目录
1、介绍
2、获取Stream流的两种方式
方式一:根据Collection获取流
方式二:Stream中的静态方法of获取流
区别
3、Stream流注意事项
4、Stream流的常用方法
forEach
count
filter
limit
skip
map
sorted
distinct
match
find
max和min
reduce
map与reduce组合使用
mapToInt
concat
5、收集Stream流中的结果
将流中的数据收集到集合中
将流中的数据收集到数组中
对流中数据进行聚合计算
对流中数据进行分组
对流中数据进行分区
对流中数据进行拼接
6、并行的Stream流
获取并行Stream流的两种方式
第一种:直接获取并行的Stream流
第二种:将串行流转成并行流
串行与并行Stream代码对比
parallelStream线程安全问题
解决方案一:同步代码块
解决方案二:使用线程安全的集合
解决方案三:使用Collections.synchronizedList方法将集合转为线程安全的
解决方案四:调用Stream流的collect/toArray
parallelStream底层
Fork/join框架介绍
Fork/join原理-分治法
Fork/join原理-工作窃取算法
1、介绍
Stream流思想类似于工厂车间的流水线,Stream流不是一种数据结构,不保存数据,而是对数据进行加工处理。
先看一段代码:我们会发现这样又循环又创建新的集合再存进去,很麻烦
public class Y {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> nameList = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(nameList,"张无忌","周芷若","赵敏","说不得","张乐");
//拿到所有姓张的放进zhangList中
List<String> zhangList = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> threeList = new ArrayList<>();
for(String name : nameList){
if(name.startsWith("张")){
zhangList.add(name);
}
}
//遍历姓张的,拿出名字长度等于3的
for(String name : zhangList){
if(name.length() == 3){
threeList.add(name);
}
}
System.out.println(threeList);
}
}Stream流优化写法:
List<String> nameList = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(nameList,"张无忌","周芷若","赵敏","说不得","张乐");
nameList.stream()
.filter((s) -> {
return s.startsWith("张");
})
.filter((s) -> {
return s.length() == 3;
})
.forEach((s) -> {
System.out.println(s);
});2、获取Stream流的两种方式
方式一:根据Collection获取流
//方式一:根据Collection获取流
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stream<String> stream = list.stream();方式二:Stream中的静态方法of获取流
Stream<String> aa = Stream.of("张无忌","周芷若","赵敏","说不得","张乐");区别
前者(of)是把集合当做一个整体处理,后者是把一个个元素分开来遍历。所以要对集合中每个元素做判断过滤,要用后者list.stream。
3、Stream流注意事项
(1)Stream只能操作一次
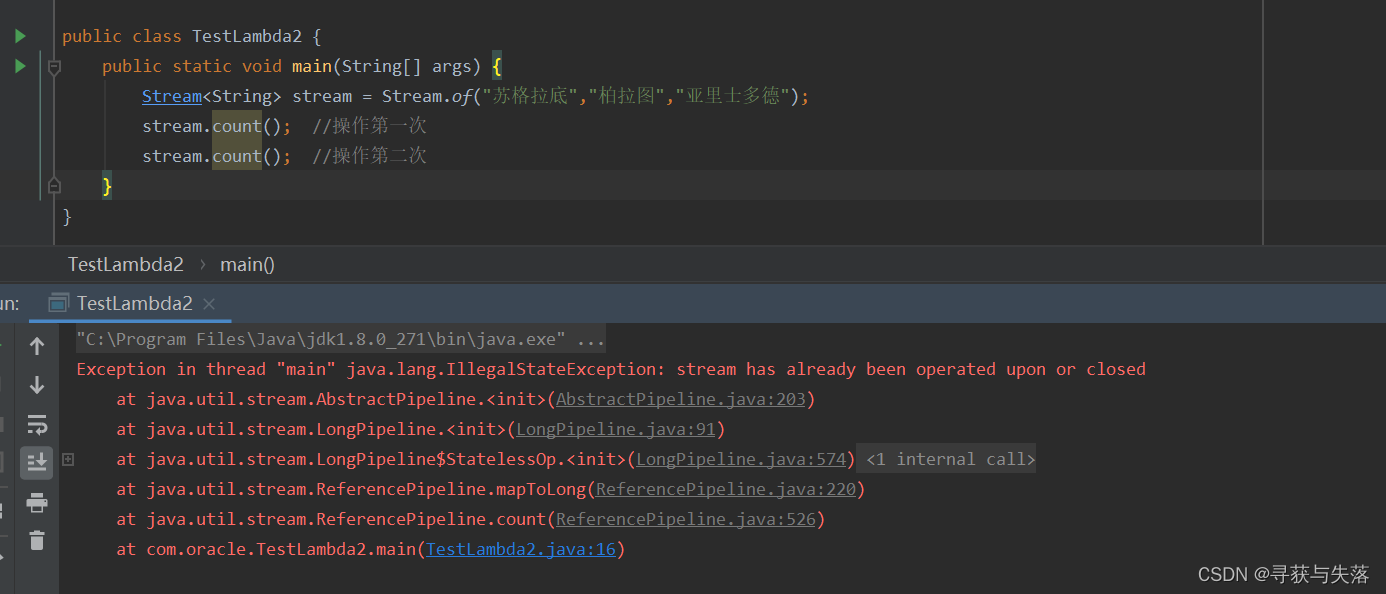
(2)Stream方法返回的是新的流
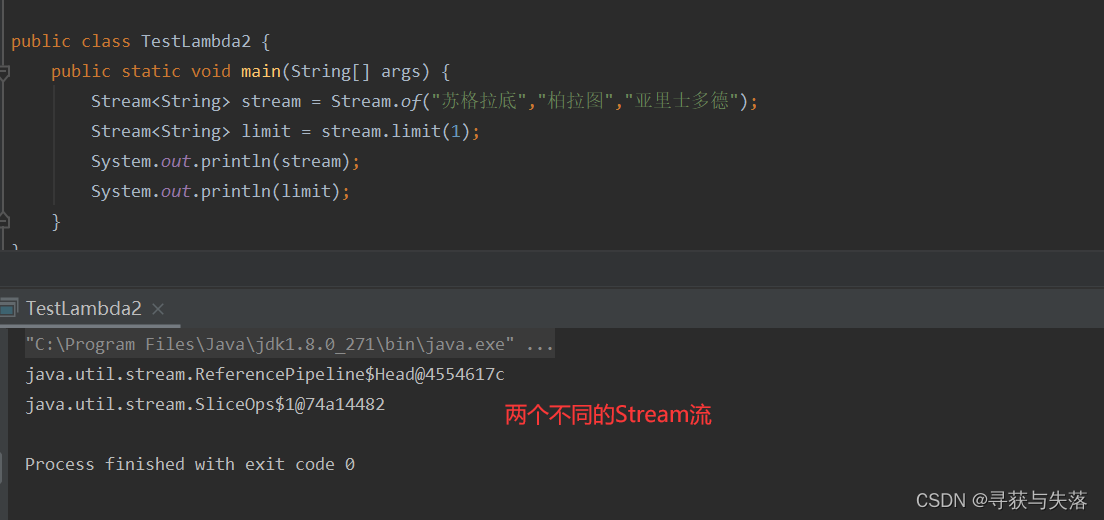
(3)Stream不调用终结方法,中间的操作不会执行
(4)如果Stream流的一些方法(limit、filter、skip等...)返回值是Stream,那么就得在最后调用终结方法(forEach、count)。
4、Stream流的常用方法
forEach
public class TestLambda2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"苏格拉底","柏拉图","亚里士多德","叔本华","尼采");
//完整版
list.stream().forEach((String str) -> {
System.out.println(str);
});
//精简版
list.stream().forEach(str -> System.out.println(str));
}
}count
统计其中的元素个数。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"苏格拉底","柏拉图","亚里士多德","叔本华","尼采");
//完整版
long count = list.stream().count();
System.out.println(count);filter
用于过滤数据,返回符合条件的数据。
public class TestLambda2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"苏格拉底","柏拉图","亚里士多德","叔本华","尼采");
//得到名字长度为3个字的人
//完整版
list.stream().filter(str -> {
return str.length() == 3;
}).forEach(System.out::println);
//精简版
list.stream().filter(str -> str.length() == 3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}limit
可以进行截取,只取用前n个。
public class TestLambda2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"苏格拉底","柏拉图","亚里士多德","叔本华","尼采");
//获取前3个元素
list.stream().limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}skip
如果希望跳过前几个元素,可以使用skip方法获取一个截取之后的新流。
public class TestLambda2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"苏格拉底","柏拉图","亚里士多德","叔本华","尼采");
//获取前3个元素
list.stream().skip(3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}map
其实就是一种类型的流转换为另一种类型的流。
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("1","2","3");
//将Stream流中的字符串转为Integer类型(完整版)
stream.map((String str) -> {
return Integer.parseInt(str);
}).forEach(System.out::println);
//简化版
stream.map(str -> Integer.parseInt(str)).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}sorted
如果需要将数据排序,可以使用sorted方法。有如下两种方法API:
Stream<T> sorted(); //根据元素的自然顺序排序
Stream<T> sorted(Comparator<? super T> comparator); //根据比较器指定的规则排序public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(6,2,5,1,8,7);
//升序排列
stream.sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
//降序排列
stream.sorted((i1,i2) -> i2 - i1).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}distinct
去除重复数据。
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(6,1,1,8,8,7,10);
//基本类型去重
stream.distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
//自定义类型去重(必须重写equals和hashcode方法)
Stream<Person> streamPerson = Stream.of(
new Person("李隆基",40),
new Person("杨玉环",20),
new Person("杨玉环",20),
new Person("李白",45),
new Person("高力士",35));
streamPerson.distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
}
}match
断言
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(6,1,8,7,10);
//匹配所有元素,判断所有元素中是否都大于3
boolean b = stream.allMatch(i -> i > 3);
//匹配某个元素,只要有其中一个元素满足即可
boolean b1 = stream.anyMatch(i -> i > 3);
//匹配所有元素,所有元素都不满足条件
boolean b2 = stream.noneMatch(i -> i > 3);
System.out.println(b); //false
System.out.println(b1); //true
System.out.println(b2); //false
}
}find
找到某些数据。
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(6,1,8,7,10);
//找到第一个元素:6
Optional<Integer> first = stream.findFirst();
System.out.println(first.get()); //6
}
}max和min
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(6,1,8,7,10);
Optional<Integer> max = stream.max((o1, o2) -> o1 - o2);
System.out.println(max.get()); //10
Optional<Integer> min = stream.min((o1, o2) -> o1 - o2);
System.out.println(min.get()); //1
}
}reduce
如果需要将所有数据归纳得到一个数据,可以使用reduce方法。
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(6,1,8,7,10);
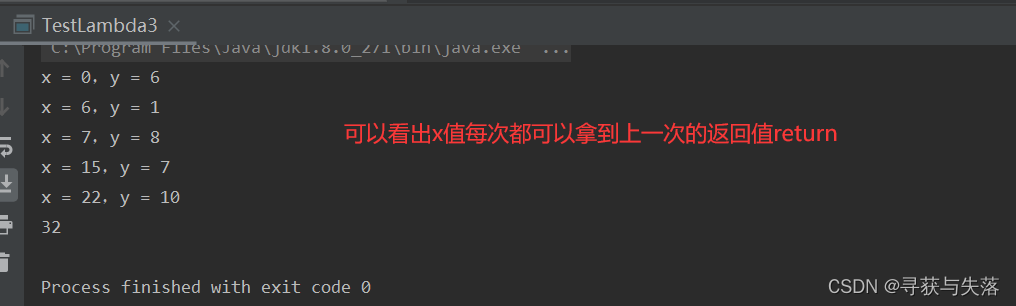
Integer reduce = stream.reduce(0, (x, y) -> {
System.out.println("x = " + x + ",y = " + y);
return x + y;
});
System.out.println(reduce); //32
}
}
map与reduce组合使用
案例1:求出所有年龄的总和
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer reduce = Stream.of(
new Person("李隆基", 40),
new Person("杨玉环", 20),
new Person("李白", 45),
new Person("高力士", 35))
.map((Person p) -> {
return p.getAge();
}).reduce(0, (x, y) -> {
return x + y;
});
System.out.println("所有人总年龄为:" + reduce); //140
}
}案例2:找出最大年龄
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer reduce = Stream.of(
new Person("李隆基", 40),
new Person("杨玉环", 20),
new Person("李白", 45),
new Person("高力士", 35))
.map(p -> p.getAge())
.reduce(0,(x,y) -> x > y?x : y);
System.out.println("最大年龄是:" + reduce); //45
}
}mapToInt
如果需要将Stream<Integer>中的Integer类型数据转成int类型,可以使用此方法。
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5);
//返回的IntStream流,内部操作的是int类型数据,就可以节省内存,减少自动装箱和拆箱
IntStream intStream = stream.mapToInt(Integer::intValue);
}
}concat
如果有两个流,希望合并成为一个流,那么可以使用Stream接口的静态方法concat。
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of("黑格尔");
Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of("第欧根尼");
Stream<String> newStream = Stream.concat(stream1, stream2);
newStream.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}5、收集Stream流中的结果
将流中的数据收集到集合中
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aa","bb","cc","dd","ee");
//最终结果收集到集合中
List<String> collect = stream.limit(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect); //[aa, bb, cc]
}
}将流中的数据收集到数组中
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aa","bb","cc","dd","ee");
//最终结果收集到数组中
String[] strings = stream.toArray(String[]::new);
}
}对流中数据进行聚合计算
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以像数据库的聚合函数一样对某个字段进行操作。比如获取最大值、获取最小值、求总和、平均值、统计数量。
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> streamPerson = Stream.of(
new Person("李隆基",40),
new Person("杨玉环",20),
new Person("李白",45),
new Person("高力士",35));
//获取最大年龄
Optional<Person> collectMax = streamPerson.collect(Collectors.maxBy((s1, s2) -> s1.getAge() - s2.getAge()));
System.out.println(collectMax.get());
//获取最小年龄
Optional<Person> collectMin = streamPerson.collect(Collectors.minBy((s1, s2) -> s1.getAge() - s2.getAge()));
System.out.println(collectMin.get());
//获取总年龄
Integer collectSum = streamPerson.collect(Collectors.summingInt(s -> s.getAge()));
System.out.println(collectSum);
//获取年龄平均值
Double collectAvg = streamPerson.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(s -> s.getAge()));
System.out.println(collectAvg);
}
}对流中数据进行分组
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> streamPerson = Stream.of(
new Person("李隆基",40),
new Person("杨玉环",20),
new Person("安禄山",20),
new Person("李白",45),
new Person("白居易",45),
new Person("高力士",35));
//根据年龄进行分组
Map<Integer, List<Person>> map = streamPerson.collect(Collectors.groupingBy((p) -> p.getAge()));
map.forEach((k,v) -> {
System.out.println(k + ":" + v);
});
}
}
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> streamPerson = Stream.of(
new Person("李隆基",40),
new Person("杨玉环",20),
new Person("安禄山",20),
new Person("李白",45),
new Person("白居易",45),
new Person("高力士",35));
Map<String, List<Person>> map = streamPerson.collect(Collectors.groupingBy((p) -> {
if(p.getAge() > 20){
return "成年";
}else{
return "未成年";
}
}));
map.forEach((k,v) -> {
System.out.println(k + ":" + v);
});
}
}
对流中数据进行分区
Collectors.partitioningBy会根据值是否为true,把集合分隔为两个列表,一个true列表,一个false列表。
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> streamPerson = Stream.of(
new Person("李隆基",40),
new Person("杨玉环",20),
new Person("安禄山",20),
new Person("李白",40));
//年龄大于30的分为true区
Map<Boolean, List<Person>> map = streamPerson.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(p -> p.getAge() > 30));
map.forEach((k,v) -> {
System.out.println(k + ":" + v);
});
}
}对流中数据进行拼接
Collectors.joining会根据指定的连接符,将所有元素连接成一个字符串。
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Person> streamPerson = Stream.of(
new Person("李隆基",40),
new Person("杨玉环",20),
new Person("安禄山",20),
new Person("李白",40));
//根据一个字符串进行拼接
String collect = streamPerson.map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("__"));
System.out.println(collect); //李隆基__杨玉环__安禄山__李白
//根据三个字符串进行拼接
String collect = streamPerson.map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("__","@","。"));
System.out.println(collect); //@李隆基__杨玉环__安禄山__李白。
}
}6、并行的Stream流
注意:目前我们使用的Stream是串行的,就是在一个线程上执行的 。
获取并行Stream流的两种方式
第一种:直接获取并行的Stream流
//第一种:直接获取并行的Stream流
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stream<String> stream01 = list.parallelStream();第二种:将串行流转成并行流
//第二种:将串行流转成并行流
Stream<String> stream02 = list.stream().parallel();串行与并行Stream代码对比
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//串行
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(5, 8, 1, 2, 7, 9);
stream.filter(i -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " " + i);
return i > 2;
}).count();
}
}
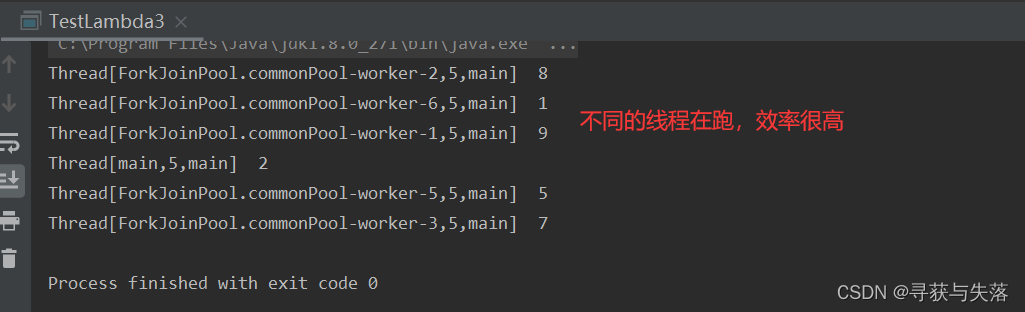
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//并行
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(5, 8, 1, 2, 7, 9);
stream.parallel().filter(i -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " " + i);
return i > 2;
}).count();
}
}
parallelStream线程安全问题
先看一个线程不安全的实例:
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
IntStream.rangeClosed(1,1000).parallel().forEach(i -> {
list.add(i);
});
System.out.println(list.size()); //928
}
}首先总共1000条数据,最后打印的集合size也应该是1000啊,结果打印出928,说明在并行的情况下,使用ArrayList是线程是不安全的。
解决方案一:同步代码块
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj = new Object();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
IntStream.rangeClosed(1,1000).parallel().forEach(i -> {
synchronized (obj){ //加入同步代码块
list.add(i);
}
});
System.out.println(list.size()); //1000
}
}解决方案二:使用线程安全的集合
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new Vector<>();
IntStream.rangeClosed(1,1000).parallel().forEach(i -> {
list.add(i);
});
System.out.println(list.size()); //1000
}
}解决方案三:使用Collections.synchronizedList方法将集合转为线程安全的
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
//将ArrayList转为线程安全的集合
List<Integer> integers = Collections.synchronizedList(list);
IntStream.rangeClosed(1,1000).parallel().forEach(i -> {
integers.add(i);
});
System.out.println(list.size()); //1000
}
}解决方案四:调用Stream流的collect/toArray
public class TestLambda3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> collect = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 1000).parallel().boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect.size()); //1000
}
}parallelStream底层
Fork/join框架介绍
parallelStream使用的是Fork/join框架。Fork/join框架自JDK1.7引入。Fork/join框架可以将一个大任务拆分为很多小任务来异步执行。
Fork/join框架主要包含三个模块:
1、线程池:ForkJoinPool
2、任务对象:ForkJoinTask
3、执行任务的线程:ForkJoinWorkerThread
Fork/join原理-分治法
ForkJoinPool主要用来使用分治法来解决问题。典型的应用比如快速排序算法,ForkJoinPool需要使用相对少的线程来处理大量的任务。比如要对1000万个数据进行排序,那么会将这个任务分割成两个500万的排序任务和一个针对这两组500万数据的合并任务。以此类推,对于500万的数据也会做出同样的分割处理,到最后会设置一个阈值来规定当数据规模到多少时,停止这样的分割处理。比如,当元素的数量小于10时,会停止分割,转而使用插入排序对他们进行排序。那么到最后,所有的任务加起来会有大概2000000+个。问题的关键在于,对于一个任务而言,只有当它所有的子任务完成之后,它才能够被执行。

Fork/join原理-工作窃取算法
Fork/join最核心的地方就是利用了现代硬件设备多核,在一个操作时候会有空闲的CPU,那么如何利用好这个空闲的CPU就成了提高性能的关键,在这里我们要提到工作窃取算法就是整个Fork/join框架的核心理念Fork/join工作窃取算法是指某个线程从其它队列窃取任务来执行。
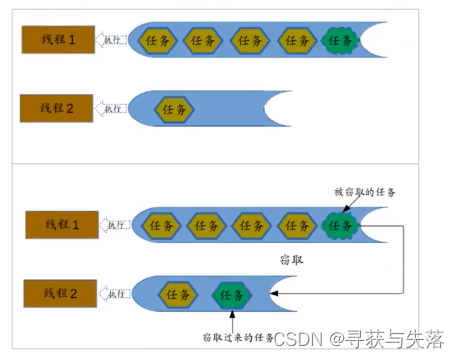
有的线程任务执行的比较快,就没事干了,这时就会窃取其它线程的任务来执行。






![[C#]yolov8-onnx在winform部署手势识别模型](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/1261a96a076b46f18162bcfb81ea3b58.jpeg)