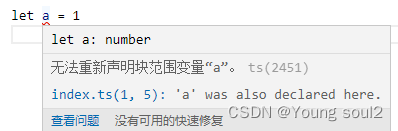
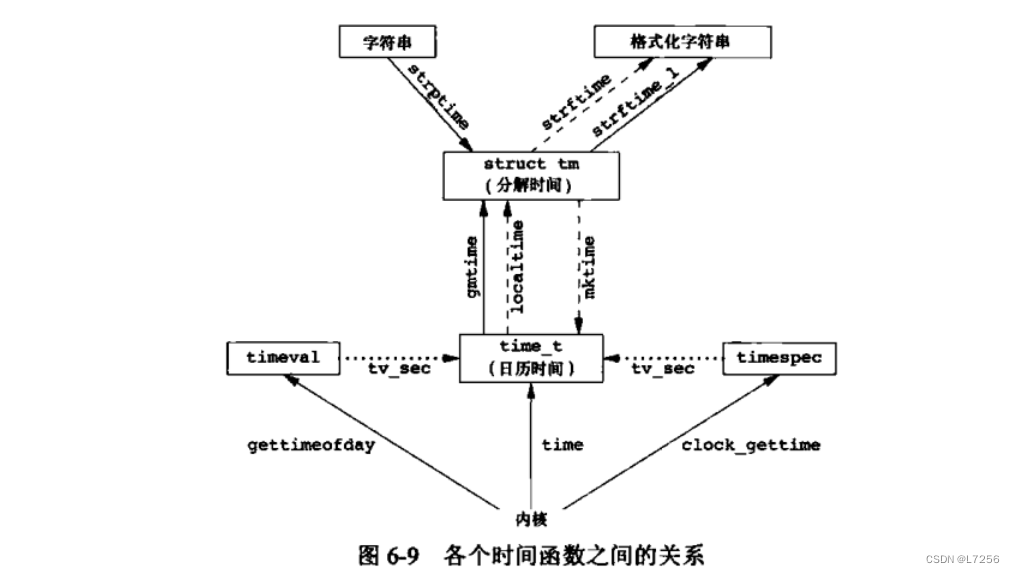
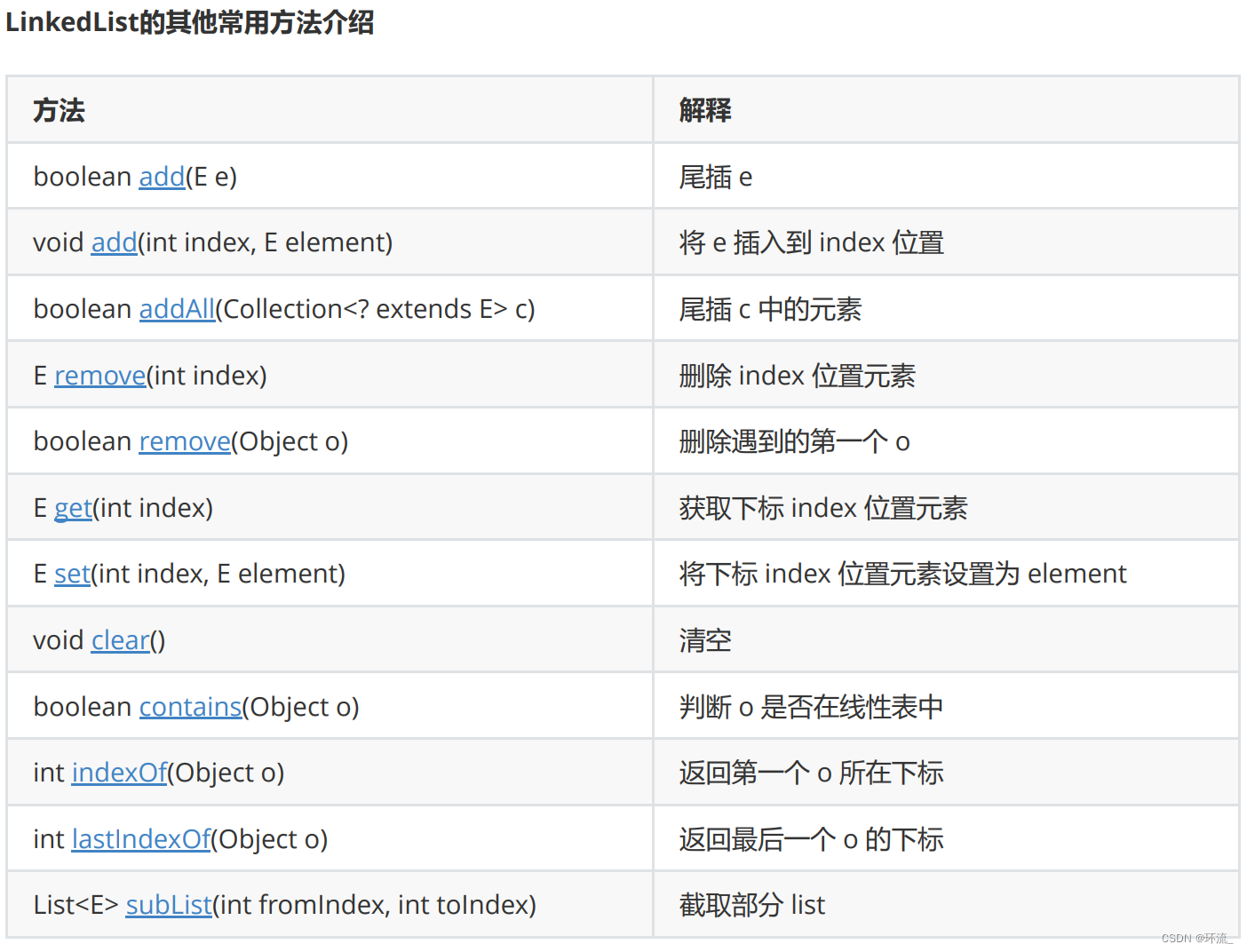
单链表
邻接表用的多 存储树和图 new()速度慢 数组模拟
模板
-1代表头节点
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
// head存储链表头
//e[]存储节点的值
//ne[]存储节点的next指针
//idx表示当前用到了哪个节点
int head, e[N], ne[N], idx;
// 初始化
void init()
{
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
// 将a插到链表头
void add_to_head(int a)
{
e[idx] = a, ne[idx] = head, head = idx ++ ;
}
//将x插入到下标是k的点的后面
void add(int k, int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx;
idx++;
}
//将下标是k的点后面的点删掉
void remove(int k)
{
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
// 将头结点删除,需要保证头结点存在
void remove()
{
head = ne[head];
}
0代表头节点
const int N = 100010;
// 0表示头节点 使得所有节点操作一致 不用考虑是否为头节点或尾结点
// ne[0] 表示第一个节点
int e[N], ne[N], idx = 1;
void insert(int k, int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx++;
}
void remove(int k, int x)
{
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
单链表
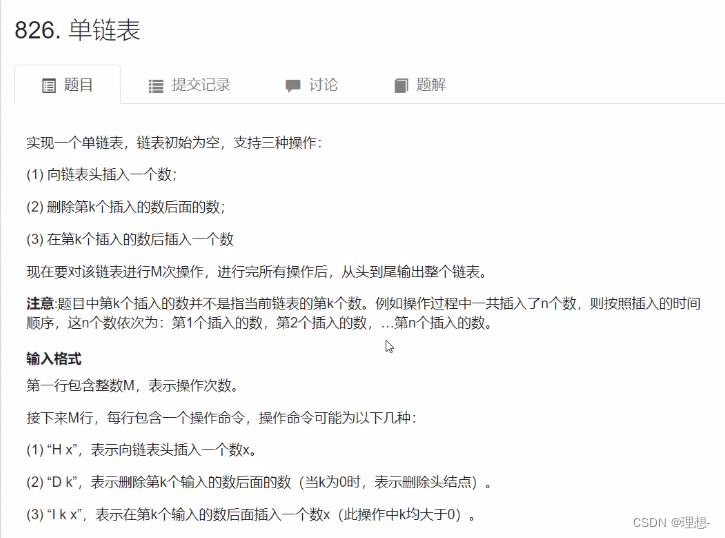
代码
-1代表头节点
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int head, e[N], ne[N], idx;
void init()
{
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
//头插
void add_to_head(int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = head;
head = idx++;
}
void remove(int k)
{
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
void insert(int k, int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx++;
}
int main()
{
int m;
cin >> m;
init();
while (m--)
{
char op;
int k, x;
cin >> op;
if (op == 'H')
{
cin >> x;
add_to_head(x);
}
else if (op == 'D')
{
cin >> k;
if (!k) head = ne[head];
else remove(k - 1);
}
else
{
cin >> k >> x;
insert(k - 1, x);
}
}
for (int i = head; i != - 1; i = ne[i]) cout << e[i] << ' ';
return 0;
}
0代表头节点
即使是一个字符 也建议用数组来存 忽略空格换行的影响
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
// 0表示头节点 使得所有节点操作一致 不用考虑是否为头节点或尾结点
// ne[0] 表示第一个节点
int e[N], ne[N], idx = 1;
void insert(int k, int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx++;
}
void remove(int k)
{
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
int main()
{
int m;
scanf("%d", &m);
//即使是一个字符 也建议用数组来存 忽略空格换行的影响
char op[2];
int k, x;
while (m--)
{
scanf("%s", op);
if (op[0] == 'H')
{
scanf("%d", &x);
insert(0, x);
}
else if (op[0] == 'D')
{
scanf("%d", &k);
remove(k);
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d", &k, &x);
insert(k, x);
}
}
for (int i = ne[0]; i != 0; i = ne[i]) printf("%d ", e[i]);
return 0;
}
双链表
模板
const int N = 100010;
int e[N], l[N], r[N], idx;
// 初始化 0头节点 1尾节点
void init()
{
r[0] = 1, l[1] = 0, idx = 2;
}
// 下标是k的右边插入一个
void add(int k, x)
{
e[idx] = x;
l[idx] = k;
r[idx] = r[k];
l[r[k]] = idx;
r[k] = idx++;
}
//删除第k个
void remove(int k)
{
r[l[k]] = r[k];
l[r[k]] = l[k];
}

- 之所以在 “D”, “IL”, “IR” 要用 k+1 的原因是 双链表的起始点是2. 所以,每个插入位置k的真实位置应该为 k-1+2 = k+1 (在单链表中为 k-1)。
- 0, 1 节点的作用是边界。0为左边界,1为右边界。他俩在这里有点类似保留字的作用。正因如此,我们的idx也是从2开始
- 最后遍历输出结果的
for (int i = r[0]; i != 1; i = r[i])。从r[0]开始是因为 0 为左边界,而终止条件 i==1是因为1为右边界(如果碰到,说明已经遍历完毕)
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100005;
int idx, e[N], l[N], r[N];
void insert(int k, int x)
{
e[idx] = x;
r[idx] = r[k];
l[idx] = k;
l[r[k]] = idx;
r[k] = idx++;
}
void remove(int k)
{
l[r[k]] = l[k];
r[l[k]] = r[k];
}
int main()
{
r[0] = 1, l[1] = 0, idx = 2;
cin >> m;
while (m--)
{
string op;
int k, x;
cin >> op;
if (op == "L") cin >> x, insert(0, x);
else if (op == "R") cin >> x, insert(l[1], x);
else if (op == "D") cin >> k, remove(k + 1);
else if (op == "IL") cin >> k >> x, insert(l[k + 1], x);
else cin >> k >> x, insert(k + 1, x);
}
for (int i = r[0]; i != 1; i = r[i])
cout << e[i] << ' ';
return 0;
}
栈
模板
// tt表示栈顶
int stk[N], tt = 0;
// 向栈顶插入一个数
stk[ ++ tt] = x;
// 从栈顶弹出一个数
tt -- ;
// 栈顶的值
stk[tt];
// 判断栈是否为空
if (tt > 0) not empty
{
}
模拟栈

代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int top, stk[N];
int main()
{
string op;
int m, x;
cin >> m;
while (m--)
{
cin >> op;
if (op == "push") cin >> x, stk[++top] = x;
else if (op == "pop") top--;
else if (op == "empty") cout << (top > 0 ? "NO" : "YES") << endl;
else cout << stk[top] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
表达式求值
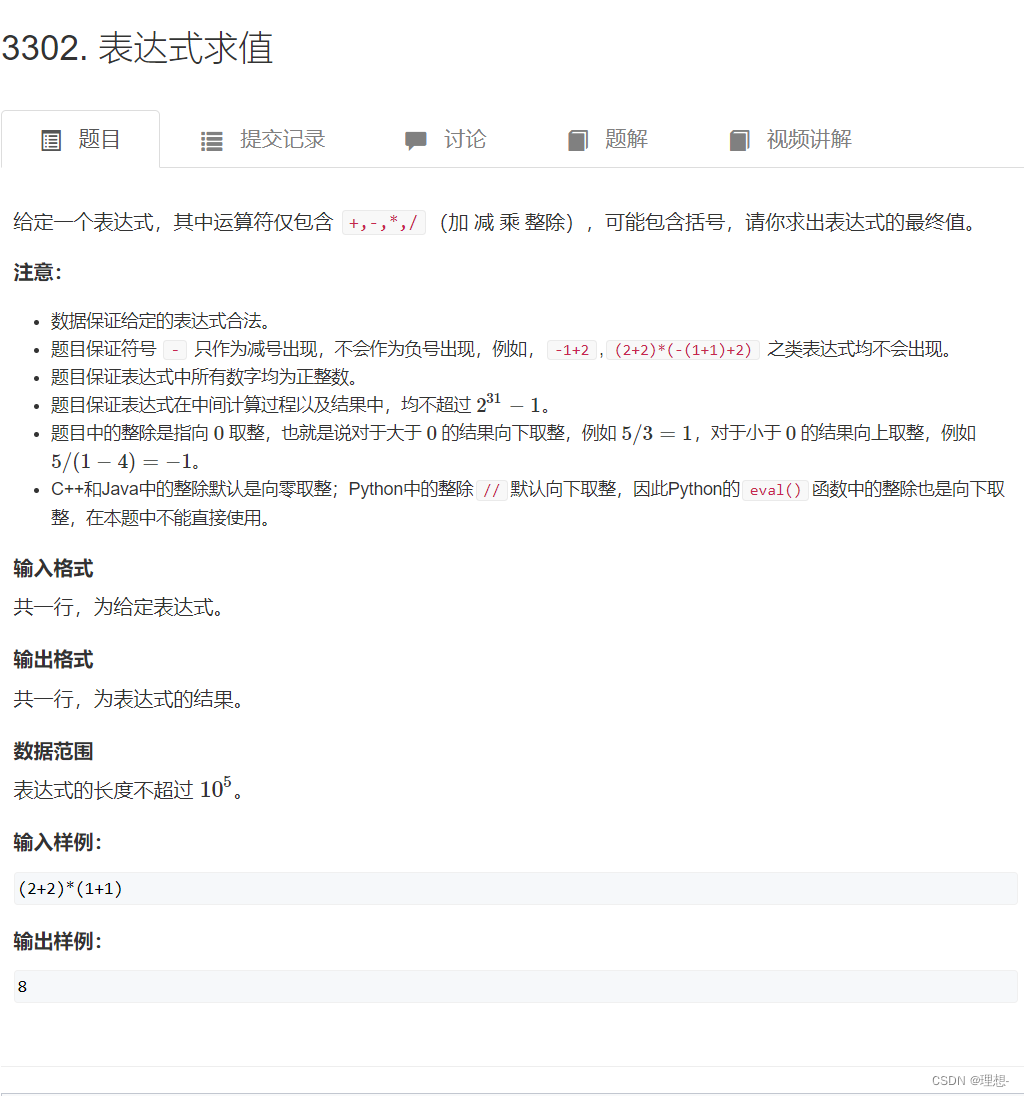
代码
队列
普通队列
// hh 表示队头,tt表示队尾
int q[N], hh = 0, tt = -1;
// 向队尾插入一个数
q[ ++ tt] = x;
// 从队头弹出一个数
hh ++ ;
// 队头的值
q[hh];
// 判断队列是否为空
if (hh <= tt) not empty
{
}
循环队列
模拟队列

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int hh, tt = -1, q[N];
int main()
{
int m, x;
string op;
cin >> m;
while (m--)
{
cin >> op;
if (op == "push") cin >> x, q[++tt] = x;
else if (op == "pop") hh++;
else if (op == "empty") cout << (hh <= tt ? "NO" : "YES") << endl;
else cout << q[hh] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
单调栈
模板
常见模型:找出每个数左边离它最近的比它大/小的数
int tt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
while (tt && check(stk[tt], i)) tt -- ;
stk[ ++ tt] = i;
}
AcWing 830. 单调栈

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int top, stk[N], n, a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
while (top && stk[top] >= a[i]) top--;
if (top) cout << stk[top] << ' ';
else cout << -1 << ' ';
stk[++top] = a[i];
}
return 0;
}
单调队列
模板
常见模型:找出滑动窗口中的最大值/最小值
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
while (hh <= tt && check_out(q[hh])) hh ++ ; // 判断队头是否滑出窗口
while (hh <= tt && check(q[tt], i)) tt -- ;
q[ ++ tt] = i;
}
154.滑动窗口
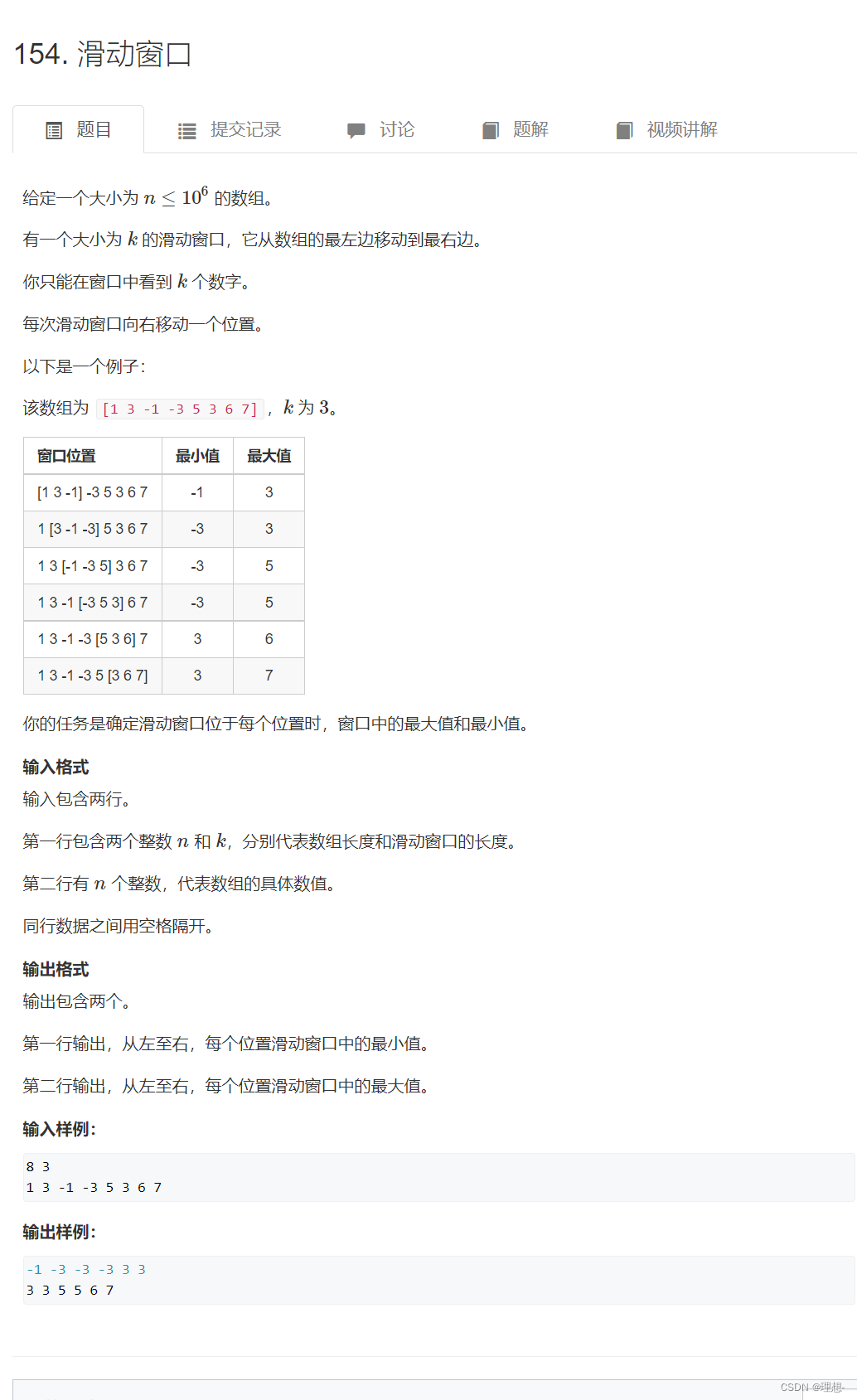
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int a[N], q[N], n, k;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// 判断队头是否滑出窗口, 队列存储下标
if (hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh]) hh++;
// 比当前元素大的时候 往前遍历
while (hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] >= a[i]) tt--;
// 在队尾加入当前元素
q[++tt] = i;
// 第k个数及以后才输出
if (i >= k - 1) printf("%d ", a[q[hh]]);
}
printf("\n");
hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// 判断队头是否滑出窗口, 队列存储下标
if (hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh]) hh++;
// 比当前元素大的时候 往前遍历
while (hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] <= a[i]) tt--;
// 在队尾加入当前元素
q[++tt] = i;
// 第k个数及以后才输出
if (i >= k - 1) printf("%d ", a[q[hh]]);
}
return 0;
}
KMP
模板
// s[]是长文本,p[]是模式串,短串,n是s的长度,m是p的长度
求模式串的Next数组:
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= m; i ++ )
{
while (j && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (p[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
ne[i] = j;
}
// 匹配
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= n; i ++ )
{
while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
if (j == m)
{
j = ne[j];
// 匹配成功后的逻辑
}
}

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = 1000010;
int ne[N];
char p[N], s[M];
int n, m;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> p + 1 >> m >> s + 1;
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
while (j && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (p[i] == p[j + 1]) j++;
ne[i] = j;
}
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; i++)
{
while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j++;
if (j == n)
{
printf("%d ", i - n);
j = ne[j];
}
}
return 0;
}
Trie树
高效地存储和查找字符串集合的数据结构
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-QIWq9VYh-1668740282430)(%E7%AC%AC%E4%BA%8C%E7%AB%A0%20%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E7%BB%93%E6%9E%84.assets/image-20221104145837283.png)]
Trie字符串统计
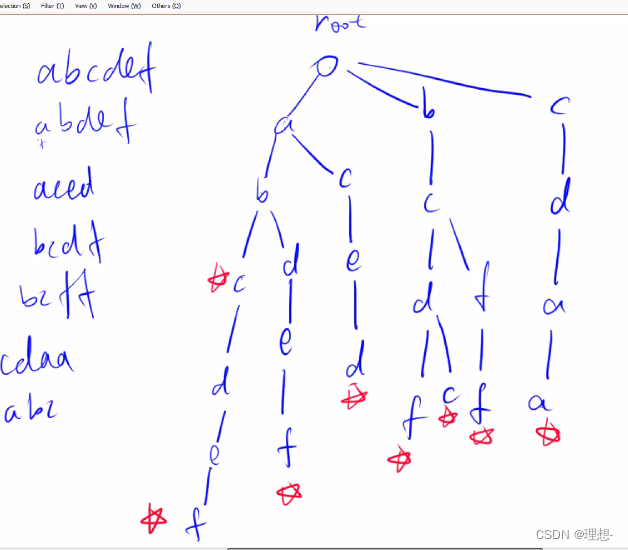
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int son[N][26], cnt[N], idx; // 下标是0的点 既是根节点又是空节点
char str[N];
void insert(char *str)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++)
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
cnt[p]++;
}
int query(char *str)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++)
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) return 0;
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n--)
{
char op[2];
scanf("%s%s", op, str);
if (op[0] == 'I') insert(str);
else printf("%d\n", query(str));
}
return 0;
}
最大异或对

代码
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = 31 * N;
int a[N], son[M][2];
int n, idx;
void insert(int x)
{
int p = 0; //
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--)
{
int u = x >> i & 1; // 取二进制数的某一位的值
if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++idx; // 如果下标为p的点的u(0或1)这个儿子不存在,那就创建
p = son[p][u];
}
}
int query(int x)
{
int p = 0, ret = 0;
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--)
{
int u = x >> i & 1;
if (son[p][!u])
{
p = son[p][!u];
ret = ret * 2 + !u;
}
else
{
p = son[p][u];
ret = ret * 2 + u;
}
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
insert(a[i]);
int t = query(a[i]);
res = max(res, t ^ a[i]);
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
并查集
合并集合
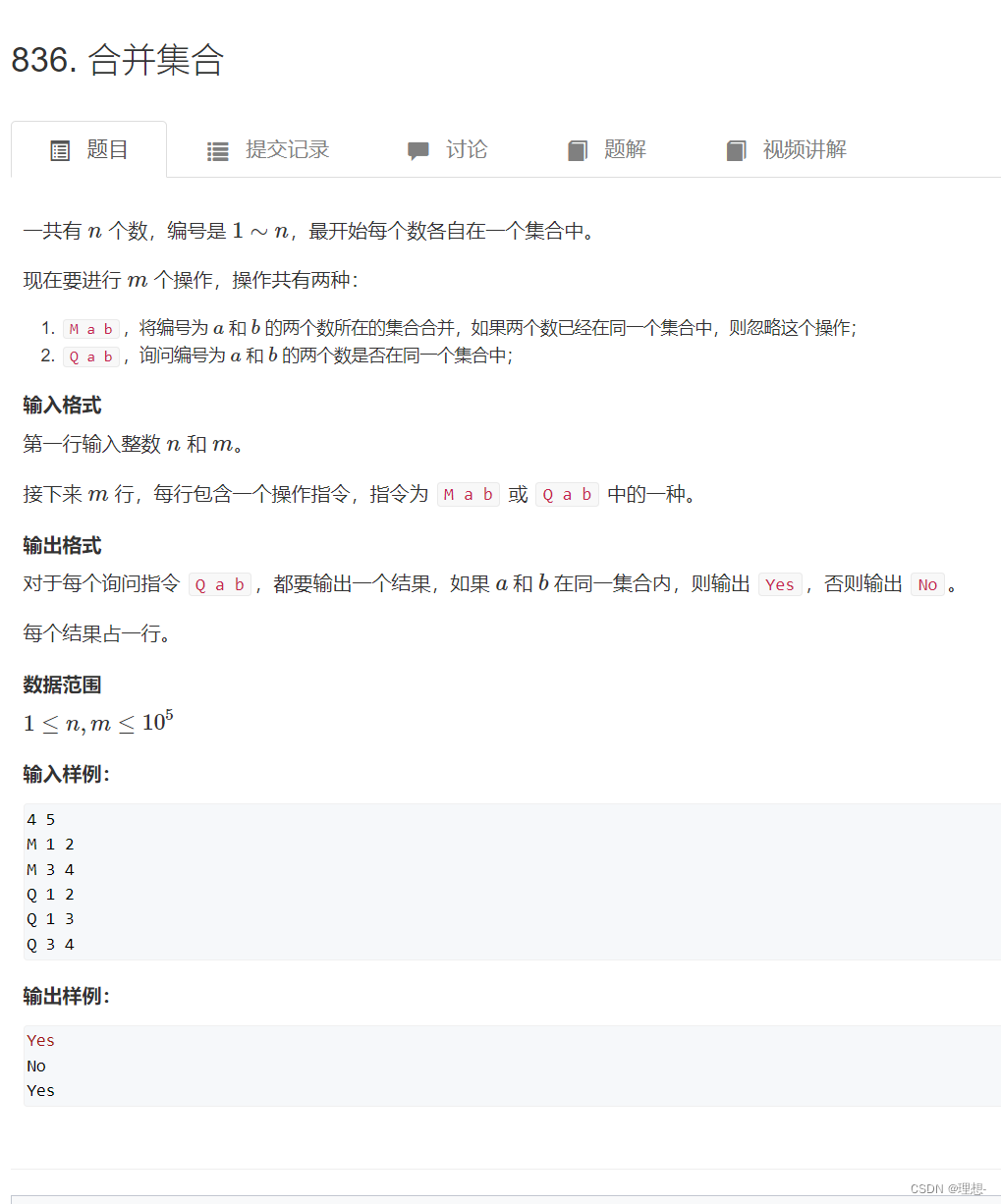
模板
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int p[N];
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i;
while (m--)
{
char op[2];
int a, b;
scanf("%s%d%d", op, &a, &b);
if (op[0] == 'M') p[find(a)] = p[find(b)];
else
{
if (find(a) == find(b)) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
}
return 0;
}
连通块中点的数量

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
// p[N]维护祖宗节点 cnt[N]维护集合的元素个数
int p[N], cnt[N], n, m;
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void con(int a, int b)
{
if (find(a) == find(b)) return;
//不在一个集合才合并数量
else
{
cnt[find(b)] = cnt[find(a)] + cnt[find(b)];
p[find(a)] = find(b);
}
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
char op[5];
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i, cnt[i] = 1;
while (m--)
{
scanf("%s", op);
if (op[0] == 'C')
{
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
con(a, b);
}
else if (op[1] == '1')
{
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
printf(find(a) == find(b) ? "Yes\n" : "No\n");
}
else
{
scanf("%d", &a);
printf("%d\n", cnt[find(a)]);
}
}
return 0;
}
堆
基本概念:一棵完全二叉树
- 小根堆
- 大根堆
基本操作
- 插入一个数
- 求集合中的最小值
- 删除最小值
- 删除任意一个元素
- 修改任意一个元素

模板
// h[N]存储堆中的值, h[1]是堆顶,x的左儿子是2x, 右儿子是2x + 1
// ph[k]存储第k个插入的点在堆中的位置
// hp[k]存储堆中下标是k的点是第几个插入的
void heap_swap(int a, int b)
{
swap(ph[hp[a]], ph[hp[b]]);
swap(hp[a], hp[b]);
swap(h[a], h[b]);
}
// 向下调整,大的元素放下面
void down(int i)
{
int t = i;
// i与左右节点最小值交换 (如果存在的话)
if (i * 2 <= len && h[i * 2] < h[t]) t = i * 2;
if (i * 2 + 1 <= len && h[i * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = i * 2 + 1;
if (i != t)
{
heap_swap(i, t);
down(t);
}
}
//向上调整,小的元素放上面
void up(int i)
{
while (i / 2 && h[i] < h[i / 2])
{
heap_swap(i, i / 2);
i /= 2;
}
}
// 初始化堆 O(n)的复杂度
for (int i = n / 2; i; i--) down(i);
堆排序

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N], n, m, len;
void down(int i)
{
int t = i;
// i与左右节点最小值交换 (如果存在的话)
if (i * 2 <= len && h[i * 2] < h[t]) t = i * 2;
if (i * 2 + 1 <= len && h[i * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = i * 2 + 1;
if (i != t)
{
swap(h[i], h[t]);
down(t);
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &h[i]);
len = n;
// 初始化堆 O(n)的复杂度
for (int i = n / 2; i; i--) down(i);
while (m--)
{
printf("%d ", h[1]);
h[1] = h[len];
len--;
down(1);
}
return 0;
}
模拟堆
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N], hp[N], ph[N], n, m, len;
void heap_swap(int a, int b)
{
swap(ph[hp[a]], ph[hp[b]]);
swap(hp[a], hp[b]);
swap(h[a], h[b]);
}
void down(int i)
{
int t = i;
// i与左右节点最小值交换 (如果存在的话)
if (i * 2 <= len && h[i * 2] < h[t]) t = i * 2;
if (i * 2 + 1 <= len && h[i * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = i * 2 + 1;
if (i != t)
{
heap_swap(i, t);
down(t);
}
}
void up(int i)
{
while (i / 2 && h[i] < h[i / 2])
{
heap_swap(i, i / 2);
i /= 2;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
string op;
int k, x;
while (n--)
{
cin >> op;
if (op == "I")
{
scanf("%d", &x);
len++;
m++;
ph[m] = len, hp[len] = m;
h[len] = x;
up(len);
}
else if (op == "PM") printf("%d\n", h[1]);
else if (op == "DM")
{
heap_swap(1, len);
len--;
down(1);
}
else if (op == "D")
{
scanf("%d", &k);
k = ph[k];
heap_swap(k, len);
len--;
down(k), up(k);
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d", &k, &x);
k = ph[k];
h[k] = x;
down(k), up(k);
}
}
return 0;
}
Hash表
模板
//(1) 拉链法
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
// 向哈希表中插入一个数
void insert(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = h[k];
h[k] = idx ++ ;
}
// 在哈希表中查询某个数是否存在
bool find(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
for (int i = h[k]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
if (e[i] == x)
return true;
return false;
}
//(2) 开放寻址法
int h[N];
// 如果x在哈希表中,返回x的下标;如果x不在哈希表中,返回x应该插入的位置
int find(int x)
{
int t = (x % N + N) % N;
while (h[t] != null && h[t] != x)
{
t ++ ;
if (t == N) t = 0;
}
return t;
}
模拟散列表

拉链法
#include<iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100003;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int n;
void insert(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = h[k];
h[k] = idx++;
}
bool find(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
for (int i = h[k]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
if (e[i] == x) return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
char op[2];
int x;
while (n--)
{
scanf("%s%d", op, &x);
if (op[0] == 'I') insert(x);
else printf(find(x) ? "Yes\n" : "No\n");
}
return 0;
}
开放寻址法,范围2~3倍
#include<iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200003, null = 0x3f3f3f3f; // 范围2~3倍 质数
int h[N];
int n;
// 如果x在哈希表中,返回x的下标;如果x不在哈希表中,返回x应该插入的位置
int find(int x)
{
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
while (h[k] != null && h[k] != x)
{
k++;
if (k == N) k = 0;
}
return k;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
// memset 按字节赋值 后八位
memset(h, 0x3f, sizeof h);
char op[2];
int x;
while (n--)
{
scanf("%s%d", op, &x);
int k = find(x);
if (op[0] == 'I') h[k] = x;
else printf(h[k] != null ? "Yes\n" : "No\n");
}
return 0;
}
字符串哈希
**核心思想:**将字符串看成P进制数,P的经验值是131或13331,取这两个值的冲突概率低
**小技巧:**取模的数用2^64,这样直接用unsigned long long存储,溢出的结果就是取模的结果


模板
typedef unsigned long long ull;
u h[N], p[N]; // h[k]存储字符串前k个字母的哈希值, p[k]存储 P^k mod 2^64
// 初始化
p[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
h[i] = h[i - 1] * P + str[i];
p[i] = p[i - 1] * P;
}
// 计算子串 str[l ~ r] 的哈希值
ull get(int l, int r)
{
return h[r] - h[l - 1] * p[r - l + 1];
}
代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
const int N = 100005, P = 131;
ull h[N], p[N]; // h[k]存储字符串前k个字母的哈希值, p[k]存储 P^k mod 2^64
char str[N];
int n, m;
// 计算子串 str[l ~ r] 的哈希值
ull get(int l, int r)
{
return h[r] - h[l - 1] * p[r - l + 1];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%s", &n, &m, str + 1);
// 初始化
p[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
h[i] = h[i - 1] * P + str[i];
p[i] = p[i - 1] * P;
}
while (m--)
{
int l1, r1, l2, r2;
cin >> l1 >> r1 >> l2 >> r2;
if (get(l1, r1) == get(l2, r2)) cout << "Yes" << endl;
else cout << "No" << endl;
}
return 0;
}



![22.11.18打卡 [传智杯 #3 初赛] 部分题](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3181223e64984ffd91e8eddef7ffb9d7.png)
![[Howto] Pytorch Window GPU 环境配置](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2cbd1119b1f246e6a1cc4967871287e4.png)