目录
一、前言
二、sysfs方式
1、sysfs简介
2、基本目录结构
3、编号计算
4、sysfs方式控制GPIO
三、libgpiod库
1、libgpiod库简介
2、API函数
四、LED灯编程
一、前言
在Linux下,我们通常使用 sysfs 和 libgpiod库 两种方式进行控制GPIO,目前,libgpiod库已成为人们广泛采用的方法。接下来,我将通过控制LED灯的亮灭来讲解Linux下如何进行GPIO编程。
我这里使用的RGB三色灯是共阳极的(大家根据硬件的实际情况进行修改)。

根据引脚实际情况进行连接,我这里选取了1、3、5、7号引脚。

- RGB三色灯 G(Gnd) 连接到了 开发板40Pin 1#脚上
- RGB三色灯 R(红灯) 连接到了 开发板40Pin 3#脚上
- RGB三色灯 G(绿灯) 连接到了 开发板40Pin 7#脚上
- RGB三色灯 B(蓝灯) 连接到了 开发板40Pin 5#脚上
二、sysfs方式
1、sysfs简介
尽管 sysfs 方式控制GPIO在现代系统中已逐渐被弃用,但了解其工作原理仍然有助于理解 Linux 内核的操作方式。sysfs 是 Linux 文件系统中的一个伪文件系统,用于导出内核对象的信息,以文件和目录的形式呈现。这些文件和目录可以被用户空间进程读取和写入,以访问和操作内核对象。
通过 sysfs,用户可以直接通过文件系统的接口来与内核进行交互,而不需要直接操作内核数据结构。这种抽象层提供了一种方便而统一的方式来管理和配置系统硬件和内核参数,使得Linux系统更加灵活和易于管理。
2、基本目录结构
我们通过查看 /sys/class/gpio 来查看基本目录结构。

(1)export:用于通知Linux内核导出需要的GPIO引脚。
(2)unexport: 用于通知Linux内核取消导出的GPIO引脚。
(3)gpiochipX:用于保存系统中GPIO寄存器的信息。
GPIO 芯片在文件系统中表示为字符设备文件,在 /dev 目录下,每个 GPIO 芯片都有一个对应的字符设备文件。
![]()
3、编号计算
要想通过 sysfs 方式控制LED灯,需要先根据引脚计算出其编号。根据引脚连接方式,我们可以知道引脚#3、#5、#7分别对应的是GPIO1_IO03、GPIO1_IO02、GPIO1_IO18。

编号计算公式为:NUM = (x - 1)* 32 + Y
接下来我都以红灯所连的 #3 引脚为例。
GPIO1_IO03 = (1-1)*32 + 3 = 3
4、sysfs方式控制GPIO
(1)通知内核导出需要的GPIO引脚

查看gpio3文件夹
![]()
- direction:gpio的输入输出属性。
- active_low:设置gpio的有效电平,由于我们常用1为高电平、0为低电平的编程习惯,active_low通常设置为0 。
- value:gpio的电平值。
(2)设置GPIO引脚为输出模式
![]()
(3)通过输出高低电平控制LED亮灭
通过上图共阳极LED原理图可知,输出高电平LED灭,输出低电平LED亮。

(4) 通知内核导出需要的GPIO引脚
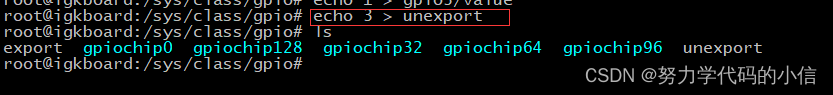
三、libgpiod库
1、libgpiod库简介
libgpiod是一个用于在Linux系统上访问GPIO设备的C库,它提供了一个用户空间API,允许开发者以编程方式控制和管理系统上的GPIO引脚。
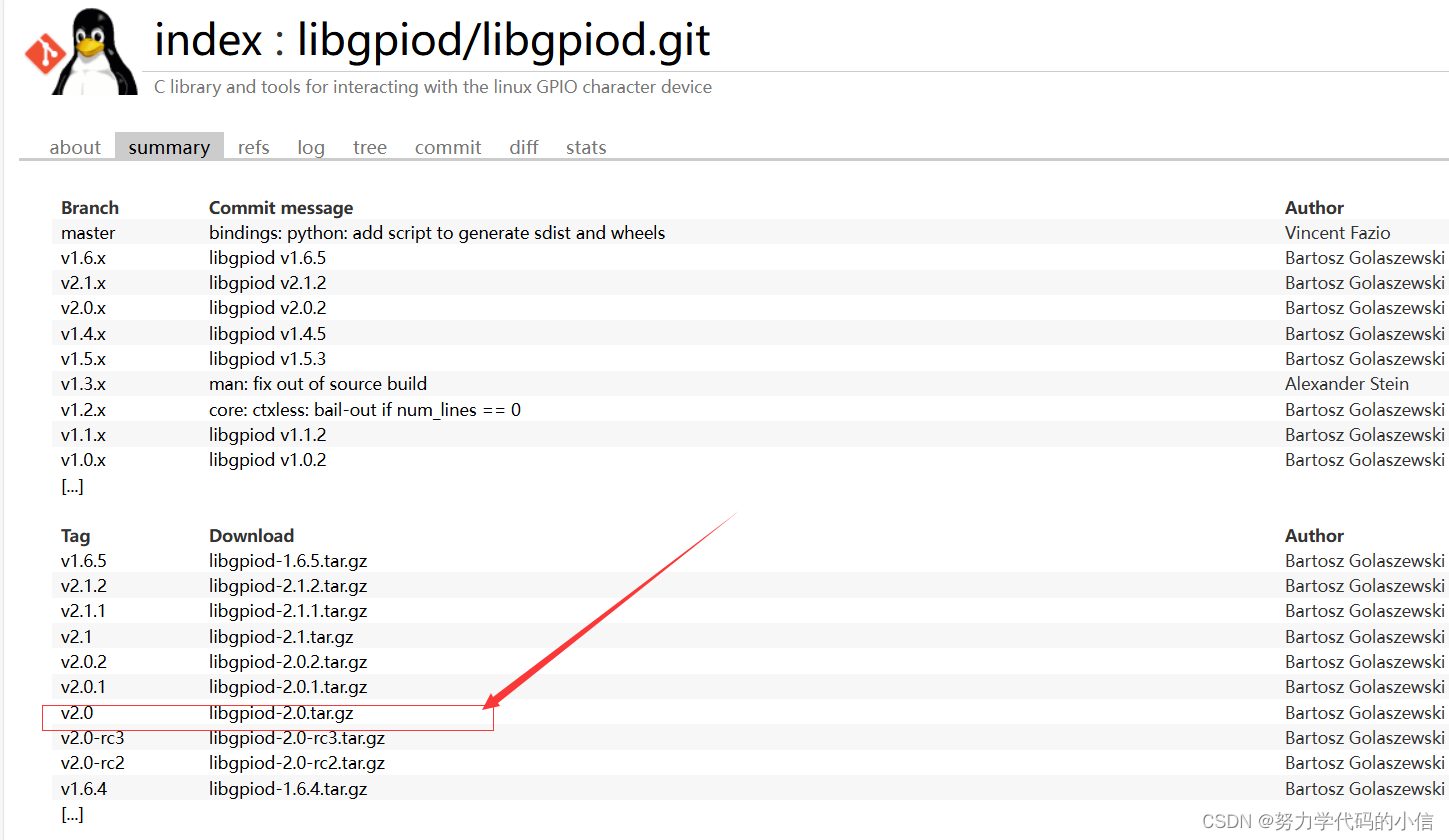
我们在服务器做交叉编译时,在编译和链接过程中需要相应的头文件和动态库文件,所以我们需要下载第三方库文件,下载时注意版本选择!
下载链接:libgpiod/libgpiod.git - C library and tools for interacting with the linux GPIO character device (kernel.org)![]() https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/libs/libgpiod/libgpiod.git
https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/libs/libgpiod/libgpiod.git
先查看板子上libgpiod库的版本号。
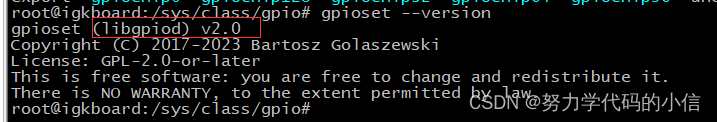
此时,在服务器上按顺序依次输入如下命令:
mkdir libgpiod && cd libgpiod
wget https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/libs/libgpiod/libgpiod.git/snapshot/libgpiod-2.0.tar.gz
tar -xzf libgpiod-2.0.tar.gz
cd libgpiod-2.0/
./autogen.sh
export CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf-
export CC=${CROSS_COMPILE}gcc
export CXX=${CROSS_COMPILE}g++
export AS=${CROSS_COMPILE}as
export AR=${CROSS_COMPILE}ar
export LD=${CROSS_COMPILE}ld
export NM=${CROSS_COMPILE}nm
export RANLIB=${CROSS_COMPILE}ranlib
export OBJDUMP=${CROSS_COMPILE}objdump
export STRIP=${CROSS_COMPILE}strip
unset CFLAGS
unset LDFLAGS
echo "ac_cv_func_malloc_0_nonnull=yes" > arm-linux.cache
./configure --prefix=`pwd`/../install --build=i686-pc-linux --host=arm-linux --enable-static --enable-tools --cache-file=arm-linux.cache
make
make installlibgpiod下载后目录结构如下:
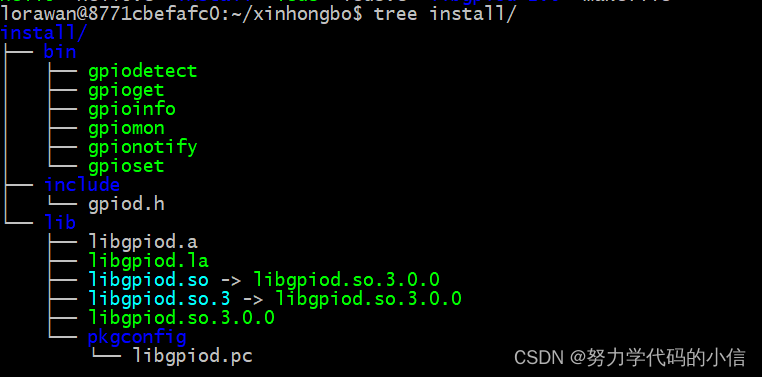
2、API函数
我在这里就整理了几个常用API函数,想查看更详细的讲解,可以看libgpiod的API文档说明。
libgpiod: GPIO chips![]() https://libgpiod.readthedocs.io/en/latest/group__chips.html(1)打开/关闭所需要的GPIO芯片
https://libgpiod.readthedocs.io/en/latest/group__chips.html(1)打开/关闭所需要的GPIO芯片
struct gpiod_chip *gpiod_chip_open(const char *path);
void gpiod_chip_close(struct gpiod_chip *chip);- path:要打开的gpiochip 设备路径(/dev/gpiochipx)。
- 返回值:成功返回GPIO芯片句柄,失败则返回NULL。
(2)申请/释放所需要的GPIO口
struct gpiod_line_request * gpiod_chip_request_lines(struct gpiod_chip *chip, struct gpiod_request_config *req_cfg, struct gpiod_line_config *line_cfg);
void gpiod_line_request_release(struct gpiod_line_request *request);- chip:GPIO芯片句柄。
- req_cfg:request的配置。
- line_cfg:line的配置。
- 返回值:成功返回GPIO口句柄,失败则返回NULL。
(3)设置GPIO输出电平
int gpiod_line_request_set_value(struct gpiod_line_request *request, unsigned int offset, enum gpiod_line_value value)- request:GPIO口句柄。
- offset:GPIO line编号。
- value:设置的逻辑电平值。
四、LED灯编程
#include <stdio.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <gpiod.h>
#define DELAY 300
#define ON 0
#define OFF 1
/*Three LEDs number*/
enum
{
LED_R = 0,
LED_G,
LED_B,
LEDCNT,
};
enum
{
ACTIVE_HIGH, /*LOW level will turn led on*/
ACTIVE_LOW, /*HIGH level will turn led on*/
};
/*Three LEDS hardware information*/
typedef struct led_s
{
const char *name;
int chip_num;
int gpio_num;
int active;
struct gpiod_line_request *request;
}led_t;
static led_t leds_info[LEDCNT] =
{
{"red", 0, 3,ACTIVE_HIGH,NULL},
{"green",0,18,ACTIVE_HIGH,NULL},
{"blue", 0, 2,ACTIVE_HIGH,NULL},
};
/*Three LEDs API context*/
typedef struct leds_s
{
led_t *leds;
int count;
}leds_t;
/*function declaration*/
int init_led(leds_t *leds);
int term_led(leds_t *leds);
int turn_led(leds_t *leds, int which, int cmd);
static inline void msleep(unsigned long ms);
static int g_stop = 0;
void sig_handler(int signum)
{
switch( signum )
{
case SIGINT:
g_stop = 1;
break;
case SIGTERM:
g_stop = 1;
break;
default:
break;
}
return ;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int rv;
leds_t leds =
{
.leds = leds_info,
.count = LEDCNT,
};
if( (rv = init_led(&leds)) < 0 )
{
printf("initial leds gpio failure,rv=%d\n",rv);
return -1;
}
printf("initial RGB LED gpios okay!\n");
signal(SIGINT, sig_handler);
signal(SIGTERM, sig_handler);
while( !g_stop )
{
turn_led(&leds,LED_R,ON);
msleep(DELAY);
turn_led(&leds,LED_R,OFF);
msleep(DELAY);
turn_led(&leds,LED_G,ON);
msleep(DELAY);
turn_led(&leds,LED_G,OFF);
msleep(DELAY);
turn_led(&leds,LED_B,ON);
msleep(DELAY);
turn_led(&leds,LED_B,OFF);
msleep(DELAY);
}
term_led(&leds);
return 0;
}
int turn_led(leds_t *leds, int which, int cmd)
{
led_t *led;
int rv = 0;
int value = 0;
if( !leds || which<0 || which>=leds->count )
{
printf("Invalid input arguments\n");
return -1;
}
led = &leds->leds[which];
value = OFF == cmd ? GPIOD_LINE_VALUE_ACTIVE : GPIOD_LINE_VALUE_INACTIVE;
gpiod_line_request_set_value(led->request, led->gpio_num, value);
return 0;
}
static inline void msleep(unsigned long ms)
{
struct timespec cSleep;
unsigned long ulTmp;
cSleep.tv_sec = ms / 1000;
if(cSleep.tv_sec == 0)
{
ulTmp = ms * 10000;
cSleep.tv_nsec = ulTmp * 100;
}
else
{
cSleep.tv_nsec = 0;
}
nanosleep(&cSleep, 0);
return ;
}
int init_led(leds_t *leds)
{
led_t *led;
int i,rv = 0;
char chip_dev[32];
struct gpiod_chip *chip;
struct gpiod_line_settings *settings;
struct gpiod_line_config *line_cfg;
struct gpiod_request_config *req_cfg;
if( !leds )
{
printf("Invalid input arguments\n");
return -1;
}
/*struct gpiod_line_settings
{
enum gpiod_line_direction direction; 设置 GPIO 线的方向(输入/输出)
enum gpiod_line_edge edge_detection; 设置 GPIO 线的边沿检测,用于捕获信号变化
enum gpiod_line_drive drive; 设置 GPIO 线的驱动模式
enum gpiod_line_bias bias; 设置 GPIO 线的偏置
bool active_low; 设置 GPIO 线是否为低电平有效
enum gpiod_line_clock event_clock; 设置事件时钟,用于时间戳事件
long debounce_period_us; 设置去抖动的时间,以微秒为单位
enum gpiod_line_value output_value; 设置 GPIO 线的输出值
};*/
settings = gpiod_line_settings_new();
if( !settings )
{
printf("unable to allocate line settings\n");
rv = -2;
goto cleanup;
}
/*struct gpiod_line_config
{
struct per_line_config line_configs[LINES_MAX]; 配置每条 GPIO 线的特性,如方向、边沿检测、驱动模式、偏置等
size_t num_configs; 指示 line_configs 数组中有多少个有效的 GPIO 线配置信息
enum gpiod_line_value output_values[LINES_MAX]; 设置每条 GPIO 线的输出值,如高电平、低电平
size_t num_output_values; 指示 output_values 数组中有多少个有效的 GPIO 线输出值
struct settings_node *sref_list; 用于管理 GPIO 线的设置信息,如方向、边沿检测、驱动模式等
};*/
line_cfg = gpiod_line_config_new();
if( !line_cfg )
{
printf("unable to allocate the line config structure");
rv = -2;
goto cleanup;
}
/*struct gpiod_request_config
{
char consumer[GPIO_MAX_NAME_SIZE]; 标识请求 GPIO 引脚的应用程序或模块
size_t event_buffer_size; 指定用于存储事件数据的缓冲区大小
};*/
req_cfg = gpiod_request_config_new();
if( !req_cfg )
{
printf("unable to allocate the request config structure");
rv = -2;
goto cleanup;
}
for(i=0; i<leds->count; i++)
{
led = &leds->leds[i];
snprintf(chip_dev, sizeof(chip_dev), "/dev/gpiochip%d", led->chip_num);
chip = gpiod_chip_open(chip_dev);
if( !chip )
{
printf("open gpiochip failure, maybe you need running as root\n");
rv = -3;
goto cleanup;
}
gpiod_line_settings_reset(settings);
gpiod_line_settings_set_direction(settings, GPIOD_LINE_DIRECTION_OUTPUT);
gpiod_line_settings_set_active_low(settings, led->active);
gpiod_line_settings_set_output_value(settings, GPIOD_LINE_VALUE_ACTIVE);
gpiod_line_config_reset(line_cfg);
gpiod_line_config_add_line_settings(line_cfg, &led->gpio_num, 1, settings);
gpiod_request_config_set_consumer(req_cfg, led->name);
led->request = gpiod_chip_request_lines(chip, req_cfg, line_cfg);
gpiod_chip_close(chip);
}
cleanup:
if( rv < 0 )
term_led(leds);
if( line_cfg )
gpiod_line_config_free(line_cfg);
if( req_cfg )
gpiod_request_config_free(req_cfg);
if( settings )
gpiod_line_settings_free(settings);
return rv;
}
int term_led(leds_t *leds)
{
int i;
led_t *led;
printf("terminate RGB LED gpios\n");
if( !leds )
{
printf("Invalid input arguments\n");
return -1;
}
for(i=0; i<leds->count; i++)
{
led = &leds->leds[i];
if( led->request )
{
turn_led(leds, i, OFF);
gpiod_line_request_release(led->request);
}
}
return 0;
}