【Java】使用Java调用Python的四种方法
fastjson的使用——JSON字符串、JSON对象、Java对象的互转
使用idea给Java程序打jar包(超简单 超详细)
1 环境准备
(1)新建Maven类型的项目,D:\processPython。
右键src/main/java,创建java类。
(2)在使用Java调用python之前,需要导入依赖环境。
如,在maven项目中,需要导入如下依赖:
目前只有2.7.X版本有相关依赖包。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.python</groupId>
<artifactId>jython-standalone</artifactId>
<!--python版本是2.x还是3.x在这里指定-->
<version>2.7.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2 调用
2.1 在java类中直接执行python语句
创建Java类JavaRunPython。
import org.python.util.PythonInterpreter;
public class JavaRunPython {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//首先调用python的解释器
PythonInterpreter interpreter = new PythonInterpreter();
//选择执行的的Python语句
interpreter.exec("import sys; ");
interpreter.exec("a='hello world123'; ");
interpreter.exec("print(sys.version,a);");
}
}
输出如下:
('2.7.1 (default:0df7adb1b397, Jun 30 2017, 19:02:43)
[Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (Oracle Corporation)]',
'hello world123')
在正常的情况下,Java工程师只需要调用python开发工程师写的脚本就行了,不会再在代码中加入python语句了。因为在Java语言中添加入其他语言,使Java的可读性下降、执行意义也不是很大。
2.2 在java中直接调用python脚本
这种方式是有些Java程序员使用调用。
(1)首先将准备好的脚本,如plus.py。
import sys
a = 100
b = 200
print(sys.version,a+b)
(2)创建java类JavaPythonFile
import org.python.util.PythonInterpreter;
public class JavaPythonFile {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PythonInterpreter interpreter = new PythonInterpreter();
//我在这里使用绝对路径
interpreter.execfile("D:\\processPython\\src\\main\\java\\plus.py");
}
}
输出如下:
('2.7.1 (default:0df7adb1b397, Jun 30 2017, 19:02:43)
[Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (Oracle Corporation)]', 300)
2.3 用Runtime.getRuntime()执行python脚本
这种办法可以让进程与程序交互,可以看到出现的问题,便于解决。
(1)首先将准备好的脚本,如plus.py。
a = 100
b = 200
print(a+b)
(2)创建java类RuntimeFunction
2.3.1 方式一系统默认python
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class RuntimeFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Process proc;
try {
proc = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("python D:\\processPython\\src\\main\\java\\plus.py");
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(proc.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
in.close();
proc.waitFor();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出如下
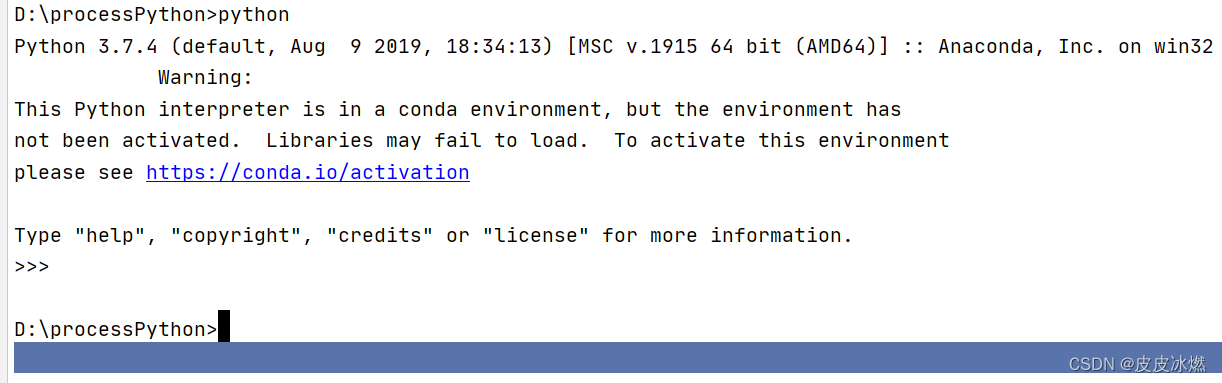
3.7.4 (default, Aug 9 2019, 18:34:13) [MSC v.1915 64 bit (AMD64)] 300
查看系统的python版本为3.7.4。
2.3.2 方式二指定python
String[] args1=new String[]{"/home/huan/anaconda2/bin/python","/home/huan/myfile/helloword.py"};
Process pr=Runtime.getRuntime().exec(args1);
附加:String数组里的那一行很重要。
首先一定要设置好你所使用的python的位置,切记不要直接使用python,因为系统会默认使用自带的python,所以一定要设置好你所使用的python的位置,否则可能会出现意想不到的问题(比如说我使用的是anaconda中的python,而ubuntu系统会默认调用自带的python,而我自带的python中并没有numpy库,所以会造成相应的代码不会执行的问题,所以设置好python的位置是很重要的)。还有就是要设置好py文件的位置,使用绝对路径。还有就是可以看出,此方法可以满足我们python代码中调用第三方库的情况,简单实用。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class RuntimeFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Process proc;
try {
String[] args1=new String[]{"D:\\Anaconda3\\envs\\python38\\python","D:\\processPython\\src\\main\\java\\plus.py"};
proc = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(args1);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(proc.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
in.close();
proc.waitFor();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
首先,为什么要创建Process proc。ProcessBuilder.start()和Runtime.exec两个方法会生成一个本地的进程,然后返回一个Processs子类的实例。通过这个实例可以控制进程以及获得关于进程的信息。这个Process类为进程提供可用于执行来自的输入的方法,然后执行输出到这个进程中,等待完成后,检查进程退出时的状态,然后停止这个进程。——换句话说,这个实例就是监视整个进程的。
通过Process的getInputStream(),getOutputStream()和getErrorStream()方法可以得到输入输出流,然后通过InputStream可以得到程序对控制台的输出信息,通过OutputStream可以给程序输入指令,这样就达到了程序的交换功能。
3 java处理json
如果使用的是maven,需要在pom.xml文件中加入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.78</version>
</dependency>
3.1 json字符串-简单对象
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
public class JavaJsonProcess {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//json字符串-简单对象
String jsonStr = "{\"studentName\":\"张三\",\"studentAge\":18}";
//简单对象
JSONObject jsonObj = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr);
System.out.println(jsonStr);
System.out.println(jsonObj);
}
}
3.2 json字符串-数组类型
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
public class JavaJsonProcess {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//json字符串-数组类型
String jsonArrStr = "[{\"studentName\":\"张三\",\"studentAge\":18},{\"studentName\":\"李四\",\"studentAge\":17}]";
//数组类型
JSONArray jsonArray = JSON.parseArray(jsonArrStr);
//遍历JSONArray方法1
for(int i = 0; i < jsonArray.size(); i++){
JSONObject jsonObj = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
System.out.println(jsonObj);
}
//遍历JSONArray方法2
for(Object obj : jsonArray){
JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) obj;
System.out.println(jsonObject);
}
}
}
3.3 json字符串-复杂对象
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
public class JavaJsonProcess {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//json字符串-复杂对象
String complexJsonStr= "{\"teacherName\":\"李寻欢\",\"teacherAge\":30,\"course\":{\"courseName\":\"武术\",\"code\":110},\"students\":[{\"studentName\":\"张三\",\"studentAge\":18},{\"studentName\":\"李四\",\"studentAge\":19}]}";
//复杂对象
JSONObject jsonObj = JSON.parseObject(complexJsonStr);
//取出复杂对象中各项内容
String teacherName = jsonObj.getString("teacherName");
Integer teacherAge = jsonObj.getInteger("teacherAge");
JSONObject course = jsonObj.getJSONObject("course");
JSONArray students = jsonObj.getJSONArray("students");
System.out.println(teacherName);
System.out.println(teacherAge);
System.out.println(course);
System.out.println(students);
}
}
输出如下:
李寻欢
30
{"courseName":"武术","code":110}
[{"studentAge":18,"studentName":"张三"},{"studentAge":19,"studentName":"李四"}]
4 方式一:传递json参数
用sys.argv接收参数。
4.1 依赖引用pom.xml
如果使用的是maven,需要在pom.xml文件中加入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.78</version>
</dependency>
4.2 配置文件pythonuse.properties
#python.path = python
python.path = D:\\Anaconda3\\envs\\python38\\python33
python.package = C:\\Users\\user\\Desktop\\aa_main.py
4.3 代码RuntimeFunction.java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Properties;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
public class RuntimeFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Process proc;
try {
//通过java反射机制获取配置文件
InputStream is = RuntimeFunction.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("pythonuse.properties");
Properties pro = new Properties();
try {
pro.load(is);
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
String pythonpath = pro.getProperty("python.path");
String pythonpackage = pro.getProperty("python.package");
//json字符串-简单对象
String jsonStr = "{\"name\":\"张三\",\"time\":\"2022-12-10 16:16:45.256\",\"age\":18}";
System.out.println(jsonStr);
//简单对象
JSONObject jsonObj = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr);
//简单对象转换为字符串
String re_str = jsonObj.toJSONString();
System.out.println(re_str);
//将“替换成\"
re_str = re_str.replaceAll("\"","\\\\\"");
System.out.println(re_str);
//String[] args1=new String[]{"D:\\Anaconda3\\envs\\python38\\python","C:\\Users\\user\\Desktop\\aa_main.py",re_str};
String[] args1=new String[]{pythonpath,pythonpackage,re_str};
//System.out.println(args1);
proc = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(args1);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(proc.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
JSONObject jsonObj1 = JSON.parseObject(line);
System.out.println(jsonObj1);
}
in.close();
proc.waitFor();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4.4 代码aa_main.py
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import sys
import json
import sys
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1 当作命令行参数,容易出现时间戳中的空格,被拆分成了多个参数
receive_msg = " ".join(sys.argv[1:]) # 用空格把分隔的参数合并起来
# 2 解析
receive_dict = json.loads(receive_msg)
# print(receive_dict["name"],receive_dict["age"],receive_dict["time"])
out_dict = {
"接收到":receive_dict
}
# 3 序列化
msg = json.dumps(out_dict)
msg = msg.replace('"','\"')
print(msg)
4.5 打包和运行
(1)打包后会自动将配置文件加载到与类文件同一级目录
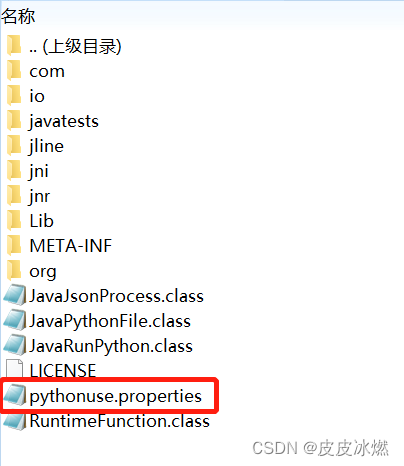
(2)执行命令
java -cp processPython.jar RuntimeFunction main

5 方式二:传递json参数
将json参数传递到控制台的命令行。
5.1 代码RuntimeFunction.java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Properties;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
public class RuntimeFunction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Process proc;
try {
//通过java反射机制获取配置文件
InputStream is = RuntimeFunction.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("pythonuse.properties");
Properties pro = new Properties();
try {
pro.load(is);
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
String pythonpath = pro.getProperty("python.path");
String pythonpackage = pro.getProperty("python.package");
//json字符串-简单对象
String jsonStr = "{\"name\":\"张三\",\"time\":\"2022-12-10 16:16:45.256\",\"age\":18}";
System.out.println(jsonStr);
//简单对象
JSONObject jsonObj = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr);
//简单对象转换为字符串
String re_str = jsonObj.toJSONString();
System.out.println(re_str);
//String[] args1=new String[]{"D:\\Anaconda3\\envs\\python38\\python","C:\\Users\\user\\Desktop\\aa_main.py",re_str};
String[] args1=new String[]{pythonpath,pythonpackage};
proc = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(args1);
// 向控制台的命令行中写入参数
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(proc.getOutputStream());
ps.print(re_str);
ps.flush();
ps.close();
// 从控制台的命令行读取返回的参数
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(proc.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
JSONObject jsonObj1 = JSON.parseObject(line);
System.out.println(jsonObj1);
}
in.close();
proc.waitFor();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
5.2 代码aa_main.py
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import sys
import json
import sys
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 方式二:直接从命令行
x = sys.stdin
for line in x:
# 2 解析
receive_dict = json.loads(line)
# print(receive_dict["name"],receive_dict["age"],receive_dict["time"])
out_dict = {
"接收到":receive_dict
}
# 3 序列化
msg = json.dumps(out_dict,ensure_ascii=False)
print(msg)
break
6 打包运行
6.1 打包
1.file ---> project structure --->Artifacts--->+ --->JAR--->
From modules with dependencies...---> Main class(选择启动类)--->
OK--->apply --->OK
2.build ---> build Artifacts--->xxx.jar ---> build
6.2 运行
直接通过命令指定运行,运行时指定的main方法:
java -cp huobi-client.jar com.huobi.start.LoadPrice main

![[前端笔记——CSS] 10.层叠与继承+选择器](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fbbfd08c59d4420d9bb683ae6779cad2.png)