题目
给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。

代码
方法一:哈希表
这个方法没有什么难度
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
hash_node=set()
while head:
if head in hash_node:
return head
hash_node.add(head)
head=head.next
return None
方法二:快慢指针
这个方法重点时想清楚:快慢指针相遇后,然后让慢指针再跑一圈算出圆的长度;然后再定义两个指针,让其中一个从头先走一圈圆的长度,然后再两个指针再一起走,最终他们会在圆的起点相遇
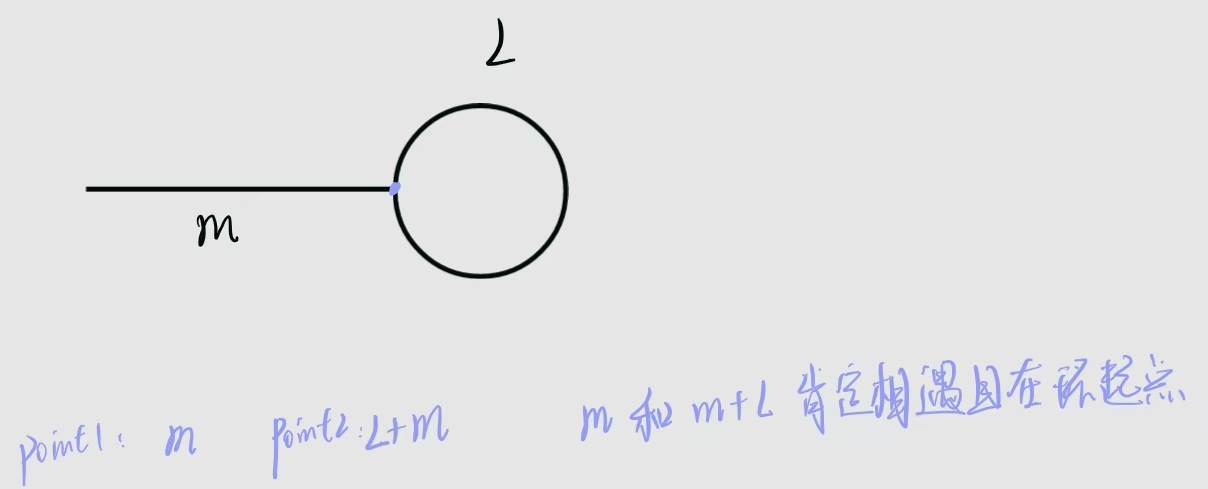
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:
return None
slow=head
fast=head.next
while slow!=fast:
if not fast or not fast.next:
return None
slow=slow.next
fast=fast.next.next
slow=slow.next
L=1
while slow !=fast:
L+=1
slow=slow.next
point1=head
while L:
point1=point1.next
L-=1
point2=head
while point1!=point2:
point1=point1.next
point2=point2.next
return point2


















![[matlab]private和+等特殊目录在新版本matlab中不允许添加搜索路径解决方法](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/5a7acc575b114197ab25124758d9c516.png)
