目录
- 1.两类过程赋值
- 2.阻塞与非阻塞赋值语句行为差别举例1
- 3.阻塞与非阻塞赋值语句行为差别举例2
- 4.阻塞与非阻塞赋值语句行为差别举例3
- 5.举例4:非阻塞赋值语句中延时在左边和右边的差别
微信公众号获取更多FPGA相关源码:

1.两类过程赋值
-
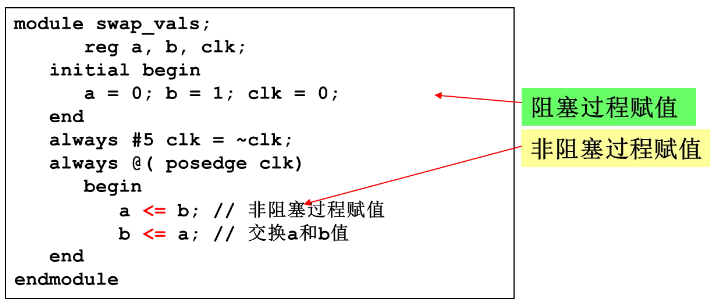
阻塞过程赋值执行完成后再执行在顺序块内下一条语句。
-
非阻塞赋值不阻塞过程流,仿真器读入一条赋值语句并对它进行调度之后,就可以处理下一条赋值语句。
若过程块中的所有赋值都是非阻塞的,赋值按两步进行:
- 仿真器计算所有RHS表达式的值,保存结果,并进行调度在时序控制指定时间的赋值。
- 在经过相应的延迟后,仿真器通过将保存的值赋给LHS表达式完成赋值。
2.阻塞与非阻塞赋值语句行为差别举例1
module non_block1;
reg a, b, c, d, e, f;
initial begin // blocking assignments
a = #10 1; // time 10
b = #2 0; // time 12
c = #4 1; // time 16
end
initial begin // non- blocking assignments
d <= #10 1; // time 10
e <= #2 0; // time 2
f <= #4 1; // time 4
end
initial begin
$monitor($ time,," a= %b b= %b c= %b d= %b e= %b f= %b", a, b, c, d, e, f);
#100 $finish;
end
endmodule
输出结果:
| 时刻 | a | b | c | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | a= x | b= x | c= x | d= x |
| 2 | a= x | b= x | c= x | d= x |
| 4 | a= x | b= x | c= x | d= x |
| 10 | a= 1 | b= x | c= x | d= 1 |
| 12 | a= 1 | b= 0 | c= x | d= 1 |
| 16 | a= 1 | b= 0 | c= 1 | d= 1 |
3.阻塞与非阻塞赋值语句行为差别举例2
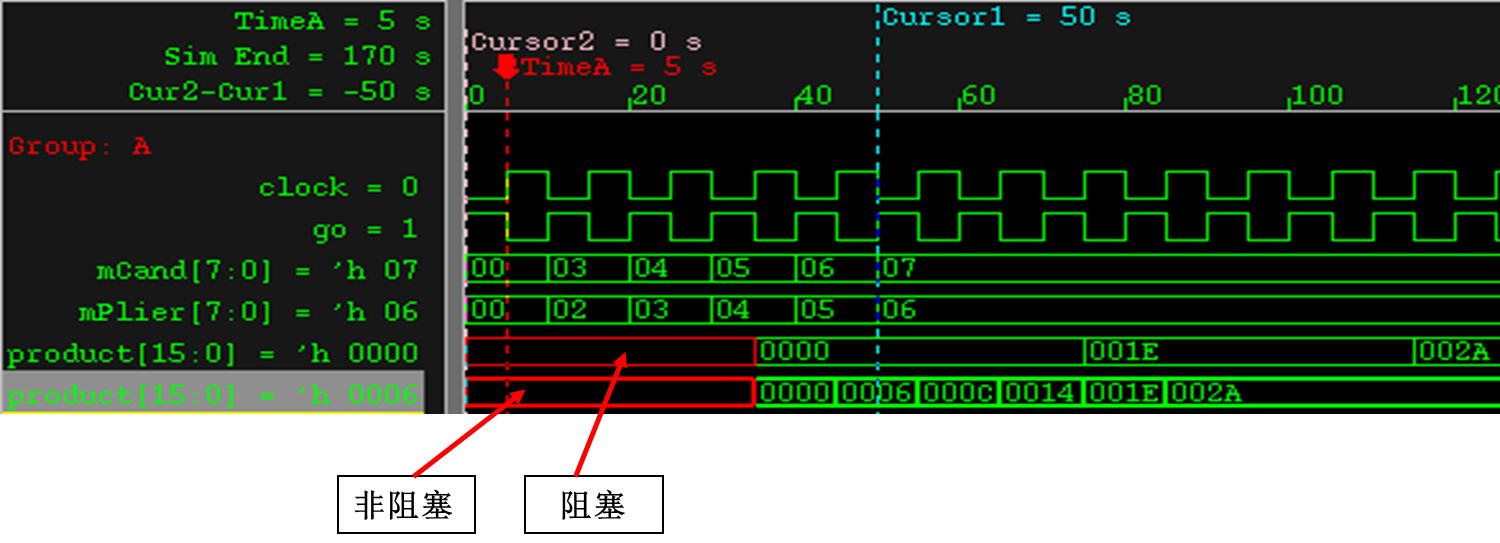
module pipeMult(product, mPlier, mCand, go, clock);
input go, clock;
input [7:0] mPlier, mCand;
output [15:0] product;
reg [15:0] product;
always @(posedge go)
product = repeat (4) @(posedge clock) mPlier * mCand;
endmodule
module pipeMult(product, mPlier, mCand, go, clock);
input go, clock;
input [7:0] mPlier, mCand;
output [15:0] product;
reg [15:0] product;
always @(posedge go)
product <= repeat (4) @(posedge clock) mPlier * mCand;
endmodule
4.阻塞与非阻塞赋值语句行为差别举例3
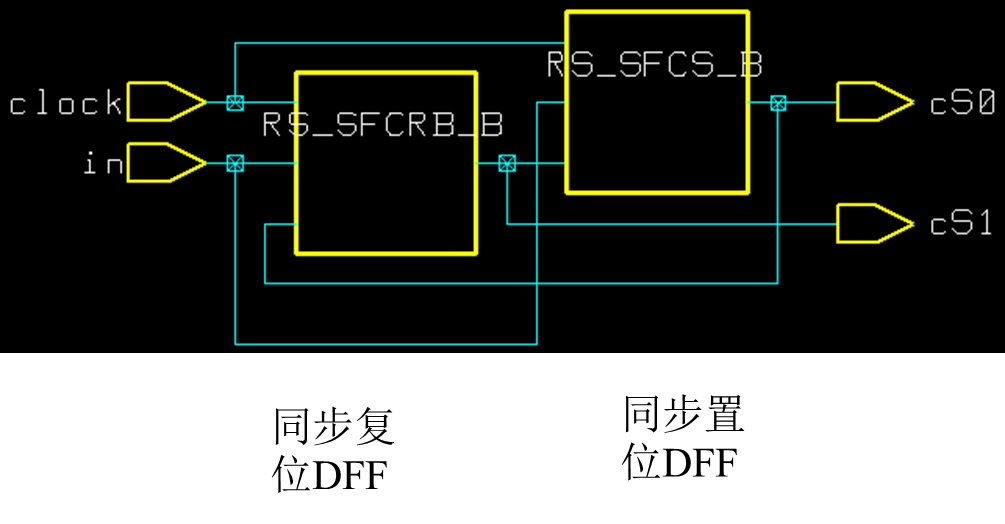
module fsm(cS1, cS0, in, clock);
input in , clock;
output cS1, cS0;
reg cS1, cS0;
always @(posedge clock) begin
cS1 = in & cS0; //同步复位
cS0 = in | cS1; //cS0 = in
end
endmodule

module fsm(cS1, cS0, in, clock);
input in , clock;
output cS1, cS0;
reg cS1, cS0;
always @(posedge clock) begin
cS1 <= in & cS0; //同步复位
cS0 <= in | cS1; //同步置位
end
endmodule
5.举例4:非阻塞赋值语句中延时在左边和右边的差别
module exchange;
reg[3:0] a, b;
initial begin
a=1; b=4;
#2 a=3; b=2;
#20 $finish;
end
initial
$monitor($time, "\t%h\t%h", a, b);
initial begin
#5 a <= b;
#5 b <= a;
end
endmodule
输出结果:
| time | a | b |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 |
module exchange;
reg[3:0] a, b;
initial begin
a=1; b=4;
#2 a=3; b=2;
#20 $finish;
end
initial
$monitor($time, "\t%h\t%h", a, b);
initial begin
a <= #5 b;
b <= #5 a;
end
endmodule
输出结果:
| time | a | b |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 4 |
| 2 | 3 | 2 |
| 5 | 4 | 1 |
微信公众号获取更多FPGA相关源码:








![[Spring] Spring配置文件](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/4bc90838c14f4ff79f71b0278d32ee81.png)