] { propGrid, btnClose, lblTitle });
detailPanel.ResumeLayout();
}
private void LoadEmployees()
{
// 模拟数据加载
var employees = new List<Employee> {
new Employee { Id = 1, Name = "张三", Department = "研发部", Position = "工程师", HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-1) },
new Employee { Id = 2, Name = "李四", Department = "市场部", Position = "经理", HireDate = DateTime.Now.AddYears(-2) }
};
dataGridView.DataSource = employees;
dataGridView.CellDoubleClick += (s,e) => ShowEmployeeDetails();
}
private void ShowEmployeeDetails()
{
if (dataGridView.CurrentRow?.DataBoundItem is Employee emp)
{
((PropertyGrid)detailPanel.Controls[1]).SelectedObject = emp;
detailPanel.Visible = true;
}
}
private void FilterEmployees(string keyword)
{
if (dataGridView.DataSource is List<Employee> data)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(keyword))
{
dataGridView.DataSource = data;
}
else
{
dataGridView.DataSource = data.Where(e =>
e.Name.Contains(keyword) ||
e.Department.Contains(keyword) ||
e.Position.Contains(keyword)).ToList();
}
}
}
// 其他事件处理方法
private void OnAddEmployee(object sender, EventArgs e) { /* 实现添加逻辑 */ }
private void OnEditEmployee(object sender, EventArgs e) { /* 实现编辑逻辑 */ }
private void OnDeleteEmployee(object sender, EventArgs e) { /* 实现删除逻辑 */ }
private void OnExportExcel(object sender, EventArgs e) { /* 实现导出逻辑 */ }
}
(二)、员工信息编辑窗体 (EmployeeForm.cs)
public class EmployeeForm : Form
{
public Employee Employee { get; private set; }
public EmployeeForm(Employee emp = null)
{
Employee = emp ?? new Employee();
InitializeComponents();
}
private void InitializeComponents()
{
this.Text = Employee.Id > 0 ? "编辑员工" : "新增员工";
this.Size = new Size(400, 350);
this.StartPosition = FormStartPosition.CenterParent;
this.FormBorderStyle = FormBorderStyle.FixedDialog;
this.MaximizeBox = false;
this.MinimizeBox = false;
TableLayoutPanel tableLayout = new TableLayoutPanel {
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
ColumnCount = 2,
RowCount = 6,
Padding = new Padding(10),
CellBorderStyle = TableLayoutPanelCellBorderStyle.None
};
tableLayout.ColumnStyles.Add(new ColumnStyle(SizeType.Percent, 30F));
tableLayout.ColumnStyles.Add(new ColumnStyle(SizeType.Percent, 70F));
// 1. 姓名
tableLayout.Controls.Add(new Label { Text = "姓名:", TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleRight }, 0, 0);
TextBox txtName = new TextBox { Dock = DockStyle.Fill, Text = Employee.Name };
tableLayout.Controls.Add(txtName, 1, 0);
// 2. 部门
tableLayout.Controls.Add(new Label { Text = "部门:", TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleRight }, 0, 1);
ComboBox cmbDept = new ComboBox { Dock = DockStyle.Fill, DropDownStyle = ComboBoxStyle.DropDownList };
cmbDept.Items.AddRange(new[] { "研发部", "市场部", "财务部", "人事部" });
cmbDept.SelectedItem = Employee.Department;
tableLayout.Controls.Add(cmbDept, 1, 1);
// 3. 职位
tableLayout.Controls.Add(new Label { Text = "职位:", TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleRight }, 0, 2);
TextBox txtPosition = new TextBox { Dock = DockStyle.Fill, Text = Employee.Position };
tableLayout.Controls.Add(txtPosition, 1, 2);
// 4. 入职日期
tableLayout.Controls.Add(new Label { Text = "入职日期:", TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleRight }, 0, 3);
DateTimePicker dtpHireDate = new DateTimePicker {
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
Value = Employee.HireDate,
Format = DateTimePickerFormat.Short
};
tableLayout.Controls.Add(dtpHireDate, 1, 3);
// 5. 照片
tableLayout.Controls.Add(new Label { Text = "照片:", TextAlign = ContentAlignment.MiddleRight }, 0, 4);
PictureBox picPhoto = new PictureBox {
Dock = DockStyle.Fill,
SizeMode = PictureBoxSizeMode.Zoom,
BorderStyle = BorderStyle.FixedSingle,
Height = 100
};
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(Employee.PhotoPath))
picPhoto.Image = Image.FromFile(Employee.PhotoPath);
Button btnSelectPhoto = new Button { Text = "选择照片...", Dock = DockStyle.Top };
btnSelectPhoto.Click += (s,e) => {
using (OpenFileDialog dlg = new OpenFileDialog())
{
dlg.Filter = "图片文件|*.jpg;*.png";
if (dlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
picPhoto.Image = Image.FromFile(dlg.FileName);
Employee.PhotoPath = dlg.FileName;
}
}
};
Panel photoPanel = new Panel { Dock = DockStyle.Fill };
photoPanel.Controls.Add(picPhoto);
photoPanel.Controls.Add(btnSelectPhoto);
tableLayout.Controls.Add(photoPanel, 1, 4);
// 按钮区
Panel buttonPanel = new Panel { Dock = DockStyle.Bottom, Height = 50 };
Button btnOK = new Button { Text = "确定", DialogResult = DialogResult.OK };
Button btnCancel = new Button { Text = "取消", DialogResult = DialogResult.Cancel };
btnOK.Click += (s,e) => {
Employee.Name = txtName.Text;
Employee.Department = cmbDept.SelectedItem?.ToString();
Employee.Position = txtPosition.Text;
Employee.HireDate = dtpHireDate.Value;
};
// 使用FlowLayoutPanel自动排列按钮
FlowLayoutPanel flowButtons = new FlowLayoutPanel {
Dock = DockStyle.Right,
AutoSize = true,
FlowDirection = FlowDirection.RightToLeft,
Padding = new Padding(0, 10, 10, 0)
};
flowButtons.Controls.AddRange(new[] { btnCancel, btnOK });
buttonPanel.Controls.Add(flowButtons);
// 设置按钮大小和间距
btnOK.Size = btnCancel.Size = new Size(80, 30);
btnOK.Margin = btnCancel.Margin = new Padding(5, 0, 0, 0);
this.Controls.Add(tableLayout);
this.Controls.Add(buttonPanel);
// 设置Accept和Cancel按钮
this.AcceptButton = btnOK;
this.CancelButton = btnCancel;
}
}
(三)数据模型 (Employee.cs)
[TypeConverter(typeof(ExpandableObjectConverter))]
public class Employee
{
[DisplayName("员工ID")]
[ReadOnly(true)]
public int Id { get; set; }
[DisplayName("姓名")]
[Category("基本信息")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[DisplayName("部门")]
[Category("工作信息")]
public string Department { get; set; }
[DisplayName("职位")]
[Category("工作信息")]
public string Position { get; set; }
[DisplayName("入职日期")]
[Category("工作信息")]
public DateTime HireDate { get; set; }
[Browsable(false)] // 不在属性网格中显示
public string PhotoPath { get; set; }
[DisplayName("工龄")]
[Category("计算字段")]
public string WorkYears => $"{DateTime.Now.Year - HireDate.Year}年";
public override string ToString() => Name;
}
(四)应用程序入口 (Program.cs)
static class Program
{
[STAThread]
static void Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
// 设置全局UI样式
SetGlobalUIStyle();
Application.Run(new MainForm());
}
static void SetGlobalUIStyle()
{
// 设置默认字体
System.Drawing.Text.PrivateFontCollection fonts = new System.Drawing.Text.PrivateFontCollection();
fonts.AddFontFile("MicrosoftYaHei.ttf");
// 使用自定义字体或系统字体
Font defaultFont = new Font("Microsoft YaHei", 9);
// 应用全局样式
foreach (Control control in new Control[] {
new Button(), new Label(), new TextBox(), new ComboBox()
})
{
control.Font = defaultFont;
}
}
}
(五)功能扩展建议
-
数据持久化:
- 添加SQLite或SQL Server数据库支持
- 实现Entity Framework Core数据访问层
-
增强功能:
- 添加数据验证逻辑
- 实现导入/导出Excel功能
- 添加图表统计展示
-
UI改进:
- 使用第三方UI控件库(如DevExpress、Telerik)
- 添加主题切换功能
- 实现多语言支持
-
架构优化:
- 采用MVP或MVVM模式
- 添加依赖注入容器
- 实现插件系统
这个综合示例展示了:
- 多种WinForms控件的协同使用
- 复杂布局的实现(使用SplitContainer和TableLayoutPanel)
- 数据绑定和展示(DataGridView和PropertyGrid)
- 对话框交互模式
- 设计时特性的应用
- 良好的代码组织结构
您可以根据实际需求进一步扩展和完善这个示例系统。
总结
本文是一份关于C#程序设计基础中控件使用的详细教程,主要面向青少年编程学习者。文章首先介绍了WinForms控件的基本概念,包括其作为可视化用户界面的基本构建块,以及属性、方法、事件三大核心特性。接着,文章详细分类并解析了多种控件,如基础输入控件、数据显示控件、容器控件等,并探讨了控件的继承体系和容器-控件关系。此外,还深入讲解了编程方式使用控件的方法,包括动态创建、事件处理、生命周期管理等。文章通过综合示例展示了如何在实际项目中应用这些控件,包括主窗体设计、数据展示、表单输入、菜单导航和对话框交互等功能。最后,还提供了功能扩展建议,如数据持久化、增强功能、UI改进和架构优化等,以帮助读者进一步提升应用开发能力。