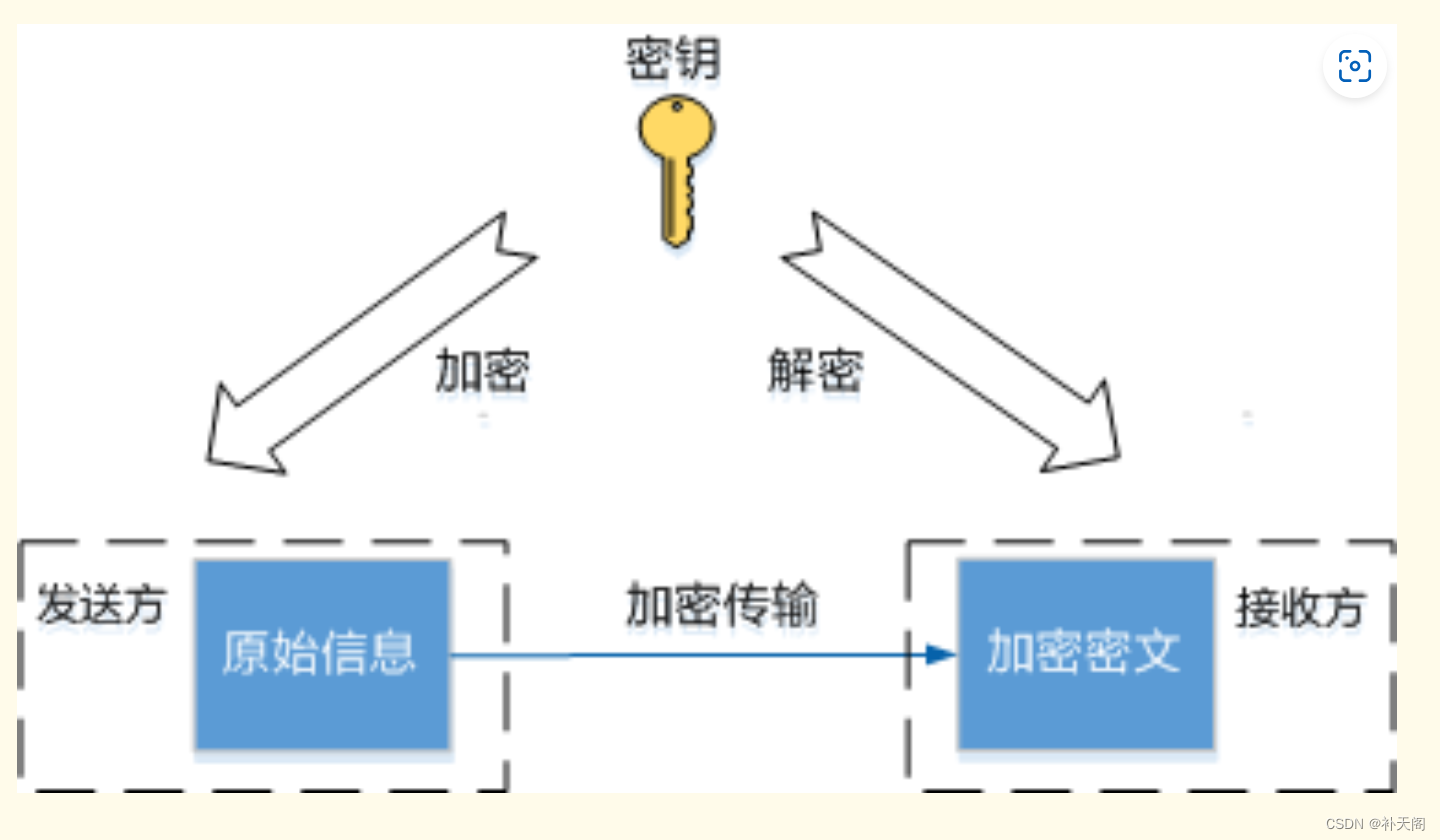
1.使用write 和 read 实现 文件夹拷贝功能,不考虑递归拷贝
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int fd=open(argv[1],O_RDONLY);
if(fd==-1)
{
perror("open");
return 1;
}
char buf[512]={0};
int res=read(fd,buf,512);
printf("有%d个字节\n",res);
close(fd);
fd=open("./zuo1.txt",O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC,0664);
if(fd==-1)
{
perror("open");
return 1;
}
write(fd,buf,res);
close(fd);
return 0;
}

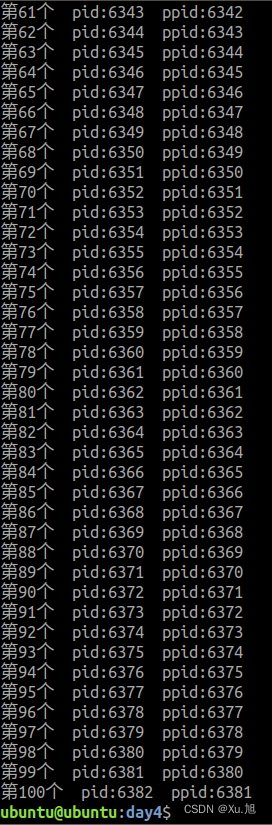
2.使用循环+fork的形式。创建一条进程链,链条上总共有100个进程 要求:程序不崩溃
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int i=0;
pid_t res;
for(i=0;i<100;i++)
{
res=fork();
if(res==-1)
{
perror("fork");
return 1;
}
else if(res==0)
{
printf("第%d个 pid:%d ppid:%d\n",i+1,getpid(),getppid());
}
else
{
break;
}
}
sleep(5);
return 0;
}