基于顺序存储结构的图书信息表的图书去重
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
char no[50];
char name[50];
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct{
Book* elem;
int len;
}SqList;
status InitList(SqList* L,int n){
L->elem=(Book*)malloc((n+5)*sizeof(Book));
if(!L->elem) exit(-1);
L->len=0;
return OK;
}
status CreateList(SqList* L,int n){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
bool flag=true;
Book b;
cin>>b.no>>b.name>>b.price;
for(int j=0;j<L->len;j++){
if(!strcmp(b.no,L->elem[j].no)){
flag=false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
L->elem[L->len]=b;
L->len++;
}
}
return OK;
}
void PrintList(SqList* L){
printf("%d\n",L->len);
for(int i=0;i<L->len;i++){
printf("%s %s %.2f\n",L->elem[i].no,L->elem[i].name,L->elem[i].price);
}
}
int main(){
SqList L;
int n=0;
cin>>n; //图书数
InitList(&L,n);
CreateList(&L,n);
PrintList(&L);
return 0;
}
终于开链表了开链表了T_T
基于链式存储结构的图书信息表的创建和输出
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iomanip>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
string no;
string name;
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct LNode{
Book data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode,*LinkList; //这样typedef,可以在后期比较方便地创建指向链表结点的指针
void InitList(LinkList& L){
L=new LNode;
L->next=NULL;
}
//创建链表(含头结点),顺便返回链表长度
int CreateList(LinkList& L){
string no,name;
float price;
LinkList r=L;
LinkList p;
int elemCnt=0;
while(1){
//后插法创建链表
cin>>no>>name>>price;
if(no=="0" && name=="0" && price==0.0)
break;
else{
p=new LNode;
p->data.no=no;
p->data.name=name;
p->data.price=price;
p->next=NULL;
r->next=p;
r=p;
elemCnt++;
}
}
return elemCnt;
}
void PrintList(LinkList& L,int n){
LinkList p=L->next;
cout<<n<<endl;
while(p){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
cout<<p->data.no<<" "<<p->data.name<<" "<<p->data.price<<endl;
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
int n=0;
InitList(L);
n=CreateList(L);
PrintList(L,n);
return 0;
} 知识点
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
需要添加头文件iomanip
这个用于精度控制(不然如果用%.2f,C和C++风格字符串混在一起也太乱糟了)
(顺便,C中其实是没有string的,如果定义了string,再用printf输出的话,要.c_str() )
基于链式存储结构的图书信息表的排序
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iomanip>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
string no;
string name;
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct LNode{
Book data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
void InitList(LinkList& L){
L=new LNode;
L->next=NULL;
}
int CreateList(LinkList& L){
string no,name;
float price;
LinkList r,p;
r=L;
int len=0;
while(1){
cin>>no>>name>>price;
if(no=="0" && name=="0" && price==0.0)
break;
p=new LNode; //不要漏掉!
p->data.no=no;
p->data.name=name;
p->data.price=price;
p->next=NULL;
r->next=p;
r=p;
len++;
}
return len;
}
//排序
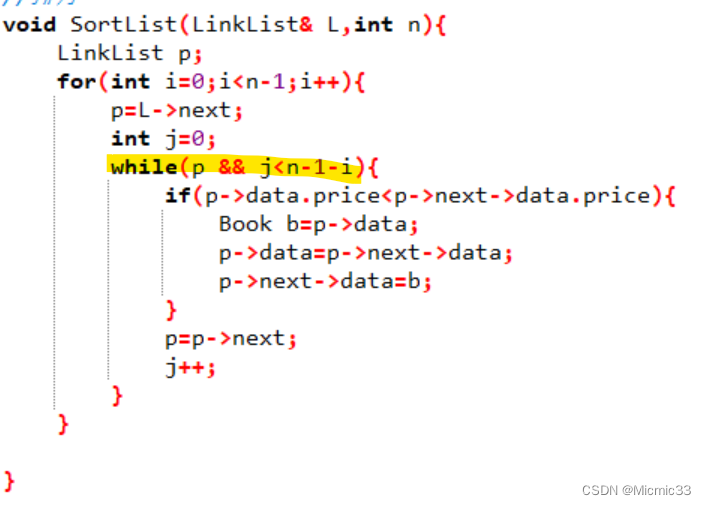
void SortList(LinkList& L,int n){
LinkList p;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){
p=L->next;
int j=0;
while(p && j<n-1-i){
if(p->data.price<p->next->data.price){
Book b=p->data;
p->data=p->next->data;
p->next->data=b;
}
p=p->next;
j++;
}
}
}
void PrintList(LinkList& L){
LinkList p=L->next;
while(p){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
cout<<p->data.no<<" "<<p->data.name<<" "<<p->data.price<<endl;
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
InitList(L);
int len=CreateList(L);
SortList(L,len);
PrintList(L);
}知识点
对于链表的冒泡排序:(在创建链表时顺便就得到了链表长度,不用再额外遍历一遍了)
另:对定义链表的语句理解:
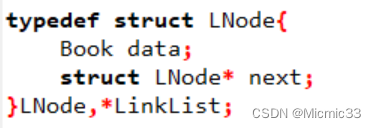
之后写LinkList L,L就是一个LinkList类型的指针,相当于一个指向链表结点的指针,包括在遍历时用到的辅助指针p等,都是这个类型的。
若想往结点里存数据,那么就先要为它开辟空间,所以常有这样的定义语句:
LinkList p;
p=new LNode;基于链式存储结构的图书信息表的修改
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iomanip>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
string no;
string name;
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct LNode{
Book data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
void InitList(LinkList& L){
L=new LNode;
L->next=NULL;
}
int CreateList(LinkList& L,float &sum){
string no,name;
float price;
LinkList r,p;
r=L;
int len=0;
while(1){
cin>>no>>name>>price;
if(no=="0" && name=="0" && price==0.0)
break;
p=new LNode; //不要漏掉!
p->data.no=no;
p->data.name=name;
p->data.price=price;
p->next=NULL;
r->next=p;
r=p;
len++;
sum+=price;
}
return len;
}
void ModifyList(LinkList& L,float avg){
LinkList p=L->next;
while(p){
if(p->data.price<avg)
p->data.price*=1.2;
else
p->data.price*=1.1;
p=p->next;
}
}
void PrintList(LinkList& L){
LinkList p=L->next;
while(p){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
cout<<p->data.no<<" "<<p->data.name<<" "<<p->data.price<<endl;
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
InitList(L);
float sum=0.0;
int len=CreateList(L,sum);
float avg=sum/(float)len;
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
cout<<avg<<endl;
ModifyList(L,avg);
PrintList(L);
}基于链式存储结构的图书信息表的逆序存储(链表逆序就用头插法实现即可,很简单)
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iomanip>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
string no;
string name;
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct LNode{
Book data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
void InitList(LinkList& L){
L=new LNode;
L->next=NULL;
}
void CreateList(LinkList& L){
int n;
cin>>n; //链表长度
string no,name;
float price;
LinkList r,p;
int cnt=0;
while(cnt<n){
cin>>no>>name>>price;
p=new LNode; //不要漏掉!
p->data.no=no;
p->data.name=name;
p->data.price=price;
p->next=NULL;
//头插法实现逆序存储
r=L->next;
L->next=p;
p->next=r;
cnt++;
}
}
void PrintList(LinkList& L){
LinkList p=L->next;
while(p){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
cout<<p->data.no<<" "<<p->data.name<<" "<<p->data.price<<endl;
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
InitList(L);
float sum=0.0;
CreateList(L);
PrintList(L);
}查找最贵图书
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iomanip>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
string no;
string name;
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct LNode{
Book data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
void InitList(LinkList& L){
L=new LNode;
L->next=NULL;
}
//返回最高图书价格
float CreateList(LinkList& L){
int n;
cin>>n; //链表长度
string no,name;
float price;
float max=0.0;
LinkList r,p;
r=L; //等于L比较好,如果等于L->next,之后会出现r=p->next的情况,这时候r的next就不太好了
int cnt=0;
while(cnt<n){
cin>>no>>name>>price;
p=new LNode; //不要漏掉!
p->data.no=no;
p->data.name=name;
p->data.price=price;
p->next=NULL;
if(price>max)
max=price;
r->next=p;
r=p;
cnt++;
}
return max;
}
//返回最贵图书的数量
int TraverseList(LinkList&L,float max){
LinkList p=L->next;
int cnt=0;
while(p){
if(p->data.price==max)
cnt++;
p=p->next;
}
return cnt;
}
void PrintList(LinkList& L,float max){
LinkList p=L->next;
while(p){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
if(p->data.price==max){
cout<<p->data.no<<" "<<p->data.name<<" "<<p->data.price<<endl;
}
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
InitList(L);
float max=CreateList(L);
cout<<TraverseList(L,max)<<endl;
PrintList(L,max);
}查找最爱图书(同顺序表,用一个数组存储待查序列,代码写的比较乱功能封装的也不好,摆烂..)
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iomanip>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
string no;
string name;
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct LNode{
Book data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
void InitList(LinkList& L){
L=new LNode;
L->next=NULL;
}
//返回最高图书价格
void CreateList(LinkList& L){
int n;
cin>>n; //链表长度
string no,name;
float price;
LinkList r,p;
r=L; //等于L比较好,如果等于L->next,之后会出现r=p->next的情况,这时候r的next就不太好了
int cnt=0;
while(cnt<n){
cin>>no>>name>>price;
p=new LNode; //不要漏掉!
p->data.no=no;
p->data.name=name;
p->data.price=price;
p->next=NULL;
r->next=p;
r=p;
cnt++;
}
}
//返回最爱图书的数量
int TraverseList(LinkList&L,string love){
LinkList p=L->next;
int cnt=0;
while(p){
if(p->data.name==love)
cnt++;
p=p->next;
}
return cnt;
}
void PrintList(LinkList& L,string love){
LinkList p=L->next;
while(p){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
if(p->data.name==love){
cout<<p->data.no<<" "<<p->data.name<<" "<<p->data.price<<endl;
}
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
InitList(L);
CreateList(L);
int num;
cin>>num;
string love[num];
for(int j=0;j<num;j++)
cin>>love[j];
for(int i=0;i<num;i++){
if(TraverseList(L,love[i])!=0){
cout<<TraverseList(L,love[i])<<endl;
PrintList(L,love[i]);
}
else cout<<"Sorry,there is no your favourite!"<<endl;
}
}基于链式存储结构的图书信息表的最佳位置图书的查找
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iomanip>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
string no;
string name;
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct LNode{
Book data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
void InitList(LinkList& L){
L=new LNode;
L->next=NULL;
}
int CreateList(LinkList& L){
int n;
cin>>n; //链表长度
string no,name;
float price;
LinkList r,p;
r=L; //等于L比较好,如果等于L->next,之后会出现r=p->next的情况,这时候r的next就不太好了
int cnt=0;
while(cnt<n){
cin>>no>>name>>price;
p=new LNode; //不要漏掉!
p->data.no=no;
p->data.name=name;
p->data.price=price;
p->next=NULL;
r->next=p;
r=p;
cnt++;
}
return n;
}
//返回最爱图书的数量
int TraverseList(LinkList&L,string love){
LinkList p=L->next;
int cnt=0;
while(p){
if(p->data.name==love)
cnt++;
p=p->next;
}
return cnt;
}
void PrintList(LinkList& L,int place,int n){
if(place<1||place>=n)cout<<"Sorry,the book on the best position doesn't exist!"<<endl;
else{
LinkList p=L->next;
int index=0;
while(p){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
if(index==place-1){
cout<<p->data.no<<" "<<p->data.name<<" "<<p->data.price<<endl;
break;
}
p=p->next;
index++;
}
}
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
InitList(L);
int n=CreateList(L);
int searchNum; //要查找的图书的数目
cin>>searchNum;
int place[searchNum];
for(int i=0;i<searchNum;i++){
cin>>place[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<searchNum;i++){
PrintList(L,place[i],n);
}
}接下来是入库出库(即插入删除)
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iomanip>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
string no;
string name;
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct LNode{
Book data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode,*LinkList; //这样typedef,可以在后期比较方便地创建指向链表结点的指针
void InitList(LinkList& L){
L=new LNode;
L->next=NULL;
}
//创建链表(含头结点),顺便返回链表长度
int CreateList(LinkList& L){
int elemCnt;
cin>>elemCnt;
string no,name;
float price;
LinkList r=L;
LinkList p;
for(int i=0;i<elemCnt;i++){
//后插法创建链表
cin>>no>>name>>price;
p=new LNode;
p->data.no=no;
p->data.name=name;
p->data.price=price;
p->next=NULL;
r->next=p;
r=p;
}
return elemCnt;
}
//插入链表
bool InsertList(LinkList& L,int n,int place,Book b){
bool flag=true;
if(place<1 || place>n){
cout<<"Sorry,the position to be inserted is invalid!";
flag=false;
}
else{
LinkList p=L;
int cnt=0;
while(cnt<place-1 && p){
p=p->next; //找到要插入位置的前一个
cnt++;
}
//已找到位置
LinkList q=new LNode;
q->data.no=b.no;
q->data.name=b.name;
q->data.price=b.price;
q->next=NULL;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
}
return flag;
}
void PrintList(LinkList& L){
LinkList p=L->next;
while(p){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
cout<<p->data.no<<" "<<p->data.name<<" "<<p->data.price<<endl;
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
InitList(L);
int n=CreateList(L);
int place;
cin>>place;
Book b;
cin>>b.no>>b.name>>b.price;
if(InsertList(L,n,place,b))
PrintList(L);
return 0;
} 知识点
当设计插入、删除这些操作时,因为要输出不合法的情况,所以可以为插入删除函数设置一个bool类型的返回值
下面是出库(搞清楚链表怎么插入怎么删除就行很简单)
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iomanip>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
string no;
string name;
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct LNode{
Book data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode,*LinkList; //这样typedef,可以在后期比较方便地创建指向链表结点的指针
void InitList(LinkList& L){
L=new LNode;
L->next=NULL;
}
//创建链表(含头结点),顺便返回链表长度
int CreateList(LinkList& L){
int elemCnt;
cin>>elemCnt;
string no,name;
float price;
LinkList r=L;
LinkList p;
for(int i=0;i<elemCnt;i++){
//后插法创建链表
cin>>no>>name>>price;
p=new LNode;
p->data.no=no;
p->data.name=name;
p->data.price=price;
p->next=NULL;
r->next=p;
r=p;
}
return elemCnt;
}
//删除链表
bool DeleteList(LinkList& L,int n,int place){
bool flag=true;
if(place<1 || place>n){
cout<<"Sorry,the position to be deleted is invalid!";
flag=false;
}
else{
LinkList p=L;
int cnt=0;
while(cnt<place-1 && p){
p=p->next; //找到要插入位置的前一个
cnt++;
}
//已找到位置
LinkList tmp=p->next;
p->next=tmp->next;
free(tmp);
}
return flag;
}
void PrintList(LinkList& L){
LinkList p=L->next;
while(p){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
cout<<p->data.no<<" "<<p->data.name<<" "<<p->data.price<<endl;
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
InitList(L);
int n=CreateList(L);
int place;
cin>>place;
if(DeleteList(L,n,place))
PrintList(L);
return 0;
} 图书去重
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iomanip>
typedef int status;
#define OK 1
using namespace std;
typedef struct{
string no;
string name;
float price;
}Book;
typedef struct LNode{
Book data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode,*LinkList; //这样typedef,可以在后期比较方便地创建指向链表结点的指针
void InitList(LinkList& L){
L=new LNode;
L->next=NULL;
}
//创建链表(含头结点),顺便返回链表长度
int CreateList(LinkList& L){
int elemCnt;
cin>>elemCnt;
int realCnt=elemCnt;
string no,name;
float price;
LinkList r=L;
LinkList p;
LinkList tmp;
for(int i=0;i<elemCnt;i++){
//后插法创建链表
cin>>no>>name>>price;
tmp=L->next;
bool ifInsert=true;
while(tmp){
if(tmp->data.no==no){
cout<<"有重名"<<endl;
realCnt--;
ifInsert=false;
}
tmp=tmp->next;
}
if(ifInsert){
p=new LNode;
p->data.no=no;
p->data.name=name;
p->data.price=price;
p->next=NULL;
r->next=p;
r=p;
cout<<"成功插入"<<endl;
}
}
return realCnt;
}
void PrintList(LinkList& L){
LinkList p=L->next;
while(p){
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2);
cout<<p->data.no<<" "<<p->data.name<<" "<<p->data.price<<endl;
p=p->next;
}
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
InitList(L);
cout<<CreateList(L)<<endl;
PrintList(L);
return 0;
}