mybatis
- 1、入门
- 2、事务管理机制
- 3、日志和junit配置
- 3、mybatis工具类
- 4、CRUD
- 4.1 insert
- 4.1.1 map方式
- 4.1.2 对象方式
- 4.2 delete
- 4.3 update
- 4.4 select(Retrieve)
- 4.4.1 查询一个结果
- 4.4.2 查询多个结果
- 4.5 命名空间
1、入门
①创建一个空项目:添加上maven和jdk
②创建一个maven module
③编写pom.xml 导入mybatis和mysql依赖
④在resouece目录下编写mybatis-config.xml文件,其实就是编写连接数据库信息的文件。
⑤编写一个pojo,就是一个实体类,对应数据库中的一张表.这里时ORM对象关系映射思想,不懂得可以去补一下。
⑥编写xxxmapping.xml文件,就是编写sql语句的。
⑦获得sqlSessionFactoryBuilder 对象
⑧获得 SqlSessionFactory 一般一个数据库对应一个SqlSessionFactory
⑨获得 SqlSession 来执行sql语句
⑩默认没有自动开启事务 要添加commit
注意
①mybatis-config配置文件不一定要叫这个名字,也不一定非要在resource目录下,但是大多数都这么做。
在resource目录下,我们可以采用
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
来获得一个流对象,可移植性强。
底层其实是ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream()类加载器。
如果不在resource目录下,我们可以使用 new FileInputStream()来获得一个流对象。
②mapping.xml文件也不一定要放在resource目录下, 但大多数都这么做。如果没有在该资源下,我们在config配置文件中可以采用
<mapper url="">
而不是
<mapper resource="CarMapping.xml"/>
2、事务管理机制
对于事务mybatis有两种机制:
①JDBC,即mybatis自己管理事务,但底层还是调用的jdbc原生代码。即不会自动提交sql语句了,需要我们自己手动提交管理事务。即默认把Autocommit设置为了false。如果我们不想要管理事务,想要让其自动提交,可以在下边图片这里填上true,默认不填是false(不建议填。)

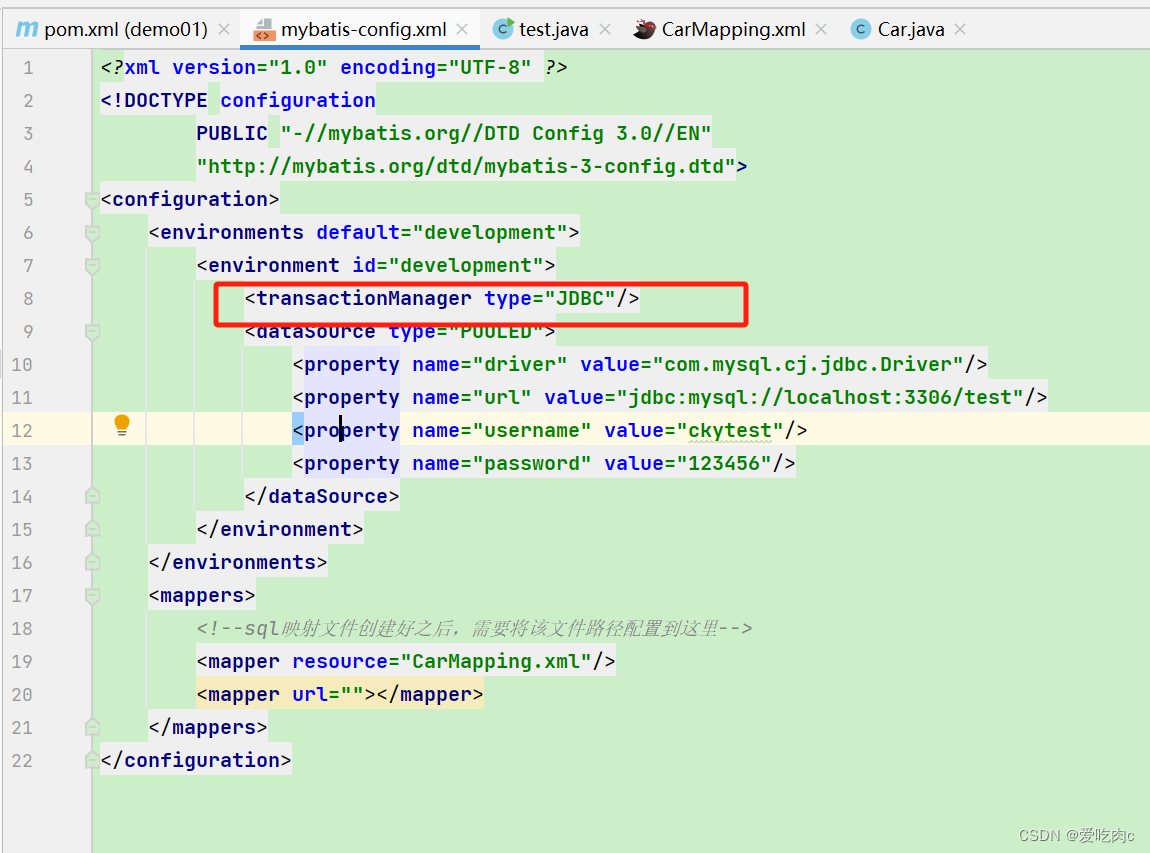
②也可以是MANAGE,即mybatis不管理事务,把事务管理交给别的容器,如果没有别的接管,那就没有事务,即默认提交。
3、日志和junit配置
首先导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.11</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
之后要配置日志的配置文件 一定要放在resouce目录下 且名字一定要是logback.xml或者logbcak-test.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration debug="false">
<!-- 控制台输出 -->
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符-->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 按照每天生成日志文件 -->
<appender name="FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--日志文件输出的文件名-->
<FileNamePattern>${LOG_HOME}/TestWeb.log.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</FileNamePattern>
<!--日志文件保留天数-->
<MaxHistory>30</MaxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder class="ch.qos.logback.classic.encoder.PatternLayoutEncoder">
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符-->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{50} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
<!--日志文件最大的大小-->
<triggeringPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy">
<MaxFileSize>100MB</MaxFileSize>
</triggeringPolicy>
</appender>
<!--mybatis log configure-->
<logger name="com.apache.ibatis" level="TRACE"/>
<logger name="java.sql.Connection" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="java.sql.Statement" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="java.sql.PreparedStatement" level="DEBUG"/>
<!-- 日志输出级别,logback日志级别包括五个:TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR -->
<root level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
<appender-ref ref="FILE"/>
</root>
</configuration>
同时要在mybatis-config.xml文件中配置 日志即我们使用的接口。
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="SLF4J" />
</settings>
logback 继承自slf4j接口。
mybatis实现了标准接口,使用如下接口时没必要导入依赖。
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING" />
</settings>
3、mybatis工具类
我们想要像jdbc一样,每次获取工具类的获取连接方式就可。
package com.cky.utils;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MybatisUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
/**
* 类加载时初始化sqlSessionFactory对象
*/
static {
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
try {
sqlSessionFactory=sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 每调用一次openSession()可获取一个新的会话,该会话支持自动提交。
*
* @return 新的会话对象
*/
public static SqlSession openSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
}
}
4、CRUD
4.1 insert
我们不能把sql语句的内容写固定,而应该通过外部传入的方式
4.1.1 map方式
package com.cky.test;
import com.cky.utils.MybatisUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test1() throws Exception{
Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("carNum","1010");
map.put("brand","比亚迪");
map.put("guidePrice",100);
map.put("produceTime","2023-03-28");
map.put("carType","电车");
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
int insertCar = sqlSession.insert("insertCar",map);
System.out.println(insertCar);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace先随意写一个-->
<mapper namespace="aaa">
<!--insert sql:保存一个汽车信息-->
<insert id="insertCar">
insert into t_car
(id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type)
values
(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType})
</insert>
</mapper>
注意 我们都是#{}来代替原来sql语句?这个占位符。
{}中写的时map的key值,如果key值不存在,就会填入null。
4.1.2 对象方式
我们可以创建一个pojo,来代表数据库中的一张表。
package com.cky.bean;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Car {
private Integer id;
private String carNum;
private String brand;
private Double guidePrice;
private String produceTime;
private String carType;
public Car(Integer id, String carNum, String brand, Double guidePrice, String produceTime, String carType) {
this.id = id;
this.carNum = carNum;
this.brand = brand;
this.guidePrice = guidePrice;
this.produceTime = produceTime;
this.carType = carType;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCarNum() {
return carNum;
}
public void setCarNum(String carNum) {
this.carNum = carNum;
}
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public Double getGuidePrice() {
return guidePrice;
}
public void setGuidePrice(Double guidePrice) {
this.guidePrice = guidePrice;
}
public String getProduceTime() {
return produceTime;
}
public void setProduceTime(String produceTime) {
this.produceTime = produceTime;
}
public String getCarType() {
return carType;
}
public void setCarType(String carType) {
this.carType = carType;
}
}
@org.junit.Test
public void test2() throws Exception{
Car car=new Car(null,"1002","五菱",100.00,"2023-03-28","电车");
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
int insertCar = sqlSession.insert("insertCar",car);
System.out.println(insertCar);
sqlSession.close();
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace先随意写一个-->
<mapper namespace="aaa">
<!--insert sql:保存一个汽车信息-->
<insert id="insertCar">
insert into t_car
(id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type)
values
(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType})
</insert>
</mapper>
注意:如果我们使用的是一个对象传值,则#{},{}里填写的是getXxx,去掉get第一个字母变小写后的名字,而不是说就是属性名。
4.2 delete
<delete id="deletecar">
delete from t_car where car_num = #{id}
</delete>
@org.junit.Test
public void test3() throws Exception{
// Car car=new Car(null,"1002","五菱",100.00,"2023-03-28","电车");
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
int insertCar = sqlSession.insert("deletecar","1010");
System.out.println(insertCar);
sqlSession.close();
}
注意 如果只传入一个值的时候 {}里的内容可以随便写,但是要见明知意。
4.3 update
<update id="updatecar">
pdate t_car set
car_num = #{carNum}, brand = #{brand},
guide_price = #{guidePrice}, produce_time = #{produceTime},
car_type = #{carType}
where id = #{id}
</update>
@org.junit.Test
public void test4() throws Exception{
Car car=new Car(null,"1002","五菱11",100.00,"2023-03-28","电车");
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
int insertCar = sqlSession.insert("insertCar",car);
System.out.println(insertCar);
sqlSession.close();
}
跟insert一样,都是getXxx后边的名字,当然也可以使用map传值。
4.4 select(Retrieve)
4.4.1 查询一个结果
<select id="selectCar" resultType="com.cky.bean.Car">
select id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type from t_car where id=#{id};
</select>
@org.junit.Test
public void test5() throws Exception{
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
Object selectCar = sqlSession.selectOne("selectCar",1);
System.out.println(selectCar);
sqlSession.close();
}
注意:我们需要指定返回的类型,因为selectone会帮我们封装成一个对象,我们指定了返回的类型之后,mybatis才能帮我们封装。
我配置文件也没有开启驼峰式映射,不知道为什么我没有起别名,但是也是对的,他自动帮我匹配到了我的类属性名,好像是会自动开启驼峰式映射?

4.4.2 查询多个结果
<select id="selectAllCar" resultType="com.cky.bean.Car">
select id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type from t_car ;
</select>
@org.junit.Test
public void test6() throws Exception{
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
List<Object> selectCars = sqlSession.selectList("selectAllCar");
selectCars.forEach(car-> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}
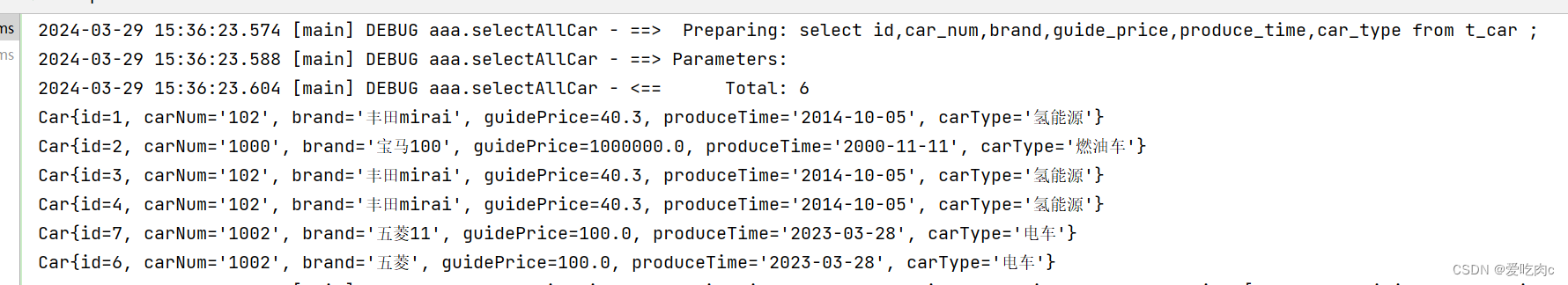
注意返回集合时,返回类型写的是集合里对象的类型!!!
4.5 命名空间
如果我们有多个mapping.xml文件,且sql语句的id是一致的,此时命名空间就很重要了,因为我们将这个xml文件都配置到mybatis-config.xml文件中,此时如果我们只写id名来找该sql语句的话,就会出错,因为不知道是哪一个。
比如
CarMapping.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace先随意写一个-->
<mapper namespace="aaa">
<select id="selectAllCar" resultType="com.cky.bean.Car">
select id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type from t_car ;
</select>
</mapper>
Car1Mapping.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace先随意写一个-->
<mapper namespace="bbb">
<select id="selectAllCar" resultType="com.cky.bean.Car">
select id,car_num,brand,guide_price,produce_time,car_type from t_car ;
</select>
</mapper>
测试
@org.junit.Test
public void test6() throws Exception{
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
List<Object> selectCars = sqlSession.selectList("selectAllCar");
selectCars.forEach(car-> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}

应该指定命名空间。
@org.junit.Test
public void test6() throws Exception{
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.openSession();
List<Object> selectCars = sqlSession.selectList("aaa.selectAllCar");
selectCars.forEach(car-> System.out.println(car));
sqlSession.close();
}


![[项目实践]---RSTP生成树](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/506c838a49524a5a946553ef54a33fdd.png)