一 inventory 主机清单
Inventory支持对主机进行分组,每个组内可以定义多个主机,每个主机都可以定义在任何一个或
多个主机组内。
如果是名称类似的主机,可以使用列表的方式标识各个主机。
vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[webservers]
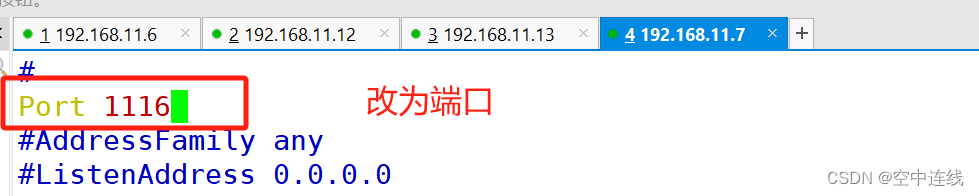
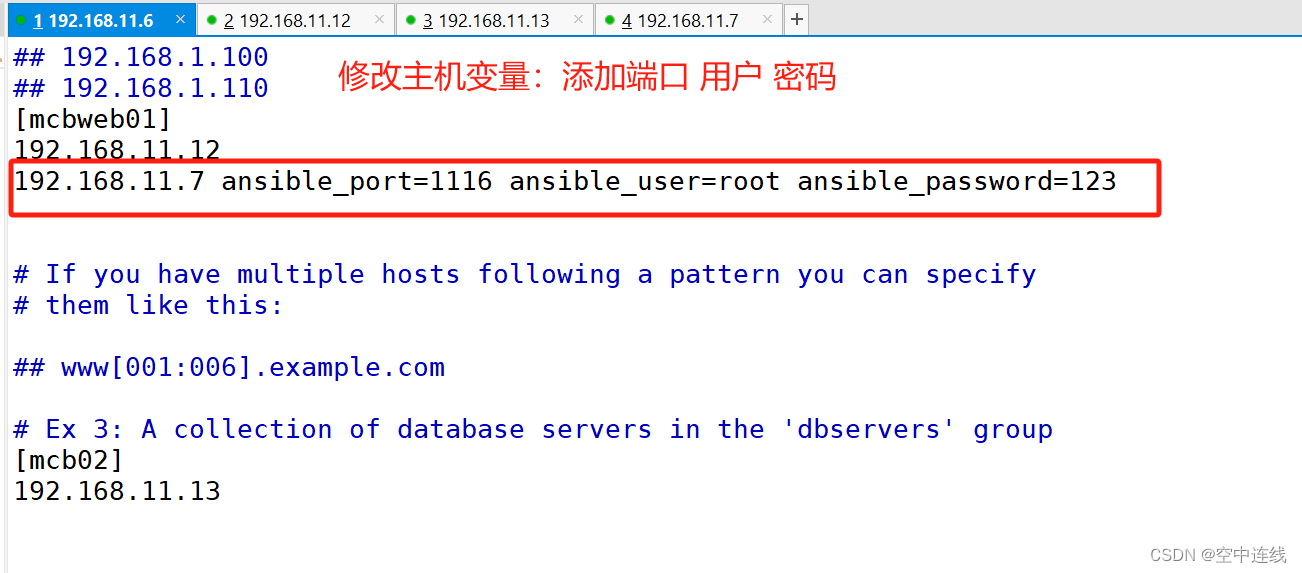
192.168.10.14:2222 #冒号后定义远程连接端口,默认是 ssh 的 22 端口
192.168.10.1[2:5]
[dbservers]
db-[a:f].example.org #支持匹配 a~finventory 中变量
Inventory变量名 含义
ansible_host ansible连接节点时的IP地址
ansible_port 连接对方的端口号,ssh连接时默认为22
ansible_user 连接对方主机时使用的主机名。不指定时,将使用执行ansible或ansible-playbook命令的用户
ansible_password 连接时的用户的ssh密码,仅在未使用密钥对验证的情况下有效
ansible_ssh_private_key_file 指定密钥认证ssh连接时的私钥文件
ansible_ssh_common_args 提供给ssh、sftp、scp命令的额外参数
ansible_become 允许进行权限提升
ansible_become_method 指定提升权限的方式,例如可使用sudo/su/runas等方式
ansible_become_user 提升为哪个用户的权限,默认提升为root
ansible_become_password 提升为指定用户权限时的密码环境准备:
| 192.168.11.6 | |||
| 192.168.11.12 | |||
| 192.168.11.13 | |||
| 192.168.11.7 |
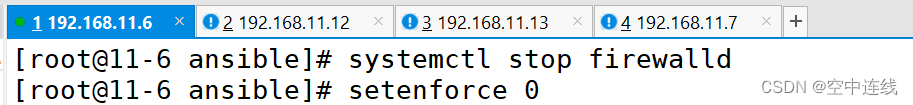
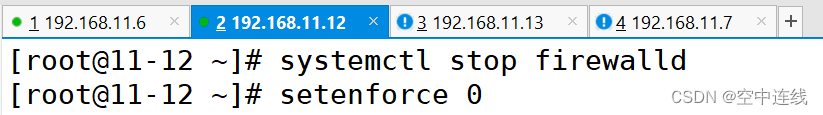
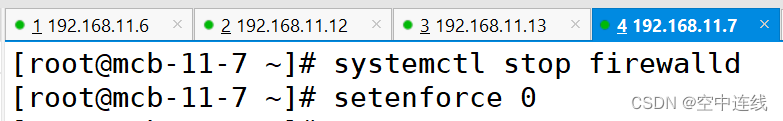
关闭 防火墙 防护

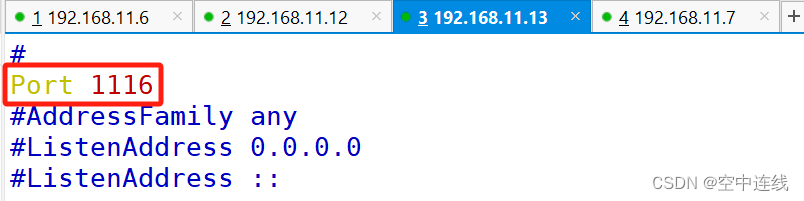
实验 1 :修改端口
连接对方端口号
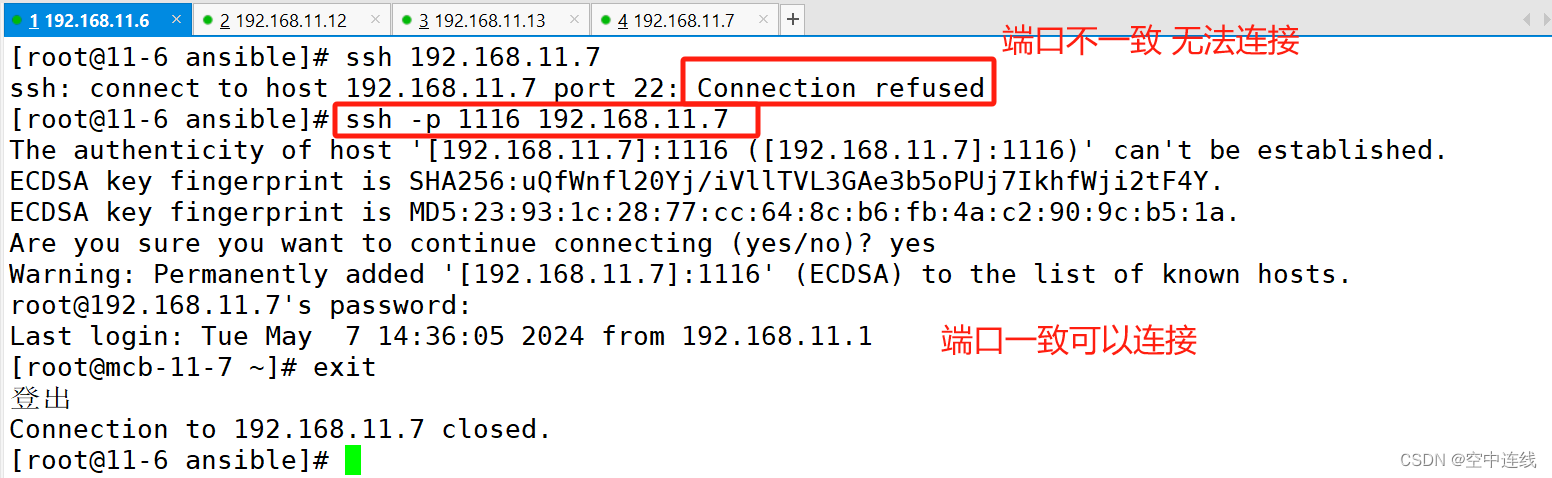
[root@11-6 ansible]# vim hosts
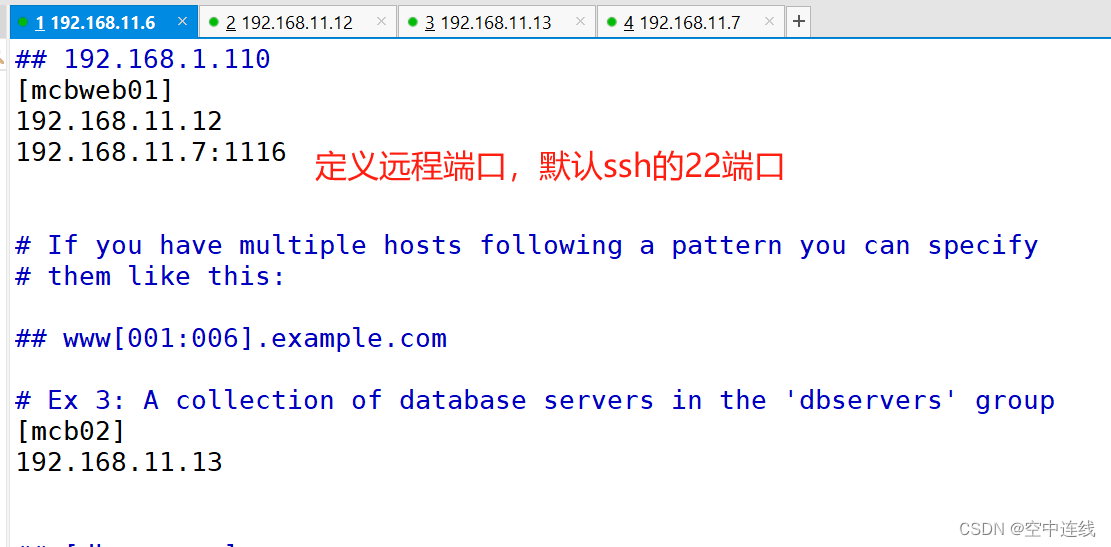
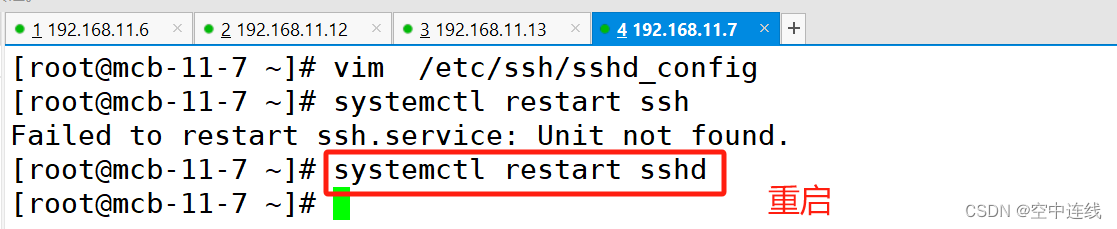
[root@mcb-11-7 ~]# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
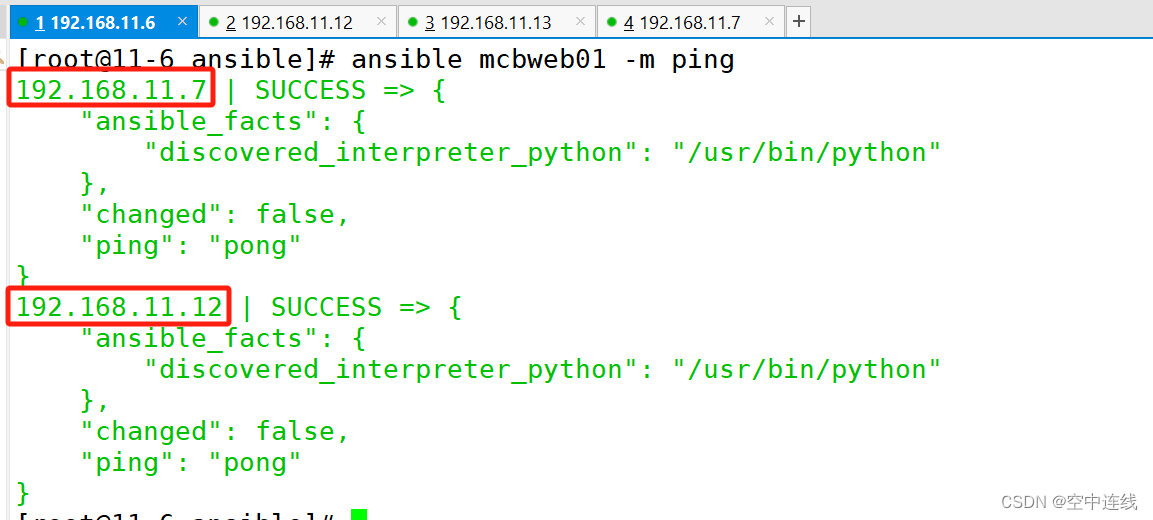
验证一下:
实验 2 :连接端口另一个写法
[webservers]
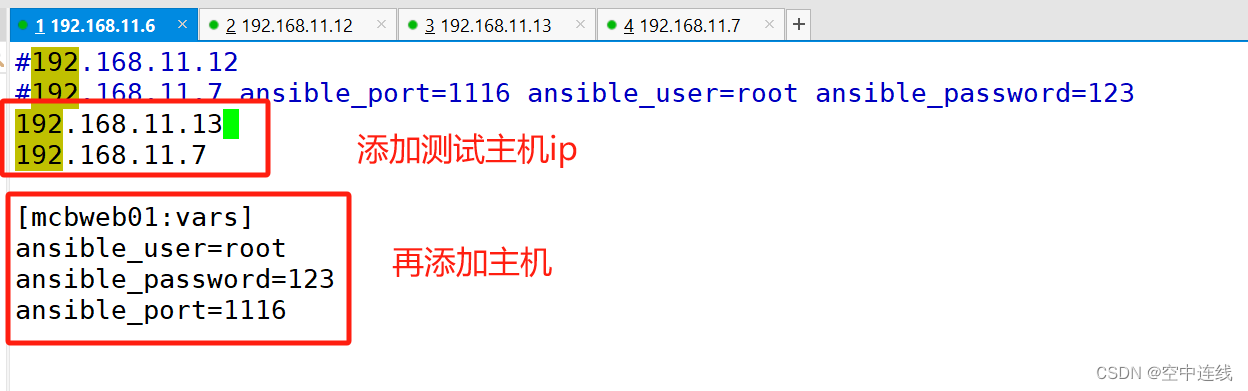
192.168.11.16 ansible_port=22 ansible_user=root ansible_password=abc1234
#加端口 加用户 加密码[root@11-6 ansible]# vim hosts
检测一下:
2 组变量
[webservers:vars] #表示为 webservers 组内所有主机定义变量
ansible_user=root
ansible_password=abc1234
[all:vars] #表示为所有组内的所有主机定义变量
ansible_port=22[root@11-6 ansible]# vim hosts
3 组嵌套
[root@11-6 ansible]# vim hosts
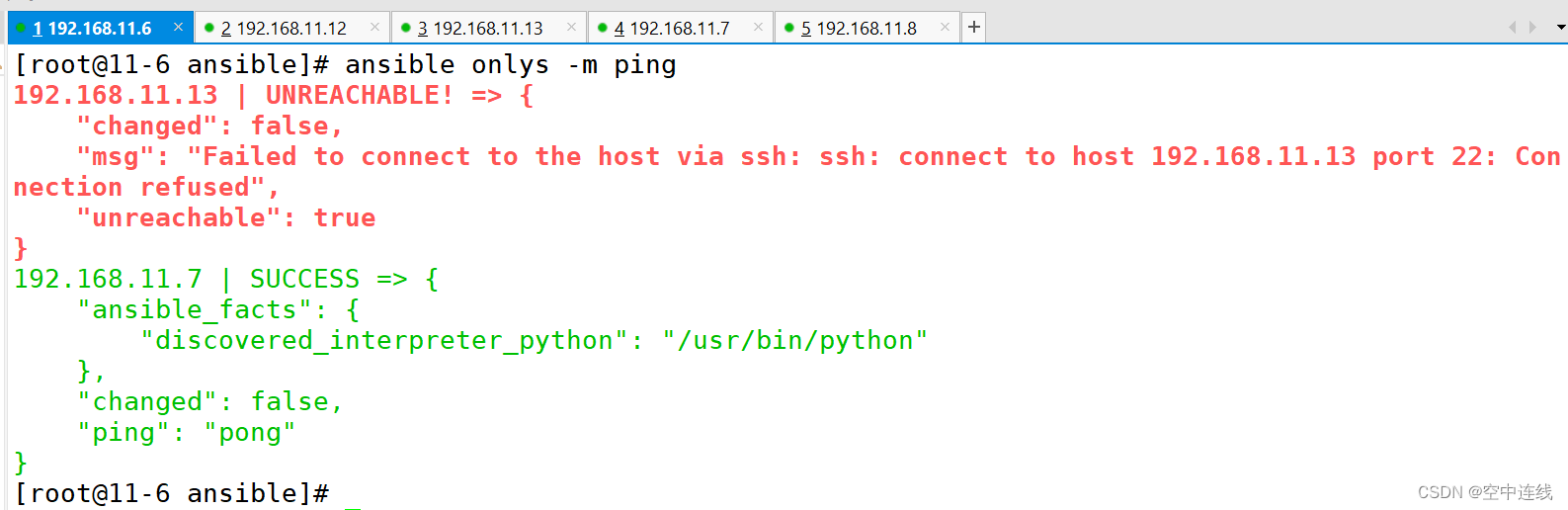
[root@11-6 ansible]# ansible onlys -m ping
检测错误:
二 Ansible 的脚本 --- playbook 剧本
1 playbooks 本身由以下各部分组成
(1)Tasks:任务,即通过 task 调用 ansible 的模板将多个操作组织在一个 playbook 中运行
(2)Variables:变量
(3)Templates:模板
(4)Handlers:处理器,当changed状态条件满足时,(notify)触发执行的操作
(5)Roles:角色2 示例:
常用属性:
vim test1.yaml --- #yaml文件以---开头,以表明这是一个yaml文件,可省略
name: first play #定义一个play的名称,可省略
gather_facts: false #设置不进行facts信息收集,这可以加快执行速度,可省略
hosts: webservers #指定要执行任务的被管理主机组,如多个主机组用冒号分隔
remote_user: root #指定被管理主机上执行任务的用户
tasks: #定义任务列表,任务列表中的各任务按次序逐个在hosts中指定的主机上执行编辑剧本:
name: test connection #自定义任务名称
ping: #使用 module: [options] 格式来定义一个任务
name: disable selinux
command: '/sbin/setenforce 0' #command模块和shell模块无需使用key=value格式
ignore_errors: True #如执行命令的返回值不为0,就会报错,tasks停止,可使用ignore_errors忽
略失败的任务
name: disable firewalld service: name=firewalld state=stopped #使用 module: options 格式来定义
任务,option使用key=value格式
name: install httpd yum: name=httpd state=latest
name: install configuration file for httpd copy: src=/opt/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
#这里需要一个事先准备好的/opt/httpd.conf文件 notify: "restart httpd" #如以上操作后为changed的
状态时,会通过notify指定的名称触发对应名称的handlers操作
name: start httpd service service: enabled=true name=httpd state=started handlers: #handlers中
定义的就是任务,此处handlers中的任务使用的是service模块
name: restart httpd #notify和handlers中任务的名称必须一致 service: name=httpd state=restarted
##Ansible在执行完某个任务之后并不会立即去执行对应的handler,而是在当前play中所有普通任
务都执行完后再去执行handler,这样的好处是可以多次触发notify,但最后只执行一次对应的
handler,从而避免多次重启。注意:
每一个名字就是一个模块
3 实验:
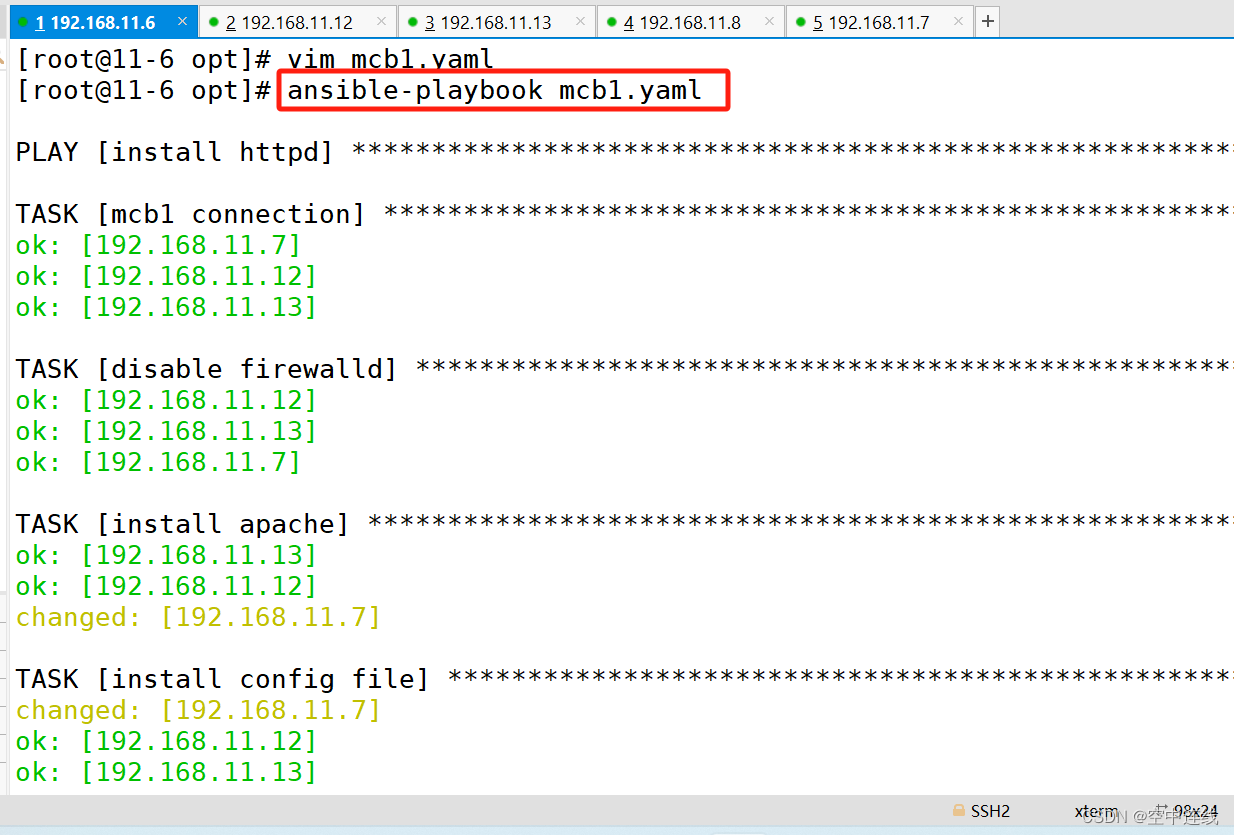
[root@11-6 opt]# vim mcb1.yaml
---
- name: install httpd
gather_facts: all
hosts: mcbweb01
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: mcb1 connection
ping:
- name: disable firewalld
service: name=firewalld state=stopped
- name: install apache
yum: name=httpd state=latest
- name: install config file
copy: src=/opt/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: "restart httpd"
- name: start httpd service
service: enabled=true name=httpd state=started
handlers:
- name: "restart httpd"
service: name=httpd state=restarted
运行playbook
ansible-playbook test1.yaml
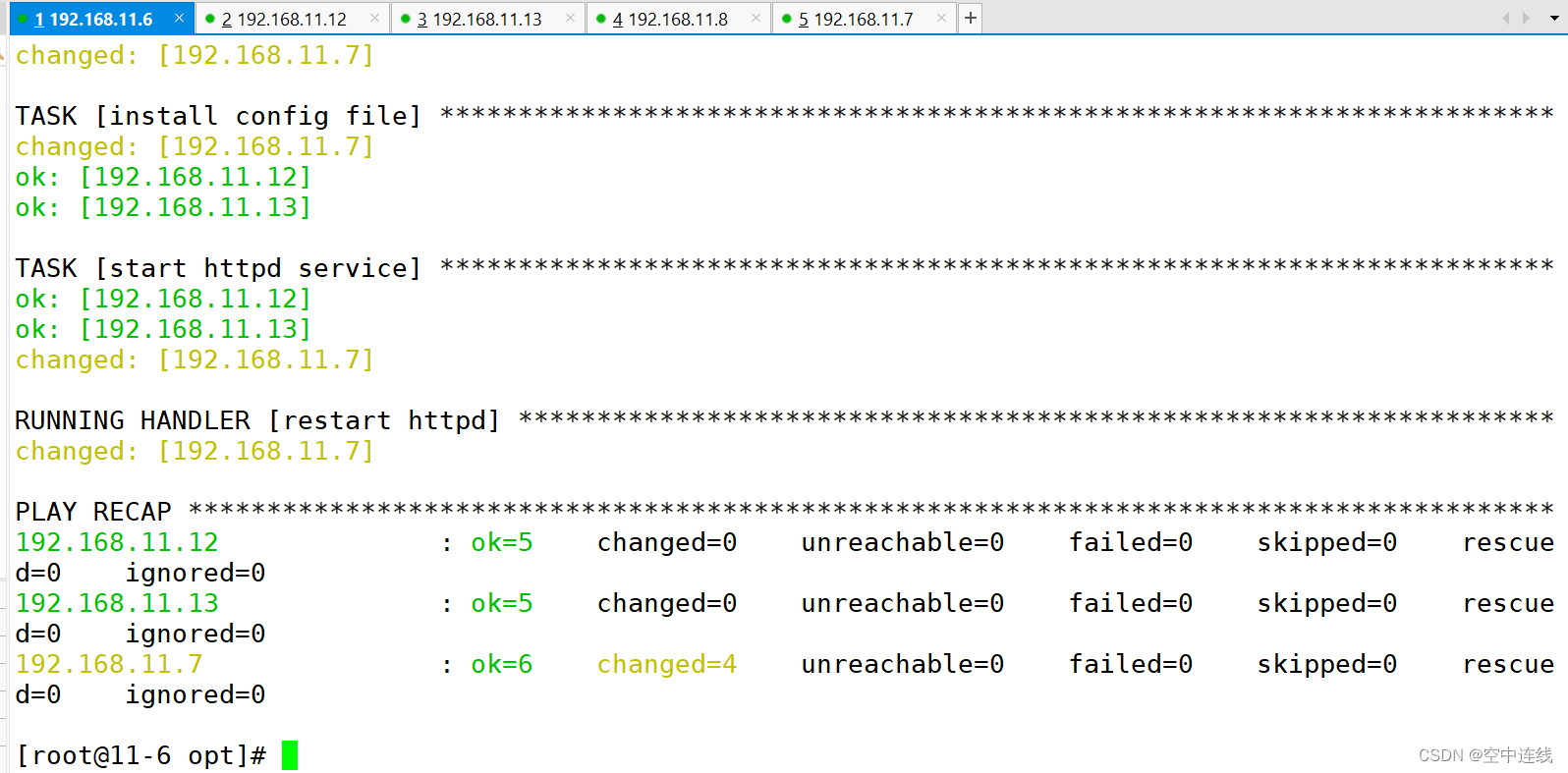
错误分析:
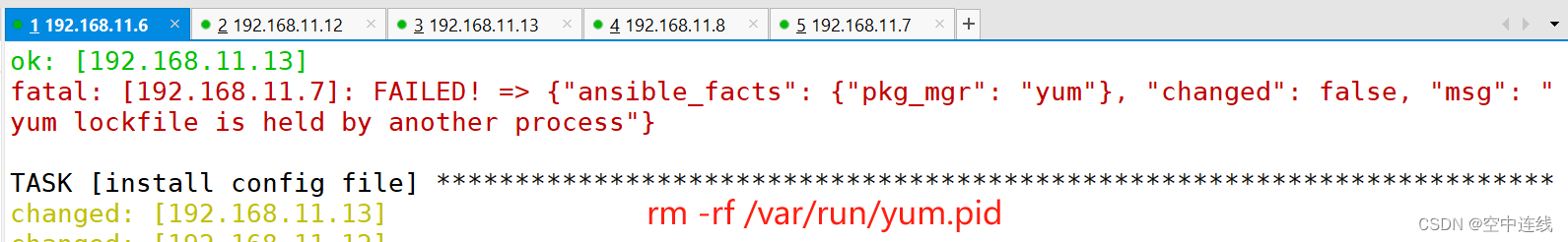
补充参数:
-k(–ask-pass):用来交互输入ssh密码
-K(-ask-become-pass):用来交互输入sudo密码
-u:指定用户 ansible-playbook test1.yaml --syntax-check
#检查yaml文件的语法是否正确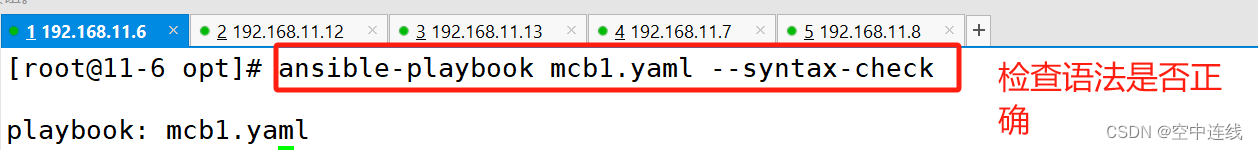
②ansible-playbook test1.yaml --list-task
#检查tasks任务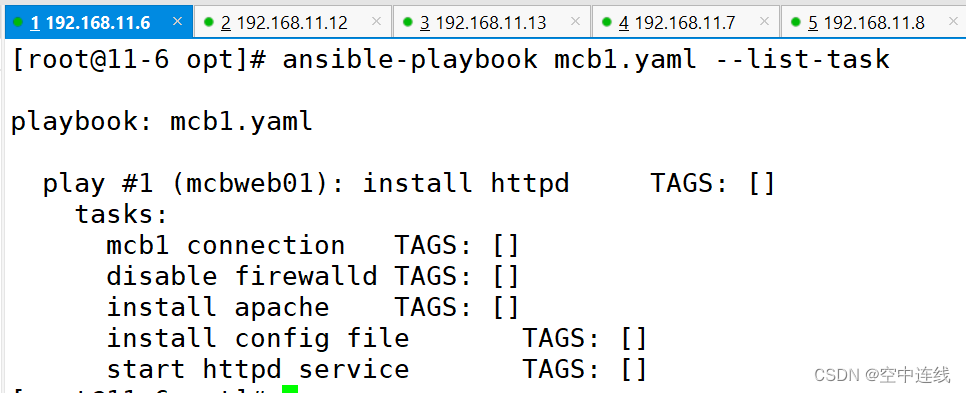
ansible-playbook test1.yaml --list-hosts
检查生效的主机
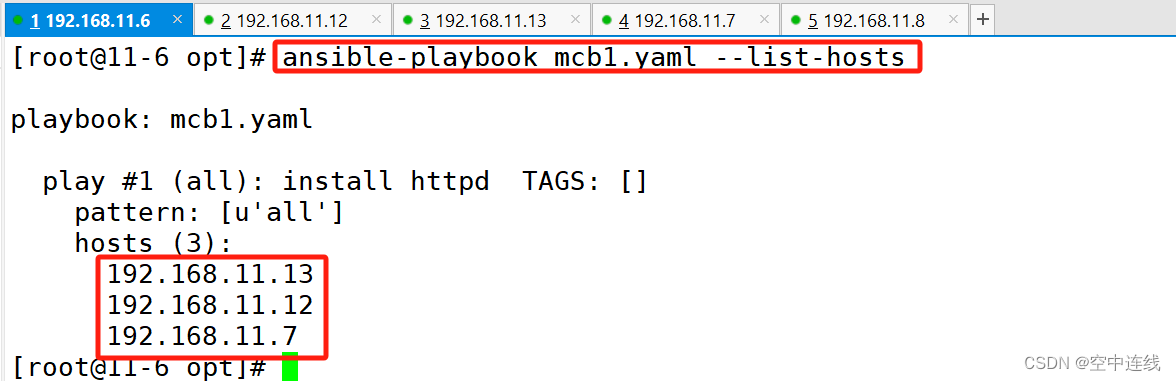
ansible-playbook mcb1.yaml --start-at-task='install apache'
指定从某个task开始运行主机检测一下:

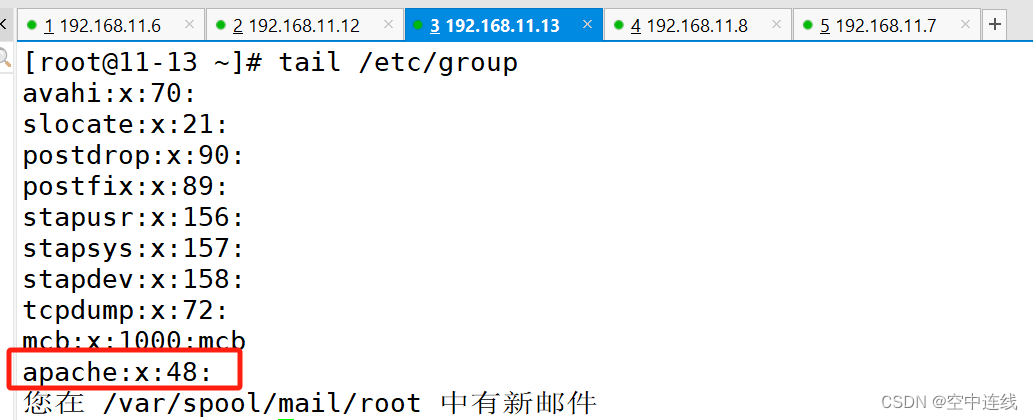

三 定义、引用变量
[root@11-6 opt]# vim mcb2.yaml---
- name: yin yong bianliang
hosts: mcb02
remote_user: root
vars:
- groupname: ky38
- username: nginx
tasks:
- name: create group
group: name={{groupname}} system=yes gid=305
- name: create user
user: name={{username}} uid=305 group={{groupname}}
- name: copy file
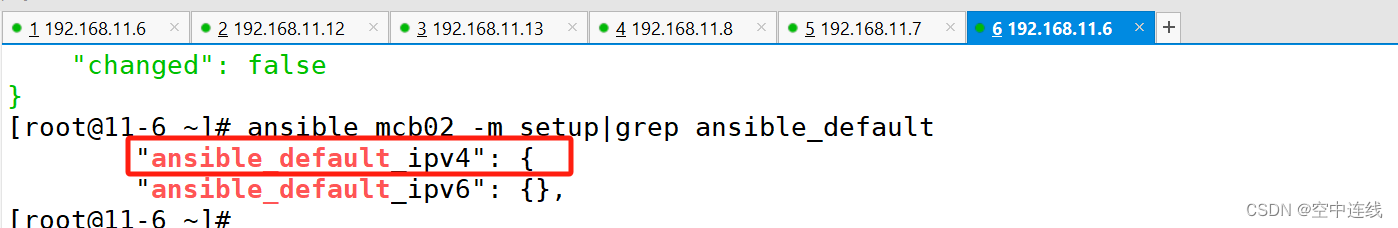
copy: content="{{ansible_default_ipv4}}" dest=/opt/ky38.txt

在命令行里定义变量
[root@11-6 opt]# ansible-playbook mcb2.yaml -e "mcb"
检测:
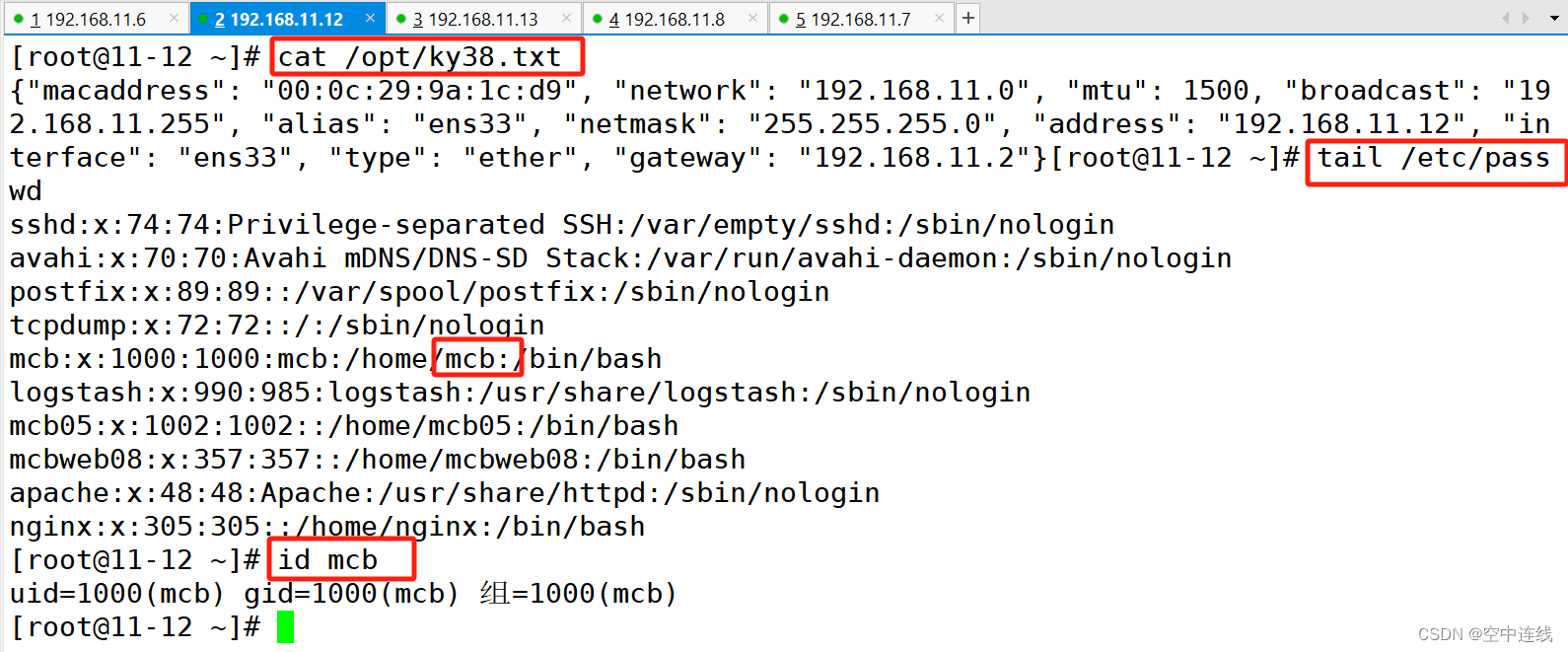
报错信息:
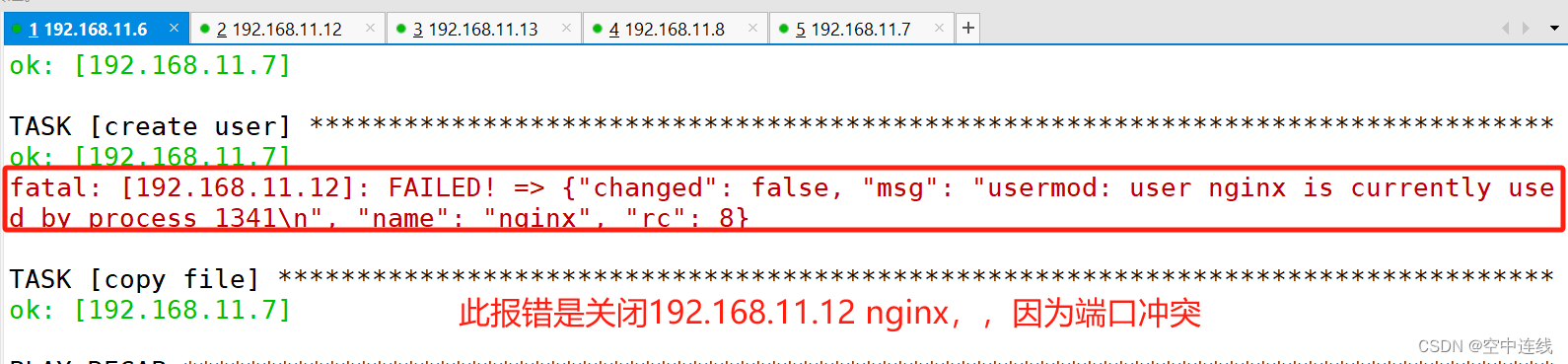
 四 指定远程主机sudo切换用户
四 指定远程主机sudo切换用户
hosts: dbservers
remote_user: zhangsan
become: yes #2.6版本以后的参数,之前是sudo,意思为切换用户运行
become_user: root #指定sudo用户为root
执行playbook时:ansible-playbook test1.yml -K <密码>
五 when条件判断
在Ansible中,提供的唯一一个通用的条件判断是when指令,当when指令的值为
true时,则该任务执行,否则不执行该任务。
when一个比较常见的应用场景是实现跳过某个主机不执行任务或者只有满足条件的主机执行任务
---
- name: restart host
hosts: mcbweb01
remote_user: root
tasks:
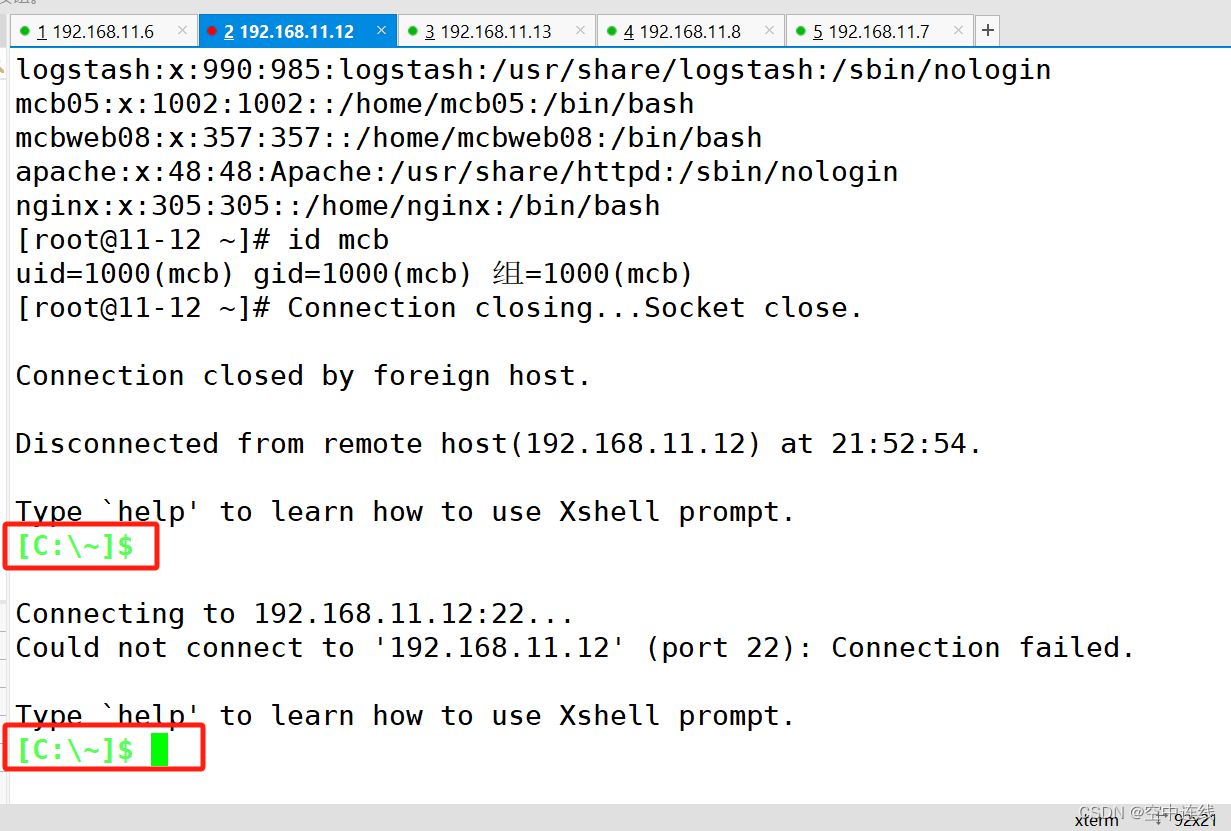
- name: shutdown host
command: /sbin/shutdown -r now
when: ansible_default_ipv4.address == "192.168.11.12"
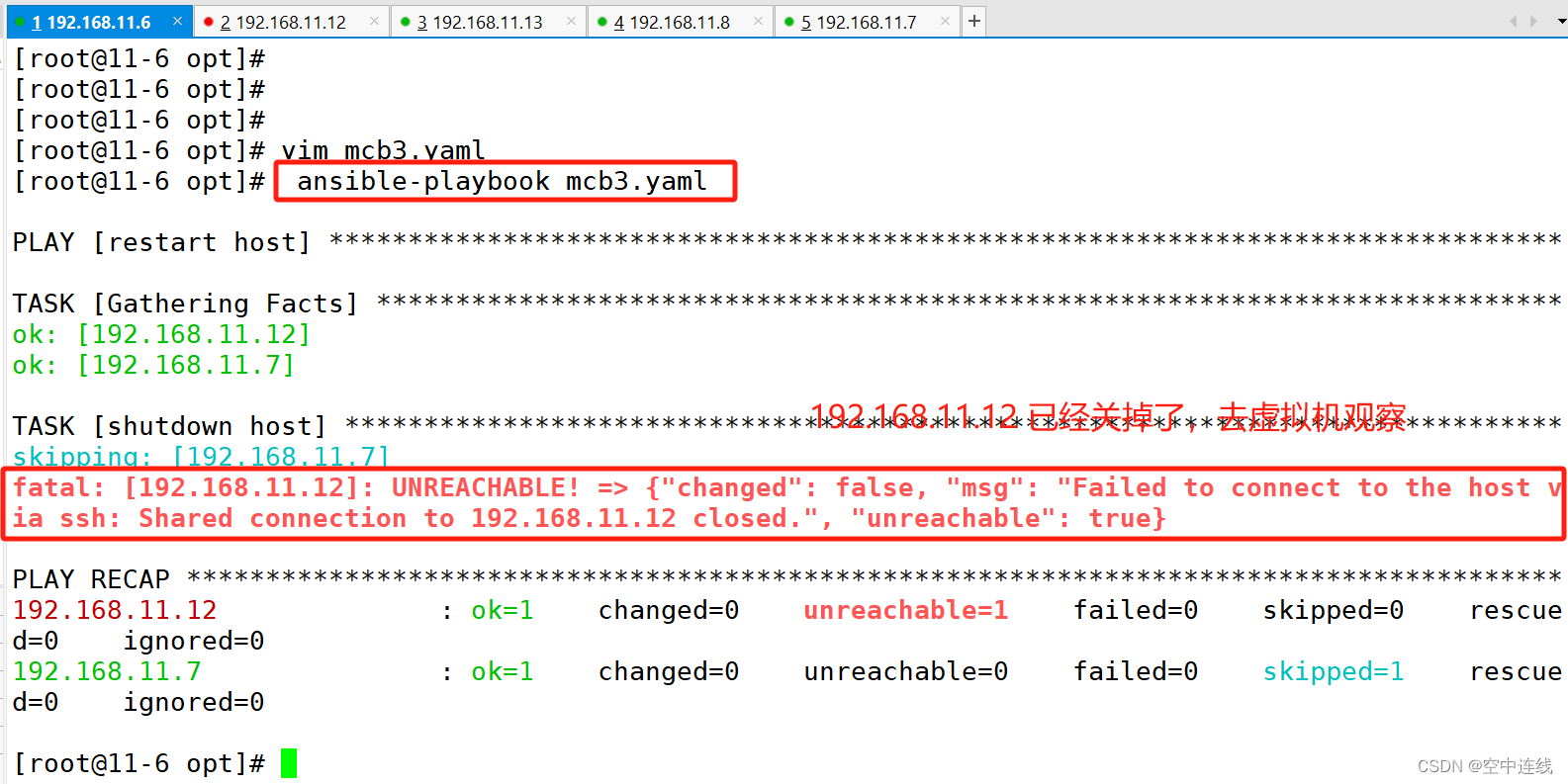 查看结果:
查看结果:
 六 迭代
六 迭代
Ansible提供了很多种循环结构,一般都命名为with_items,作用等同于 loop 循环。
实验 1:
[root@11-6 opt]# vim mcb4.yaml
---
- name: mcb4
hosts: mcbweb01
tasks:
- name: create dir
file: path={{item}} state=directory
with_items:
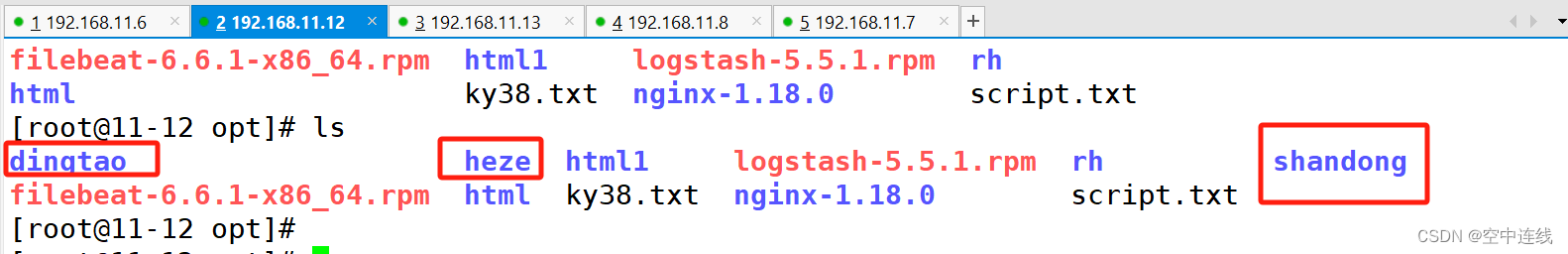
- /opt/heze
- /opt/dingtao
- /opt/shandong
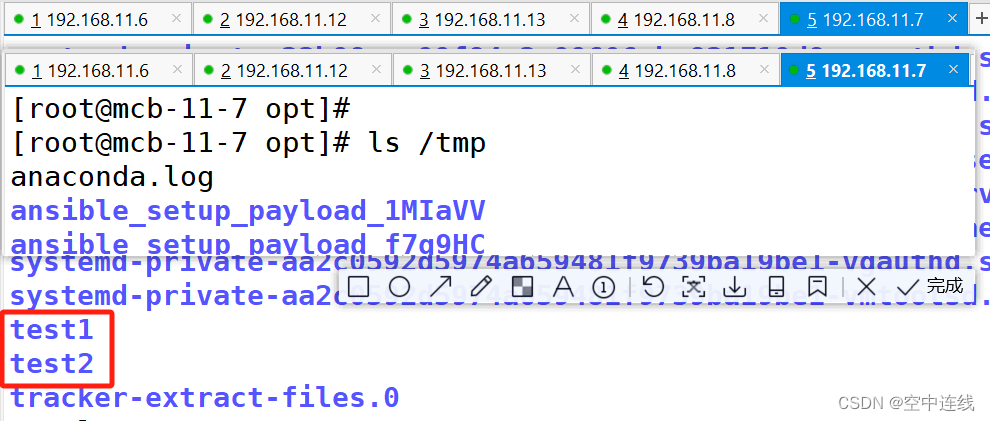
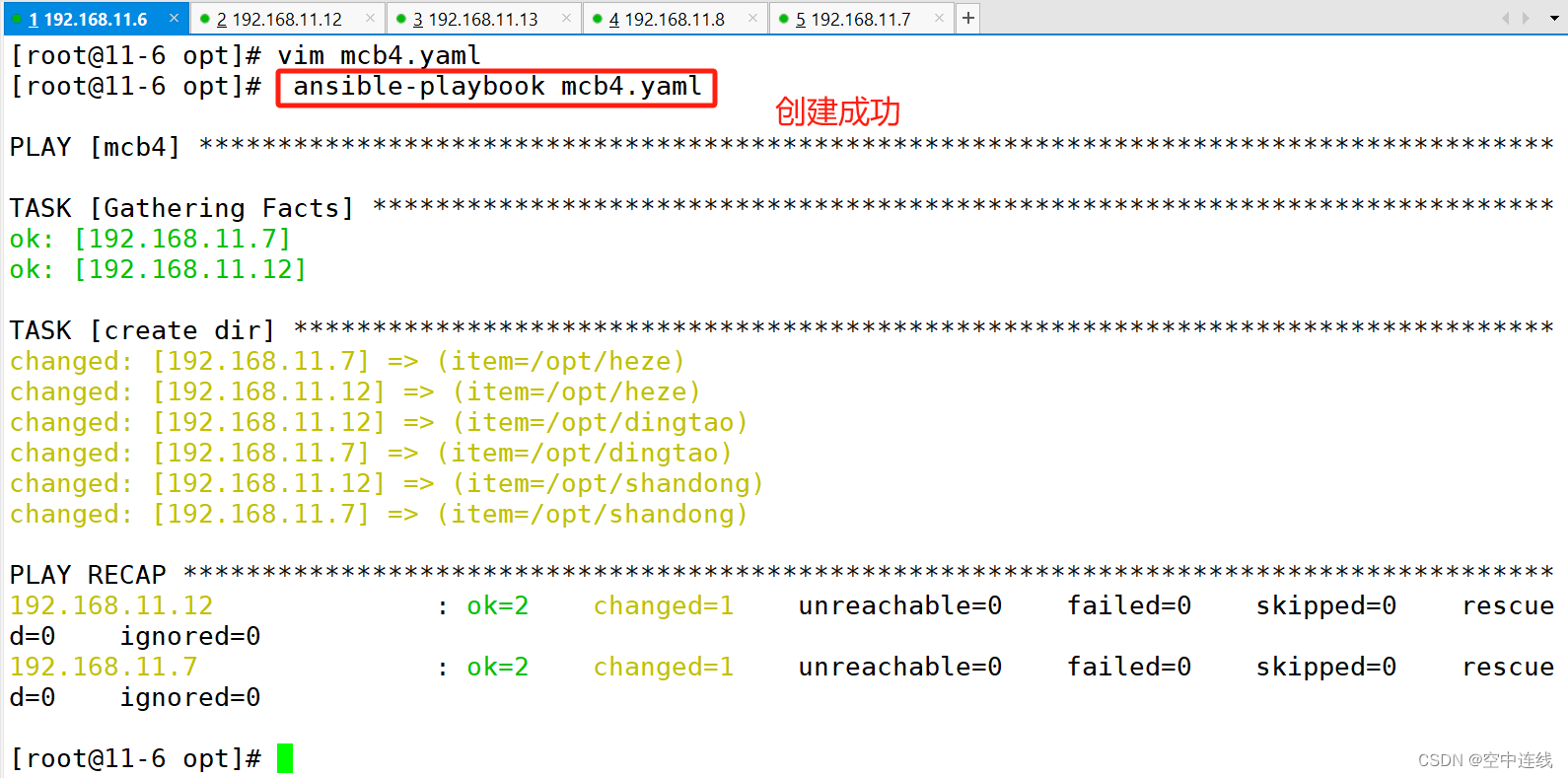 检测一下:
检测一下:
实验 2:
---
- name: play1
hosts: mcbweb01
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: create directories
file:
path: "{{item}}"
state: directory
with_items:
- /tmp/test1
- /tmp/test2
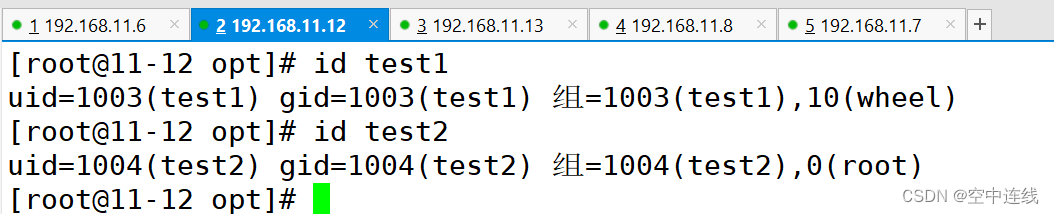
- name: add users
user: name={{item.name}} state=present groups={{item.groups}}
with_items:
- name: test1
groups: wheel
- name: test2
groups: root
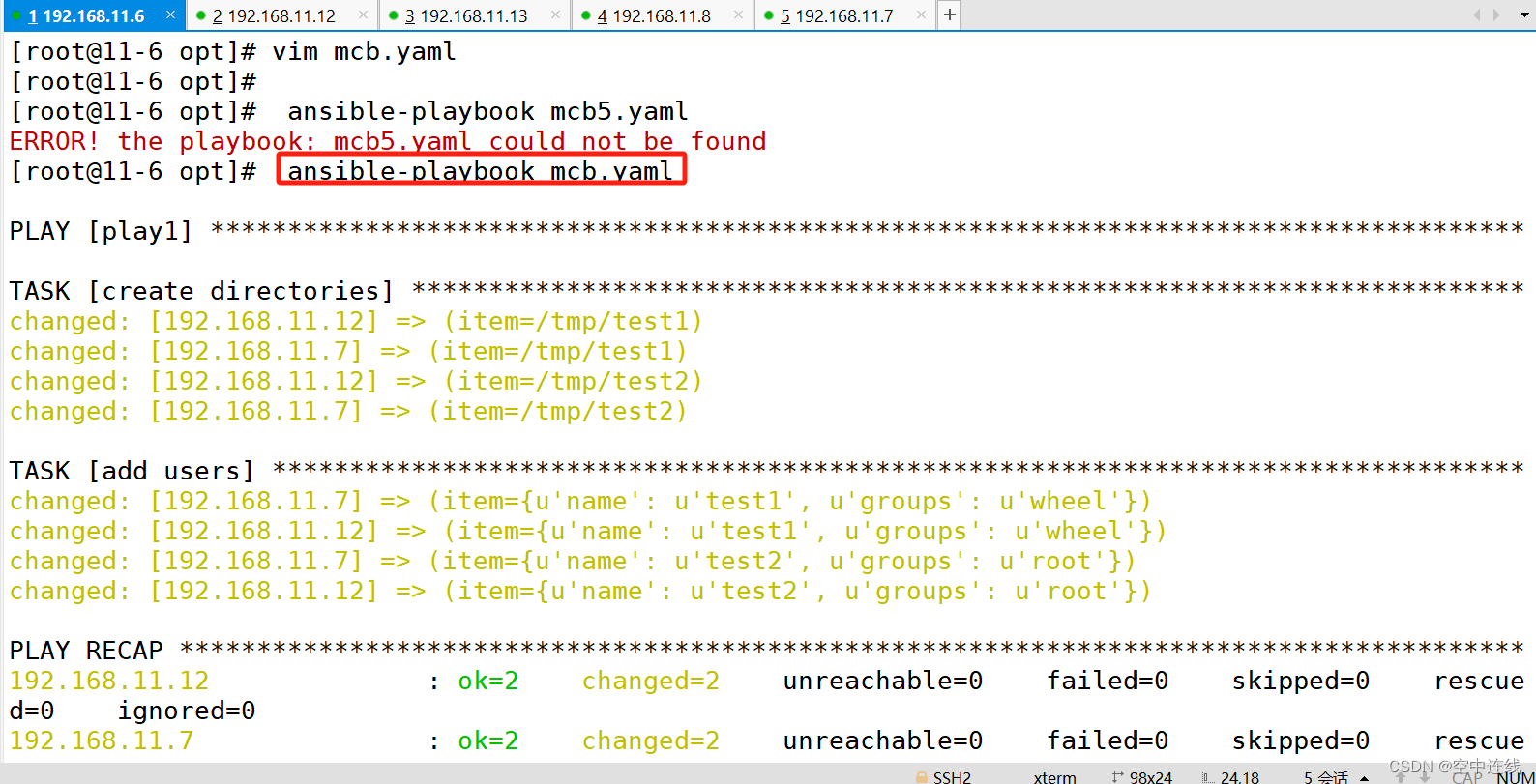 检测一下:
检测一下: